Unit 1a
1/82
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
83 Terms
sensory/afferent neurons
neurons that carry incoming information from the sensory receptors to the brain and spinal cord
motor/efferent neurons
neurons that carry outgoing information from the brain and spinal cord to the muscles and glands
Synapse/synaptic gap
the junction between the axon tip of the sending neuron and the dendrite or cell body of the receiving neuron
somatic nervous system
the division of the peripheral nervous system that controls the body's skeletal muscles
consciously sense and do
sympathetic nervous system
the division of the autonomic nervous system that arouses the body, mobilizing its energy in stressful situations (fight or flight)
pituitary gland
The endocrine system's most influential gland. Under the influence of the hypothalamus, it regulates growth and controls other endocrine glands.
lesion
tissue destruction. Naturally or experimentally caused destruction of brain tissue
fMRI
A technique for revealing blood flow and brain activity by comparing successive MRI scans.
Brain stem
the oldest part and central core of the brain, beginning where the spinal cord swells as it enters the skull; responsible for automatic survival functions
reticular formation
a nerve network in the brainstem that plays an important role in controlling arousal and general ability to focus
region present inside the medulla, containing a network of nerve fibers. It is involved in increasing alertness, attention, and consciousness (sleep-wake cycles)
Thalamus
the brain's sensory switchboard, located on top of the brainstem; it directs messages to the sensory receiving areas in the cortex and transmits replies to the cerebellum and medulla
relay station
Cerebellum
the "little brain" at the rear of the brainstem; functions include processing sensory input and coordinating movement output and balance
Amygdala
two lima bean-sized neural clusters in the limbic system; linked to emotion (fear, emotional memory and aggression)
part of the limbic system
cerebral cortex
The intricate fabric of interconnected neural cells covering the cerebral hemispheres; the body's ultimate control and information-processing center.
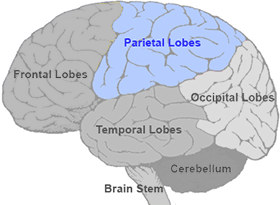
parietal lobes
portion of the cerebral cortex lying at the top of the head and toward the rear
receives sensory input for touch and body position (manages 5 senses)
Broca's area
Controls language expression - an area of the frontal lobe, usually in the left hemisphere, that directs the muscle movements involved in speech.
Heritability
The proportion of variation among individuals that we can attribute to genes. May vary depending on the range of populations and environments studied.
A neurotransmitter that affects hunger, sleep, arousal, and mood.
Lack of this leads to depression, anxiety, insomnia, OCD
arousal in the fight/flight response when in danger. Also stress, arousal, and eating
undersupply can depress mood, anxiety, stress, nervous tension
Acetylcholine
Enables involuntary muscle action (central nervous system - cardiac contractions, blood pressure), learning, and memory
Linked with Alzheimer's disease and paralysis
Enhances transmission of information to the brain
Too much can cause seizures or migraines
GABA
a major inhibitory neurotransmitter
Helps balance and offset other excitatory messages (calming)
Regulates sleep-wake cycles
Lacking can cause anxiety, seizures, tremors, or insomnia
Too much can cause sleeping disorders or some eating disorders
Endorphins
natural, opiate-like neurotransmitters linked to pain control and to pleasure.
Involved in pain control
Released during aerobic exercise & linked to positive emotions (i.e. "runners high")
Not enough can cause the body to experience pain
Too much, body may not give adequate warning about pain
You can have an artificial high
Many of our most addictive drugs deal with these
Dopamine
Involved in voluntary muscle movements, attention, learning, memory, emotional arousal, & rewarding sensations
Lack of it has been linked to Parkinson's disease
Too much has been linked to addiction, schizophrenia or schizophrenic-like symptoms such as hallucinations and perceptual disorders
substance P
Pain perception and the immune system
primarily associated with the transmission of pain signals, making it essential for the body's pain perception mechanism. This neuropeptide can be released in response to various stimuli, including physical injury, stress, and inflammatory processes.
Too much can cause chronic pain
CT vs PET
CT: scans pass x-rays through the body to create images, in minutes
PET: uses radioactive material which emits energy to produce images, more time consuming
refractory period
state of recovery that occurs after a neuron has fired an action potential
neurons firing is all or nothing