Chapter 11: Motivation and Emotion
1/99
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
100 Terms
motivation
the urge to move toward one's goals; to accomplish tasks.

needs
inherently BIOLOGICAL states of deficiency (cellular or bodily) that compel drives. (What your body needs) Example:
Water, food, oxygen

drives
the perceived internal states of tension/arousal that occur when our bodies are deficient in some need, creating an urge to relieve the tension. Example: thirst, hunger
Motivated behavior results from:
needs and drives
incentive
any external object or event that motivates behavior. (comes from the environment). Example: financial independence, a gold medal, academic success.

__________ come from the body. whereas _______________ come from the environment
drives; incentives
homeostasis
the process by which all organisms work to maintain physiological equilibrium or balance around an optimal set point.
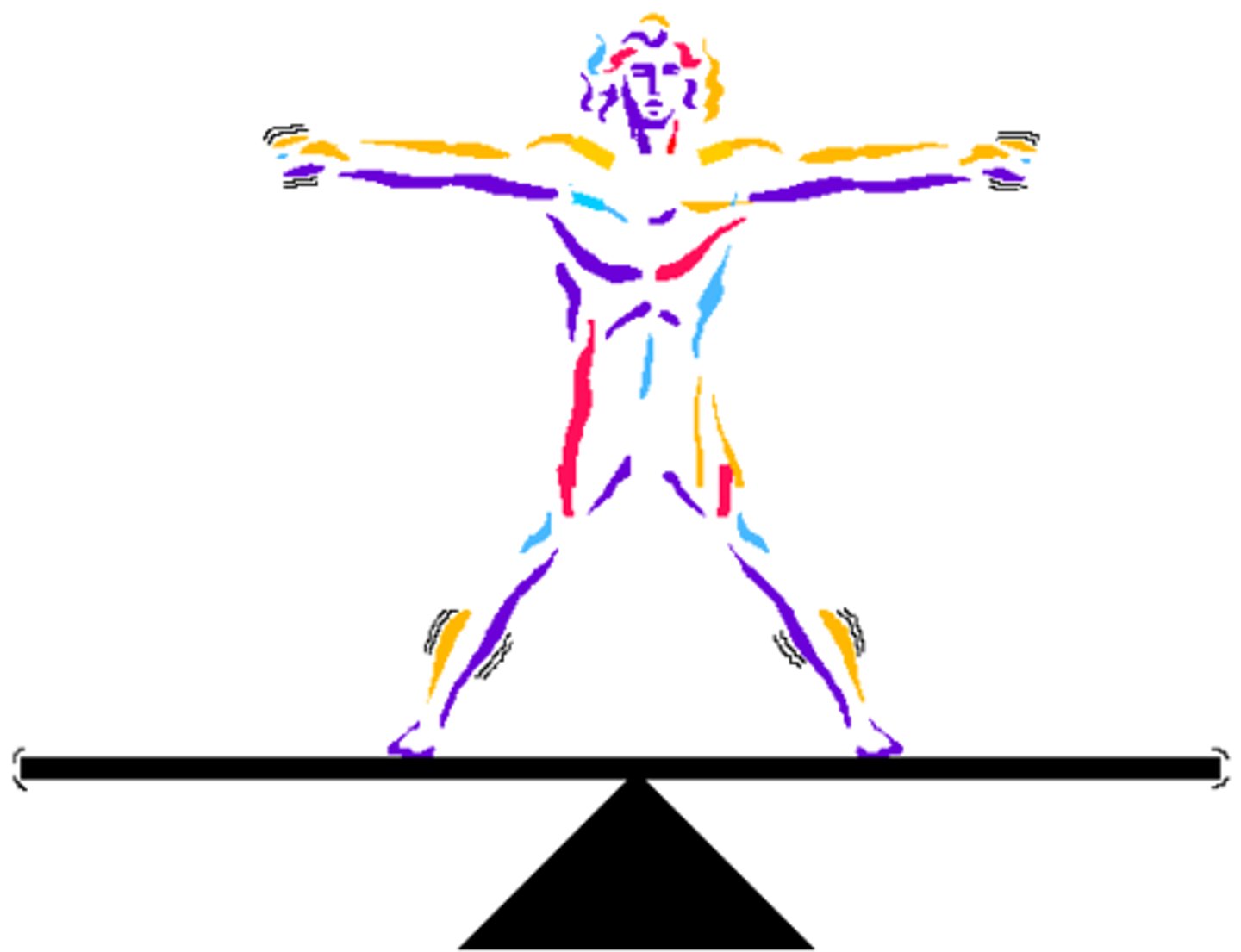
set point
the ideal fixed setting of a particular physiological system, such as internal body temperature.

