Key Concepts in Management Functions and Strategies
1/76
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
77 Terms
Planning
The process of setting goals and determining how to achieve them.
Organizing
The process of arranging resources to carry out the organization's plans.
Leading
The process of motivating and directing employees to achieve organizational goals.
Controlling
The process of monitoring performance and making adjustments to meet objectives.
Management
The process used to accomplish organizational goals through planning, organizing, leading and controlling people and other organizational resources.
Vision
More than a goal, it's a broad explanation of why the organization exists and where it's trying to go.
Mission Statement
Outlines the organization's fundamental purposes, including self-concept, philosophy, long-term survival needs, customer needs, social responsibility, and nature of the product or service.
Goals
The broad, long-term accomplishments an organization wishes to attain.
Objectives
Specific, short term statements detailing how to achieve the organization's goals.
Strategic Planning
Done by top management and determines the major goals of the organization and the policies, procedures, strategies and resources it will need to achieve them.
Tactical Planning
The process of developing detailed, short-term statements about what is to be done, who is to do it and how.
Operational Planning
The process of setting work standards and schedules necessary to implement the company's tactical objectives.
Contingency Planning
The process of preparing alternative courses of action the firm can use if its primary plans don't work out.
SWOT Analysis
Analyzes the organization's Strengths, Weaknesses, Opportunities and Threats.
Autocratic Leadership
Making managerial decisions without consulting others.
Participative or Democratic Leadership
Managers and employees work together to make decisions.
Free-Rein Leadership
Managers set objectives and employees are free to do whatever is appropriate to accomplish those objectives.
Organization Chart
A visual device that shows relationships among people and divides the organization's work; it shows who reports to whom.
Empowering Employees
Progressive leaders give employees the authority to make decisions on their own without consulting a manager.
Economies of Scale
Companies can reduce their production costs by purchasing raw materials in bulk.
Hierarchy
A system in which one person is at the top of an organization and there is a ranked or sequential ordering from the top down.
Chain of Command
The line of authority that moves from the top of the hierarchy to the lowest level.
Top Management
The highest level, consists of the president and other key company executives who develop strategic plans.
Middle Management
Includes general managers, division managers, and branch and plant managers who are responsible for tactical planning and controlling.
Supervisory Management
Those directly responsible for supervising workers and evaluating daily performance.
Bureaucracy
An organization with many layers of managers who set rules and regulations and oversee all decisions.
Centralized Authority
When decision-making is concentrated at the top level of management.
Decentralized Authority
When decision-making is delegated to lower-level managers and employees more familiar with local conditions than headquarters is.
Span of Control
The optimal number of subordinates a manager supervises or should supervise.
Tall Organization Structures
An organizational structure in which the organization chart would be tall because of the various levels of management.
Flat Organization Structures
An organizational structure that has few layers of management and a broad span of control.
Departmentalization
Divides organizations into separate units.
Line Organization
Has direct two-way lines of responsibility, authority and communication running from the top to the bottom.
Matrix Organization
Specialists from different parts of the organization work together temporarily on specific projects, but still remain part of a line-and-staff structure.
Restructuring
Redesigning an organization so it can more effectively and efficiently serve its customers.
Production
The creation of goods using land, labor, capital, entrepreneurship and knowledge.
Operations Management
A specialized area in management that converts or transforms resources into goods and services.
Just-in-Time (JIT) Inventory Control
The production process in which a minimum of inventory is kept and parts, supplies and other needs are delivered just in time to go on the assembly line.
Intrinsic Rewards
Personal satisfaction you feel when you perform well and complete goals.
Extrinsic Rewards
Something given as a recognition of good work.
Scientific Management
Studying workers to find the most efficient ways of doing things and then teaching people those techniques.
Time-Motion Studies
Studies of which tasks must be performed to complete a job and the time needed to do each task.
Hawthorne Effect
People act differently when they know they are being studied.
