AP bio unit 5
1/38
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
39 Terms
Phenotype
The observable traits or characteristics of an organism
Genotype
The genetic makeup of an organism, determined by the combination of alleles for a particular trait. It refers to the specific genes an individual carries, which may or may not be expressed in their phenotype.
What do you do to determine the probability of A or B happening? (they are mutually exclusive)
add the two probabilities
What do you do to determine the probability of A and B happening? (they are independent of each other)
multiply the two probabilities
Homozygous
having two identical alleles for a particular gene. (Ex. AA or aa)
Heterozygous
Having two different alleles for a particular gene. (Ex. Aa)
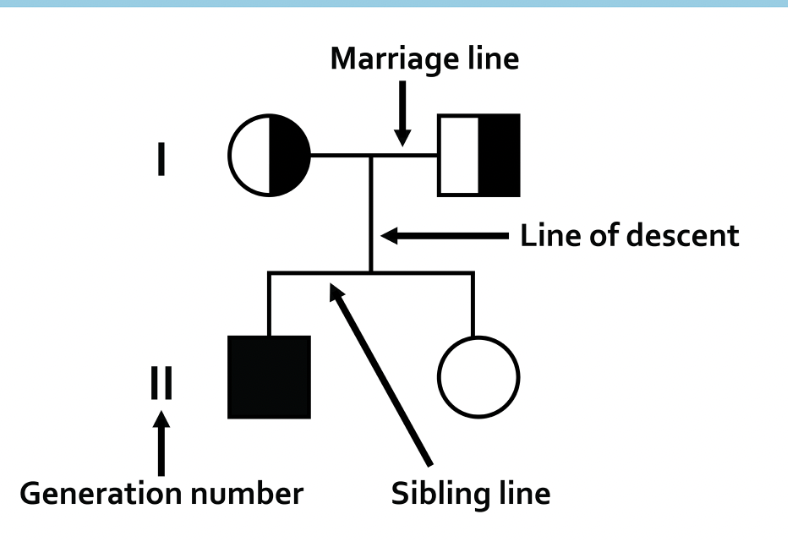
On a pedigree, what does a circle represent?
a female
On a pedigree, what does a square represent?
a male
On a pedigree, what does a shaded circle/square represent?
this person has the trait that is being studied
On a pedigree, what does a unshaded circle/square represent?
this person does not have the trait that is being studied
On a pedigree, what does a half-shaded circle/square represent?
this person is a carrier for the trait being studied (will be heterozygous)
On a pedigree what is a marriage and sibling line?
Show family relations
Autosomal
a gene not located on a sex chromosome
Sex-linked
a gene located on a sex chromosome (X or Y)
In a dihybrid cross, if two parents, heterozygous for both alleles are crossed what is the phenotypic ratio?
9 dominant for both traits: 3 dominant for one trait: 3 dominant for the other trait: 1 recessive for both traits
Incomplete dominance
the phenotype of the heterozygote is an intermediate between the two homozygotes (Ex. if a red flower (AA) breeds with a white flower (aa), its offspring (Aa) will be pink)
Codominance
neither allele is dominant and the heterozygote shows both aspects of the phenotype (Ex if a red flower (AA) breeds with a white flower (aa), its offspring (AA) will be white with red spots)
Multiple alleles
more than two alleles exist for each gene but each individual only has two (Ex. for flower color alleles exist for purple, red, white, blue, yellow, etc. but a individual plant will only have at most two different ones)
4 rules for x-linked pedigrees
affected mothers must have affected sons
if both parents are affected all children will be affected
unaffected fathers will have no affected daughters
unaffected mothers can have both affected or unaffected sons when heterozygous
Polygenic traits
genetic traits that are controlled by more than one gene
non-nuclear inheritance
traits that are controlled by genes on DNA that is not located in the nucleus (they are on mitochondrial or chloroplast DNA). Mitochondria are transmitted to the egg but not the sperm during reproduction so traits controlled by the mitochondria are maternally inherited and a female with the trait will pass it to all her offspring.
