Lipid Metabolism
1/62
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
63 Terms
triaglycerols
these are responsible for 1/3 of our dietary needs
a glycerol head with 3 fatty acid chains attached
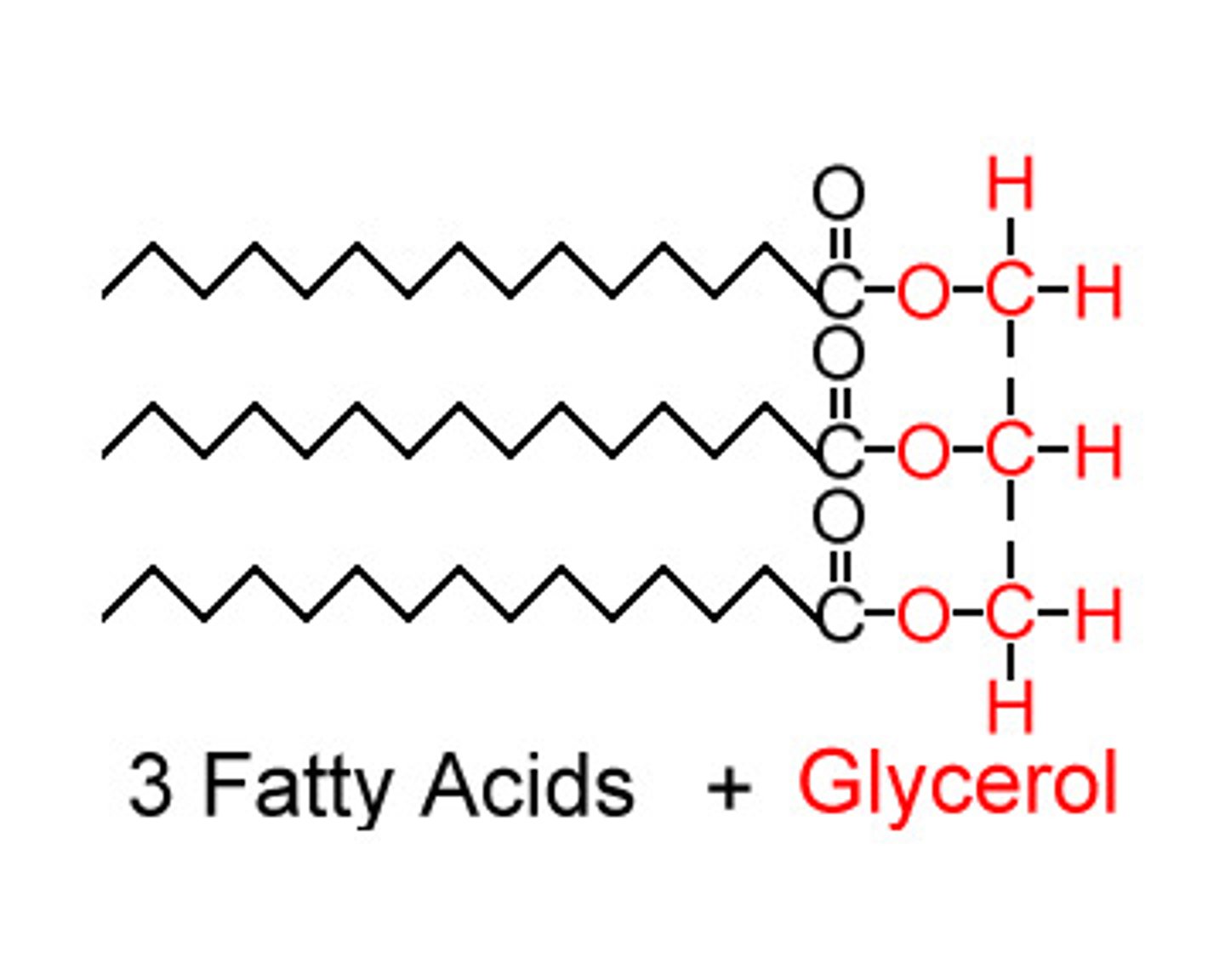
80%
fatty acid oxidation meets this percent of energy needs in the mammalian heart and liver
hibernate
animals that do this rely extensively on fat
more energy since more reduced, less water since non-polar
advantages of fats over carbohydrates
long term energy needs, storage, and slow delivery
three characteristics of fats in relation to the glucose/glycogen for quick delivery
interfacial activation
The increase in activity when a lipid-specific enzyme contacts the lipid-water interface.
property of lipases and phospholipases, which are soluble enzymes but must break down an insoluble material
lipid-water interface
location where lipid emulsification takes place:
bile from the liver helps emulsify the fats, the increases surface area from emulsification increases this, which then enhances the rate of lipid digestion
surface area
this of the lipid-water interface is the main factor for the rate of the lipid digestion reaction
increase emulsification with bile acids, peristaltic movement of the small intestine
ways to increase surface area of lipid-water interface
peristaltic movement
Contractions of circular muscles in anterior end lengthen the body pushing the anterior end forward
helps allow more thorough mixing of fats with bile and digestive enzymes
chylomicrons
take dietary triaglycerols from intestine to muscle as well as dietary cholesterol from intestine to liver
intestine to muscle
chylomicron transfer path for dietary triacylglycerols
intestine to liver
chylomicron transfer path for dietary cholesterol
dietary fats to storage pathway
1) Bile salts emulsify dietary fats forming miscelles
2) Intestinal lipases degrade triacylglycerols
3) FA and other products taken up by intestinal mucosa and converted to triaclyglycerols
4) Chylomicrons get incorporated with chyomicrons, along with cholesterol and apolipoproteins
5) Chylomicrons move through the lymphatic system
6) Lipoportein lipase is active in capillaries and breaks down triaclyglycerols into fatty acids and glycerol
7) Fatty acids used as fuel or storage in the cells
High-density lipoprotein (HDL)
good cholesterol - moves triaclyglycerols and cholesterol from the tissues to the liver
very low density lipoprotein, low density lipoprotein, intermediate density liporprotein
transport triaclyglycerols and cholesterol from the liver to the tissues
pancreatic lipase
catalyxes fat hydrolysis at the 1 and 3 positions
enzymatic activity increases with increased lipid-water interface interactions
serine protease
phospholipase a2
enzyme that converts a phospholipid into a lysophospholipid - has carboxyllic acid byproduct
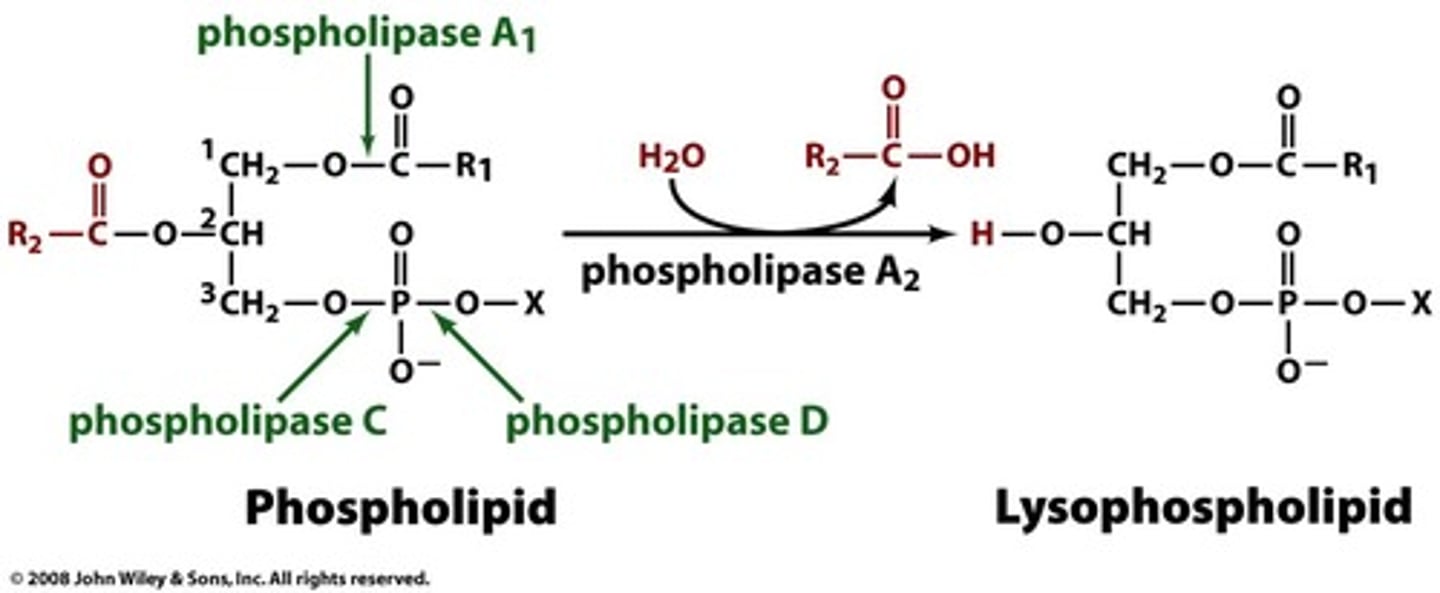
phospholipid + h2o --> lysophospholipid + carboxyllic acid
net reaction for the phospholipase reaction
fatty acid binding protein
Proteins that bind to fatty acids and enable them to be transported into cells.