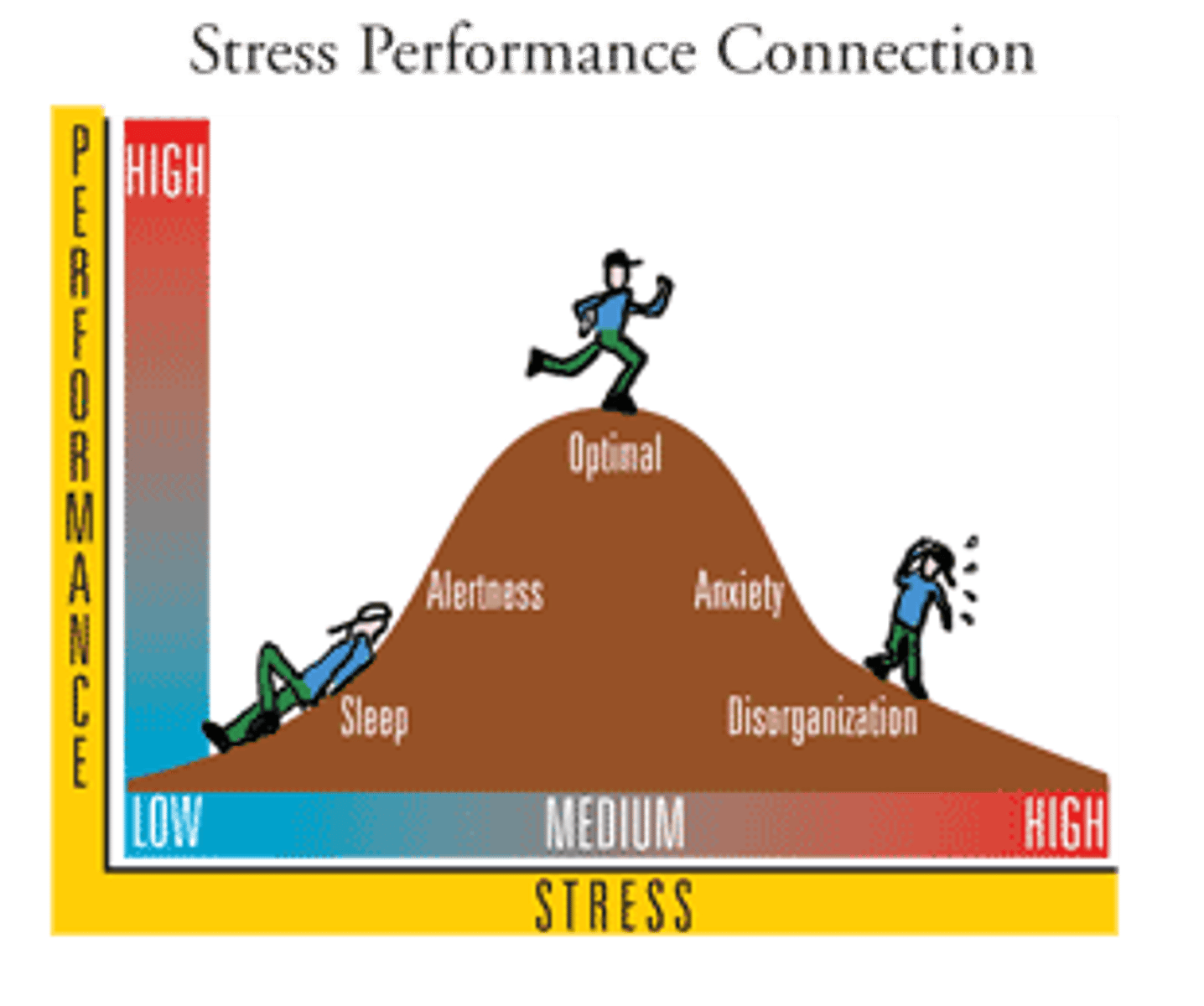
Yerkes-Dodson law
the principle that moderate levels of arousal lead to optimal performance. Achievement motivation a desire to do things well and overcome obstacles.
Motivation serves to ______________ behavior
energize and direct
__________________ approaches suggest that a lack of some basic biological requirement, such as water, produces a drive to obtain that requirement
Drive reduction
On a very hot day when we are extremely thirsty, we simply must get that drink of water. This illustrates the concept of ___________.
drives
If you anticipate that you will be getting a good grade, you are expecting an _______________.
incentive
4 models of motivation:
-Drive reduction
-Optimal arousal
-Evolutionary model
-Hierarchial (Maslow)
self-actualization
the inherent drive to realize one's full potential.
glucose
a simple sugar that provides energy for cells throughout the body, including the brain.

