Bio 1 lab ksu
1/134
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
135 Terms
1) Which sequence shows the steps of the process of science in an order in which they might occur?
a) Experiment, conclusion, exploration, application
b) Question, observation, experiment, analysis, prediction
c) Exploration, hypothesis, prediction, experiment
d) Exploration, question, opinion, conclusion, hypothesis
c) Exploration, hypothesis, prediction, experiment
1) Read the following story. Notice that there are numbers at the end of some of the
sentences or at the end of parts of some of the sentences. Refer to these numbers when answering the questions below.
You get in your car to drive to class. You turn the key and the engine starts making a
clicking sound, but does not start (1). You think to yourself, “the battery must be dead (2)” so you go in the garage and borrow the battery from your neighbor’s car (with permission, of course) and exchange it for the one in your car (3). You figure that if the battery in your car is dead and you replace it, then the car will start (4). You get in the car again, turn the key and the car starts right up and you make it to class on time (5).
a) Which sentence or part of a sentence in the story is a hypothesis?
the battery must be dead
1) Read the following story. Notice that there are numbers at the end of some of the
sentences or at the end of parts of some of the sentences. Refer to these numbers when answering the questions below.
You get in your car to drive to class. You turn the key and the engine starts making a
clicking sound, but does not start (1). You think to yourself, “the battery must be dead (2)” so you go in the garage and borrow the battery from your neighbor’s car (with permission, of course) and exchange it for the one in your car (3). You figure that if the battery in your car is dead and you replace it, then the car will start (4). You get in the car again, turn the key and the car starts right up and you make it to class on time (5).
Which sentence or part of a sentence in the story is an observation?
engine makes clicking sound, but does not start
1) Read the following story. Notice that there are numbers at the end of some of the
sentences or at the end of parts of some of the sentences. Refer to these numbers when answering the questions below.
You get in your car to drive to class. You turn the key and the engine starts making a
clicking sound, but does not start (1). You think to yourself, “the battery must be dead (2)” so you go in the garage and borrow the battery from your neighbor’s car (with permission, of course) and exchange it for the one in your car (3). You figure that if the battery in your car is dead and you replace it, then the car will start (4). You get in the car again, turn the key and the car starts right up and you make it to class on time (5).
Which sentence or part of a sentence in the story is an experiment?
borrow battery, exchange it
1) Read the following story. Notice that there are numbers at the end of some of the
sentences or at the end of parts of some of the sentences. Refer to these numbers when answering the questions below.
You get in your car to drive to class. You turn the key and the engine starts making a
clicking sound, but does not start (1). You think to yourself, “the battery must be dead (2)” so you go in the garage and borrow the battery from your neighbor’s car (with permission, of course) and exchange it for the one in your car (3). You figure that if the battery in your car is dead and you replace it, then the car will start (4). You get in the car again, turn the key and the car starts right up and you make it to class on time (5).
Which sentence or part of a sentence in the story is a prediction?
if you replace the battery, the car will start
1) Read the following story. Notice that there are numbers at the end of some of the
sentences or at the end of parts of some of the sentences. Refer to these numbers when answering the questions below.
You get in your car to drive to class. You turn the key and the engine starts making a
clicking sound, but does not start (1). You think to yourself, “the battery must be dead (2)” so you go in the garage and borrow the battery from your neighbor’s car (with permission, of course) and exchange it for the one in your car (3). You figure that if the battery in your car is dead and you replace it, then the car will start (4). You get in the car again, turn the key and the car starts right up and you make it to class on time (5).
Which sentence or part of a sentence in the story supports the hypothesis about the battery?
car starts and you make it to class
1) The figure below was taken from a primary research article that was published, by authors Ignato, Pecoraro et al., in 2022. The authors evaluated the effects of promethazine hydrochloride (abbreviated PM) on brine shrimp. Promethazine hydrochloride is a commonly used medication that has been found in wastewater. Answer the following question using information in this figure. Which of the following is a likely hypothesis being tested by the scientists that published these results.
