proteins and enzymes
1/71
Earn XP
Description and Tags
3.1.4.1- 3.1.4.2
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
72 Terms
draw the structure of amino acids
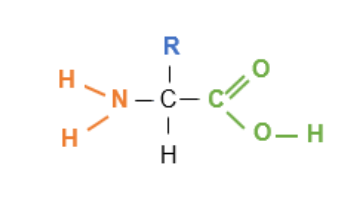
which elemts make up amino acids and amino acids are the monomers of ******
Proteins are made from amino acids with the elements carbon, hydrogen, oxygen, nitrogen and sulphur (note - only two amino acids contain sulphur).
amino acids are the monomers of proteins
what is made when two amino acids join? what is made when more than two amino acids? Proteins are made of how many polypeptides?
a dipeptide is formed when two amino acids join (via condensation)
a polypeptide is formed when more than two amino acids join together (via condensation)
proteins are made up of one or more polypeptides
name what groups and atoms that make up an amino acid
carboxyl group (-COOH)
hydrogen atom
amine group (-NH2)
an R group (also known as variable side group)
how many amino acids do organisms have? how do these amino acids differ (two points)
20 amino acids
they differ in what makes up their R group
Some are polar (hydrophilic), others are non-polar (hydrophobic).
what kind of reaction occursbetween two amino acids to form a ***** bond
condensation reaction to make polypeptides/ dipeptides. PEPTIDE BOND. A molecule of water is released.
The reverse occurs in digestion - hydrolysis
define polypeptide and how are they formed
long chain of amino acids.
formed by the condensation of many amino acids (usually hundereds)
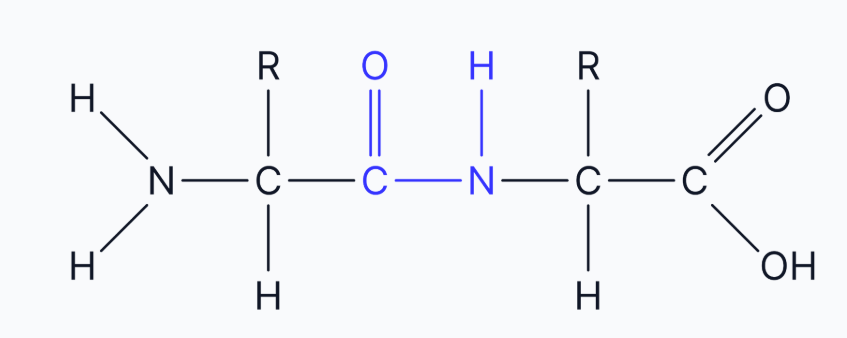
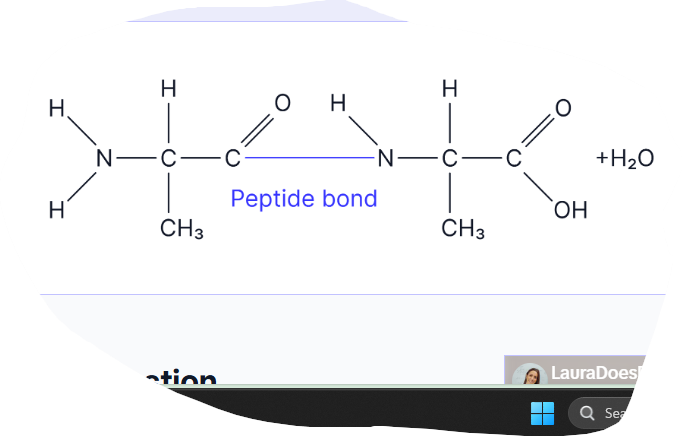
where does the peptide bond form? what type fo bonding is the bond? draw a diagram
The peptide bond forms between the carboxyl group of one amino acid and the amine group of the next. This is a strong, covalent bond.