4 components of hunger:
the stomach, the blood, the brain, and hormones & neurotransmitters
The brain can only use:
glucose
The hypothalamus function in hunger:
regulates all basic physiological needs and acts as hunger's sensory detector. Monitors glucose levels triggers the drive to obtain food.
hormones that stimulate appetite:
neuropeptide Y (NPY) and Ghrelin
hormones that suppress appetite:
insulin and leptin
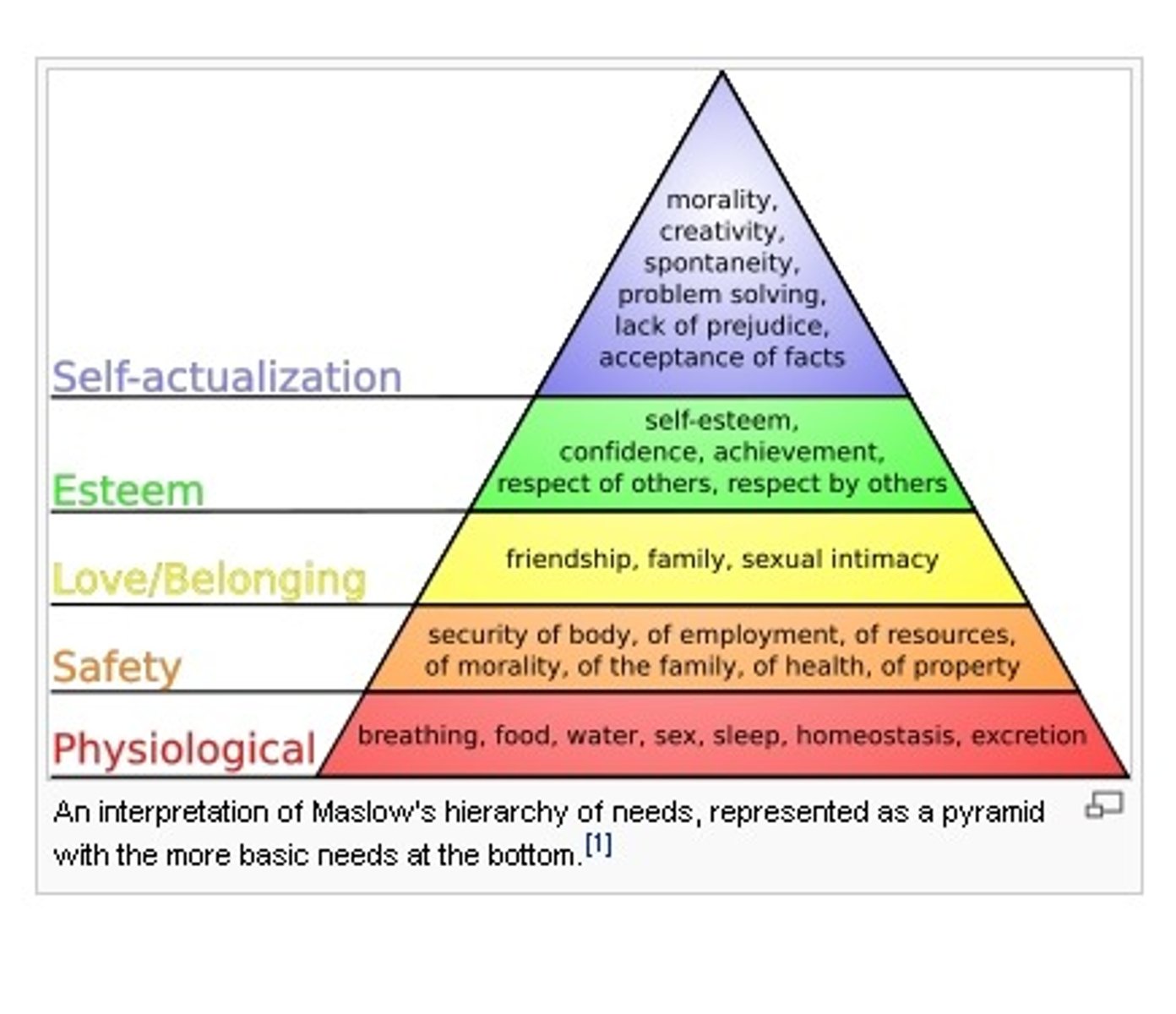
