L3// Biology: Atomic Structure, Chemical Bonds, and Water Properties
1/49
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
50 Terms
What are the basic components of an atom?
protons, neutrons, and electrons.
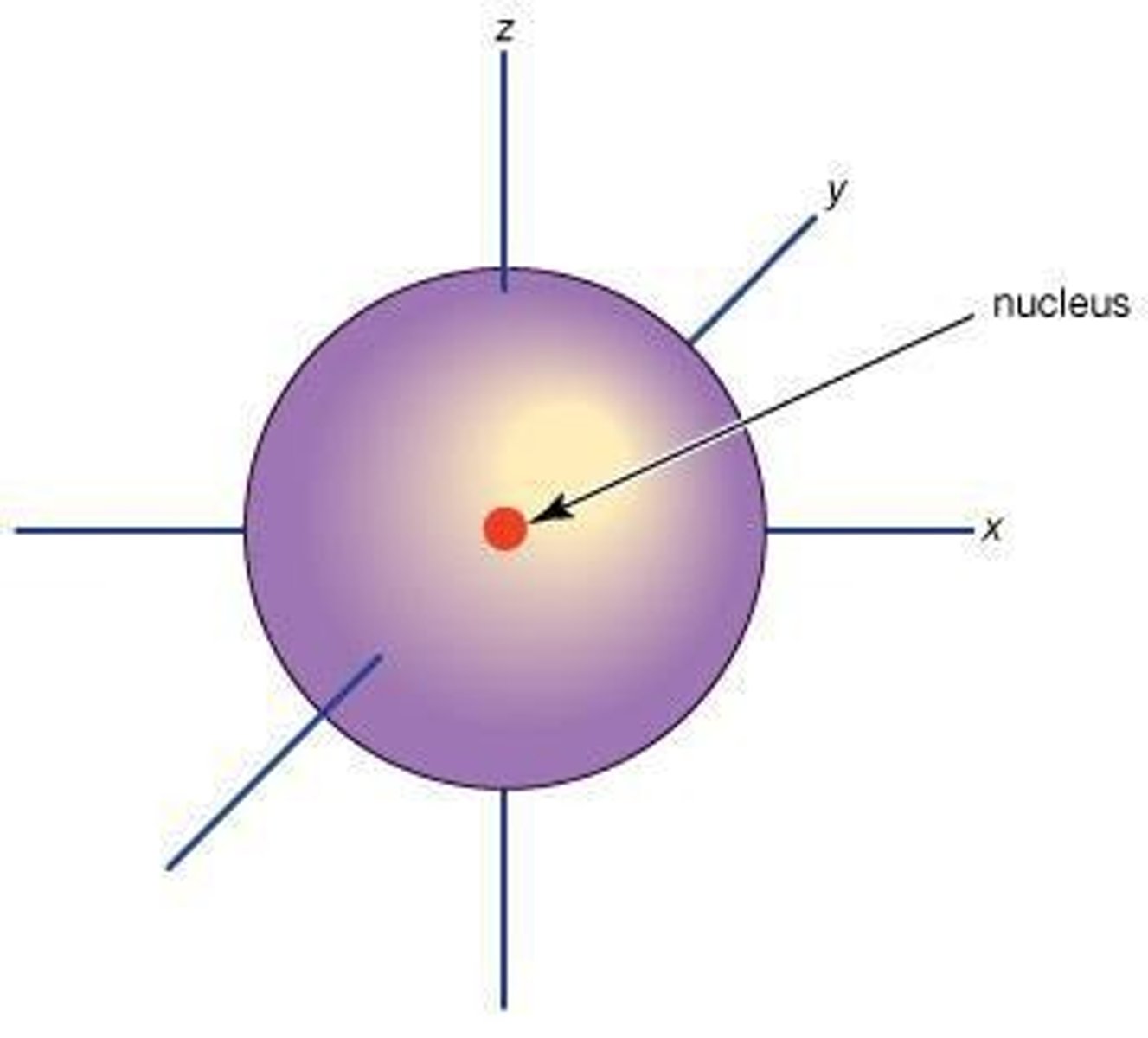
What is the charge of protons, neutrons, and electrons?
Protons are positively charged, neutrons are neutral, and electrons are negatively charged.
Where are protons and neutrons located in an atom?
Protons and neutrons are located in the nucleus.
What is the atomic number of an element?
The atomic number is the number of protons in the nucleus of an atom.
What are isotopes?
Isotopes are forms of an element with different numbers of neutrons.
What is the mass number of an atom?
The mass number is the sum of protons and neutrons in the nucleus.
