! BIOL 1410 Special senses
1/64
Earn XP
Description and Tags
LECTURE 20
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
65 Terms
The eye is a _ layered sphere fill with fluid
“3”
What are the 6 structural features of the eye?
Fibrous tunic, vascular tunic, nervous (sensory) tunic/retina, lens, anterior segment, posterior segment
What are the 3 parts of the fibrous tunic?
Sclera, cornea, conjunctiva
Is the sclera or cornea white? Which is transparent?
Sclera (white), cornea (transparent)
The sclera and cornea both consist of _________ (vascularity) CT
“avascular”
What does the conjunctiva of the fibrous tunic cover?
Anterior sclera
What is the vascularity and type of membrane of the conjunctiva?
Vascular, mucous membrane
What do we see when vessels of the conjunctiva dilate?
Bloodshot eyes
What are the 4 parts of the vascular tunic?
Choroid, ciliary body, iris, pupil
Which is anterior/posterior; choroid and ciliary body
Choroid (posterior), ciliary body (anterior)
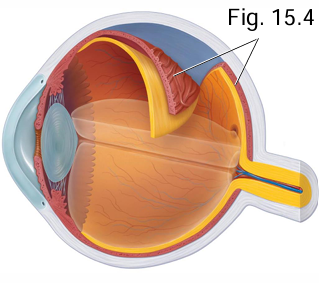
What is contained in the choroid of the vascular tunic?
Melanin
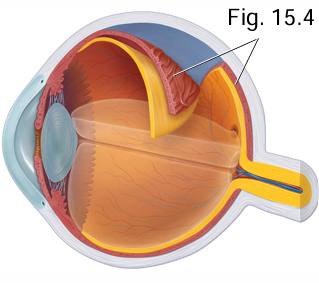
What is the vascularity of the choroid?
Highly vascular
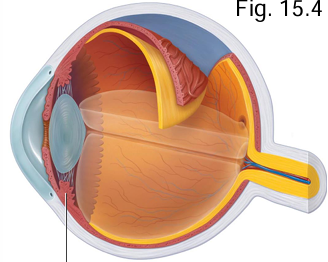
What 2 parts of the ciliary body form the focus lens?
Ciliary muscle + ciliary processes
What is the iris?
Coloured part of the eye
What is the pupil?
Dark hole in iris
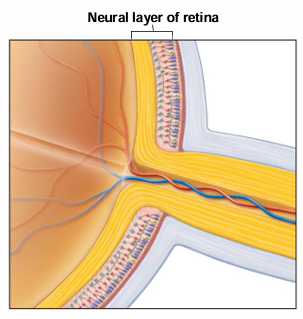
What are the 4 parts of the nervous (sensory) tunic/retina?
Outer pigmented layer, inner neural layer, fovea centralis, optic disc
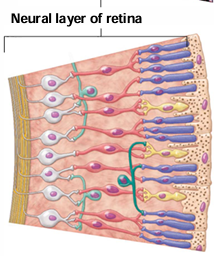
What are the 3 layers of neurons within the inner neural layer of the nervous (sensory) tunic/retina?
Photoreceptors, bipolar cells, ganglion cells
What are the 2 types of photoreceptors in the retina?
Rods, cones
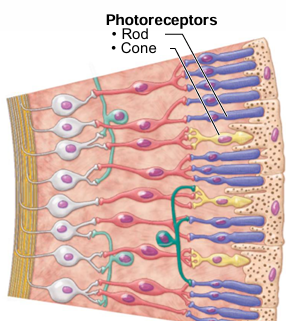
Of rods and cones, one is black/white and one is colour. Which is which?
Rods (black + white), cones (colour)
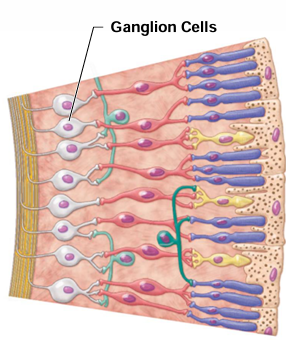
What do axons of ganglion cells form?