increases the intestinal absorption of lipids - process takes place in the liver and the kidneys
Adipocytes
fats are stored here, triggered by hormone sensitive lipases
Hormone --> adenylate cyclase activated --> cAMP --> protein kinase --> triacylglycerol lipase --> dicylglycerol (from tricylglycerol) --> other lipases turn: glycerol + fatty acids released into blood stream
hormone cascade to release fatty acids from adipocytes
albumin
fatty acids bind to this to increase their solubility and increase their absorbtion into cells once stimulated to be released from adipocytes
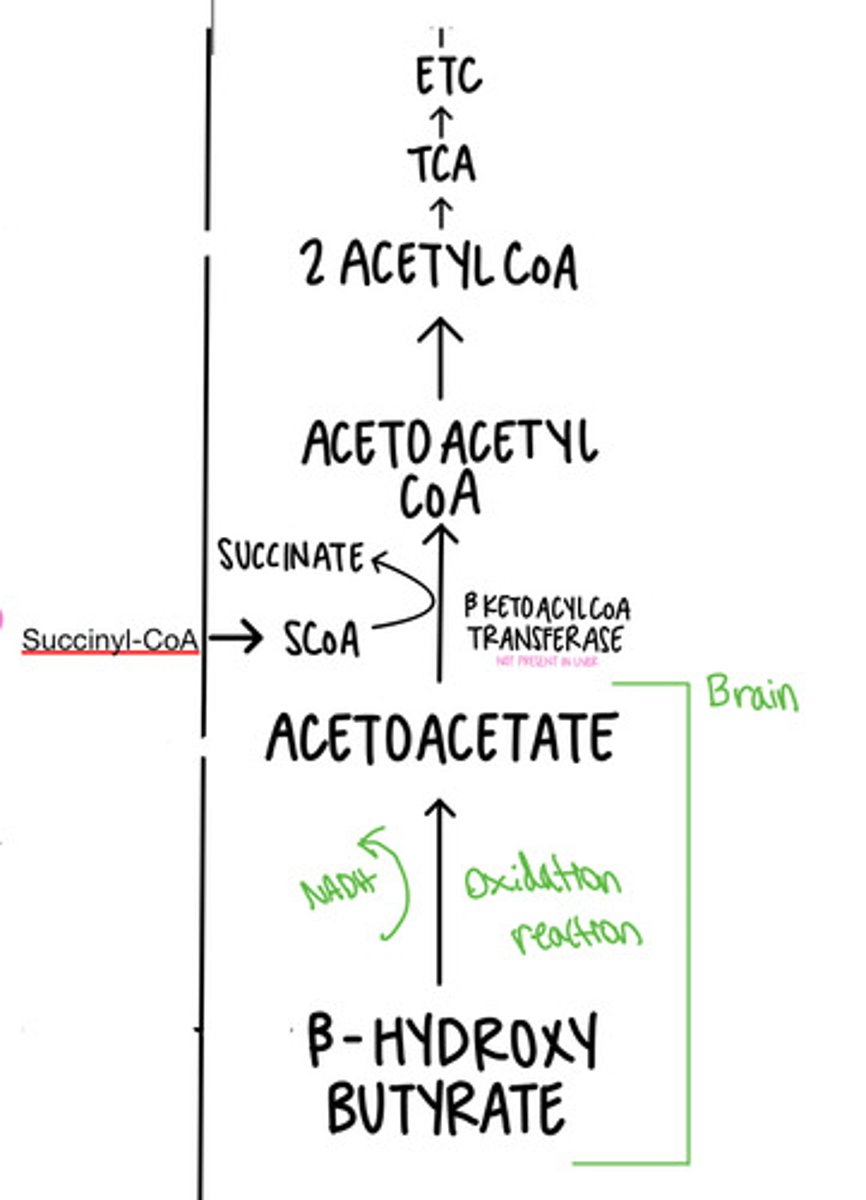
beta oxidation
A metabolic sequence that breaks fatty acids down to two-carbon fragments that enter the citric acid cycle as acetyl CoA.
Knoop's experiment
proved beta oxidation:
for odd chain fatty acid had benzoic acid was breakdown product and hippuric acid as excretion product