Maslow's hierarchy of needs from highest to lowest:
-Self-actualization
-Esteem
-Love and belongingness
-Safety and security
-Physiological
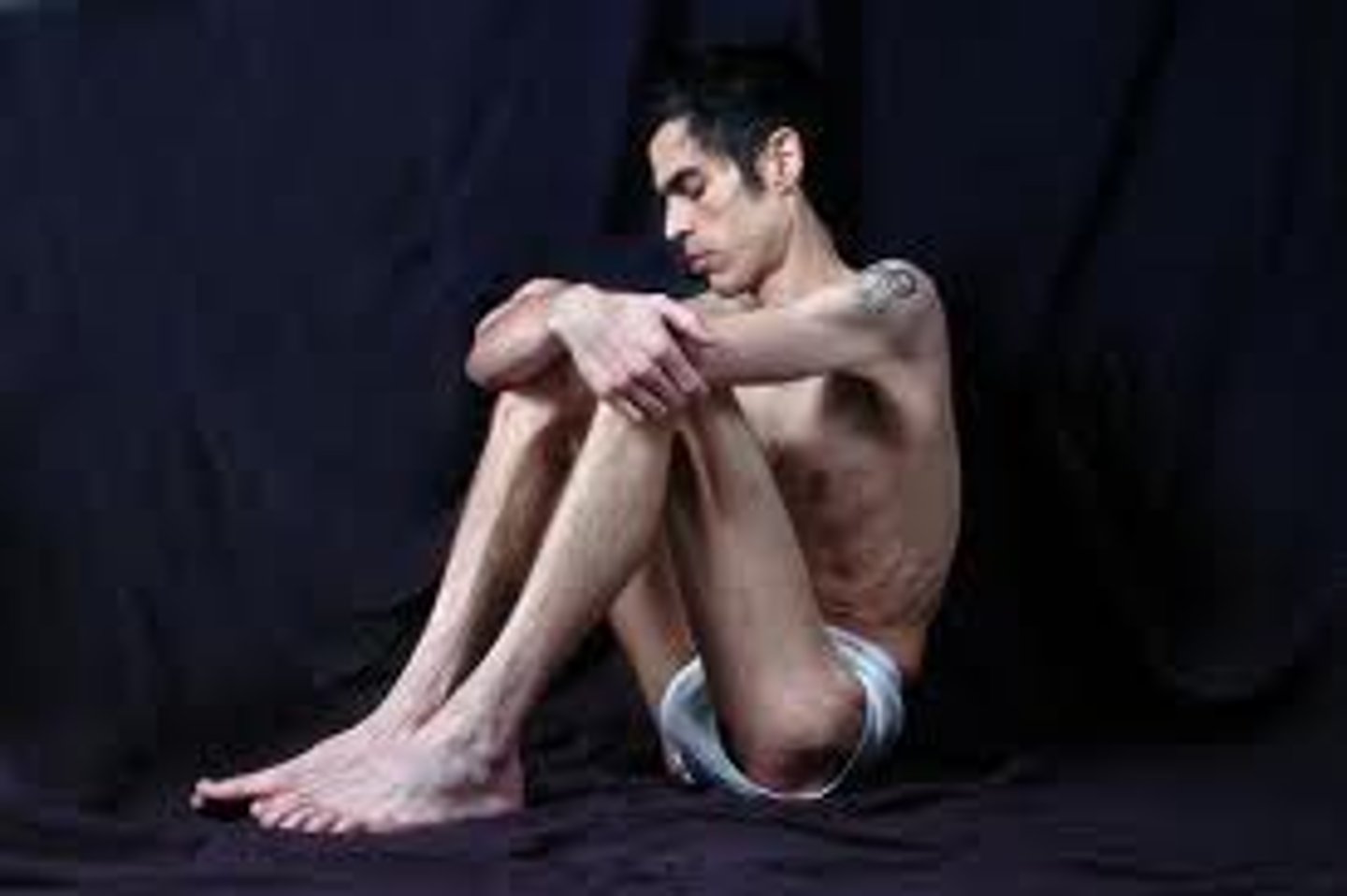
anorexia nervosa
an extreme fear about being overweight that leads to a severe restriction of food intake.
bulimia nervosa
prone to binge eating and feeling a lack of control during the eating session
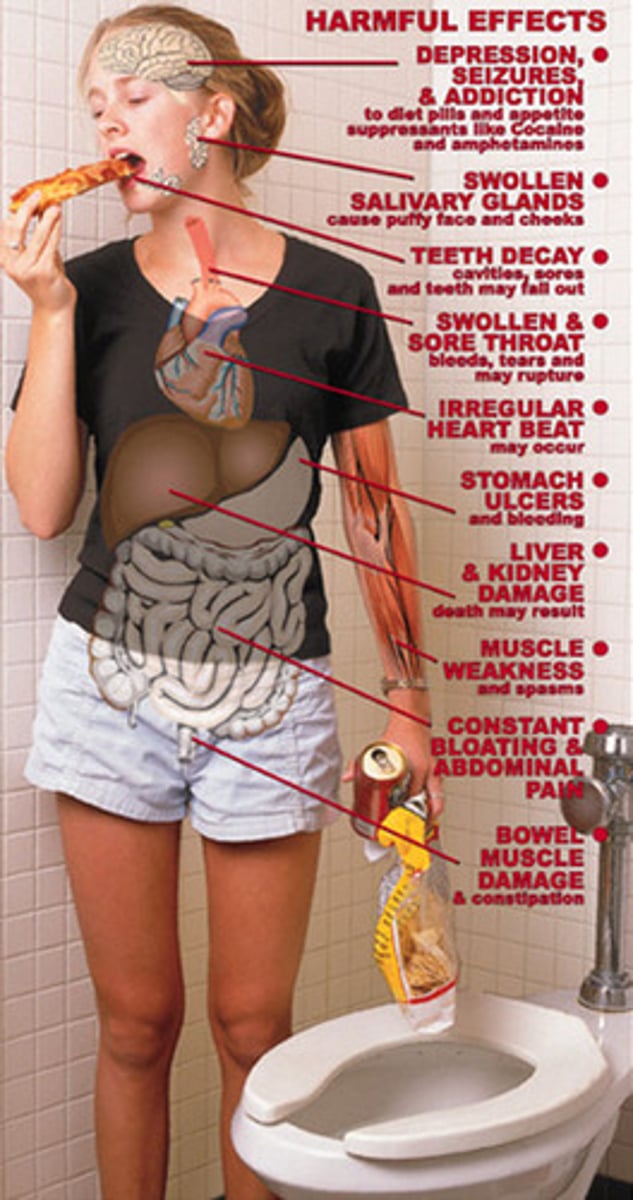
sexual behavior
actions that produce arousal and increase the likelihood of orgasm.