Optic nerve (CN II)
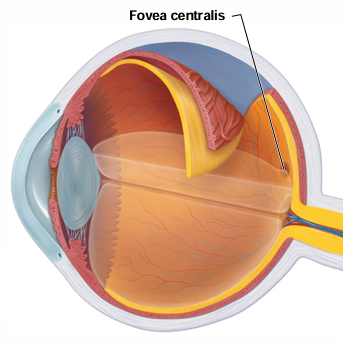
The fovea centralis is significant because?
It is where light is focused

The fovea centralis is the area of greatest visual acuity. What does this mean?
Visual acuity relates to how sharp and clear your eyesight is, specifically your ability to focus on objects and see fine details
Are only rods or only cones found in the fovea centralis?
Only cones
The optic disc is the blind spot where what 2 structures exit the eye?
Blood vessels + optic nerve
What is the vascularity and transparency (white/transparent) of the lens?
Avascular, transparent
What are cataracts?
Clouding of the lens
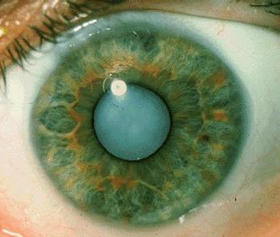
The anterior and posterior segments (individual structural features of the eye) are anterior/posterior to what previously mentioned feature?
Lens
What is contained in the anterior segment?
Aqueous humor
What is the aqueous humor similar to?
Plasma
What is contained in the posterior segment?
Vitreous humor
What is the physical consistency of the vitreous humor?
Gel-like
What are the 5 parts of the ear?
External ear, middle ear, inner ear (labyrinth), cochlea, receptors in inner ear
What does the external ear and middle ear both do?
Conducts sound
What are the 3 parts of the external ear?
Auricle (pinna), external auditory canal (meatus), tympanic membrane
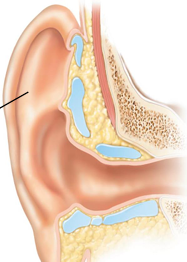
What is the auricle pinna physically made of (tissue type + what it’s covered with)?
Elastic cartilage covered with skin
What is the tympanic membrane more commonly referred to?
Eardrum
What are the 2 parts of the middle ear?
Eustachian tube, ear ossicles (bones)
What is the eustachian tube also called?
Pharyngotympanic tube
What are the 3 ossicles (found in each ear)?
Malleus, incus, stapes
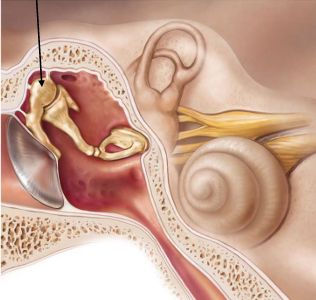
What structure is the malleus secured to?
Tympanic membrane (eardrum)
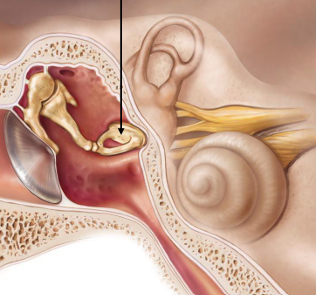
What does the stapes do?
Transmits sound → inner ear
Via what structure does the stapes transmit sound through?
Oval window
What are the 2 parts of the inner ear (labyrinth)?
Bony labyrinth, membranous labyrinth
The bony labyrinth consists of tunnels in what cranial bone?
Temporal bone
What is contained in the bony labyrinth?
Perilymph
What are the 3 further parts of the bony labyrinth?
Semicircular canals, vestibule, cochlea
What 2 parts of the bony labyrinth promote equilibrium?
Semicircular canals + vestibule

The cochlea works for what sense?
Hearing
How does the membranous labyrinth relate to the bony labyrinth?