What is the significance of electron arrangement in atoms?
Electron arrangement determines the chemical properties of an atom.
What is a valence shell?
The valence shell is the outermost occupied shell of an atom that contains valence electrons.
What is a covalent bond?
A covalent bond is formed when unpaired valence electrons are shared between two atoms.
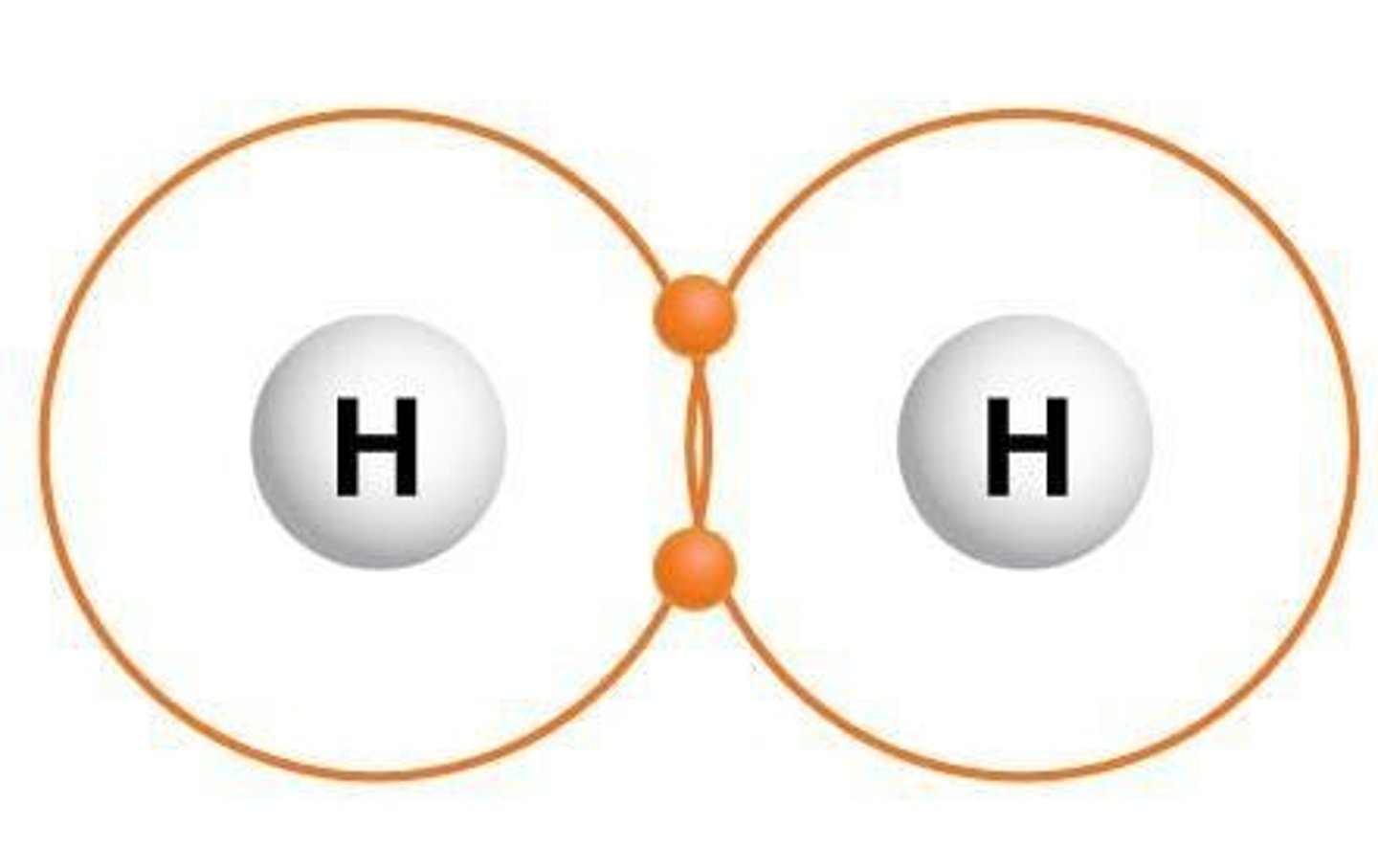
What distinguishes a polar covalent bond from a nonpolar covalent bond?
In a polar covalent bond, electrons are shared unequally, resulting in partial charges, while in a nonpolar covalent bond, electrons are shared equally.
What is an ion?
An ion is an atom or molecule that carries a charge.
What is the difference between a cation and an anion?
A cation is a positively charged ion that loses electrons, while an anion is a negatively charged ion that gains electrons.
