Light Independent Stage
1/15
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
16 Terms
Light Independent Stage
Hydrogen from reduced NADP (NADPH) and carbon dioxide is used to build organic molecules, such as glucose. ATP supplies the required energy.
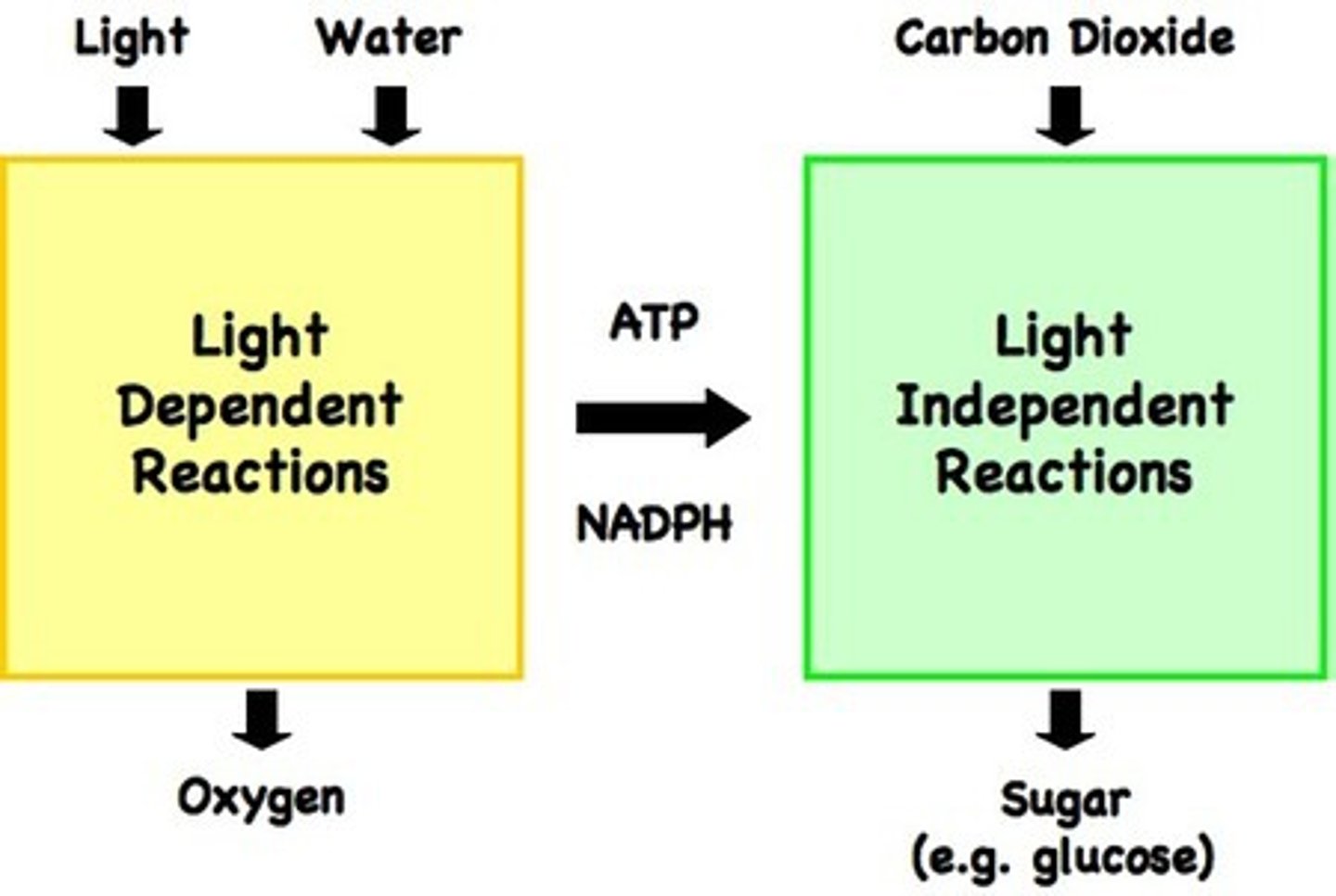
Where does the LIR / Calvin cycle take place?
Stroma
1)
- Carbon fixation
CO2 is combined with 5C molecule "ribulose bisphosphate" (RuBP)
The enzyme "Ribulose bisphosphate carboxylase" (RuBisCO) catalyses the reaction and an unstable 6C intermediate is produced
What is RuBisCO completely inhibited by?
Oxygen
2)
The unstable 6C compound breaks down to form 2x 3C glycerate 3-phosphate (GP) molecules
3)
- Each GP molecule is converted to another 3C molecule, triose phosphate (TP)
- It converted by using a H atom from reduced NADP (NADPH - this is oxidation of NADPH) and energy supplied by ATP (ATP --> ADP).
- Both of these are from the LDR
4)
TP is a carbohydrate 3C sugar, and the majority of which is recycled to regenerate RuBP so that the Calvin cycle can continue.
Fixation
Carbon dioxide is fixed (incorporated into in organic molecule) in the first step
Reduction
GP is reduced to TP by the addition of hydrogen from reduced NADP using energy supplied by ATP
Regeneration
RuBP is regenerated from the recycled TP
1) Regeneration of RuBP
For 1 glucose molecule to be produced, 6 carbon dioxide molecules have to enter the Calvin cycle, resulting in 6 full turns of the cycle
2) Regeneration of RuBP
This will result in 12 TP molecules, 2 of which will be removed to make the glucose molecule
3) Regeneration of RuBP
This means 10x TP molecules are recycled to regenerate 6x RuBP molecules
4) Regeneration of RuBP
10 x 3C TP = 30 carbons
5) Regeneration of RuBP
This gives 5 x 5C RuBP = 30 carbons
6) Regeneration of RuBP
Energy is supplied by ATP for the reactions involved in the regeneration of RuBP