chemistry 2.3
1/14
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
15 Terms
Atoms
Electrons surrounding a nucleus that contains neurons and protons
Aufbau Principle
In the ground state of an atom or ion, electron fill atomic orbitals of the lowest available energy levels before occupying higher levels
Hund's rule

Electron configuration
.

Pauli Exclusion principle
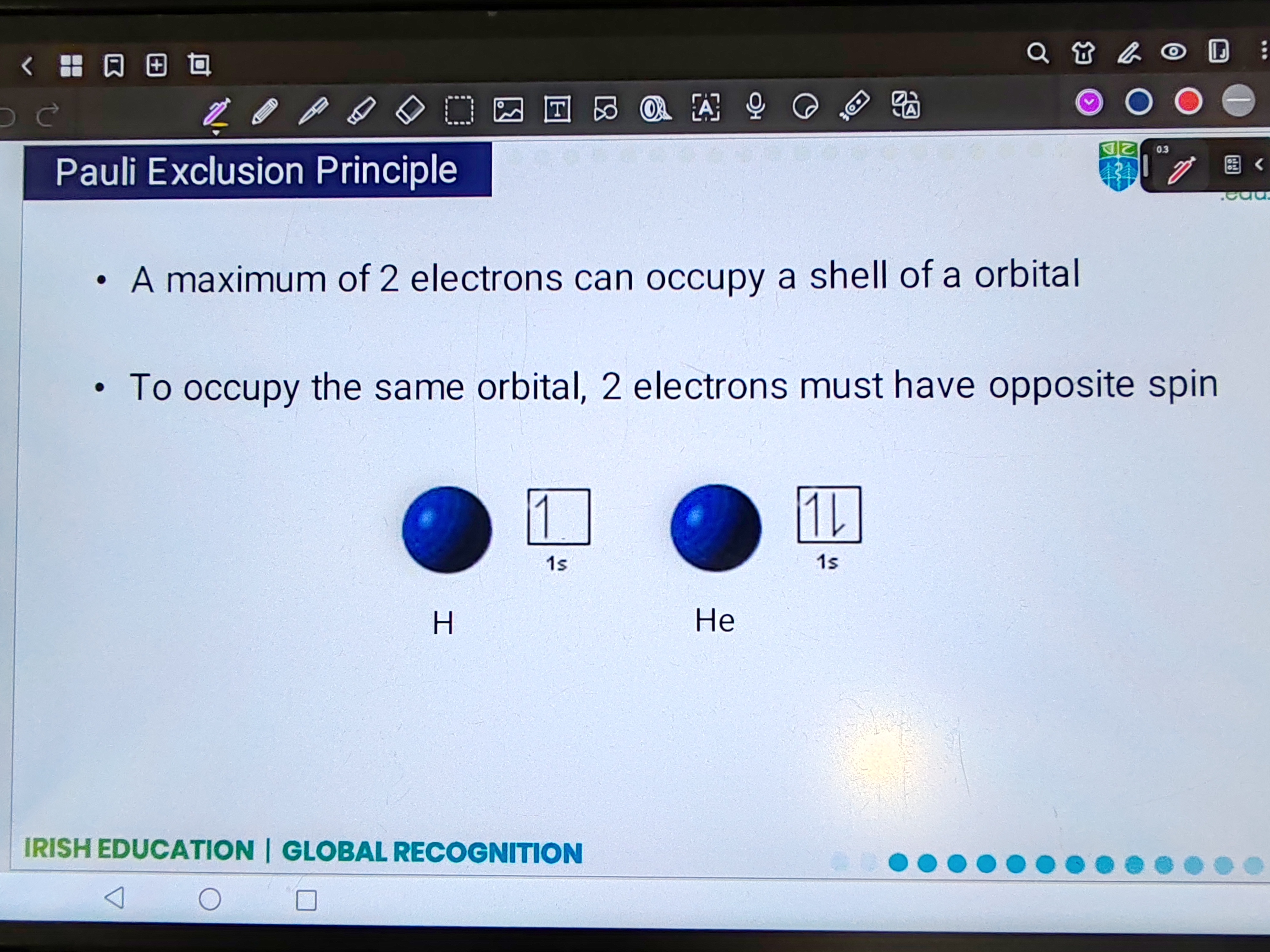
Hybridization
The mixing of two or more non equivalent atomic orbitals to form a set of equivalent hybrid orbitals of the same shape and energy
Sigma bond
Head on overlap of two atomic orbital on adjacent atom
Pie bond
A covalent bond formedby sideways overlap of two atomic p orbitals on adjacent atom
Atomic orbital
Region of space around nucleus of atom where an electron is likely to be found
Alkane
Saturated hydrocarbon
Free radical
Neutral, poor electron chemical species with unpaired electron in their structure
Axial positions
6 axial positions perpendicular to the ring and the ring axis of cyclohexane
Equatorial position
6 Equatorial positions are in the rough plane of the ring around the ring equator
Cahn Ingold Prelog rules
Sequence rules that assign priority to the substituent group on double bond carbon
Markovnikov rule
In the addition of HX to an unsymmetrical alkene, the H+ adds to the carbon with greater number of hydrogens attached to it and the X adds to the other carbon