4 phases of sexual arousal:
excitement, plateau, orgasm, and resolution
Adrenal glands produce ______________
testosterone.
3 kinds of societies in terms of sexual attitudes:
-Restrictive(restrict sex before & outside marraige)
-Semirestrictive (place formal prohibitions on pre- and extramarital sex that are not strictly enforced)
-Permissive( place few restrictions on sex)
sexual orientation
the disposition to be attracted to either the opposite sex (heterosexual), the same sex (homosexual), or both sexes (bisexual).

What is the ideal BMI?
between 20 and 25
Our genetics are about _____ responsible for adult weight.
70%
How might the hormone leptin explain obesity?
The gene for leptin, which suppresses appetite, may be mutated in some individuals and lead to obesity.
2 common myths about dieting:
-thinking that low-carb and low-fat diets and good and vice versa
-eating smaller more frequent meals per day is a good way to lose weight
Most evidence in dieting research suggests that dieting does not work
long-term
Example of a healthy eating behavior?
Stopping eating only when you feel full
excitement phase of sexual arousal characterized by
vaginal lubrication in women and erection in men
achievement motivation
a desire to do things well and overcome obstacles.

3 functions of tendencies to achieve success:
-motivation to succeed
-expectation of success
-incentive value of the success
3 models of how to best motivate workers(employee motivation):
-Extrinsic motivation
-Instrinsic motivation
-Perceived organizational support for the well-being of employees
extrinsic motivation
motivation that comes from outside the person and usually involves rewards and praises. Example: Allowance, a raise. Drawbacks: requires reward to be constant.
intrinsic motivation
motivation that comes from within a person and includes the elements of challenge, enjoyment, mastery, and autonomy. Changes as lifestyle circumstances change.
4 components of intrinsic motivation:
-challenge
-enjoyment
-mastery
-autonomy
perceived organizational support
employees' beliefs about how much the organization appreciates and supports their contributions and well-being.
Which model of motivation can be compared to the thermostat in you house?
drive-reduction
Testosterone is associated with sex drive in men only (True or False)
False
emotions
brief, acute changes in conscious experience and physiology that occur in response to a personally meaningful situation.
Emotions can overide biological ________
drives. Example: Disgust turns off drive of hunger
Emotions can turn off the _________ of hunger, thirst, and sex.
drives
moods.
affective states that operate in the background of consciousness and tend to last longer than most emotions

affect
a variety of emotional phenomena: emotions, moods, and affective traits.
Affective traits
Stable predispositions towards certain types of emotional repsonses. The enduring part of out personalities that set threshold for occurence of particular emotional states, such as hostility or anxiety.
basic emotions
set of emotions that are common to all humans. Includes: anger, disgust, fear, happiness, sadness, and surprise.
broaden-and-build model
Fredrickson's model for positive emotions, which posits that they widen our cognitive perspective and help us acquire useful life skills.