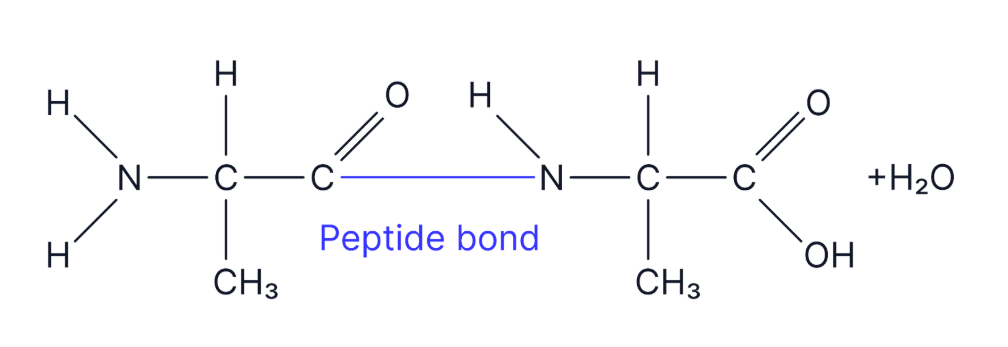
This is the amino acid alanine. Draw a diagram of the dipeptide formed when two molecules of alanine are joined together. Label the bond and show anything else that is produced in this reaction (3 marks)
define protein
Protein: A macromolecule composed of amino acids that performs various biological functions
they are a large complex molecule composed of several different polypeptides
how many levels of protein structure are there
4
describe the role of hydrogen bonds in protein structure
hydrogen bonds form between amino acids in the chain and cause the chain to coil into alpha helix or fold into a beta pleated sheet- this is the secondary structure
describe the role of ionic bonds in protein structure. what is their strength and how are they broken
ionic bonds form between any carboxyl and amino acid groups that arn’t involved in forming peptide bonds. Or in other words, the attraction between negative and positive charges on different parts of the molecule) Ionic bonds are weaker than disulphide bridges and broken by changes in ph
how many types of bonding hold the tertiary structure. Put into order of strength
3- hydrogen ionic and disulphide bridges
disulphide is strongest
ionic- high temps or change in ph
hydrogen bonding- weak intermolecular forces so broken by high temps or extreme ph
describe the role of disulphide bridges
fairly strong bonds that form whenever two molecules of the amino acid cystine come close together- the sulfur atom in one cystine bonds to the sulfur atom in the other.
name some key roles of proteins in organisms
Enzymes (e.g., catalase)
Structural components (e.g., collagen)
Transport molecules (e.g., haemoglobin)
Signalling molecules (e.g., insulin)
Hormones - Some of these are proteins that act as chemical messengers in the body.
Muscle contraction - Muscles are made up of proteins.
Antibodies - These proteins are involved in the immune response
when do you call a polypeptide a protein?
once the polypeptide folds into it’s correct shape for it’s function, then you can call it a protein
define the primary structure of a protein
the specific order of amino acids in a polypeptide chain. the amino acids are held together by peptide bonds (C-N)
why is the primary stucture of the protein really important
because it helps to determine the final 3D shape of the protein molecule. Even one change in one amino acid in primary stucture can alter the final shape of the protein- whic can prevent the protien from carrying out it’s function effectively
which groups have a small negative charge and which have a small postive charge. This attraction causes the formation of what type of bond
the N-H gorups have a small positive charge
the C-_O groups have a small negative charge
the attraction forms hydrogen bonds between the groups all along the polypeptide chain
what is the secondary strcture
hydrogen bonds between N-H groups (slightly postive) and C-_O groups (slightly negative) cause the polypeptide chain to twist and fold into the secondary structure.
the secondary structure that is formed depends on the amino acids present
what two types of shape can the polypeptide chain adopt in secondary structure from hydrogen bonding
alpha helix or beta pleated sheets
what type of bonds hold the secondary structure in place
hydrogen bonds
what is the tertiary structure
determines specific 3D shape of protein
held together by hydrogen, ionic and disulphide bonds BETWEEN DIFFERENT PARTS OF THE CHAIN (only between two cystine R groups that contain sulfur)
these bonds form between R groups
eg after forming secondary structure and forming beta pleated/ alpha helix sheet, the protein will continue to fold and coil more to form the final teritary
tertiary structure determines the active site of an enzyme
for proteins made of a single polypeptide, what type of bondind will form their final 3D structure
teritiary
large molecules/ proteins tend to be made up of **** polypeptides
many!
