M9 Hypertension___Antihypertensives *
1/49
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
50 Terms
What is the equation for Blood Pressure (BP)?
BP = CO x SVR (Cardiac Output x Systemic Vascular Resistance)
What condition is indicated by blood pressure persistently elevated above 139/89 mmHg?
Hypertension
What are common symptoms of hypertension?
Headaches, tinnitus, vertigo, syncope, or asymptomatic.
What stimulates the cardioinhibitory center in blood pressure homeostasis?
Impulses from baroreceptors.
What is primary hypertension also known as?
Essential hypertension.
What are some uncontrollable risk factors for hypertension?
Genes, age, sex, race.
What is the role of the renin-angiotensin system?
Regulates blood pressure and fluid balance.
What does ACE stand for in the renin-angiotensin system?
Angiotensin-Converting Enzyme.
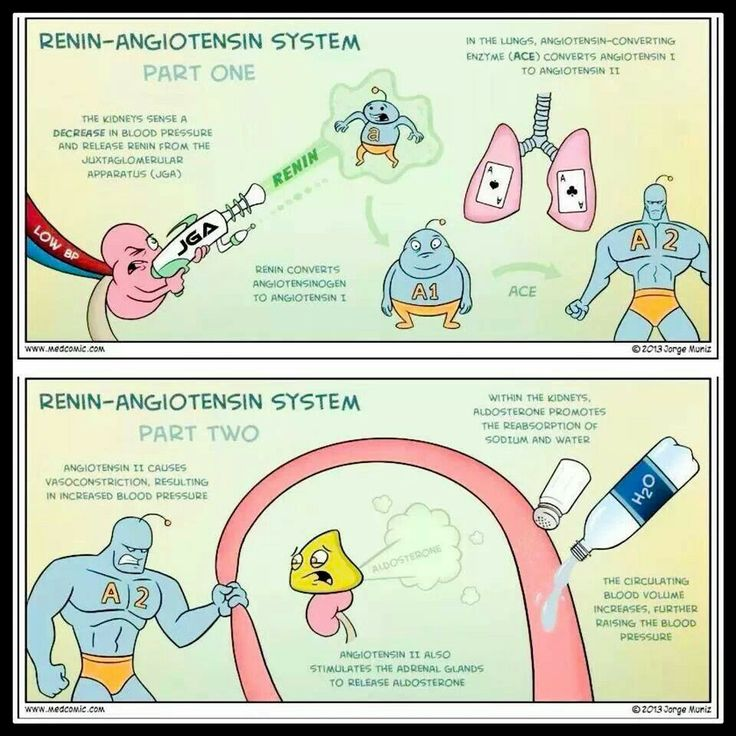
What does aldosterone promote in the kidneys?
Reabsorption of sodium and water.
What are some common medications used to treat hypertension?
4x
ACE inhibitors,
beta blockers,
calcium channel blockers, and
diuretics.
What is a common side effect of ACE inhibitors?
Cough.
What should be monitored when a patient is on ACE inhibitors?
Serum creatinine and potassium levels.
What do ARBs inhibit?
Angiotensin II from binding to angiotensin type 1 receptors.
What are the indications for using ARBs?
Hypertension, renal failure, chronic kidney disease, heart failure.
What is the common side effect of diuretics that affects potassium levels?
Hypokalemia.
What is the mechanism of action of loop diuretics?
Inhibits the reabsorption of Na+, K+, and Cl- in the ascending loop of Henle.
What is the golden rule regarding sodium and water?
Water follows sodium.
What type of diuretic is Hydrochlorothiazide?
Thiazide diuretic.
What is a major concern when using loop diuretics? 1 drug example
hypokalemia
Lasix (bumetanide)
Loop diuretics can lead to electrolyte imbalances, particularly low potassium levels (hypokalemia), dehydration, and renal impairment.
What do potassium-sparing agents do?
Act in the collecting ducts to reabsorb potassium.
What dietary changes can help manage hypertension?
Sodium reduction and weight reduction.
What is the goal of hypertension treatment?
Maximal protection against cardiovascular consequences with minimal bother to the patient.
What effect do beta blockers have on the renal system?
Inhibit the release of renin.
What is a significant side effect of thiazide diuretics?
Electrolyte imbalance.
What condition could result from the use of potassium-sparing diuretics?
Hyperkalemia.
What are some controllable risk factors for hypertension?
