cell bio unit 1
1/127
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
128 Terms
biosphere
everywhere where there are living organisms
ecosystem
live and non-living things in a (large) region
community
collection of all species that live in an area
populations
specific species
organism
single individual
organs
collection of tissues forming focused role
tissues
collections of cells working to perform focused role
cell
basic unit of life, all living things made up of at least one cell
organelles
specialized sub cellular structures perofrming focused roles
molecules
2 or more atoms bound together
atoms
basic unit, building block of chem
particles
building blocks of atoms
neutron
neutral charge, in nucleus, makes up part of atomic mass
proton
positive charge, in nucleus, makes up part of atomic mass
electron
negative charge, in shells, basically no mass
valence shells
outermost shell
ions
result form imbalance of protons and electrons (gain or loss of electron)
anion
negative, gained electron
cation
positive, lost electron
isotopes
atom w extra neutron than would normally have
molecule
2 or more atoms bound together
physical bond
sharing of electrion (covalent bond)
charge based bond
joined by attraction of oppostive charges, ionic, vanderwaals, hydrogen bonds
covalent bonds
sharing of a pair of electrons between valence shells of atoms (strongest in bio)
electronegativity
strength of which an atom holds it electrons
polar covalent bonds
unequal sharing of electrons b/w atoms
ionic bonds
attraction b/w anionic & cationic atom
hydrogen bond
involves part of molecule that has a partial charge due to polar covalent bond within molecule involving H
van der waals interaction
very small partial charges devleop across bond due to brief unequal distribution of electrons (non polar)
cohesion
water molecules interact w/ other water molecules (stick together)
adhesion
water molecule interacts w/other molecules (sticks to others/adhere)
hydrophobic
non-polar, does not like to interact w/water (no partial charges)
hydrophilic
polar bonds/molecules, interacts w/water (partial charges)
hydroxyl
makes molecule more hydrophilic, acts as weak acid, molecule neg charge
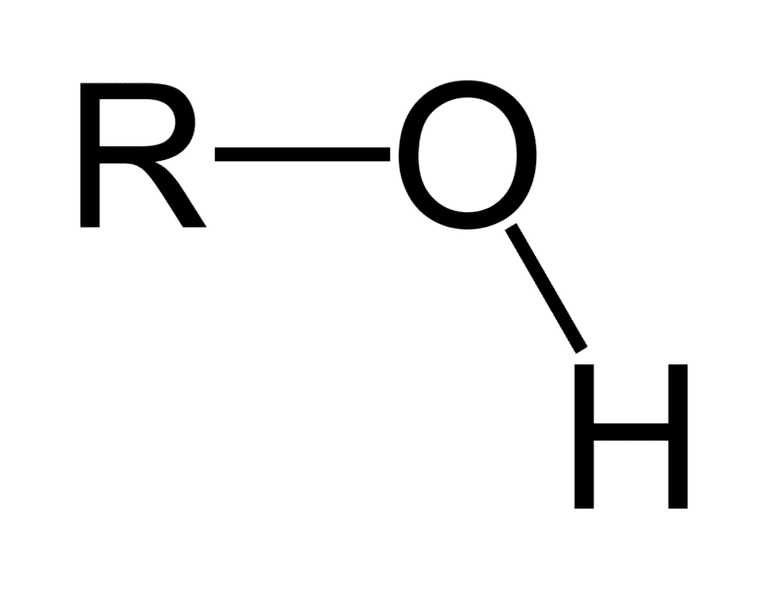
carboxyl
acts as acid, molecule neg charged, makes molecule more hydrophilic
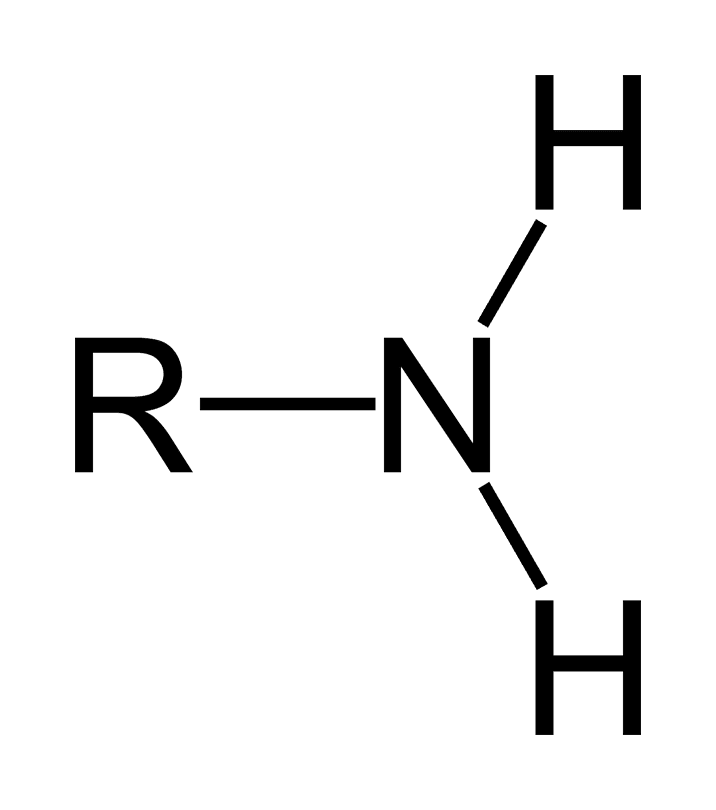
amine/amino
acts as base, makes molecule pos charged, makes molecule more hydrophilic
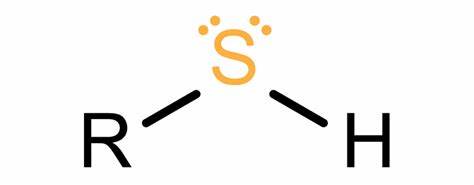
sulfhydryl
when 2 groups meet form bond w disulfide bridge
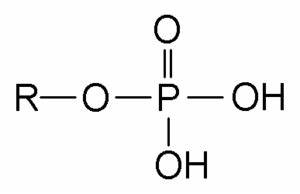
phosphate
acts as an acid, makes molecule neg charged, makes molecule more hydrophilic
monomer
molecule bonded to identical molecules that make up polymers
polymer
substance with molecular structure consisting of large number of similar units bonded together
dehydration/condensation rxn
removal of water to form polymers
hydrolysis rxn
addition of water to break down polymer
carbohydrates
starches and sugars, typically end in “ose” made of C1H2O1 ratio
lipids
fats and oils, hydrophobic, C-H bonds,
polysaccharides
polymer of carbohydrates
glycogen
longs strands of glucose for storage in humans
starch
long strands of glucose for storage in plants
cellulose
glucose strands for cell wall in plants
fatty acids
long hydrocarbon chains w/carboxyl group at the end, chain length varies & internal structure of chain, 2 types
unsaturated fatty acid
has double bonds, change orientation, kinks, does not stack nicely, easier to break apart
saturated fatty acid
all carbon-carbon single bonds, stacks nicely, more fluid, harder to break apart bc closer together
polyunsaturated fatty acid
multiple double bonds
carbohydrate roles in cell
energy, cell signaling, structure
lipids roles in cell
membrane components, signaling