what is the quaternary structure of a protein
the protein consists of more than one polypeptide chains held together by bonds TO FORM A LARGER 3D STRUCTURE
the quaternary stucture is the way these polypeptide chains are assembled together
hydrogen, ionic, disulphide bonds hold the polypeptide together
for proteins made up of more than one polypeptide chain (eg insulin, haemoglobin, collagen) th quaternary stucture is the proteins final 3D structure
what are polypeptides sometimes referred to as
subunits
whats the name of non protein molecules forming part of the structure? what the name of the proteins that have these prosthetic groups?
prosthetic groups
they help the protein carry outs it role
eg haemoglobin contains the prosthetic group haem which binds to oxygen
the proteins are called conjugated proteins
exam Q: explain why the specific tertiary structure of a protein is dependant on the primary structure of the polypeptide chain
the primary structure is the order/ sequence of amino acids in the polypeptide
the primary structure determines the order/ sequence of ‘R’ groups
the tertiary structure is held together by hydrogen, ionic and disulphide bonds
these bonds form between the ‘R’ groups
a mutation for example in Dna, causes a different sequence of animo acids which causes a different primary structure and a different sequence of R groups- meaning the bonds holding the tertiary sturcture form in different positions whihc affects the overall 3D structure of the protein, which in turn affects the functionality of that protein eg an enzyme. If the enzymes tertiary structure is altered, the active site changes shape and the enzyme-substrate complexes cannot form so it cannot do it’s function.
EQ: describe how a peptide bond is formed between two amino acids to form a dipeptide
-formed via a condensation reaction/ formed when a molecule of water is removed
-the peptide bonds forms between the carbon in the carboxyl group of one amino acid and the nitrogen in the amine gorup of the other amino acid.
EQ- the secondary structure of a polypeptide is produced by bonds between amino acids. Descibe how (2)
-hydrogen bonds form between amine group and carboxyl group of the amino acids
-which causes the polypeptide chain to coil or fold creating alpha helix or beta pleated sheets
EQ- two proteins have the same number and type of amino acids but different tetriary structures(or 3D shape). Explain how
they must have a different order/sequence of amino acids/ primary structures
so the bonds that hold the tertiary structure together form in different positions eg hydrogen, ionic or disulphide that form between the ‘R’ groups
Consolidation: Describe the levels of protein structure, explaining how bonds contribute to the final 3D shape of a protein. (6 marks)
The primary structure of a protein is the specific sequence of amino acids in a polypeptide chain
held together by peptide bonds.
The secondary structure forms due to hydrogen bonding between amino acids
leading to α-helices or β-pleated sheets.
The tertiary structure arises from further folding and coiling of the polypeptide, stabilised by hydrogen bonds, ionic bonds, and disulfide bonds.
between R groups.
The quaternary structure results from the association of multiple polypeptide chains.
EQ: Describe how the structure of a protein is related to its function. (4 marks)
Primary structure determines the sequence of amino acids and thus the protein's properties. (1)
Secondary structure forms α-helices or β-pleated sheets through hydrogen bonding. (1)
Tertiary structure determines the 3D shape of the protein, held together by hydrogen, ionic and disulphide bonds. (1)
Quaternary structure allows proteins to function as multi-polypeptide complexes, such as hemoglobin. (1)
how do polypeptides differ
number of amino acids in the polypeptide chain
sequence/ order of amino acids
type of amino acids
where does protein synthesis take place in a cell
ribosomes.( in translation that occurs at ribosomes.)
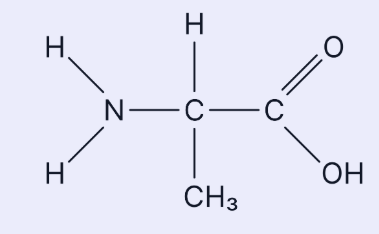
EQ : This is the amino acid alanine. Draw a diagram of the dipeptide formed when two molecules of alanine are joined together. Label the bond and show anything else that is produced in this reaction (3 marks)
describe the test for proteins
buriet test
place your prepared food sample in a test tube
add the buriet solution (at an equal volume)- made up of sodium hydroxide and copper sulfate
what is the positive and negative result for the buriet test
if proteins are present, the solution will turn from blue to purple
if proteins are not present, the solution will stay nlue
why is sodium hydroxide a component of the buriet test solution
in order to make the soluition alkaline
define an enzyme. What do enzymes lower
biological catalysts that speed up metabolic reactions without being used up
enzymes reduce the activation energy of a reaction, making the reaction more likely to occur and therefore increase the rate
what type of molecule is a enzyme
globular protein
enzymes allow biochemical reactions to take place at much ***** temperatures- this speeds up the **** of reaction
lower
rate
true or false: enzymes act intracellular and extracellular
true
name the complex formed with enzymes and their substrate- you should always mention this in exam questions
enzyme-substate complex
describe how an enzyme speeds up rate of reaction for: joining substrate molecules, catalysing a breakdown reaction
if two substrate molecules need to be joined, being attatched to the enzyme holds them close together- reducing any repulsionbetween the molecules so they can bond more easily
if the enxyme is catalysing a breakdown reation, fitting into the active site puts a strain on the bonds in the substrate, so the substrate molecule breaks up more easily
describe the lock and key model
The active site is complementary to one substrate
The substrate fits into the enzyme's active site exactly, like a key in a lock.