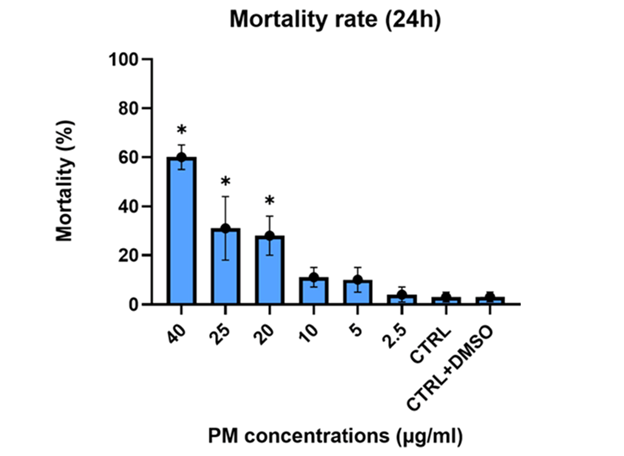
a) High levels of promethazine hydrochloride (PM) can be measured in inland saltwater lakes.
b) The fertility of brine shrimp is reduced by the presence of promethazine hydrochloride (PM) in their environment.
c) Increased amounts of promethazine hydrochloride (PM) are associated with a higher mortality of brine shrimp.
c) Increased amounts of promethazine hydrochloride (PM) are associated with a higher mortality of brine shrimp.
1) Based on the graph above, what is the dependent variable?
a) Number of brine shrimp
b) Mortality (%)
c) PM Concentrations
b) Mortality (%)
1) A student tested the effect of different concentrations of alcohol on brine shrimp. Indicate any thing(s) that are incorrect with the representation below (select all that apply)
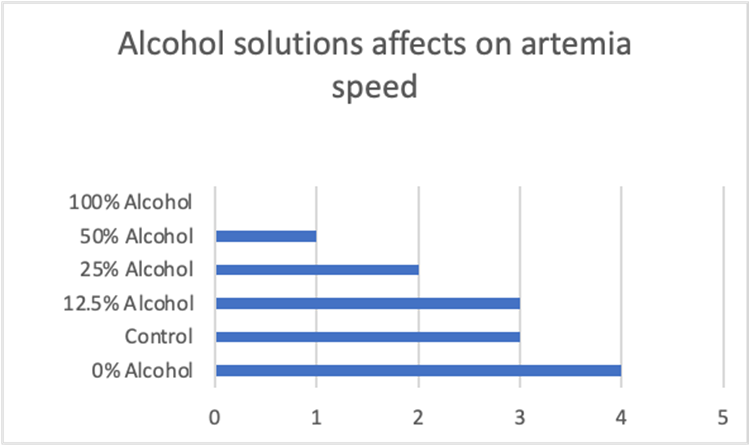
a) Unlabeled axis
b) Title has errors
c) Missing figure legend
All of the above
1) Based on the graph above, what is the independent variable?
a) Number of brine shrimp
b) Mortality (%)
c) PM Concentrations
c) PM Concentrations
1) You are making a serial dilution of NaCl. You need 5 mL of 1 M, 0.5M and 0.25 M NaCl to perform your experiment. Lucky for you someone in the lab already made 2M NaCl. You decide to dilute that to make your different solutions. The first solution you make is the 1M NaCl. What volume of 1M NaCl and water do you need to make your next solution?
a) 5 mL of each
b) b. 2.5 mL of 1M NaCl and 2.5 mL of water
c) c. 2.5 mL of 2M NaCl and 2.5 mL of water
d) d. 1 mL of 2M NaCl and 4 mL of water
b) 2.5 mL of 1M NaCl and 2.5 mL of water
1) 5 milliliters (ml) of a solution is equivalent to how many microliters (µl)?
a) 5
b) 50
c) 500
d) 5000
d) 5000
1) Precision is the degree to which
a) Measurements are not reproducible when repeated.
b) A device can be used to measure more than 50% of its total volume.
c) Measurements are reproducible when repeated.
d) An observed value corresponds to a true value.
c) Measurements are reproducible when repeated.
1) You are wanting to make 10 ml solutions different concentrations of caffeine solution from your stock solution of 5 ml, which has a concentration of 32.00 mg/ml. Using the serial dilution method, calculate how you will create concentrations of 16.00 mg/ml, 8.00 mg/ml, 4.00 mg/ml, and 2.00 mg/ml. Don’t forget to include how much water.
a) Calculate the dilution factor for each step.
Dilution factor: 1/2 each time (cutting concentration in half)
32 → 16: mix 5 mL stock + 5 mL water
16 → 8: mix 5 mL of 16 mg/mL + 5 mL water
8 → 4: mix 5 mL of 8 mg/mL + 5 mL water
4 → 2: mix 5 mL of 4 mg/mL + 5 mL water
1) If 750mL of a 1mg/mL NaCl solution is diluted with water to give a final volume of 5ml,
what is the final concentration of NaCl in the new solution.
a) Calculate the dilution factor for each step.