for even chain fatty acid had phenylacetic acid as breakdown product and phenylaceturic acid as excretion product
benzoic acid and hippuric acid
breakdown and excretion product of Knoop's experiment for an odd chained fatty acid
pheylacetic acid and phenylaceturic acid
breakdown and excretion product for Knoop's experiment for an even chained fatty acid
Lehninger's experiment
showed that a rat liver needed and input of ATP to have FA metabolism
hence FA metabolism needs activation
acyl co-A
this product activates fatty acid breakdwon - can be used for fatty acids that are 2-16 carbons in length
formed in the cytosol
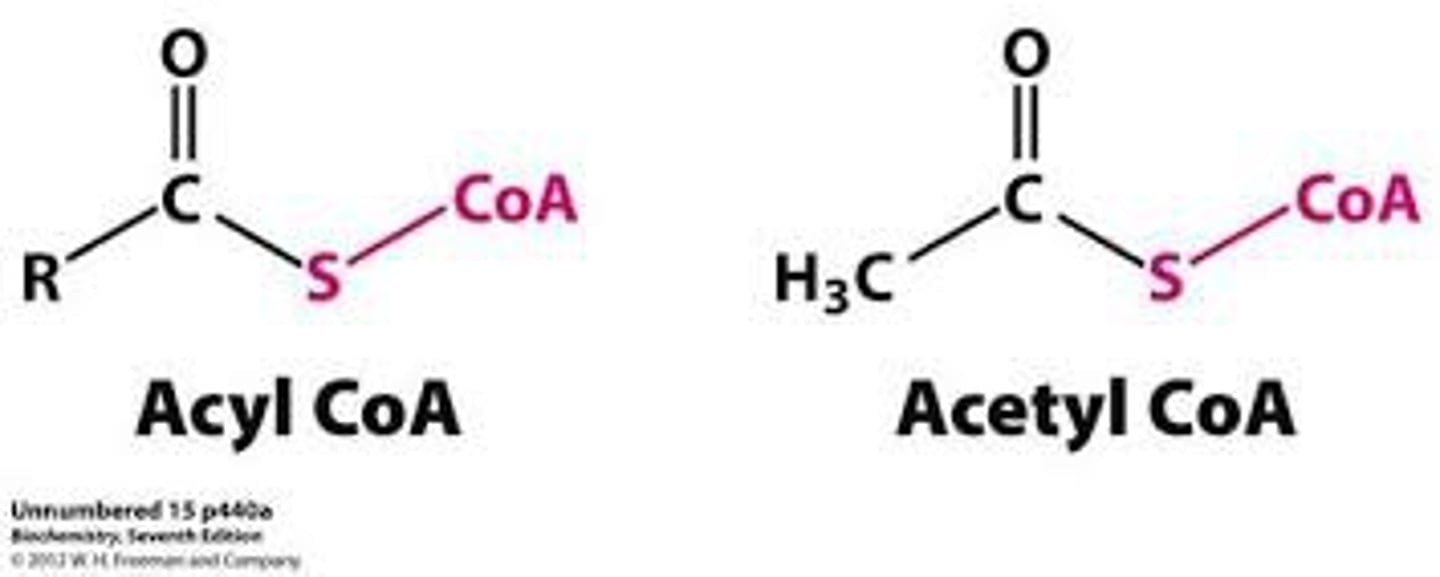
2-16
length limit for carbon chains with acyl co-A synthetase
Acyl Co A Synthetase
enzyme that converts fatty acid to acyl-coA through three main steps in the cytosol
Fatty acid + ATP --> PPi + Acyladenylate mixed anhydride
PPi + H2O --> 2Pi
CoASH + Acyladenylate mixed anhydride --> Acyl-coA and AMP
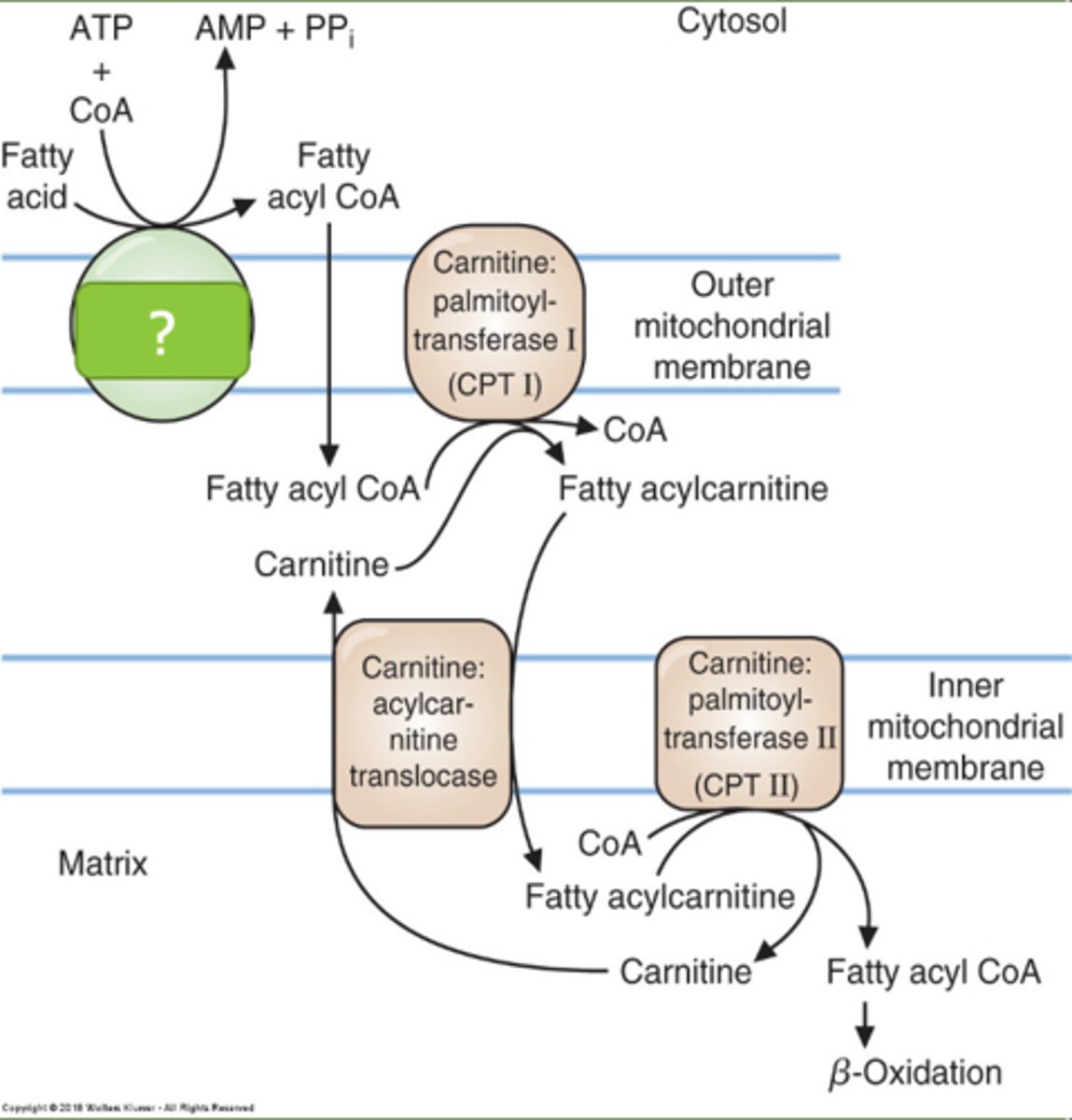