The enzyme remains unchanged after the reaction.
why is the lock and key model not considered anymore
This model is now considered too simplistic as it does not explain flexibility in the active site or how the activation energy of the reaction is reduced.
describe the induced fit model
The active site is not a perfect fit initially but changes shape slightly when the substrate binds.
This leads to tighter binding and strains the bonds in the substrate, lowering activation energy. (alternatively reactants are held closer together overcoming any repulsive forces, lowering the activation energy)
This model better explains how enzymes work in real biological systems.
describe the process of enzyme action- complex, lowering of activation energy, product formation, what the enzyme is able to do after
1. Formation of Enzyme-Substrate Complex:
The specific substrate binds to the enzyme’s complementary active site.
2. Lowering of Activation Energy:
The enzyme strains bonds in the substrate, lowering the activation energy.
3. Product Formation:
The substrate is converted into the product, which then leaves the active site.
4. Enzyme Reusability:
The enzyme remains unchanged and can catalyse more reactions.
EQ: Explain how the induced fit model of enzyme action allows reactions to happen at normal body temperature. (3 marks)
When the substrate binds, the active site changes shape to fit around it more tightly.
This places strain on the substrate’s bonds,
Lowering the activation energy and enabling the reaction.
Explain why maltase can only break down maltose (2 marks).
The enzymes active site is complementary to only maltose
Only maltose can form an enzyme-substrate complex with maltase
what is special about the active site of an enzyme? How many substrates can fit?
the active site is very specific and will only fit one complementry substrate
what determines sthe active site of an enzyme
the tertiary structure. (detemined by primary/ sequence of amino acids)
each different enzyme has a different tertiary stucture and so a different shaped active site
define denaturation
Denaturation: A permanent change in enzyme structure due to high temperature or extreme pH.
define saturation point
Saturation Point: When all active sites are occupied; increasing substrate further does not increase the reaction rate.
define Vmax
Vmax: Maximum rate of reaction when an enzyme is fully saturated with substrate.
describe what will happen if the teritary structure of an enzyme changes
the shape of the active site changes. This means the substrate won’t fit and the enzyme-substrate complex cannot form- so can’t carry out it’s function.
describe what will happen if there is a mutation in the gene that codes for a enzyme (protein)
the primary structure (amino acid sequence) is determined by a gene. If a mutation occurs in that gene, the sequence of amino acids is different and bonds in the teritary structure (between R groups)(ionic, hydrogen, disulphide) will form at different places on the polypeptide chain. This means the enzyme will have a different final 3D form and so the enzyme may have a different active site (as the tertiary structure determines the shape of this) and not be able to complete it’s function via forming enzyme-substrate complexes.