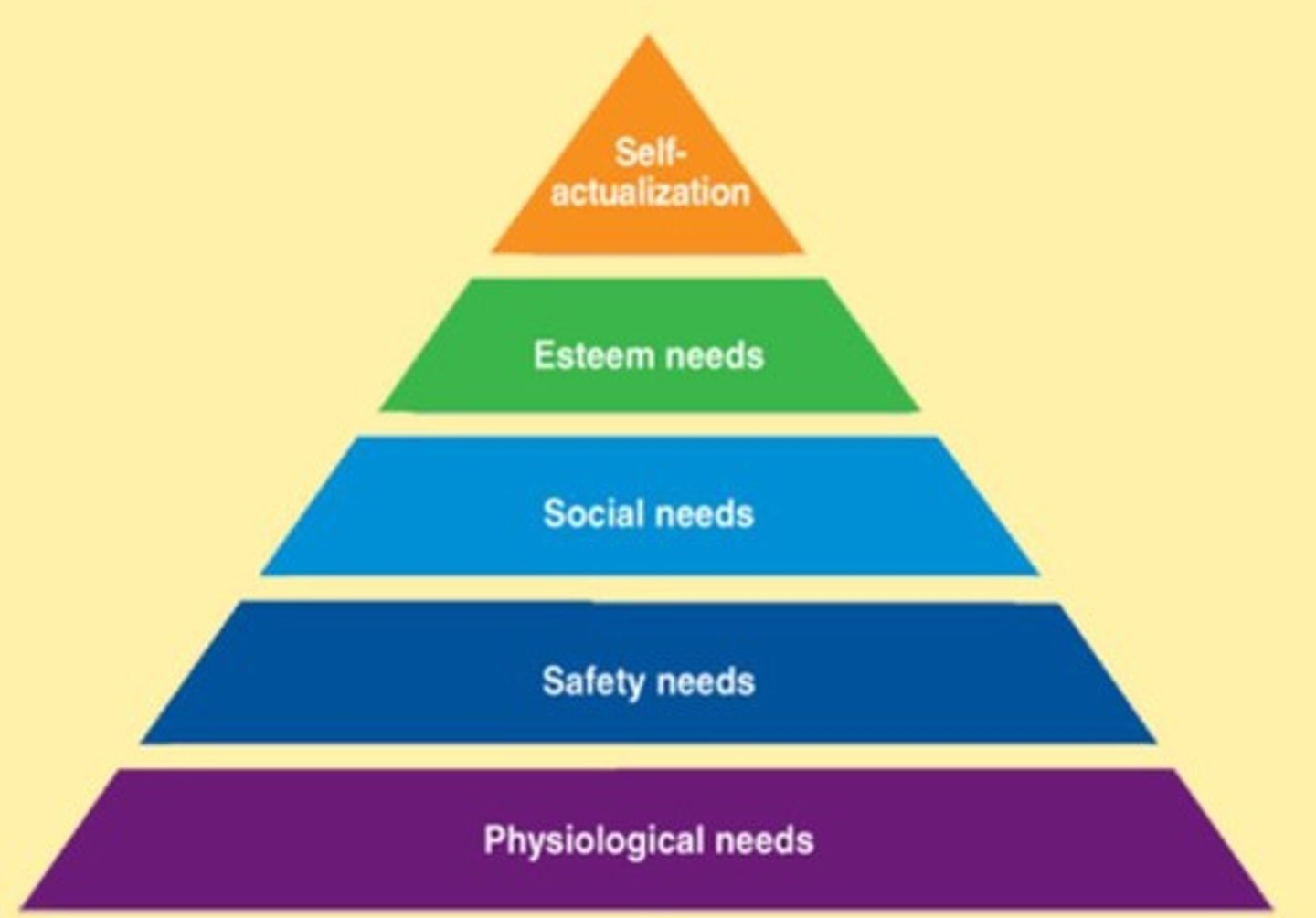
Hierarchy of Needs
Theory of motivation based on unmet human needs from basic physiological needs to safety, social and esteem needs to self-actualization needs.
Herzberg's Motivators and Hygiene Factors
Research centered on factors controlled by managers that are most effective in increasing worker motivation and how workers rank job-related factors in order of importance.
Theory X
Assumes workers dislike work and seek to avoid it, requiring force or punishment to perform.
Theory Y
Assumes people like work, seek goals, and are motivated by a variety of rewards.
Theory Z
A hybrid approach of Type A (individual focus) and Type J (group commitment) in organizational culture.
Job Enrichment
A motivational strategy that emphasizes motivating the worker through the job itself.
Job Enlargement
A job enrichment strategy that involves combining a series of tasks into one challenging and interesting assignment.
Job Rotation
A job enrichment strategy that involves moving employees from one job to another.
Human Resource Management (HRM)
The process of determining human resource needs and then recruiting, selecting, developing, motivating, evaluating, compensating and scheduling employees to achieve organizational goals.
Civil Rights Act of 1964
Prohibits discrimination in employment based on race, religion, creed, sex, age, and national origin.
Americans with Disabilities Act of 1990 (ADA)
Requires employers to give applicants with physical or mental disabilities the same consideration for employment as people without disabilities.
Age Discrimination in Employment Act (ADEA)
Protects workers 40 and over from employment and workplace discrimination.
Job Analysis
A study of what employees do who hold various job titles.
Job Description
A summary of the objectives of the job, the type of work, the responsibilities and duties, working conditions and relationship to other jobs.
Job Specifications
A summary of the minimum qualifications needed to do a particular job.
Recruitment
The set of activities for obtaining the right number of qualified people at the right time.
Selection
The process of gathering information and deciding who should be hired under legal guidelines.
Performance Appraisal
An evaluation that measures employee performance against established standards.
Fringe Benefits
Sick leave, vacation pay, pension and health plans that provide additional compensation beyond base wages.
Cafeteria-Style Fringe Benefits
Allow employees to choose the benefits they want up to a certain dollar amount.
Unions
Employee organizations whose main goal is to represent members in employee-management negotiations.
Craft Union
An organization of skilled specialists in a particular craft or trade.
Industrial Unions
Labor unions of unskilled or semiskilled workers in mass production industries.
Collective Bargaining
The process whereby union and management representatives form an agreement for employees.
Mediation
The use of a third party to encourage both sides to keep negotiating to resolve key contract issues.
Arbitration
An agreement to bring in a third party to render a binding agreement.
Strike
A strategy in which workers refuse to go to work.
Lockout
An attempt by management to put pressure on workers by closing the business.
Injunction
A court order directing someone to do something or refrain from doing something.
Strikebreakers
Workers hired to do the work of striking workers until the labor dispute is resolved.
Bargaining Zone
The range of options between initial and final offers that each side will consider before negotiations dissolve.
Flextime Plan
Gives employees some freedom to choose which hours to work as long as they complete their tasks.
Compressed Work Week
Employees work the full number of work hours, but in fewer than the standard number of days.
Job Sharing
Lets two or more part-time employees share a full-time job.