acyl coA and AMP
2 main products of the acyl co a synthetase reaction
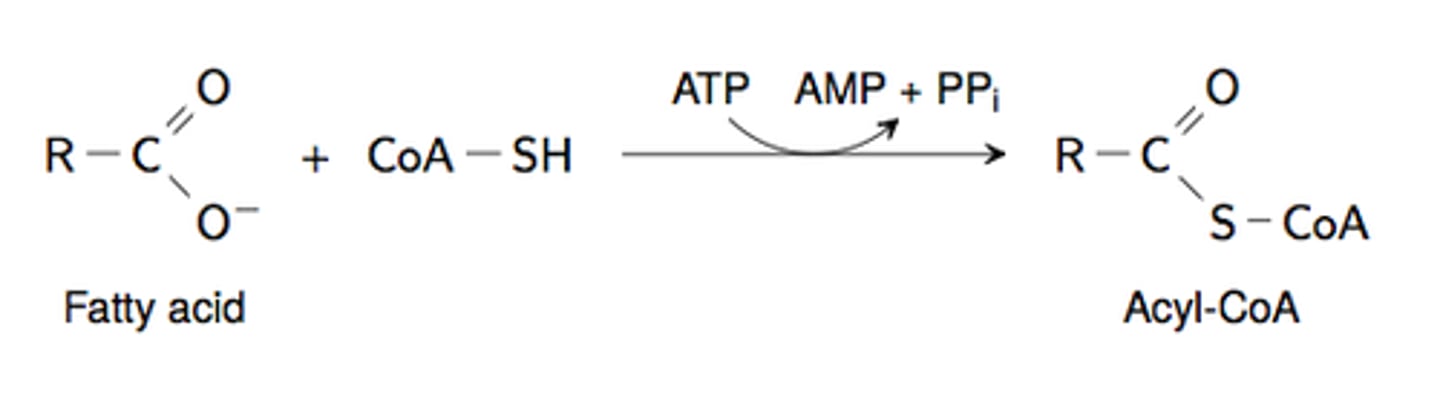
fatty acid + coash + atp --> acyl coA + amp
net reaction of acyl coA reaction
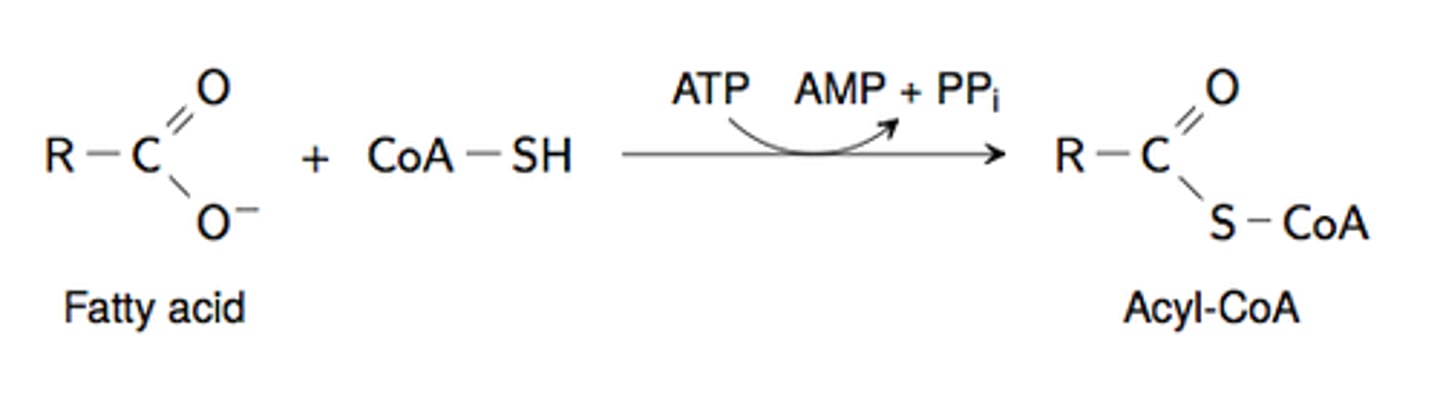
cytosol
intracellular location of the acyl-coA synthetase reaction
carnitine
a nonessential, nonprotein amino acid made in the body from lysine that helps transport fatty acids across the mitochondrial membrane
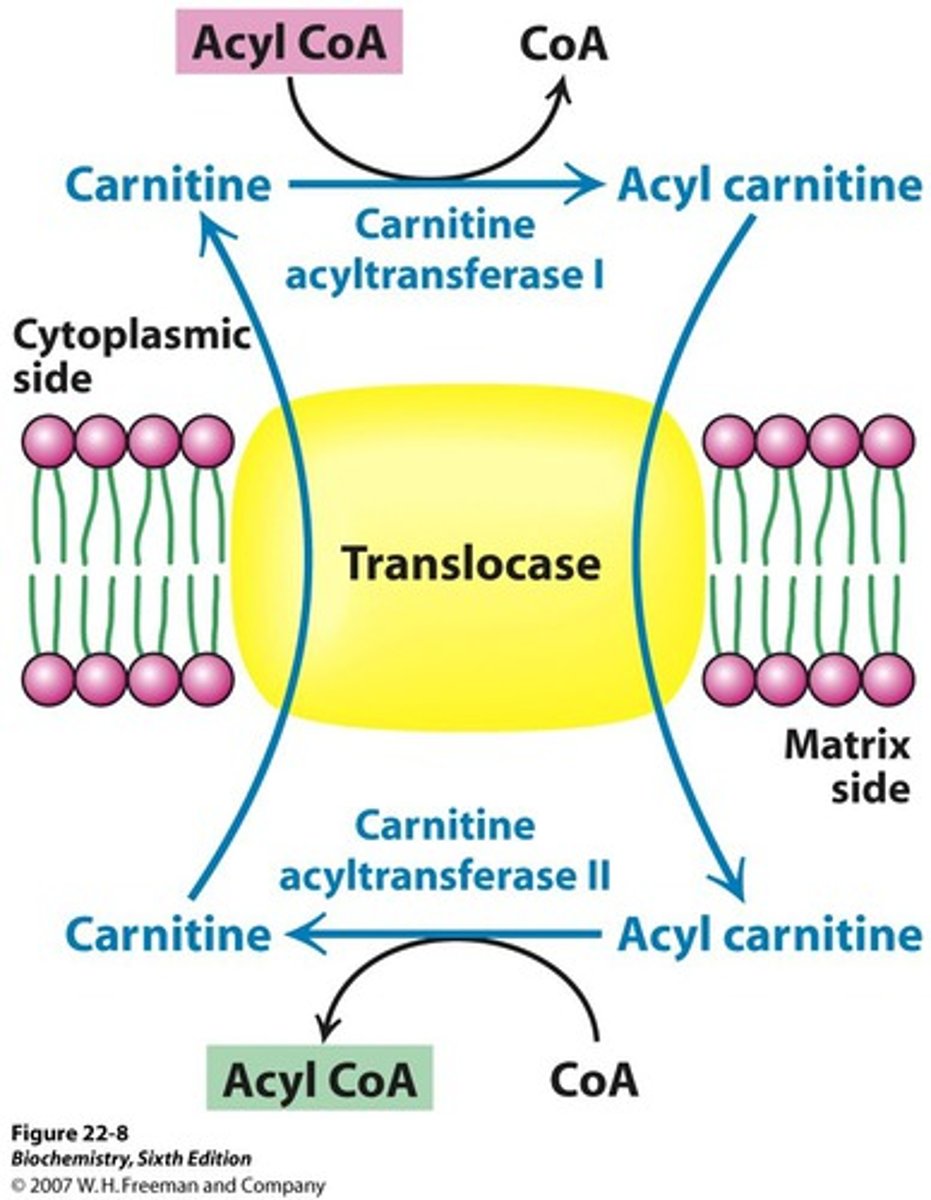
acyl-carnitine
Acyl-CoA molecules are translocated into the mitochondria as what molecule? This molecule is formed after the reaction with acyl CoA and carnitine
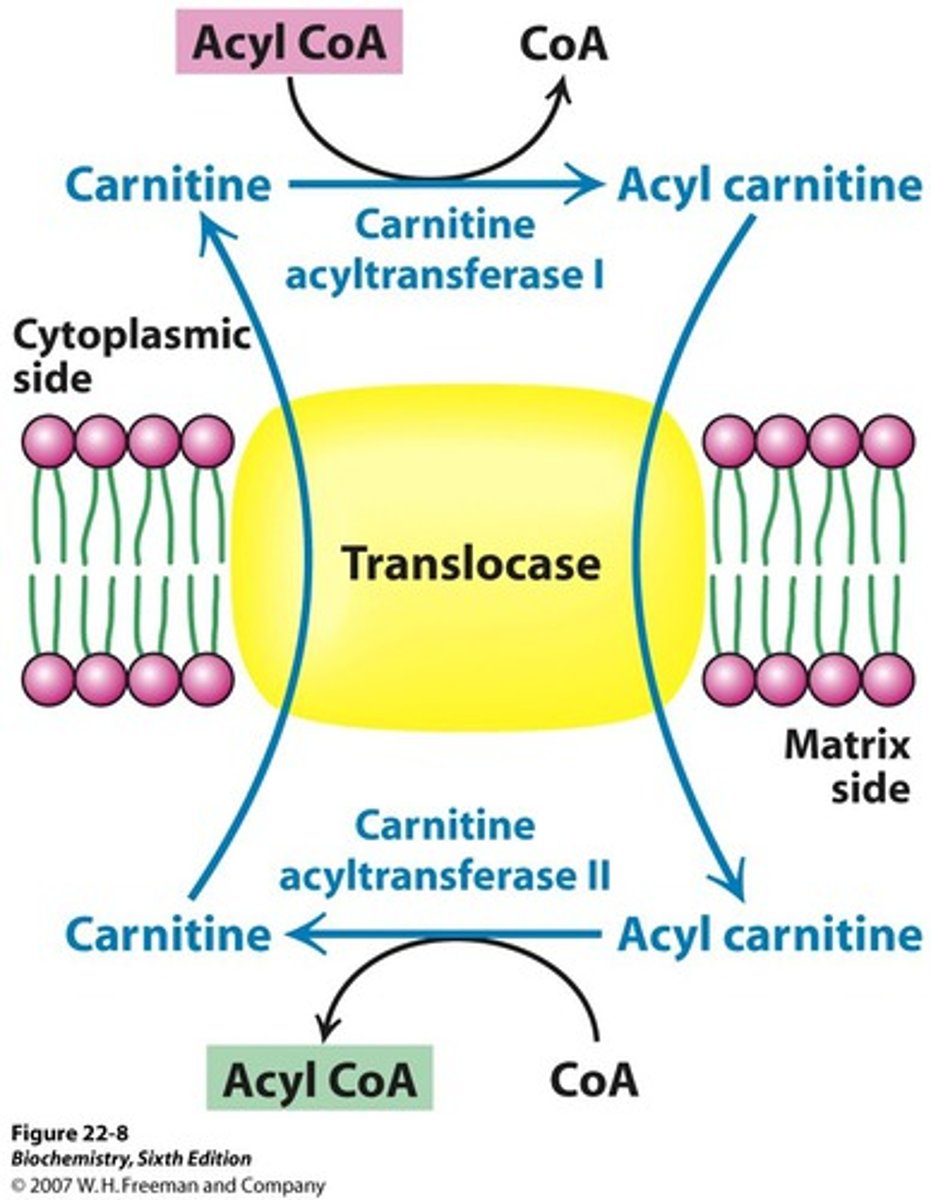
acyl CoA + carnitine <--> acylcarnitine + CoA
reaction by carnitine palmitotransferase in the cytosol and the mitochondrial matrix
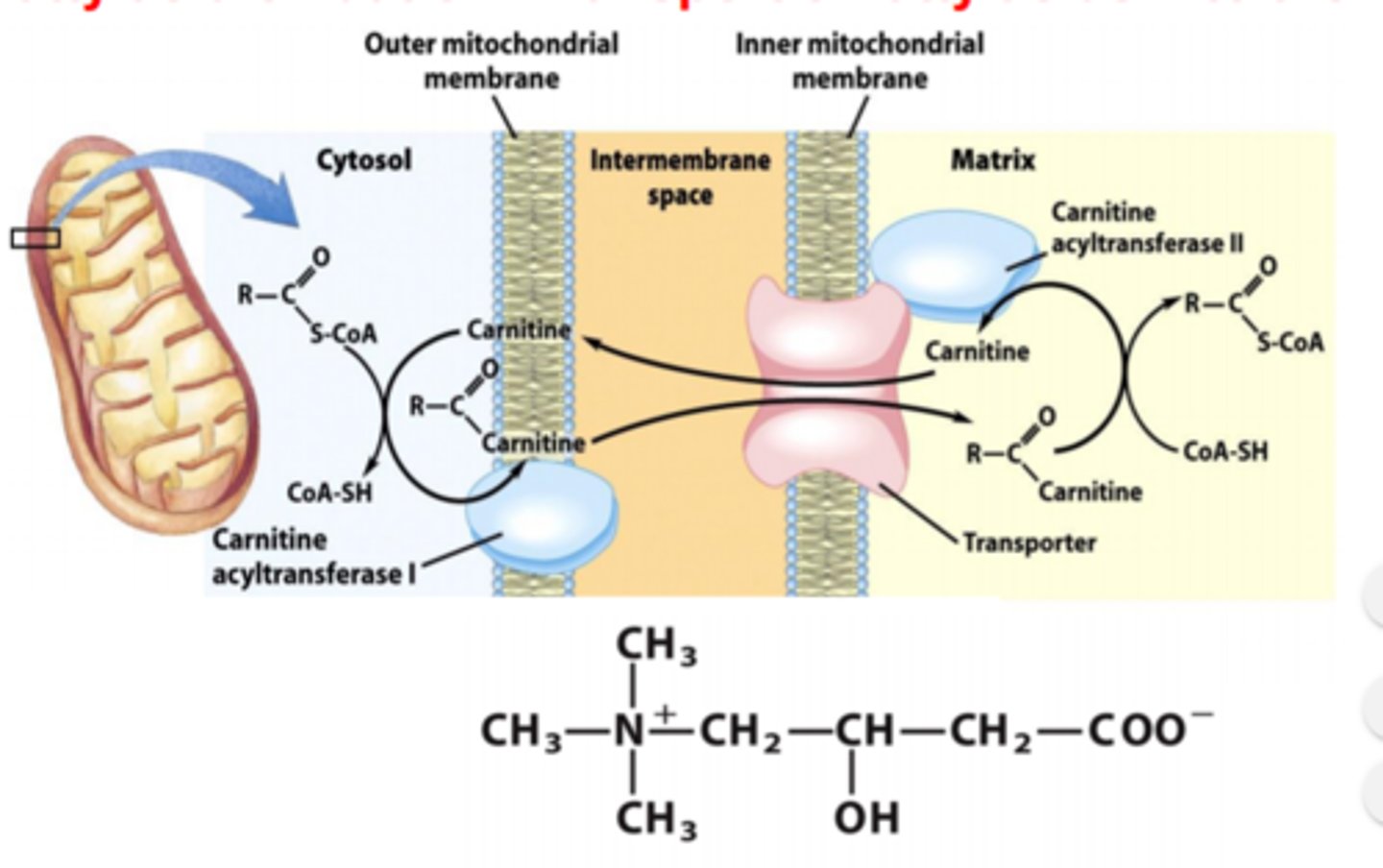
carnitine palmitoyltransferase
Enzyme facilitating fatty acid transport into mitochondria.