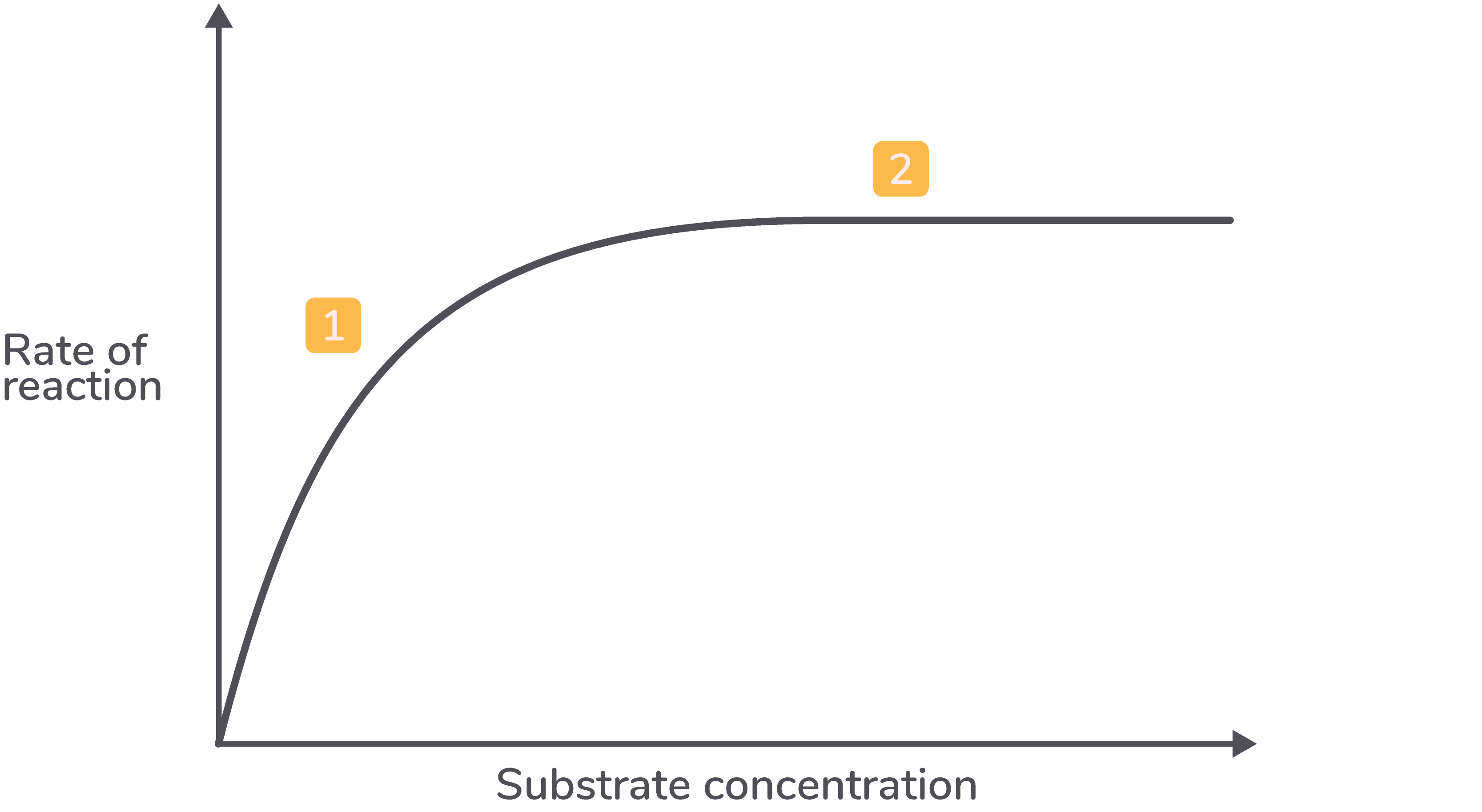
how does substrate conc affect rate of reaction
Increasing substrate concentration raises the reaction rate as more enzyme-substrate complexes form.
However, if enzyme concentration is constant, a saturation point is reached where all active sites are occupied, therefore no more enzyme substrate complexes can be formed, and adding more substrate will no longer increase the reaction rate. Beyond this point, excess substrate molecules remain unbound.
describe the graph for substrate concentration affecting enzyme activity
As the substrate concentration increases, the rate of reaction increases.
As the substrate concentration increases further, the rate of reaction plateaus (levels off).
how does enzyme concentration affect rate of reaction
Higher enzyme concentration provides more active sites, increasing the chances of enzyme-substrate complex formation.
When sufficient substrate is available, the initial reaction rate rises linearly with increasing enzyme concentration.