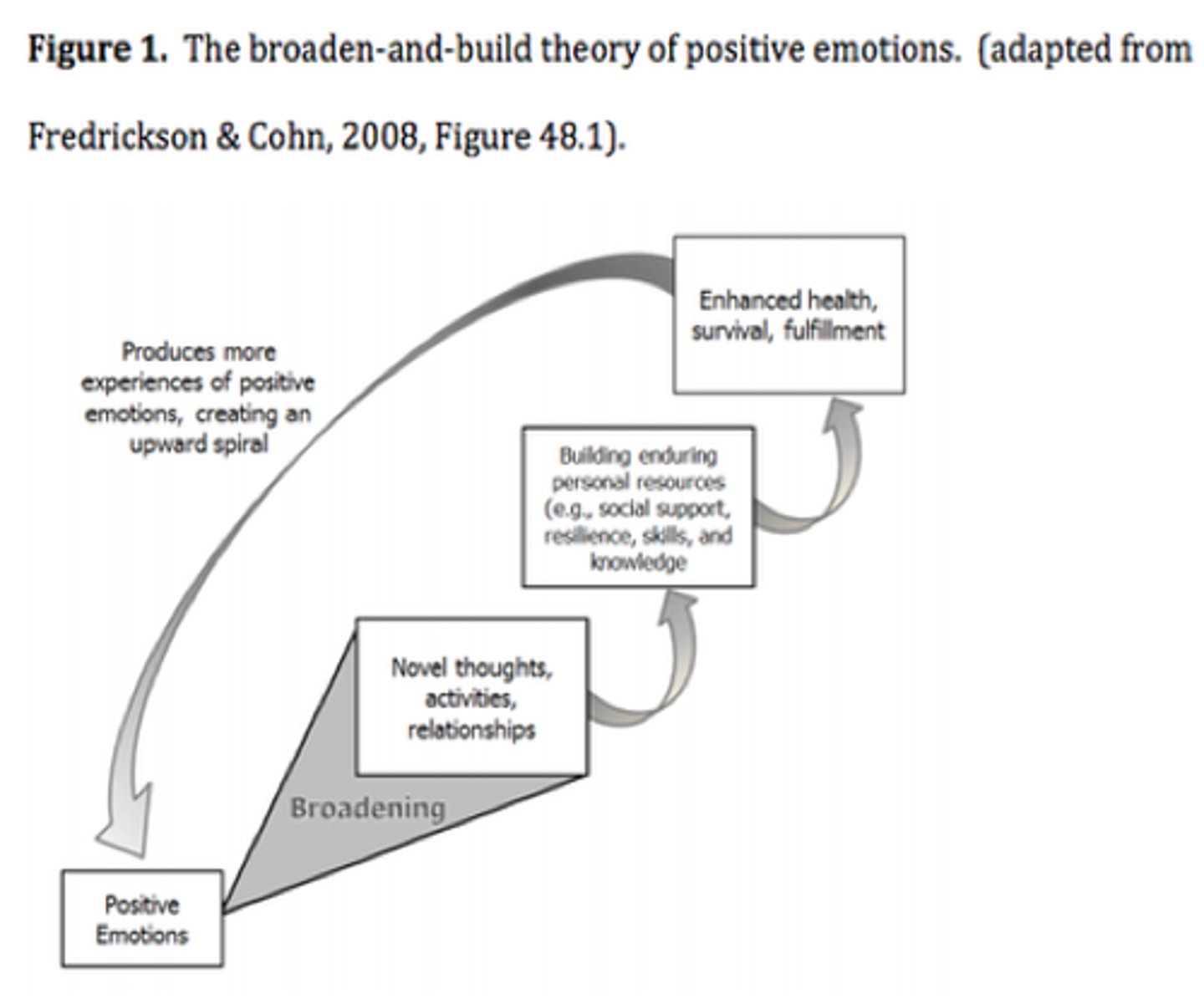
emotion regulation
the cognitive and behavioral efforts people make to modify their emotions.
self-conscious emotions
types of emotion that require a sense of self and the ability to reflect on actions; they occur as a function of meeting expectations (or not) and abiding (or not) by society's rules.

appraisal
the evaluation of a situation with respect to how relevant it is to one's own welfare; drives the process by which emotions are elicited.
reappraisal
an emotion regulation strategy in which one reevaluates an event so that a different emotion results.
expressive suppression
a response-focused strategy for regulating emotion that involves the deliberate attempt to inhibit the outward manifestation of an emotion.
emotional response
the physiological, behavioral/expressive, and subjective changes that occur when emotions are generated.
universal
term referring to something that is common to all human beings and can be seen in cultures all over the world.
Facial Action Coding System (FACS)
a widely used method for measuring all observable muscular movements that are possible in the human face.