Find dilution factor: 750 μL / 5000 μL = 0.15
New concentration = 0.15 mg/mL
1) A hypothesis is a(n)…
a) Proposed explanation for a set of observations.
b) Theory determined after data collection.
c) Guess made to determine what observations and explorations are necessary.
d) Observation made to determine a theory.
a) Proposed explanation for a set of observations.
1) When applying the process of science, which of these is tested?
a) An observation
b) A question
c) A hypothesis
d) A result
c) A hypothesis
1) Observation: I have noticed that my tomato plants grow taller in June than in February.
a) Form a hypothesis to explain why this is.
Tomato plants grow taller in June because there is more sunlight.
1) Observation: I have noticed that my tomato plants grow taller in June than in February.
a) Make a prediction based on your hypothesis.
If tomato plants get more sunlight, then they will grow taller.
1) Observation: I have noticed that my tomato plants grow taller in June than in February.
a) What is the independent variable, dependent variable, and control group?
Independent: Amount of sunlight
Dependent: Height of tomato plants
Control group: Plants grown under normal/constant conditions
1) “If I add salt to fresh water, then the water will freeze at a lower temperature.” This statement is an example of a
a) Hypothesis
b) Prediction
c) Positive Control
d) Negative Control
b) Prediction
1) Some of your classmates decided to record the number of Artemia that died when exposed to the different concentrations of NaCl solutions. The data recorded by these classmates is____?
a) Qualitative data
b) Quantitative data
b) Quantitative data
1) In observing the Artemia in the different concentrations of NaCl, you decided to record the amount of movement (behavior) in the different test solutions compared to when in their natural habitat. One would be right in saying that this data is___?
a) Qualitative data
b) Quantitative data
a) Qualitative data
1) Given the prediction: If salinity has an adverse effect on plant growth then the height of Mung beans plants will decrease as the salinity of irrigation water increases.
a) The dependent variable is:
i) The amount of light the mung beans are grown in.
ii) The height of the mung beans.
iii) The salinity of the irrigation water.
a) Dependent variable: ii) The height of the mung beans
1) Given the prediction: If salinity has an adverse effect on plant growth then the height of Mung beans plants will decrease as the salinity of irrigation water increases.
b) The independent variable is:
i) The amount of light the mung beans are grown in.
ii) The height of the mung beans
iii) The salinity of the irrigation water.
b) Independent variable: iii) The salinity of the irrigation water
1) In a scientific experiment, what is the function of the control group?
a) The control group is required for the validity of discovery science.
b) The control group serves as a basis of comparison with the experimental group.
c) The control group serves to increase the sample size of the experiment.
d) The control group is the sample that is subjected to the factor whose effect is being tested.
e) The control group allows for the simultaneous testing of multiple factors.
b) The control group serves as a basis of comparison.
1) The dissecting microscope is typically used for (select all that apply)
a) Extremely small specimens.
b) Dissecting small organisms.
c) Thick specimens.
d) Organelles
b) Dissecting small organisms
c) Thick specimens
1) An experiment…
a) Is an activity designed to test a hypothesis.
b) Involves only collecting numerical data.
c) Is designed to generate new scientific theories.
Often involves manipulating as many variables as possible
a) An activity designed to test a hypothesis.
1) What is the difference between a positive control and a negative control?
Positive control: Expected to produce a known result
Negative control: Expected to show no effect
1) In the scientific article entitled "The brine shrimp Artemia survives in diluted water of Lake Bunyampaka, an inland saline lake in Uganda," what was the…
a) Independent variable?
Salinity of the water
1) In the scientific article entitled "The brine shrimp Artemia survives in diluted water of Lake Bunyampaka, an inland saline lake in Uganda," what was the…
a) Dependent variable?
Survival of Artemia
1) You are given the following data table collected by two students, who were asked to pipette 315 uL of water into a weigh boat Which student was more accurate?
Measurement # | Student 1 | Student 2 |
1 | 315mg | 315mg |
2 | 316mg | 320mg |
3 | 317mg | 325mg |
4 | 315mg | 321mg |
a) Student 1
b) Student 2
a) Student 1
1) Osmosis is the special case of diffusion where the particles moving are
a) solute molecules moving across a semi permeable membrane.
b) water molecules any time they move.
c) water molecules and the movement is across a semi permeable membrane.
d) moving against their concentration gradient.
c) Water molecules moving across a semi-permeable membrane.
1) What happens to the flow of water by osmosis, when a cell is placed into a solution that is hypertonic relative to its contents?
a) Will rush into the cell and the cell will burst.
b) Will rush into the cell and the cell will shrivel.
c) The cell will stay the same.
d) Will rush out of the cell and the cell will shrivel.
d) Water rushes out and the cell shrivels.