If substrate is limited, increasing enzyme concentration beyond a certain point will not increase the reaction rate, as substrate availability becomes the limiting factor.
describe the graph for enzyme concentration affecting enzyme activity
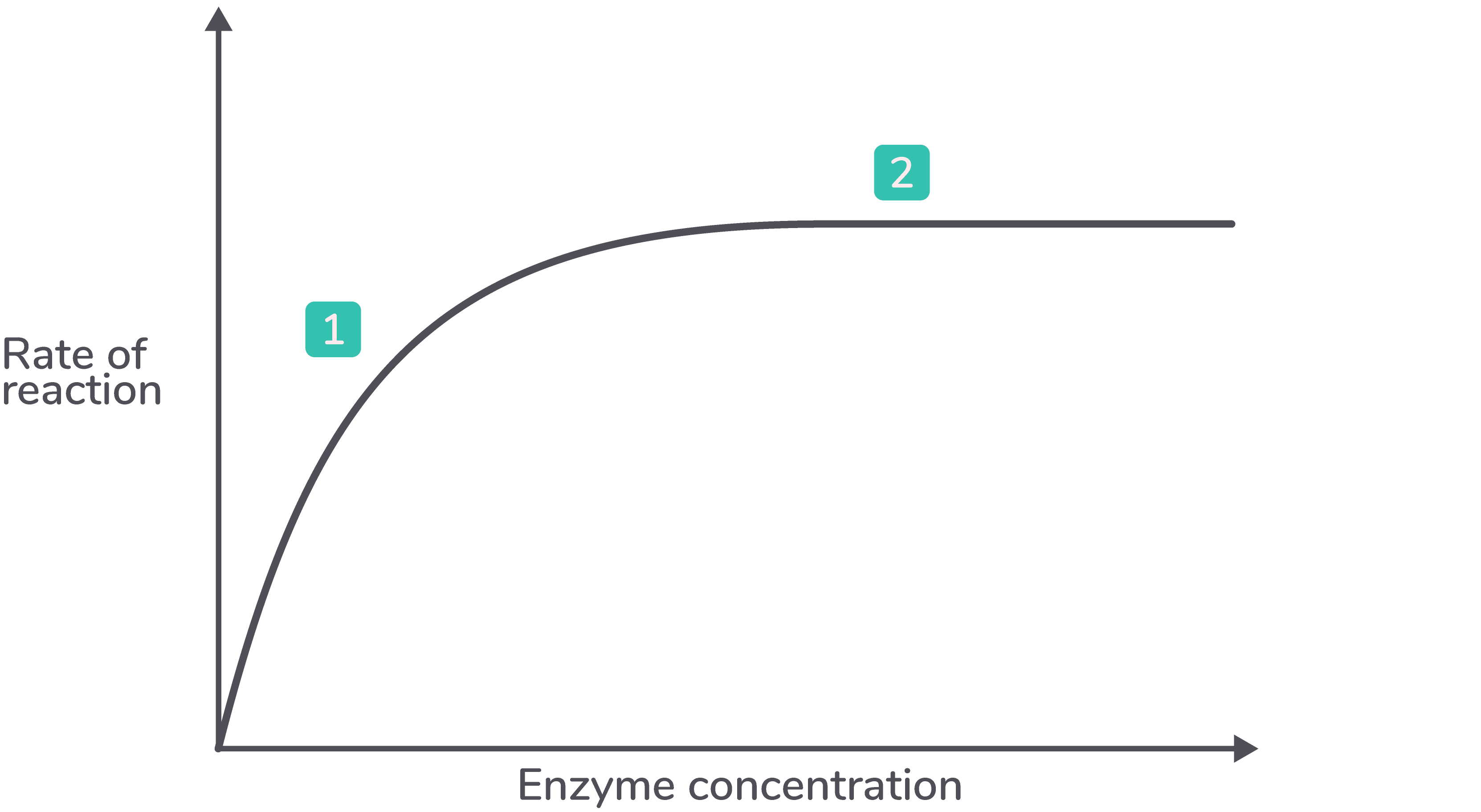
As the enzyme concentration increases, the rate of reaction increases.
As the enzyme concentration increases further, the rate of reaction plateaus (levels off).
