Mitosis and Meiosis Definitions
1/15
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
16 Terms
Prophase (Mitosis)
DNA condenses and winds up tightly
Nuclear envelope breaks down
Centrioles move to opposite ends of the cell and spindles begin to form
Spindle fibres stretch across cell

Metaphase (Mitosis)
Chromosomes line up in the middle of cell
Spindle fibres attach to the centromeres
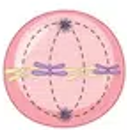
Anaphase (Mitosis)
Centromeres divide
Chromosome move to opposite ends of the cell
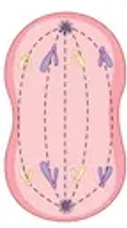
Telophase (Mitosis)
Chromosomes uncoil
Spindle fibres break down
New nuclear envelope begins to form
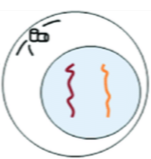
G1 Stage (Interphase)
Cytoplasmic components are replicated
The cell grows in size
Carries out assigned functions via producing specific proteins
S Stage (Interphase)
All DNA in the nucleus is copied to create two identical strands of each chromosome
G2 Stage (Interphase)
Second growth stage where mitochondria are replicated
DNA is checked and repaired before division
Centrioles begin to form
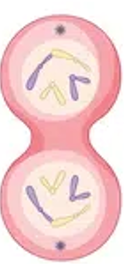
Cytokinesis
The cytoplasm divides along a cleavage furrow
New cell membranes form around daughter cells
Prophase 1 (Meiosis)
DNA condenses
Nuclear envelope breaks down
Chromosomes pair up and recombination can occur
Centrioles go to either end of the cell and spindle forms
Anaphase 1 (Meiosis)
Spindle fibres pull one of each pair of chromosomes to opposite sides of the cell
Telophase 1 (Meiosis)
Spindle disappears, nuclear envelope reforms
Cytokinesis divides the cells into two
Prophase 2 (Meiosis)
Nuclear envelope fragments, centrioles move to opposite ends of the cell and spindle fibres form
Metaphase 2 (Meiosis)
Chromosomes line up down the middle of the cell
Spindle fibres attach to centromeres
Anaphase 2 (Meiosis)
The arms of each chromosome move to each end of the cell
Mitosis
Occurs in most of the body cells where 2 new cells are formed
Meiosis
Only used to produce gametes where 4 new cells are formed