Two types: carnitine acyltransferase 1 and carnitine acyltransferase 2
net reaction is:
1) acyl CoA + carnitine --> acylcarnitine + CoA at acyltransferase
2) crosses mitochondrial matrix through transporter
3) acylcarnitine + CoA <--> acyl CoA + carnitine in matrix, at carnitine acyltransferase 2
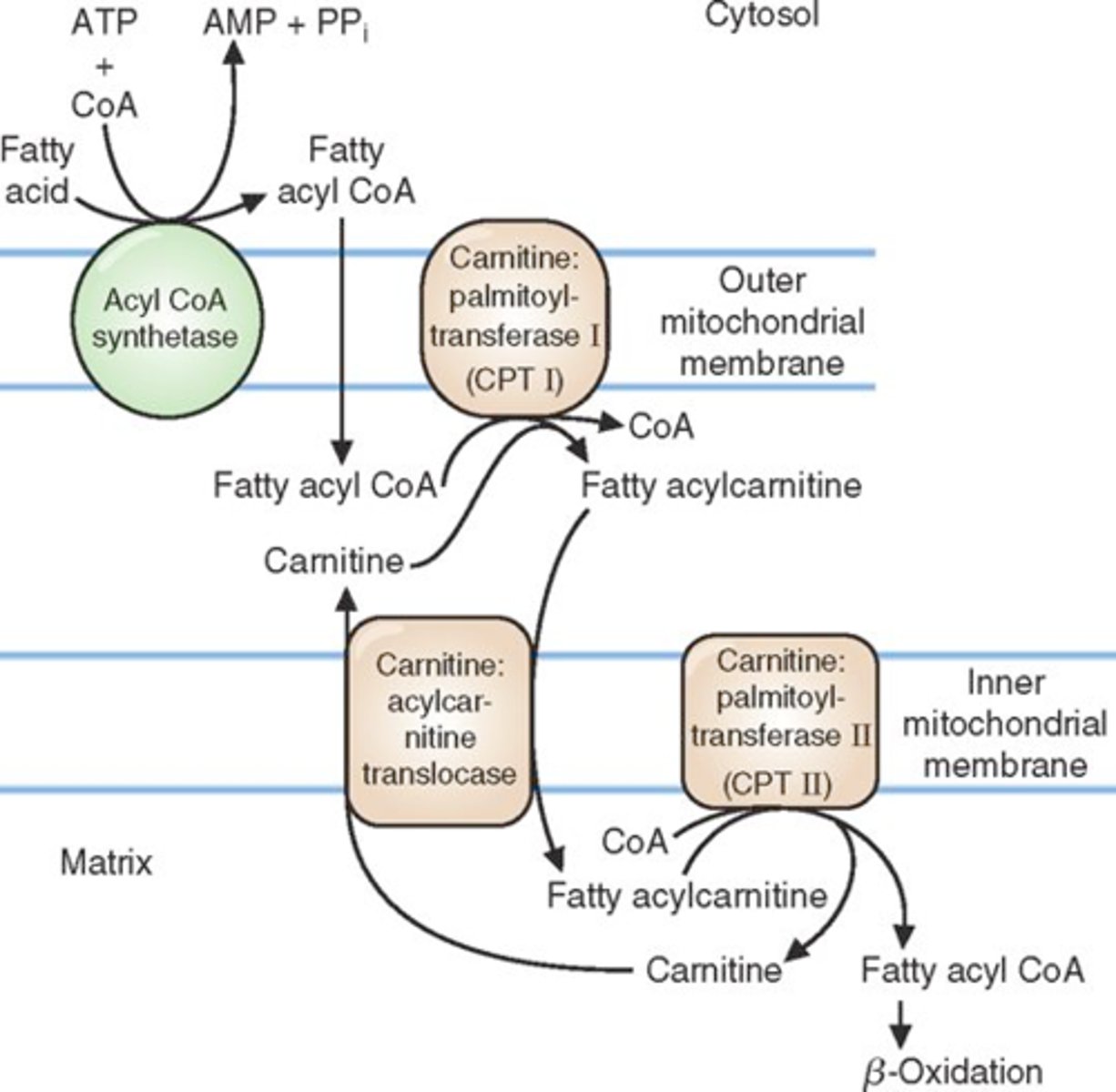
1) Beta-oxidation: acetyl coA, NADH, FADH2
2) TCA: ATP, NADH, FADH2
3) ETC: ATP
3 stages to fatty acid oxidation and their products (in terms of energy)
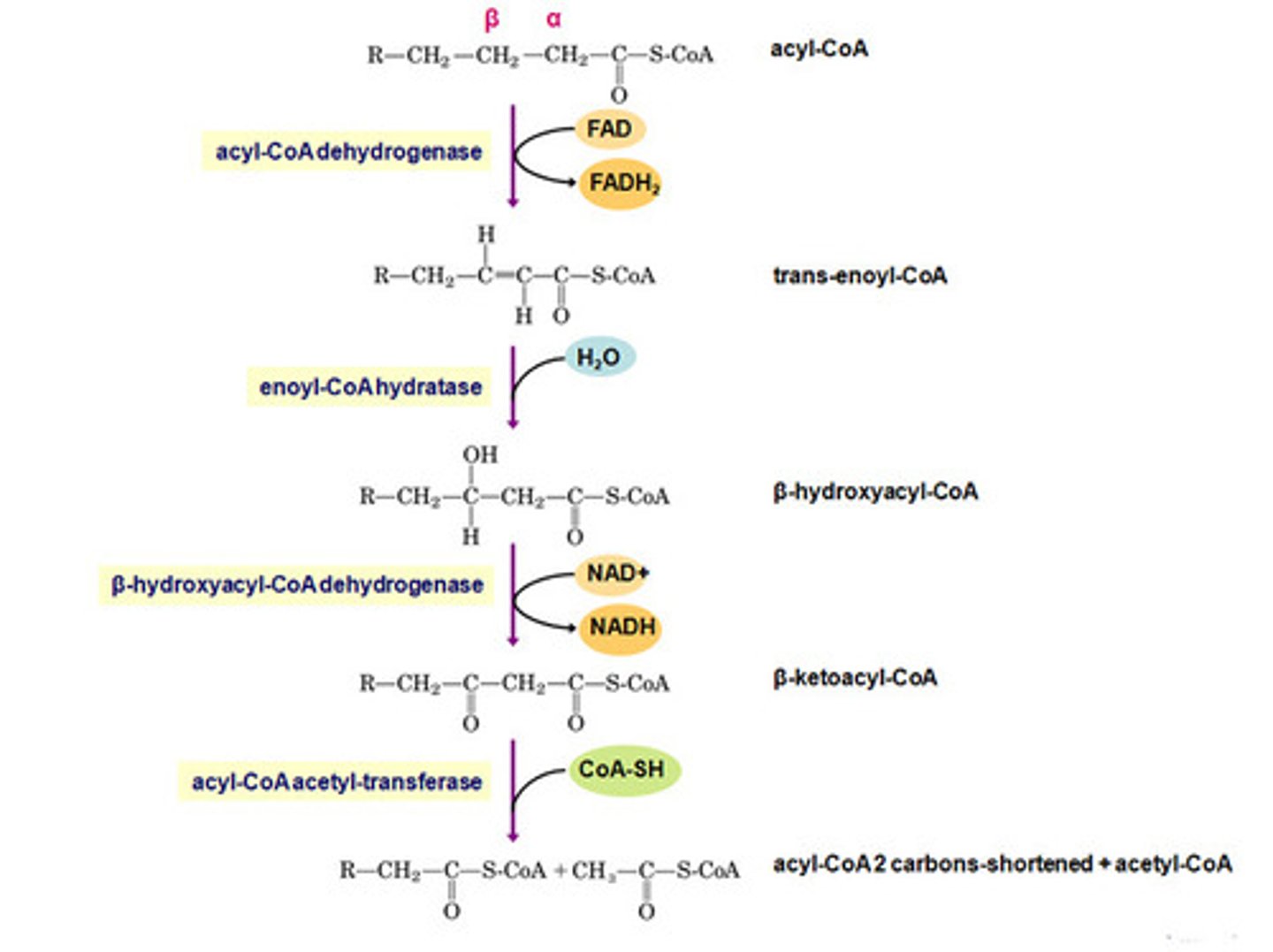
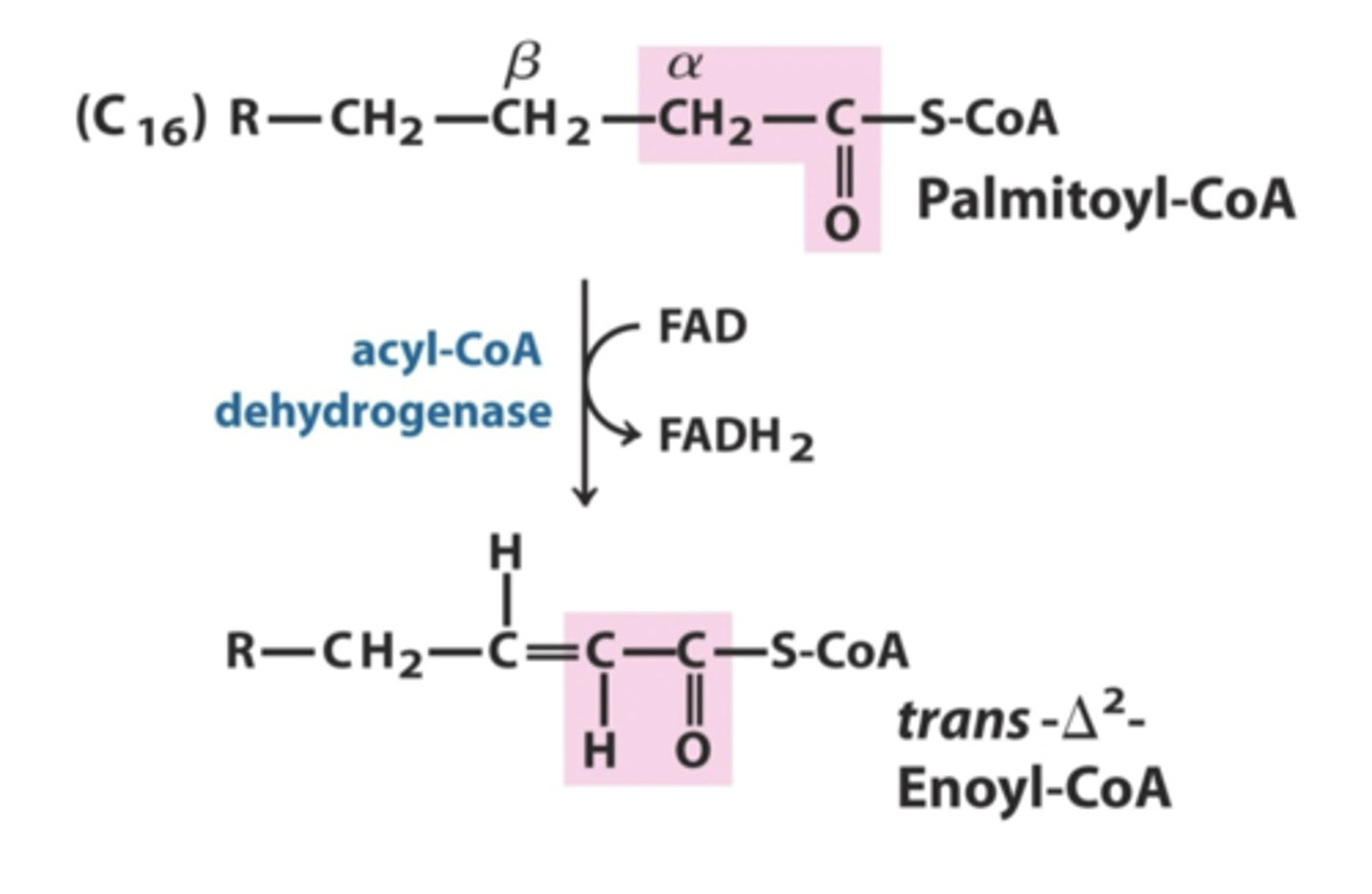
acyl co-A dehydrogenase
converts:
FA-acyl CoA + FAD --> FADH2 + trans-delta-2-enoyl coA
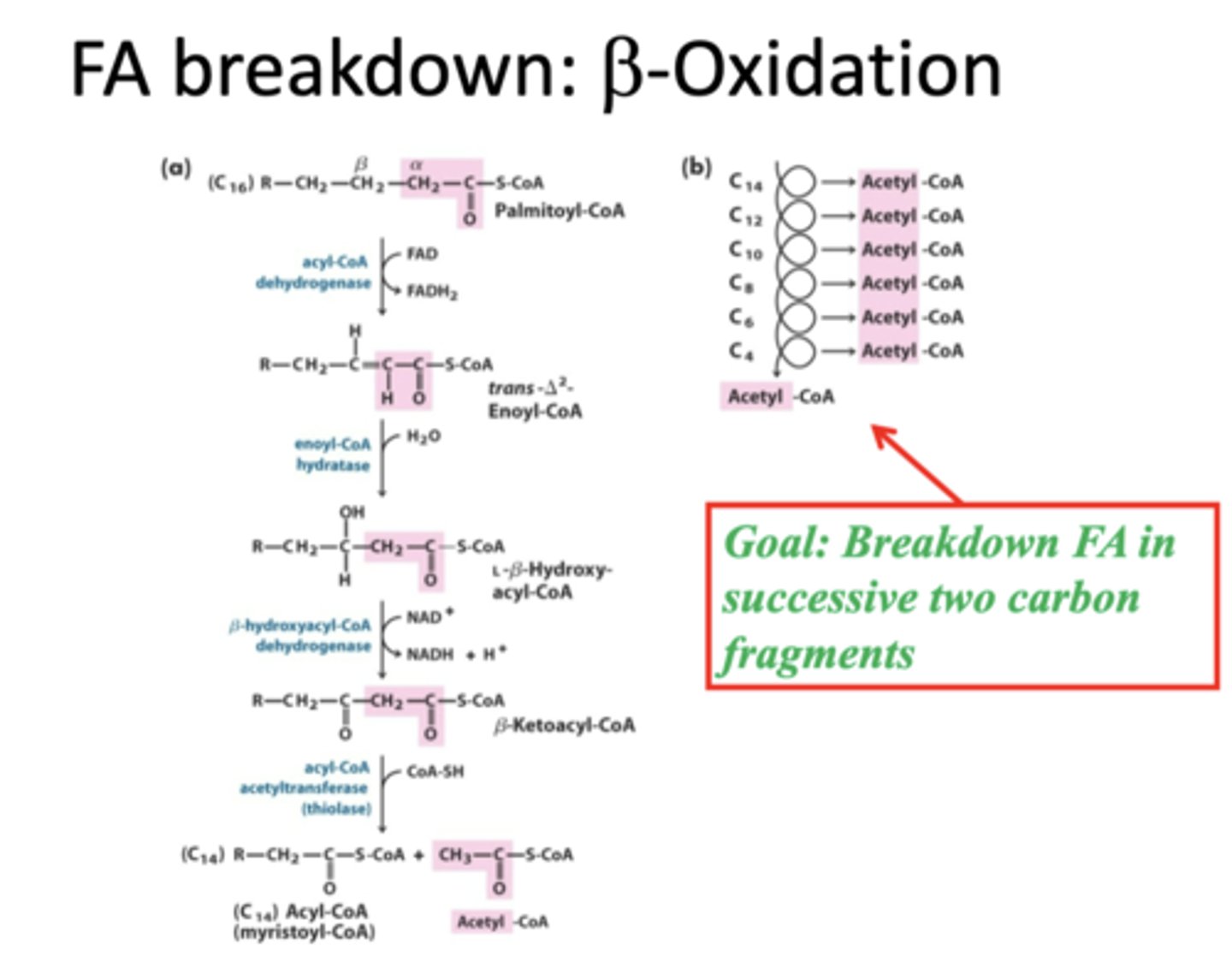
FA-acyl CoA + FAD --> FADH2 + trans-delta-2-enoyl coA
acyl co-A dehydrogenase net reaction
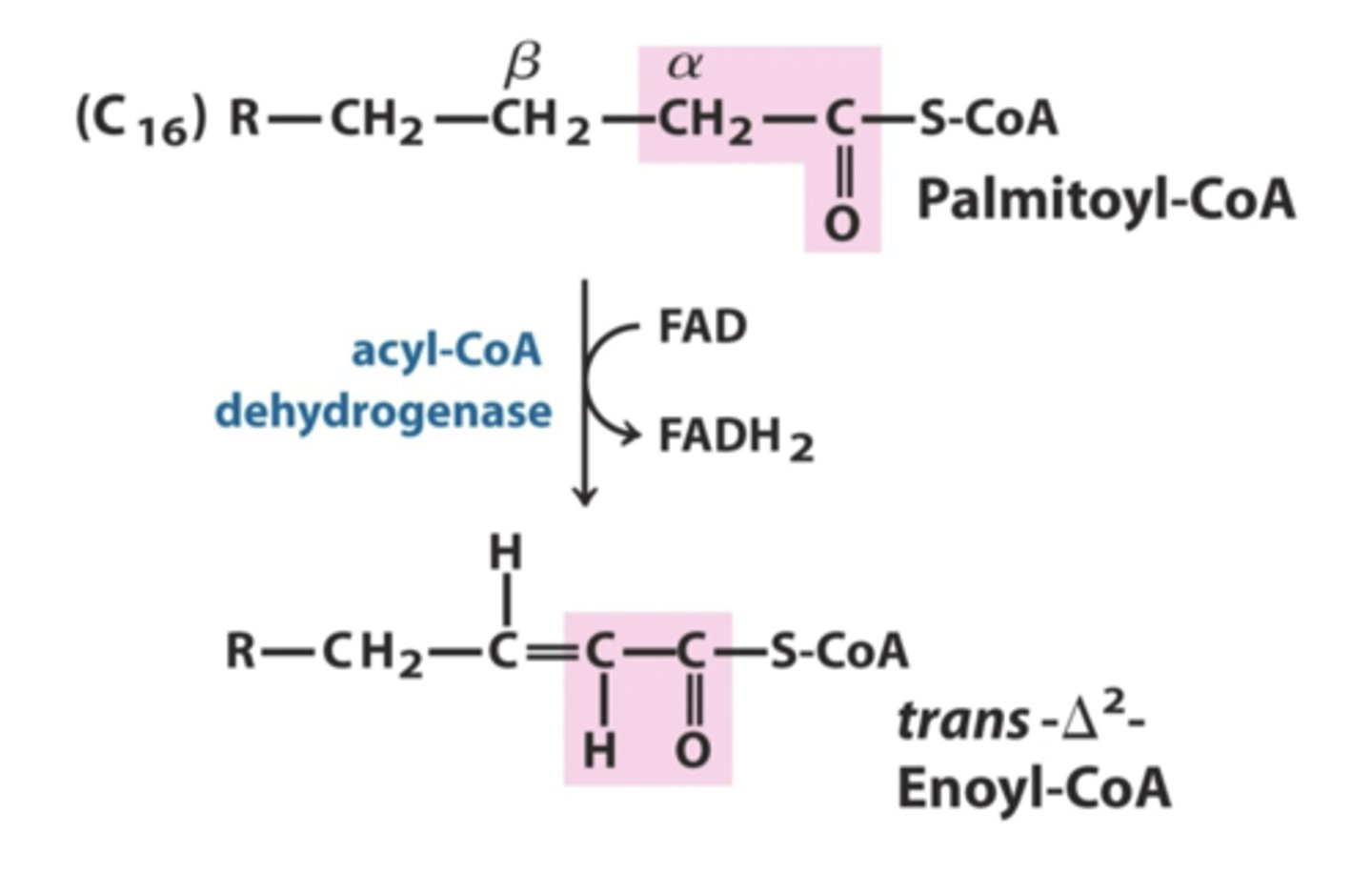
transdelta 2 enoyl co A
product of the acyl co-A dehydrogenase net reaction along with FADH2
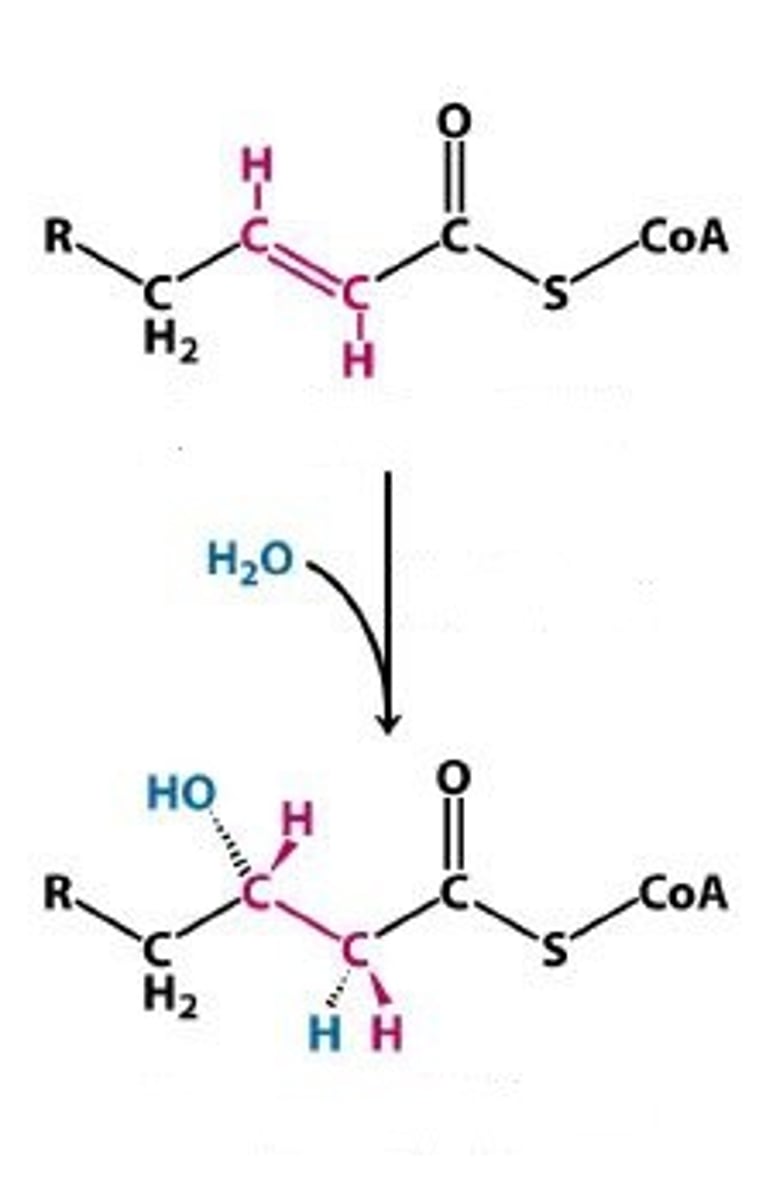
Enoyl Co-A hydratase