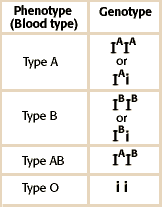
Genotype of the 4 different blood types?
Shown in picture, if A and B are together they are codominant but i is just recessive.
non-mendelian patterns of inheritance
they do not follow the ratios predicted by Mendel’s law. (Ex. sex linked and linked genes)
linked genes
genes located near each other on the same chromosome and they are usually inherited together unless separated during crossing over
map distance
how close together a pair of linked genes is and it is found by looking at the percent of time they are separated
How to tell if a gene is linked or not?
If your observed ratios are close to the expected ratios then they are not linked
recombinant phenotypes
Recombinant phenotypes are offspring with new combinations of traits different from their parents. (Ex. If red flower and white flower produce offspring, the offspring that are pink have recombinant phenotypes.)
parental phenotypes
phenotypes that are the same as the parents (Ex. If red flower and white flower produce offspring, the offspring that are red or white have parental phenotypes.)
recombination frequency
calculated by taking the number of individuals with recombinant phenotypes and dividing by total number of individuals and then multiplied by 100. This will give you percent which is equal to map units which is the distance between the genes on the chromosome

Autosomal dominant
caused by a mutation in a gene on one of the autosomes (1-22) and its inherited the same way in males and females. (AA, Aa are affected and aa are unaffected)
autosomal recessive
caused by a mutation in a gene on one of the autosomes (1-22) and inherited the same way in males and females. (AA, Aa unaffected and aa are affected)
X-linked recessive
caused by mutation on the X chromosome so it is expressed differently in females and males. (X^A X^A, X^A X^a unaffected female X^aX^a affected female: X^A Y unaffected male, X^a Y affected male)
non-disjunction
failure of chromosomes to separate so result in one to many or one to little chromosomes
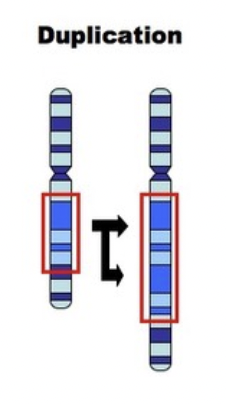
duplication
part of the chromosome duplicates
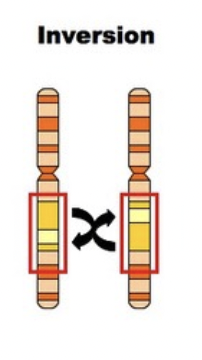
inversion
a part of the chromosome flips so it changes order or alleles
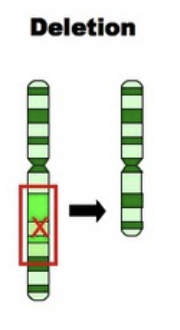
deletion
part of the chromosome gets deletes
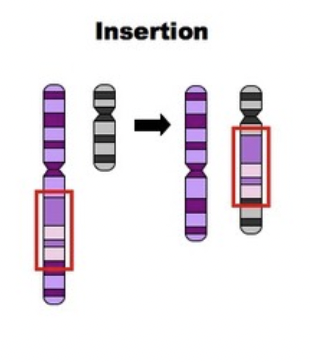
insertion
a part of the chromosome transfers to another chromosome
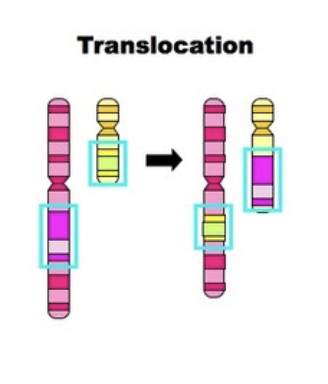
translocation
two pieces of different chromosomes switch places
epigenetics
changes in gene expression that do not change the gene expression