1) If a cell is in a solution that contains a less concentrated solute than what is inside the cell, this solution is?
a) Hypertonic
b) Hypotonic
c) Isotonic
b) Hypotonic
1) If a cell is in a solution that contains a higher concentrated solute than what is inside the cell, this solution is?
a) Hypertonic
b) Hypotonic
c) Isotonic
a) Hypertonic
1) If a cell is in a solution that contains concentrated solute that is the same as what is inside the cell, this solution is?
a) Hypertonic
b) Hypotonic
c) Isotonic
c) Isotonic
1) A cell whose cytoplasm has a concentration of 0.02 M glucose is placed in a test tube of water containing 0.02 M glucose. Assuming that glucose is not actively transported into the cell, which of the following terms describes the tonicity of the external solution relative to the cytoplasm of the cell?
a) Hypotonic
b) Isotonic
c) Hypertonic
b) Isotonic
1) You add 1 teaspoon of table salt (approximately 6 grams) to 1 cup of water (approximately 240 mL) and mix well. What is the concentration of your solution?
a) 0.025 g/mL
b) 2 M
c) 4 g/mL
6g / 240mL = 0.025 g/mL
Answer: a) 0.025 g/mL
1) You added the Orbeez to the salt solution you made and let the Orbeez "soak" in it overnight. The next day you make another solution. This time you add not 1 teaspoon but 4 teaspoons of salt and add that the same volume of water (1 cup). You transfer the Orbeez from the overnight solution to your new salt solution. Relative to the overnight solution, is this new solution hypotonic, isotonic, or hypertonic?
a) Hypotonic
b) Isotonic
c) Hypertonic
c) Hypertonic
1) A group of students graphed the optical densities of their known starch concentrations. The linear regression equation of the trend line was y = 9.346x. Next, they measured the optical density of an unknown starch sample. The optical density of the unknown sample was 1.2. What was the concentration of their unknown starch sample?
a) 9.35 g/L
b) 0.13 g/L
c) 11.22 g/L
d) 7.79 g/L
Answer: b) 0.13 g/L
1) If upon constructing the standard curve for the absorbance of the various concentrations of starch solutions and the unknown starch solution (which had an absorbance of 1.75 at 580nm), you came upon with the following; then based on the information from the graph what would you say is the approximate starch concentration of the unknown starch solution?
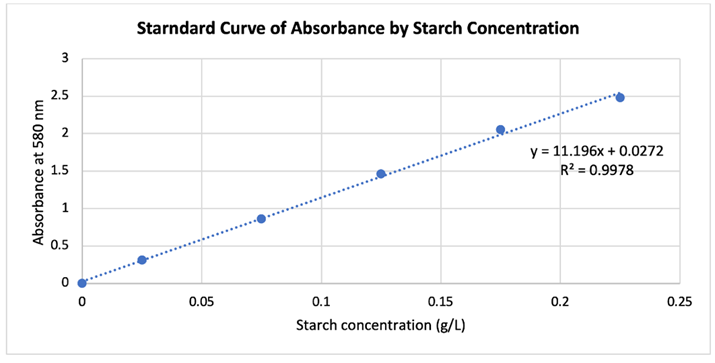
a) 0.25 g/L
b) 0.15 g/L
c) 0.10 g/L
d) 0.23 g/L
a) 0.25 g/L
1) Calculate the concentration of each cuvette.
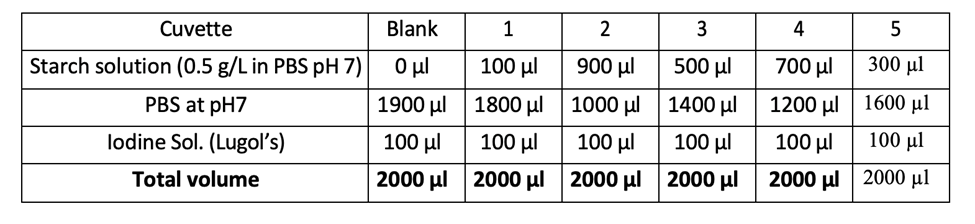
(You’ll use C₁V₁ = C₂V₂ for each cuvette — can go through specific examples if you post their numbers!)
1) Below is a standard curve of starch concentration by absorbance. It was generated to determine the unknown concentration of starch in a particular sample. After performing the iodine-starch test, the absorbance of the color in the unknown sample was measured and recorded as 1.20. What is the starch concentration of the unknown?

a) 0.01 g/L
b) 0.1 g/L
c) 0.7 g/L
d) 0.07 g/L
c) 0.7 g/L