carries of the net reaction that oxidizes the beta position
trans-2-enoyl co-A + H2O --> 3,1-hydroxyacyl-coA
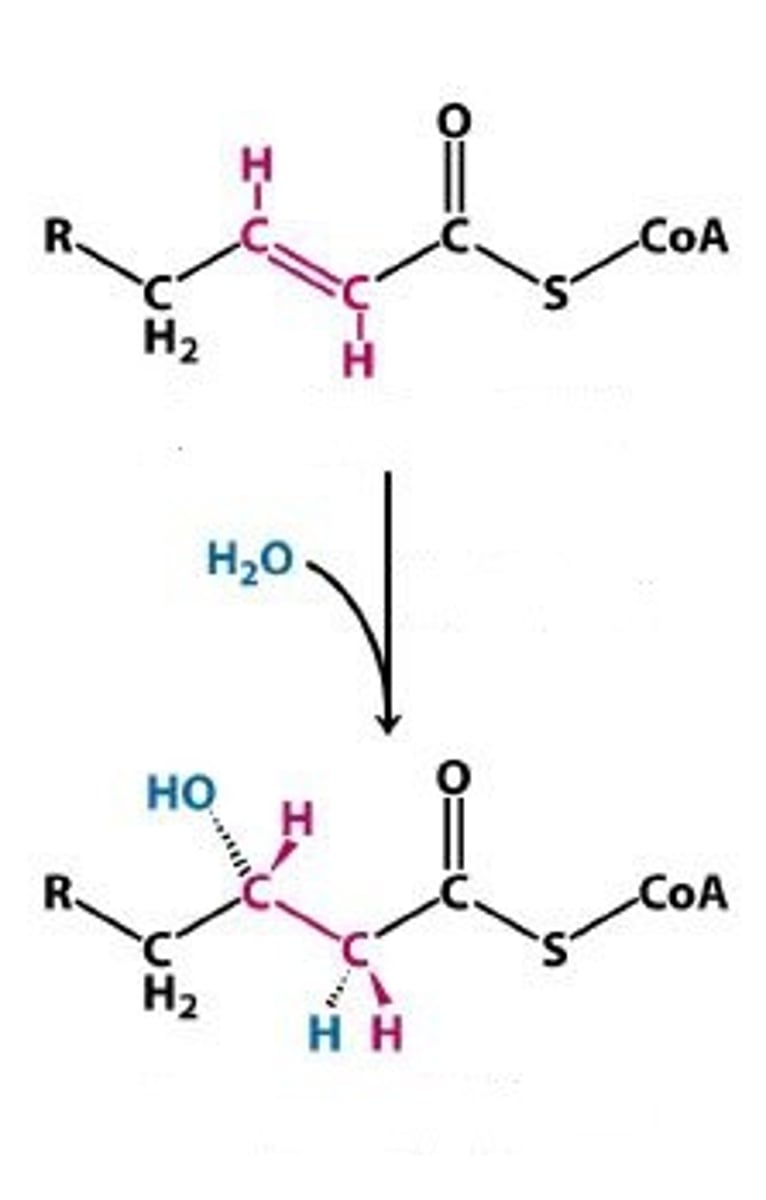
3,1-hydroxyacyl-coA
product of the Enoyl Co-A hydratase net reaction
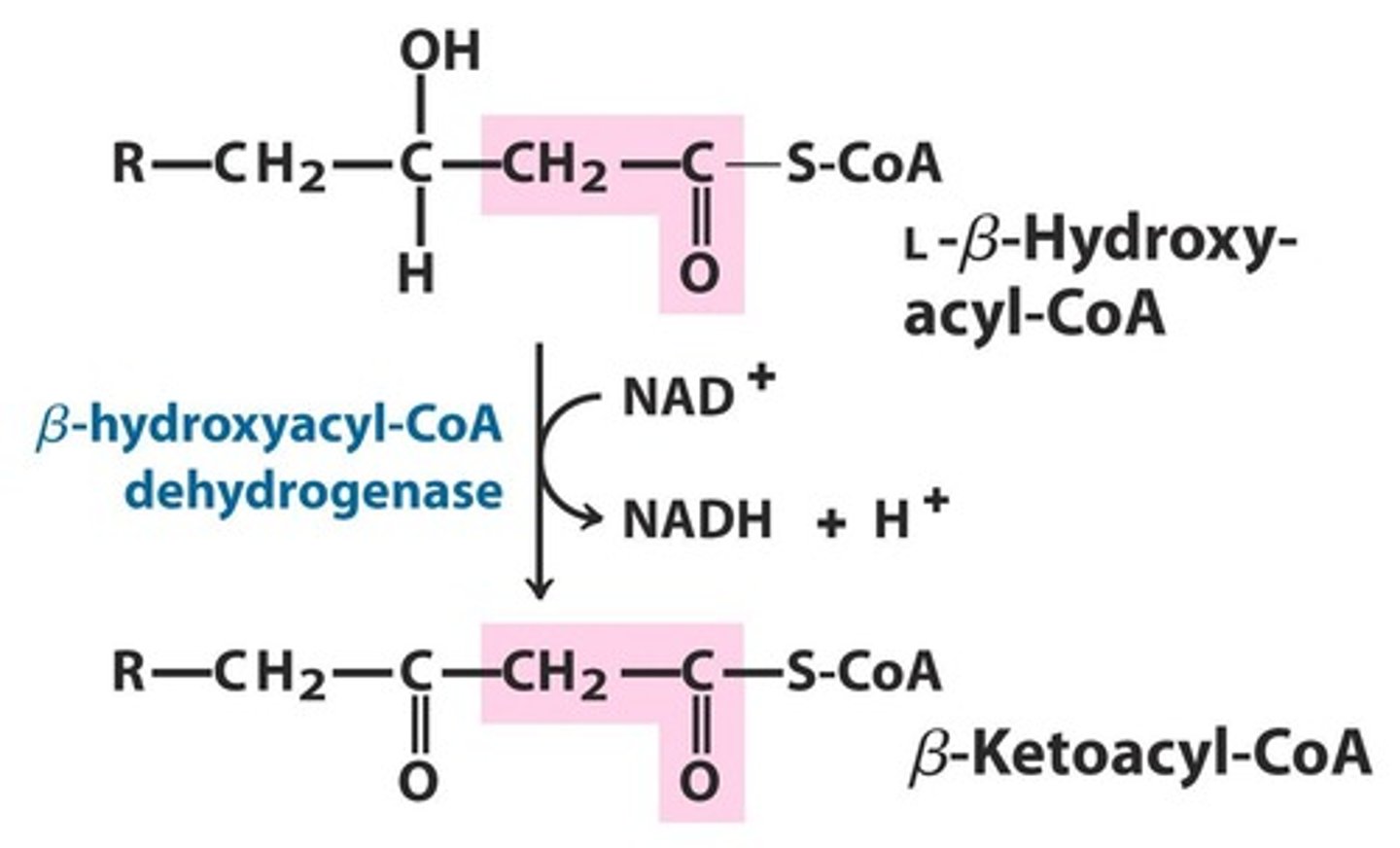
3,1-hydroxyacyl-coA dehydrogenase
carries out this reaction:
NAD+ + 3,1-hydroxyacyl-coA --> NADH + beta-ketoacyl-coA
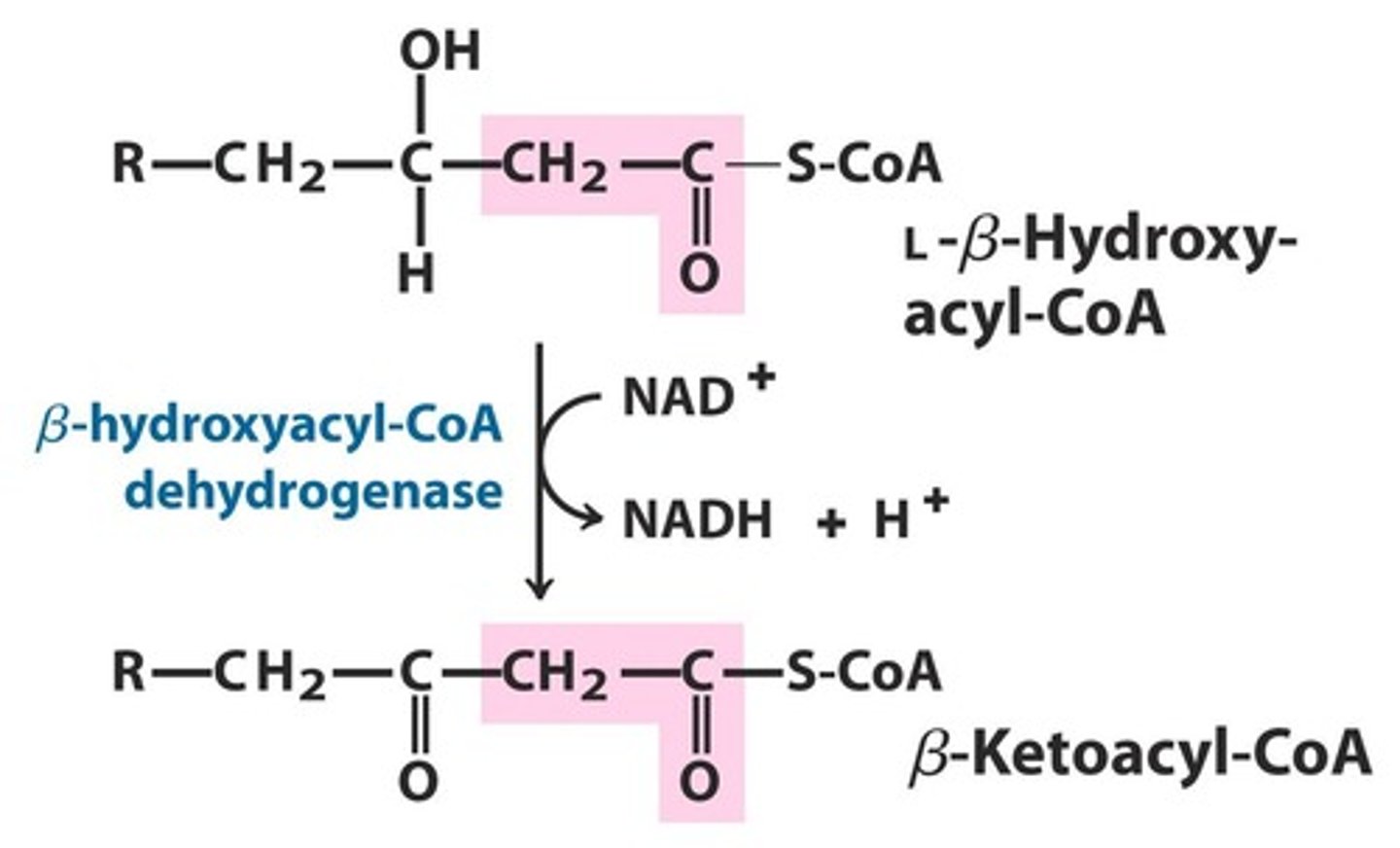
beta-ketoacyl-coA
product of the 3,1-hydroxyacyl-coA dehydrogenase net reaction
NAD+ + 3,1-hydroxyacyl-coA --> NADH + beta-ketoacyl-coA
net reaction of the 3,1-hydroxyacyl-coA dehydrogenase reaction
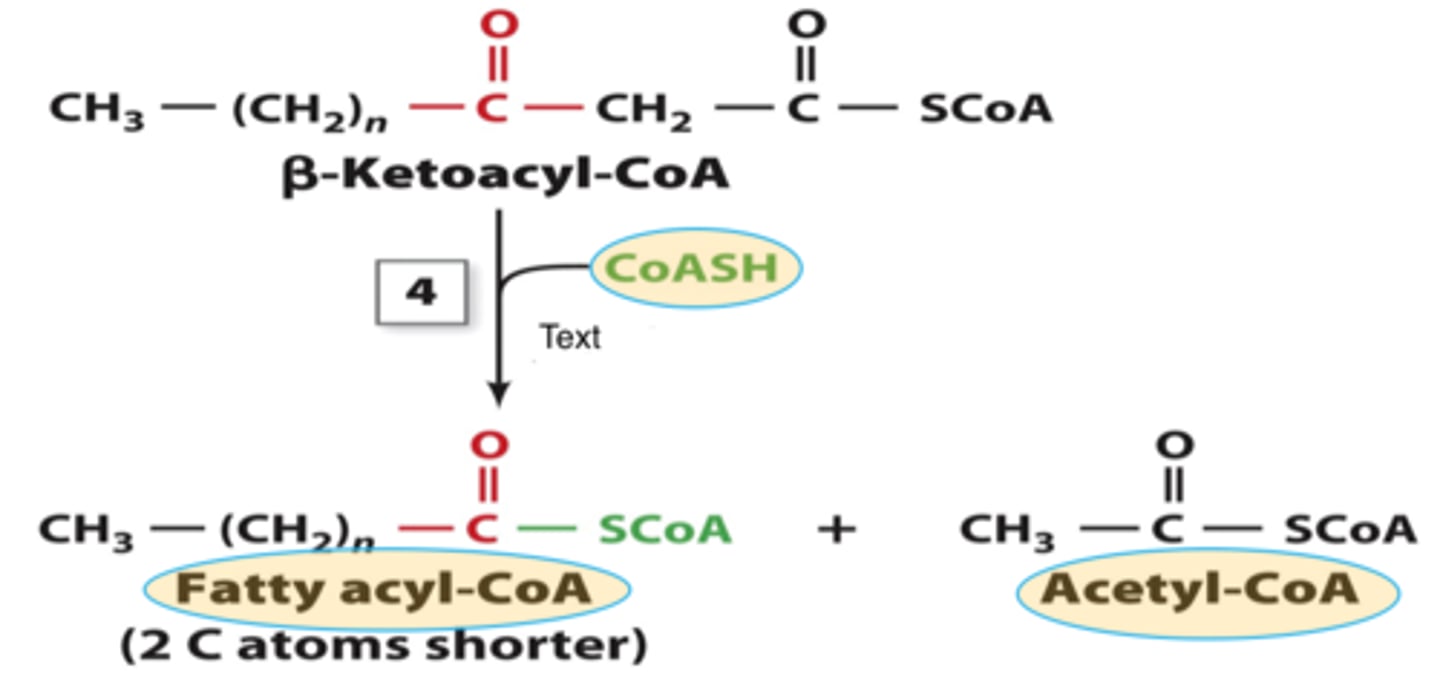
beta-ketoacyl thiolase
last step in one round of beta oxidation:
beta-ketoacyl-coA + CoASH --> acetyl-coA + FA-CoA
Fatty acid is not two lengths shorter
ACAD (acetyl-coA) dehydrogenase
MADD disease biochemical basis
MADD disease
multiple acyl-coA dehydrogenase deficiency
caused by acetyl-coA dehydrogenase (ACAD) deficiency