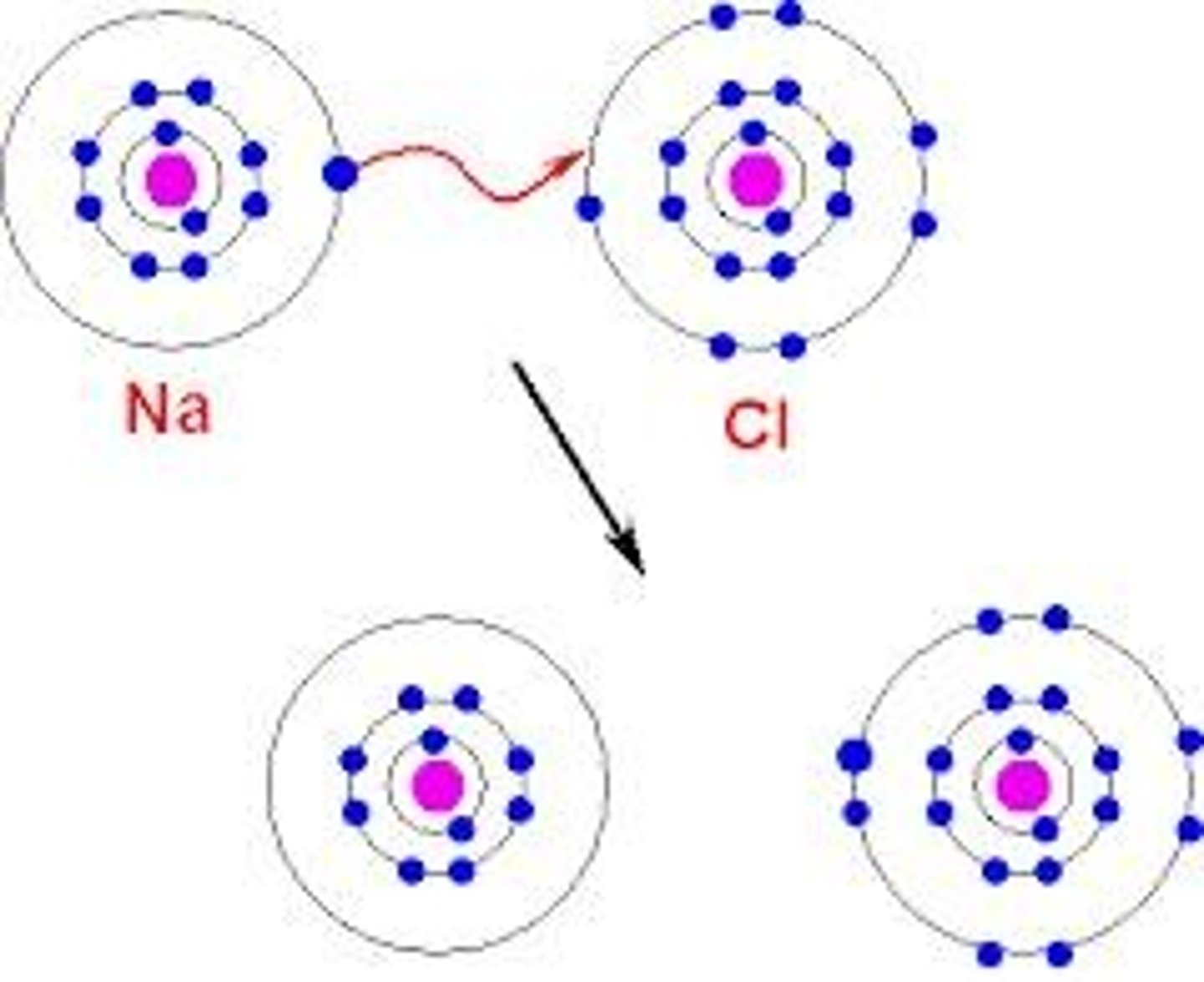
What is an ionic bond?
An ionic bond is the attraction between oppositely charged ions.
What is the role of chemistry in the evolution of life?
Chemistry is linked to the evolution of life through the formation of complex organic molecules from simple inorganic ones.
What are the two types of homework assignments mentioned?
The two types of homework assignments are a SmartBook assignment and a regular homework assignment.
What is the due date for homework assignments for Week 2?
Homework assignments are due on Sunday, September 7th at 9:00 PM.
What happens if a student does not submit the attendance sheet?
If a student does not submit the attendance sheet, their assignment may not be graded.
What is the maximum number of electrons that can occupy an orbital?
Each orbital can hold up to two electrons.
How are electron shells organized?