The bony labyrinth surrounds + protects the membranous labyrinth
What is contained in the membranous labyrinth?
Endolymph
What are the 3 further parts of the membranous labyrinth?
Semicircular ducts, utricle + saccule, cochlear duct
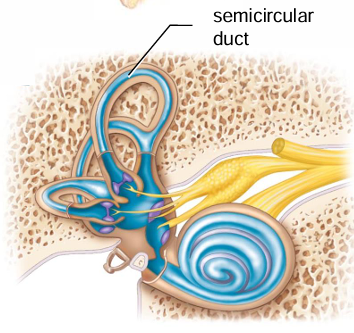
The semicircular duct is found within what structures?
Canals
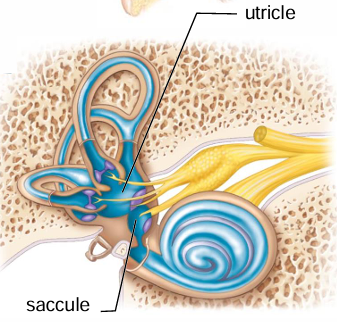
The utricle + saccule is found within what structure?
Vestibule
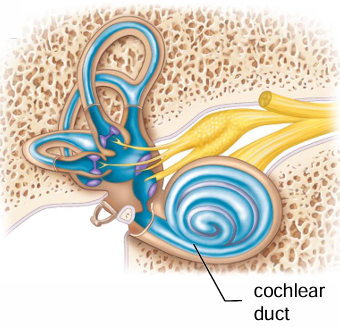
The cochlear duct is found within what structure?
Cochlea
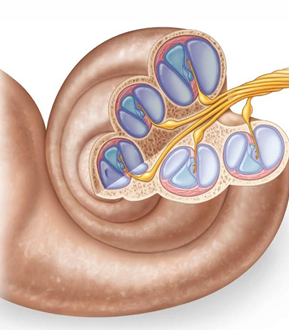
The cochlea is a coiled structure, with each coil consisting of what 3 channels (upper → lower)?
Scala vestibuli, cochlear duct, scala tympani

Which 2 channels of the coils of the cochlea contain perilymph, and which contains endolymph?
Scala vestibuli + scala tympani (perilymph), cochlear duct (endolymph)
What are the 3 membranes of the cochlea?
Vestibular membrane, basilar membrane, tectorial membrane
The vestibular membrane of the cochlea is found between what 2 channels of the cochlea’s coils?
Cochlear duct + scala vestibuli
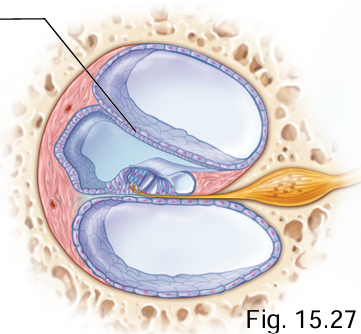
The basilar membrane of the cochlea is found between what 2 channels of the cochlea’s coils?
Cochlear duct + scala tympani
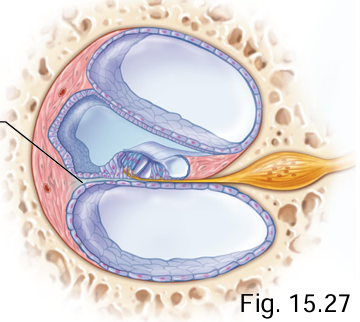
Which cochlear membrane is within the cochlear duct?
Tectorial membrane
What does the tectorial membrane cover?
Hair cells (receptor cells)
What are the receptors in the inner ear?
Hair cells that synapse with neurons
The receptors/hair cells in the inner ear send impulses to the brain via what nerve?
Vestibulocochlear nerve (CN VIII)
The hairs in the inner ear are cilia that extend into?
Endolymph
Where are the tips of cilia embedded in?
In tectorial membrane (stability)