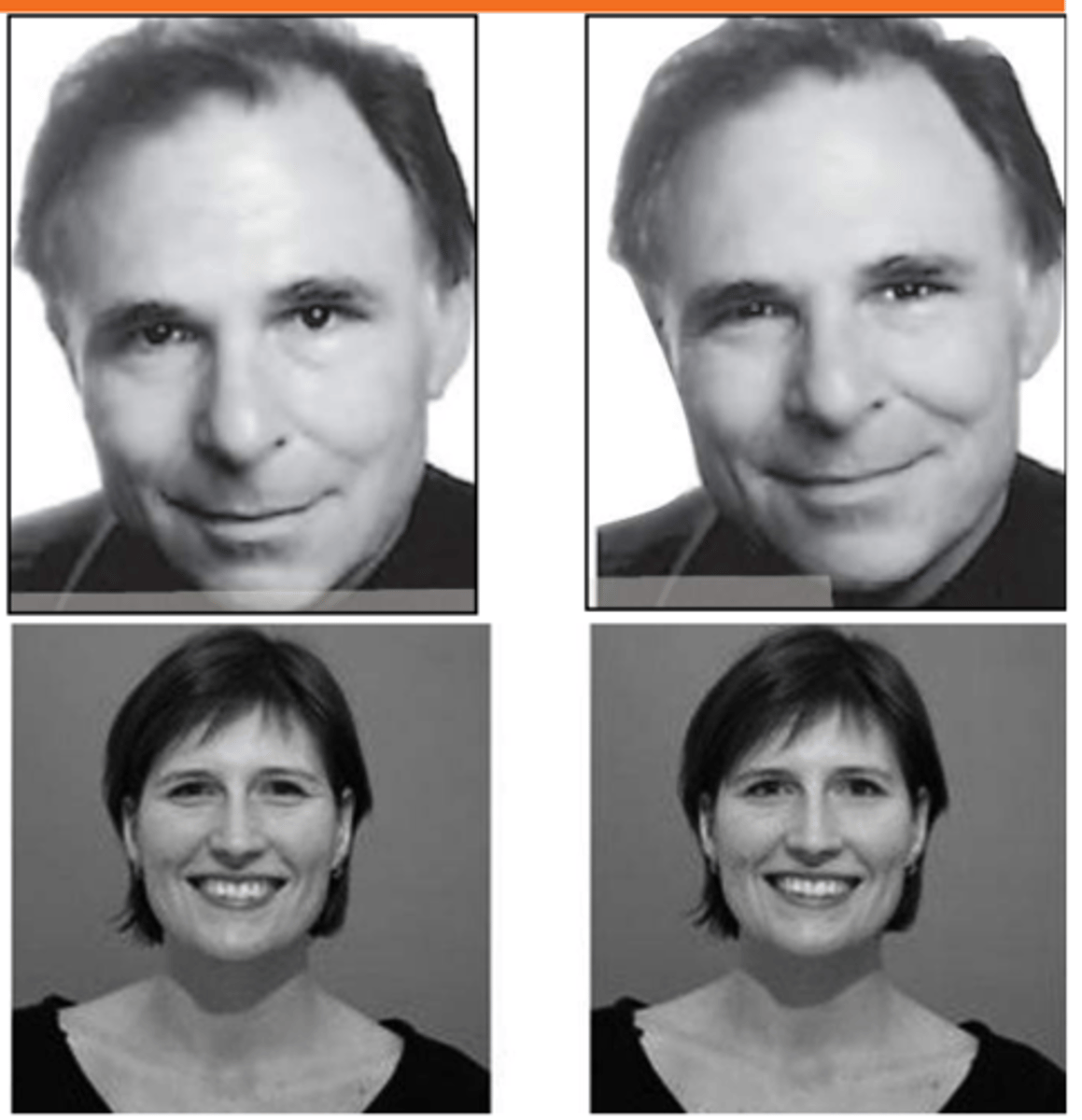
Duchenne smile
a smile that expresses true enjoyment, involving both the muscles that pull up the lip corners diagonally and those that contract the band of muscles encircling the eye.

subjective experience of emotion
the changes in the quality of our conscious experience that occur during emotional responses.