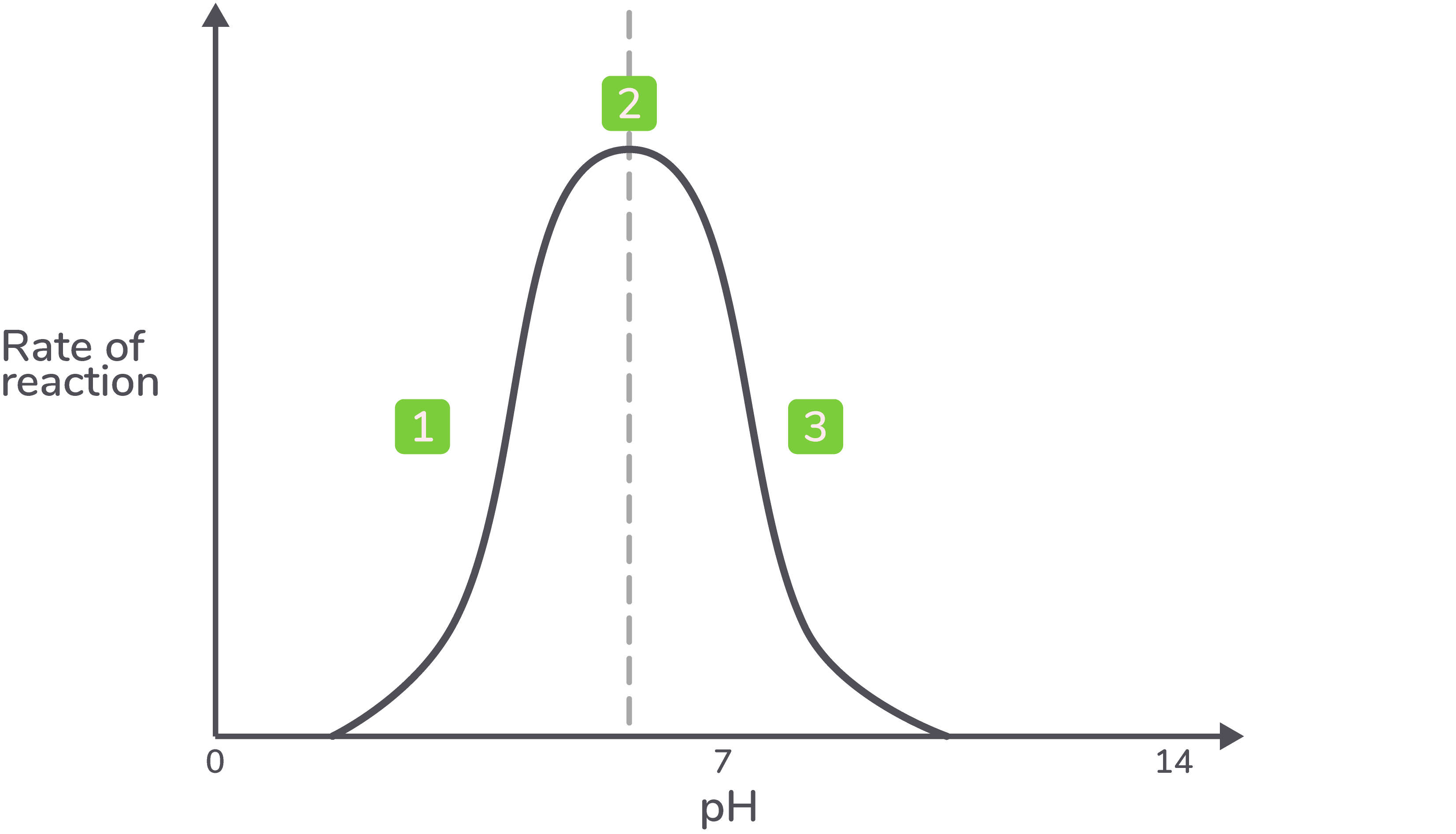
how does ph affect rate of reaction
Enzymes are denatured at extremes of pH, anything higher or lower than the optimum pH.
The excess of H+ and OH- in solution will disrupt and break the hydrogen and ionic bonds in the tertiary structure of the enzymes and will denature the enzyme.
Once the enzyme has denatured the active site is no longer complementary to the substrate and no enzyme substrate complexes will form.
Different enzymes will have a different optimum pH. The optimum pH can indicate where in the body the enzyme may act. For example, a protease, pepsin, has an optimum pH of 2 because it is secreted in the stomach.
describe the graph showing ph against enzyme activity
Below the optimum pH, the rate of reaction is low or zero.
The maximum rate of reaction is reached at the optimum pH.
Above the optimum pH, the rate of reaction is low or zero.
how does temp affect rate of reaction
describe the graph showing te,p against enzyme activity