INTRODUCTION TO MEDICAL ENTOMOLOGY
1/45
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Overview of Medical Entomology
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
46 Terms
Explain how arthropods can become ectoparasites. Give examples of these arthropods and the visible effects of ectoparasitoses.
Arthropods can directly cause disease by bloodfeeding, burrowing, crawling, and scraping.
Examples:
Ticks - bloodsucking
fleas -bloodsucking
lice -bloodsucking
Mites (Scabies mites) - burrowing
Manifestations of ectoparasitoses include reactions such as dermatoses, allergic reactions, and loss of efficiency and productivity. They can also cause weight loss and lowered milk production for cattles.
Explain how arthropods can become endoparasites. Give examples of these arthropods and the visible effects of endoparasitoses.
Arthropods can directly cause disease by invading tissues or body cavities of vertebrate hosts.
Examples
“Chigoe” or “Chigger” flea - swelling of host tissues surrounding the feeding site
Fly maggots - myiasis
Give examples of arthropods involved in envenomation.
Wasps, bees, and spiders
Venom are a type of _____________, which are often ________ that cause poisonous reactions in other animals.
toxin; proteins
What is delusory parasitosis?
a psychopathic condition that is manifested by a strong sense of being infested by arthropods
What is a vector?
any agent by which a pathogen is transmitted from one host to another.
The long evolutionary history of insects stretches back at least into the ____________ period
Devonian (450 mya)
Dipterans are believed to have first appeared no later than the _________ period, about 200 mya
triassic
The mosquito fossils of the Eocene epoch of the Quaternary Period (40-60 mya) is remarkably similar to the present-day ____________ species
Culex
Most entomologists believe that the __________ habit in mosquitoes had already developed by the time birds and mammals arose late in the __________Era (70-230 million years ago)
bloodsucking; Mesozoic
Before, infectious diseases are generally believed to have been caused by __________, and not microorganisms.
helminths
generally regarded to have begun the modern period of medical entomology
Patrick Manson
What is the important findings of Patrick Manson\s research?
mosquitoes became infected with immature stages of filarial worms (microfilariae) in the process of taking a bloodmeal
association between insects and parasites
What are the findings of Theobald Smith and F.L. Kilbourne in their research?
demonstrated the transmission of Texas cattle fever (piroplasmosis) by the cattle tick, Boophilus annulatus.
Revealed that pathogenic microorganisms can be transferred from arthropods to vertebrate animals
Pathogenic microorganisms can be transferred from adult female arthropod to its progeny through transovarial transmission, wherein eggs are infected
Who hypothesized that the yellow fever mosquito, now known as Aedes aegypti, was the vector of the disease?
Carlos Finlay
Who proved Finlay’s hypothesis?
Major Walter Reed, leader of the Yellow Fever Commission
Scientists of the Yellow Fever Commission that participated in a series of experiments that demonstrated conclusively that Ae. aegypti mosquitoes could transmit the virus from infected patients in hospitals to uninfected volunteers, and that the disease could not be transmitted through direct contact with contaminated food or bedding, nor with infected patients.
James Carroll, A. Agramonte, and Jesse Lazear
lost his life by permitting infected mosquitoes to feed upon him
Jesse Lazear
discovered that trypanosome parasites (later named Trypanosoma brucei in his honor) present in the blood of cattle caused. nagana, a fatal disease of cattle and horses
David Bruce
demonstrated that the parasites were transmitted by flies in the genus Glossina (tsetse)
David Bruce
reported that tsetse transmitted the related parasite T. gambiense to humans, resulting in African sleeping sickness.
David Bruce and David Nabarro
became the first to observe malarial parasites in the blood of infected patients
Charles Laveran in 1894
observed the developing malarial parasites in mosquitoes that he characterized as "dapple-winged."
Ronald Ross in 1897
discovered that Culex mosquitoes transmitted parasites causing bird malaria
Ronald Ross in 1898
demonstrated the complete developmental cycle of malarial parasites in Anopheles mosquitoes
Battista Grassi in 1898
confirmed that only anopheline mosquitoes transmitted human malarial parasites
Malcom Watson in Malaya and by Sir Rickard Christophers in India
their discoveries laid the basis for the concept of vector competence
Malcom Watson in Malaya and by Sir Rickard Christophers in India
__________made the significant discovery in Beruit in 1902 that mosquitoes were the vectors of the then unknown organism causing dengue
H. Graham
Investigated that fleas were vectors of plague
W.B. Liston and D.B.Verjbitski
A Brazilian parasitologist that discovered a disease prevalent in South America was caused by a trypanosome parasite he named Trypanosoma cruzi.
Carlos Chagas
In 1908, ___________reported that the triatomid bug Panstrongylus megistus transmitted these trypanosome parasites, causing the disease now called ____________ disease
Carlos Chagas; Chagas
In 1926, ____________discovered that black flies (Simuliidae) vectored the parasite causing onchocerciasis, or river blindness
D.B. Blacklock
____________ and ______________conducted their pioneering research in the Yakima Valley of Washington that led to the understanding of the basic ecology of western equine encephalomyelitis and St. Louis encephalitis
William McD. Hammon and William C. Reeves
demonstrated that the mosquito Culex tarsalis, which feeds mainly on birds, was the primary vector of the viruses causing both diseases
The decade of the __________ saw the isolation and identification of the causal agents of Lyme borreliosis and ehrlichiosis
1980s
What is the main problem of solving diseases in medical entomology nowadays?
solutions to problems in medical entomology often have been sought in a relatively vertical, single-objective framework
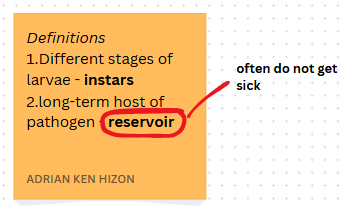
Different stages of larvae are referred to as the ______________
instars
___________ is defined as the long term host of the pathogen
reservoir
What is the generalized life cycle of a holometabolous insect?
egg, larvae, pupae, adult
What is the generalized life cycle of a hemimetabolous insect?
egg, nymph, adult or imago
______________ depends on the pathogenic microorganism’s ability to replicate and invade the insect’s hemolymph, which can then be transferred to its salivary glands.
vector competence
Evolutionarily speaking, being a vector may be considered as a ____________ trait
homoplastic
Why insects have no capability of spreading other diseases like COVID?
vector competence
Can bed bugs be considered as vectors?
No, because of low vector competence despite being morphologically and functionally similar to usual vectors
The three types of transmission are:
vertical, horizontal, transstadial
What does transstadial transmission means?
e.g. nymph to nymph, larvae to larvae transmissions
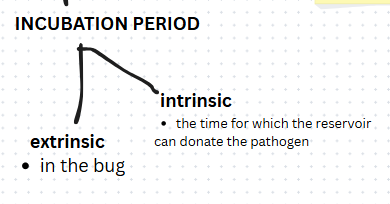
Differentiate extrinsic and intrinsic incubation periods