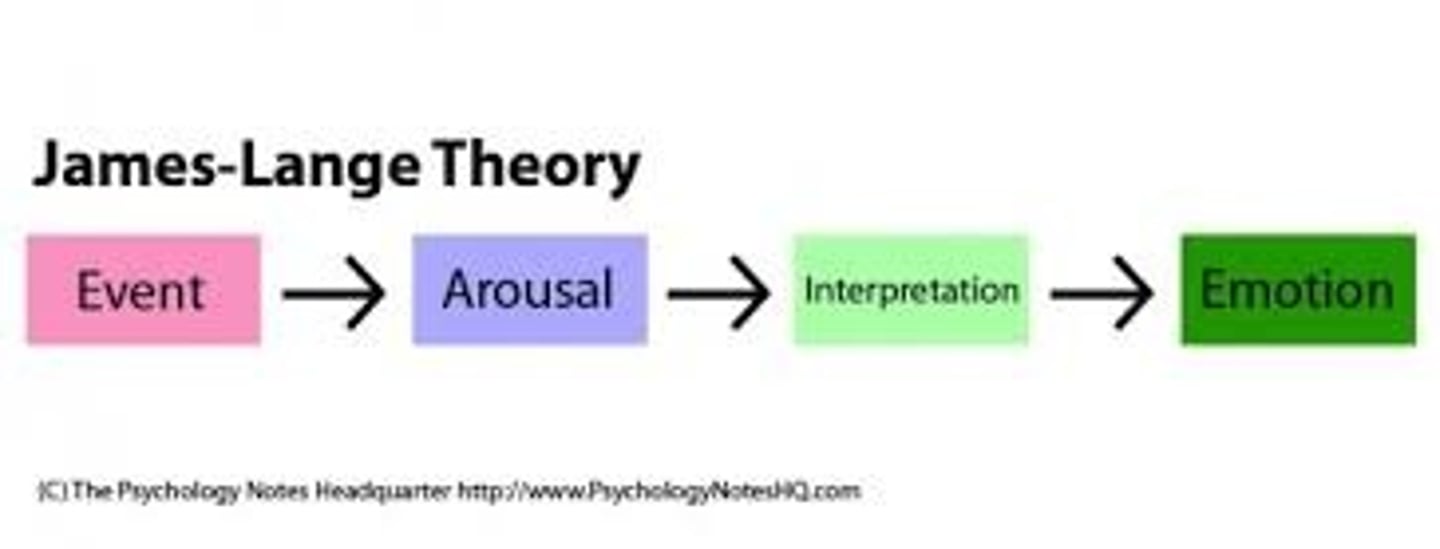
James-Lange theory of emotion
the idea that it is the perception of the physiological changes that accompany emotions that produces the subjective emotional experience.
facial feedback hypothesis
sensory feedback from the facial musculature during expression affects emotional experience
neurocultural theory of emotion
Ekman's explanation that some aspects of emotion, such as facial expressions and physiological changes associated with emotion, are universal and others, such as emotion regulation, are culturally derived. (Some aspects of emotion are universal and others are culturally derived.)
display rules
learned norms or rules, often taught very early, about when it is appropriate to express certain emotions and to whom one should show them.
How many emotions are expressed facially in the same way by all members of the human race?
six
emotional intelligence
the ability to recognize emotions in oneself and others, empathic understanding, and skills for regulating emotions in oneself and others.
emotion family
categories or groups of related emotions
Re-appraisal and expressive suppression are examples of what?
emotion regulation
Types of emotion regulation?
-Re-appraisal
-Expressive suppression
life satisfaction
the overall evaluation we make of our lives and an aspect of subjective well-being.
antecedent event
a situation that may lead to an emotional response.
Subjective well-being
state that consists of life satisfaction, domain satisfactions, and positive and negative affect.
That fact that sexual orgasm cannot occur unless the areas of the brain involved in fear and anxiety are shut down illustrates what basic feature of emotions versus drives?
Emotions can override biological drives
Which of the following is NOT a self-conscious emotion?
hostility
According to the view of emotions as a process, _____________ drive(s) the process by which emotions are elicited.
appraisal
Which of the following is NOT a basic emotion?
shame
The social norm set forth by our culture, which says that winners should not gloat, is an example of a(n)
display rule
The ___________ appears to play a very important role in appraisal of the emotional significance of stimuli, with a specialized function of noticing fear-relevant information.
amygdala
Which kind of emotion phrases are women more apt to use than men?
more specific comments, such as "I am upset and angry"
Optimal level of arousal Model
proposes that we function best when we are moderately aroused, or energized. Argues that humans are motivated to be in situations that are neither too stimulating nor not stimulating enough
In acheivement motivation, _______________ stems from two factors: the importance of succeeding and the difficulty of the task
incentive value
Our genetics are about ________ responsible for adult weight.
70%
Drive-reduction theory:
When our physiological systems are out of balance or depleted, we are driven to reduce this depleted state.
3 models of employee motivation:
-Perceived organizational support
-Intrinsic motivation
-Extrinsic motivation
Important factors of incentive value:
-Difficulty of the task
-Importance of succeeding
emotion family (Ekman)
a group of related emotions
6 basic emotions of the human race:
-Happiness
-Disgust
-Fear
-Sadness
-Anger
-Surprise
The _____________ triggers the drive to obtain food.
Hypothalamus
What regulates all basic physiological needs and act's as hungers sensory detector?
the hypothalamus
What we eat is both shaped by ____________ and _____________.
nature; nurture
Our choice of what we eat is also driven by__________.
culture
In some obese people, the gene that produces the hormone leptin has suffered a ____________.
mutation.
Affliation
the need to for social contact and belonging
Achievement
The need to excel and compete
Atkinson said the tendency to acheive success is a function of three things:
-motivation to succeed
-the expectation of success
-incentive value of the success
In addition to blood sugar (glucose) and the hypothalamus, and as discussed in this chapter, what is another important biological system involved in regulating hunger?
Hormones
Most reserarch on weight loss has reported that:
losing weight is relatively easy initially, but keeping it off is very difficult