Obesity, sedentary lifestyle, alcohol consumption, diet (sodium intake), stress.
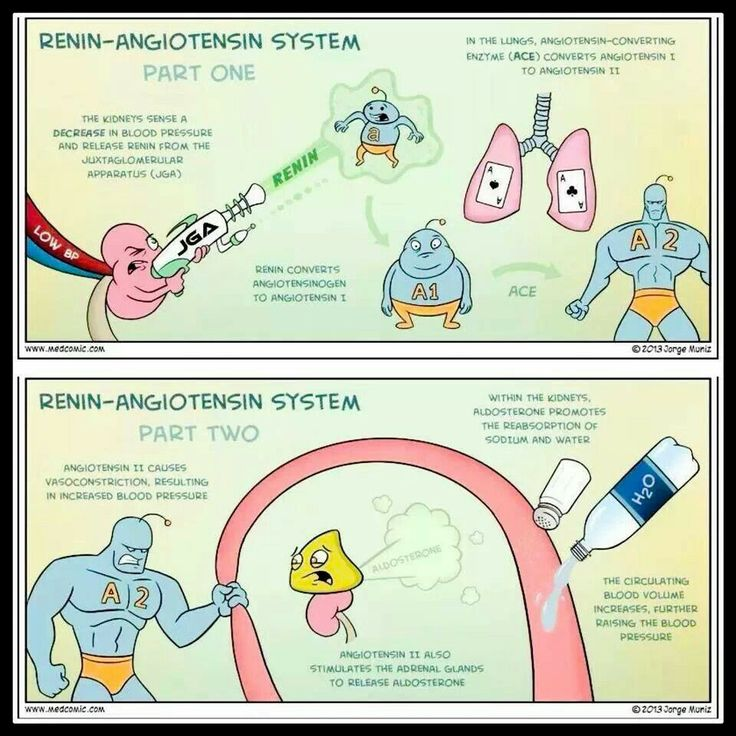
What happens to blood pressure when aldosterone is released?
Circulating blood volume increases, raising blood pressure.
What type of diuretics are typically the first line treatment for hypertension?
Thiazide diuretics.
What is the action of calcium channel blockers?
Reduce systemic vascular resistance (SVR).
What prominent feature characterizes secondary hypertension?
It is due to the presence of a specific disease or medical condition.
What do anti-hypertensives aim to achieve?
Lowering blood pressure effectively.
In which part of the nephron do loop diuretics act?
Ascending loop of Henle.
What side effect is particularly noted in African-American patients with ARBs?
Overall better outcomes compared to ACE inhibitors.
What is the primary effect of nitrates in hypertension management?
Reduce venous blood volume, decreasing preload and blood pressure.
What are the contraindications for using ACE inhibitors?
Bilateral renal artery stenosis, pregnancy, known allergy, hyperkalemia.
What results from angiotensin II causing vasoconstriction?
Increased blood pressure.
Why are thiazide diuretics longer acting than loop diuretics?
They act in the distal convoluted tubule rather than the ascending loop of Henle.
Which drug class inhibits angiotensin II from binding at the AT1 receptor?
Angiotensin II Receptor Blockers (ARBs).
What are the implications of a chronic dry cough in a patient on ACE inhibitors?
It may indicate a common side effect requiring medication adjustment.
What role do baroreceptors play in blood pressure regulation?
They sense blood pressure changes and send signals to adjust heart rate and vessel diameter.
What can excessive sodium intake lead to in patients predisposed to hypertension?
Exacerbation of high blood pressure.
What is the main downside to aggressive blood pressure management?
Potential for adverse effects and patient discomfort.
What does 'compliance' mean in the context of hypertension treatment?
The patient's adherence to prescribed medication and lifestyle changes.
In the context of hypertension management, what is the purpose of lifestyle modifications?
To reduce blood pressure and prevent complications.
What are Angiotensin-Converting Enzyme (ACE) inhibitors primarily used to treat?
Hypertension and heart failure.
What electrolytes must be monitored in patients taking diuretics?
Sodium, potassium, and chloride.
What condition do diuretics primarily target in patients with heart issues?
Fluid retention.
Where does reabsorption occur when using potassium-sparing diuretics?
In the collecting ducts of the nephron.
What is one major benefit of using ARBs over ACE inhibitors?
Lower incidence of cough and angioedema.
What happens to blood pressure after vasodilation occurs?
Blood pressure decreases.