Electron shells are numbered based on their distance from the nucleus, with smaller numbers being closer.
What is the significance of valence electrons?
Valence electrons determine how an atom will bond with other atoms.
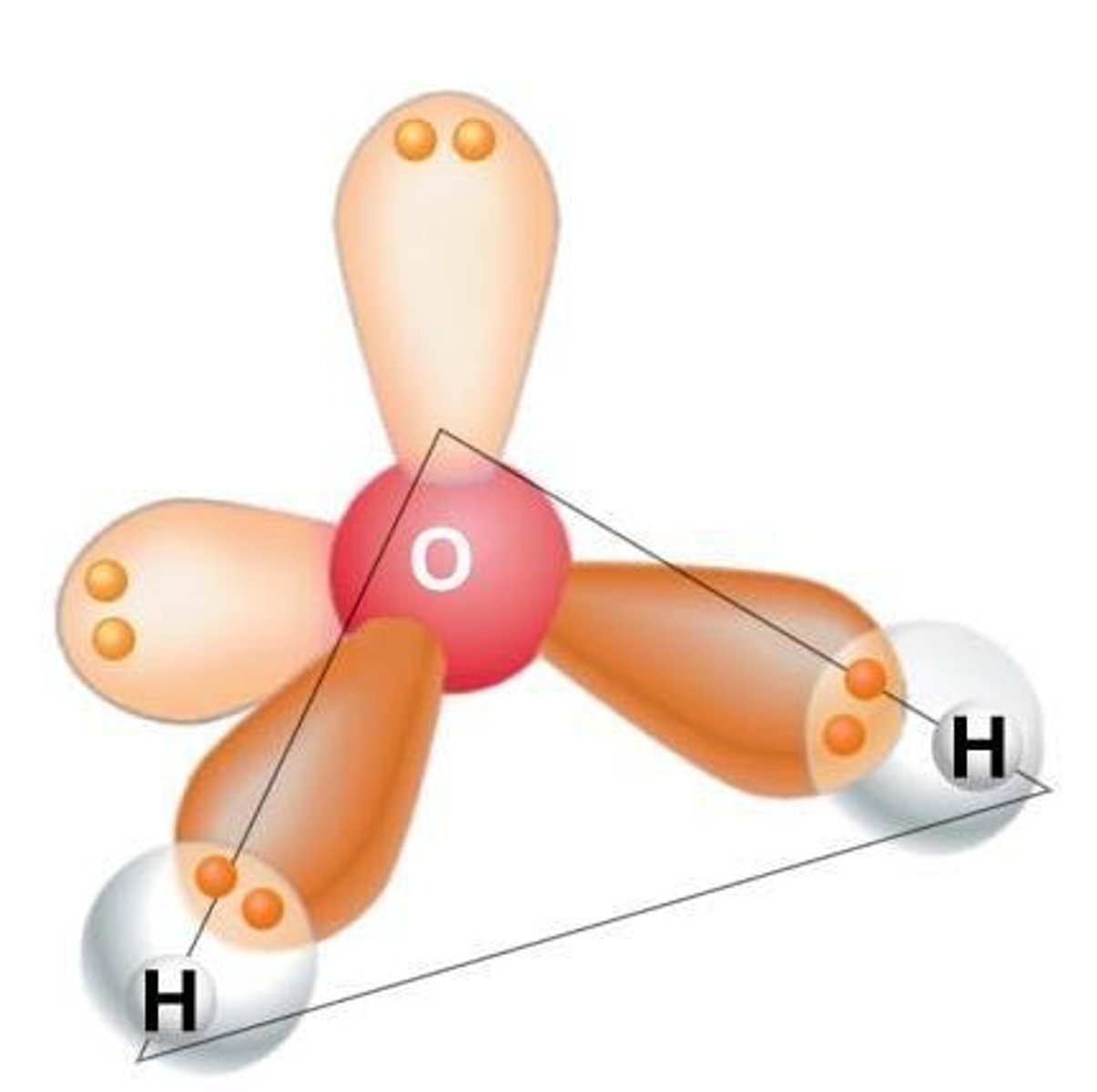
What is the structure of a water molecule in terms of covalent bonding?
In a water molecule, oxygen is more electronegative than hydrogen, leading to a polar covalent bond.
What is the relationship between the number of protons and electrons in a neutral atom?
In a neutral atom, the number of protons equals the number of electrons.
What does it mean for an atom to be stable?
An atom is most stable when each of its electron orbitals is filled.
What is the role of the Diagnostic Exam in the course?
The Diagnostic Exam assesses students' understanding and helps determine who needs to take Recitation.