cannot process FA appropriately to get energy
riboflavin
treatment for late onset MADD - as stimulates energy releasing pathways
mcad (medium-chain acyl-coA dehydrogenase)
deficiency in this enzyme leads to 10% of deaths in SIDS (sudden infant death syndrome)
8 acetyl-coA, 7 NADH, 7 FADH2
is 16 carbon fat will undergo how many around of beta oxidation, product how many FADH2, NADH, and acetyl-coA
1 NADH, 1 FADH2, 1 acetyl-CoA
every turn of the fatty acid cycle produces ___
except the last round which makes 2-acetyl co-A
exergonic
fatty acid synthesis is highly this
129 ATP
net energy gain for complete fatty acid oxidation of a 16 C carbon
recall acyl coA requires 2 ATP
cis
naturally occurring unsaturated fatty acids have theset ype of double bonds and therefore cannot be substrate for enoyl-coA hydratase
isomerase and reductase
two additional enzymes required for beta oxidation of cis-unstaurated fatty acids
2,4 dienonyl reductase
this enzyme involved in cis-unsaturated fat synthesis reduces bonds not at carbon 3
used only by polyunsaturated fats
uses NADPH to have only 1 FADH2 loss
have a 2,3 trans bond and a 4,5 cis bond - converts to 3,4 trans bond with NADPH
isomerase then converts back to 2,3 cis-bond so beta oxidation can continue
delta 3, delta 2 enonyl isomerase
this enzyme involved in cis-unsaturated fatty acid synthesis converts cis double bonds to trans double bond at carbon 3
mono-unsaturated fatty acids only need this
also used by polyunsaturated fats
1 FADH2
cost of using isomerase in beta oxdiation of a cis unsaturated fatty acid
double bond must be between 2 and 3 position
acyl co A dehydrogenase step is skipped
3 and 4
cis double bond must be between these two positions for the isomerase to work
now have a double bond between positions 2 and 3 that is trans
nadph
used by reducatase in polyunsaturated fatty acid synthesis to make trans double bond at 3,4 position - started with DB at the 4,5 position and 2,3 position