monosaccharide
specific monomer for carbohydrates
disulfide bridge
covalent bonds formed b/w 2 sulfhydryl groups on proteins, role in protein folding
triglyceride
storage form of fatty acids, glycerol molecule bonded to 3 fatty acids
phospholipids
glycerol molecule with 2 fatty acids and one phosphate group, hydrophilic and hydrophobic parts of molecule
sterols/steroids
very hydrophobic, hydrocarbon rings, type of lipid
protein roles
enzymes (ase), structural components (in)
protein monomer
amino acid
protein polymer
polypeptide
amino acid
amine group (N terminus) and carboxyl functional group (C terminus) with R group that varies
primary structure
strands of amino acids in order and length, held together by covalent bonds
secondary structure
folding driven by hydrogen bonds b/w amino acids, alpha helices and beta sheets
tertiary structure
protein folds all over itself, many proteins at this stage are finished, held together through ionic bonds (charged R groups), covalent bonds (disulfide bridges), hydrogen bonds (partially charged R groups), and van der waals interactions (hydrophobic clustering)
quaternary structure
joining of 2 or more polypetpdides in the tertiary structure that cannot function yet because they are not in the right shape, held together by same bonds as tertiary
nucleic acids
information carrying molecules, DNA and RNA
nucleic acid monomer
nucleotide
nucleotide
made up 3 parts, sugar, phosphate, nitrogenous base, varies in RNA and DNA
ribonucleotide
ribose, pentose, ring form, 2 OH groups, on 2’ and 3’, phosphate on 5’, nitrogenous base on 1’, (AGCU)
deoxyribonucleotide
deoxyribose, pentose, ring form, H on 2’, OH on 3’, phosphate group on 5’, nitrogenous base on 1’ (AGCT)
purines (ribonucleotide/deoxyribonucelotide)
2 rings, adenine, guanine
pyrimidines (ribonucleotide)
1 ring, cytosine, uracil
pyrimidine (deoxyribonucleotide)
1 ring, cytosine, thymin
nucleic acid polymer
polynucleotides, dinucleotides…
micelle
1 type of natural soln formed to minimize FA exposure to water, lipids organize themselves into circle with hydrophilic pieces facing out towards water
phospholipid bilayer
multiple rows of lipids with hydrophobic pieces touching and hydrophilic pieces facing out toward water
cytoplasmic membrane
phospholipid bilayer, contains phospholipids, proteins, cholesterol, and carbohydrates
proteins
2 types, integral and peripheral, aid in membrane transport
integral protein
spans membrane, at least one hydrophobic portion, involved in membrane transport
peripheral protein
stay to periphery of membrane, more hydrophilic
cholesterol
lipid, multi ringed, very hydrophobic, sits with fatty acids to break up their stacking, breaks up fluidity
carbohydrates (w cytoplasmic membrane)
polysaccharide chains attached to membrane components (2 types)
glycoprotein
sugars attached to proteins
glycolipid
sugars attached to phospholipids
gradient
difference in concentration of “stuff” across a space
diffusion
movement with the gradient
channel protein
provides open path for molecules, molecules diffuse down gradient, facilitated diffusion
carrier proteins
active transport, go against energy to move, going against conc. gradient
bulk transport
method of transporting bulky molecules across membrane, two types
endocytosis
bulk transport, bringing molecules into cell
exocytosis
bulk transport, cell membrane fuses with an organelle membrane to release material out of the cell
phagocytosis
endocytosis with food particles
pinocytosis
endocytosis with liquid
hypotonic solution
solution has low conc. gradient, water goes into the cell
isotonic
no conc. gradient, at equilibrium
hypertonic
soln has high conc. gradient, water moves out of cell
nucleus
contains dna in eukaryotes
smooth endoplasmic reticulum
lipid synthesis in cell