What is the significance of the atomic mass measured in Daltons?
Atomic mass in Daltons reflects the mass of an atom based on its protons and neutrons.
What is the relationship between chemical evolution and organic molecules?
Chemical evolution involves the spontaneous reactions that generate complex organic molecules essential for life.
What forms the Electron-Sharing Continuum in chemical bonds?
The continuum ranges from equal sharing in nonpolar covalent bonds to unequal sharing in polar covalent bonds, to complete transfer of electrons in ionic bonds.
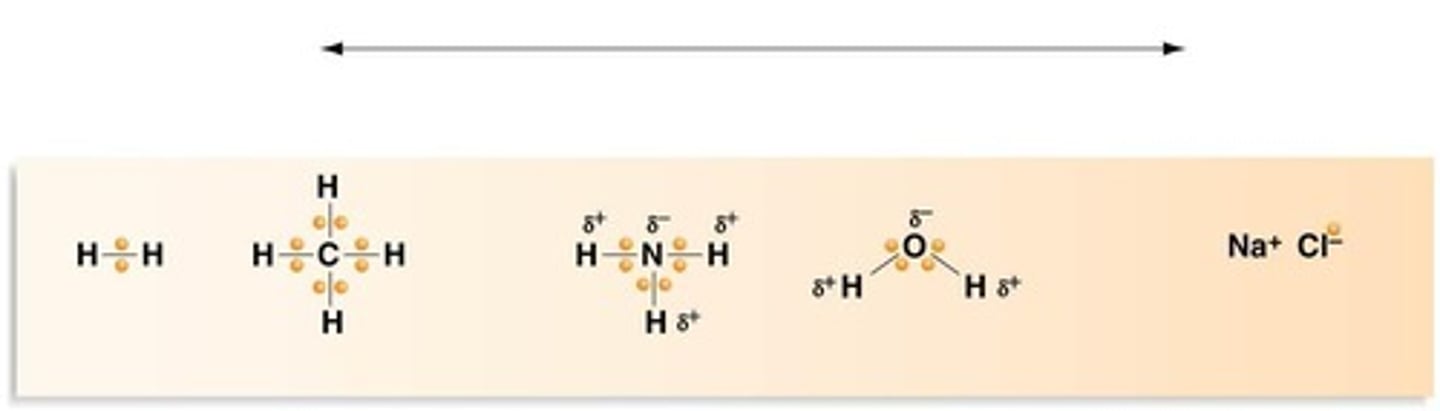
What type of bond involves equal sharing of electrons?
Nonpolar covalent bonds.
What type of bond involves unequal sharing of electrons?
Polar covalent bonds.
What type of bond involves the complete transfer of electrons?
Ionic bonds.
What determines the number of bonds an atom can form?
The number of unpaired electrons.
What is a chemical reaction?
A process where substances are combined, rearranged, or broken down, involving the breaking and forming of chemical bonds.
What are the molecular formulas for water and methane?
Water: H2O, Methane: CH4.
What is the significance of carbon in organic molecules?
Carbon's four valence electrons allow it to form a diverse array of covalent bonds and molecular shapes.
What is the pH scale based on?
The concentration of protons (H+) in a solution.
What pH value indicates a neutral solution?
A pH of 7.
What characterizes acids and bases in terms of pH?
Acids have a pH < 7, while bases have a pH > 7.
What are buffers?
Compounds that minimize changes in pH.
What is the role of functional groups in organic molecules?
They determine the chemical behavior and properties of the molecules.
What is the importance of hydrogen bonds in water?
They create weak attractions between water molecules, contributing to water's unique properties.
What does it mean for water to be a polar molecule?
Water has a partial negative charge on oxygen and a partial positive charge on hydrogen, leading to hydrogen bonding.
What is cohesion in the context of water?
The attraction between water molecules that results in high surface tension.
What is adhesion in the context of water?
The attraction between water molecules and other substances, allowing water to climb surfaces.
What property of water allows ice to float?
Water is less dense as a solid than as a liquid.
What is high specific heat in water?
The amount of energy required to raise the temperature of 1 gram of water by 1 °C.
What happens to water molecules during dissociation?
They split into hydrogen ions (H3O+) and hydroxide ions (OH-).
What is a strong acid's behavior in water?
It readily donates protons when reacting with water.
What is a strong base's behavior in water?
It readily acquires protons when reacting with water.
What are the four most abundant elements in living matter?
Carbon, hydrogen, oxygen, and nitrogen.
What is the significance of hydrogen bonds in biological systems?
They allow for the solubility of polar and charged molecules in water, facilitating biochemical reactions.