synthetic polymers updated
1/28
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
29 Terms
what are polymers
- substances of high average relative molecular mass
- made by joining up lots of small repeating units called monomers
what do the monomers that make up addition polymers have
a double covalent bond
what is addition polymerisation
- when lots of unsaturated monomer molecules (alkenes)
- can open up their carbon-carbon double bonds
- and join together to form polymer chains
where does the name of a polymer come from
- u just put brackets around the type of monomer it is made from
- then u put the word "poly" in front of it
- e.g propene becomes poly(propene)
how do u get the formula of the polymer
- just put the formula of the monomer in brackets
- then put a "n" after it
e.g C3H6 becomes (C3H6)n
how do u draw the displayed formula of an addition polymer
- replace the carbon-carbon double bond with a single
- put a pair of brackets around the repeating bit
- then put an "n" after it
- and extend the two end bonds so they come out the brackets
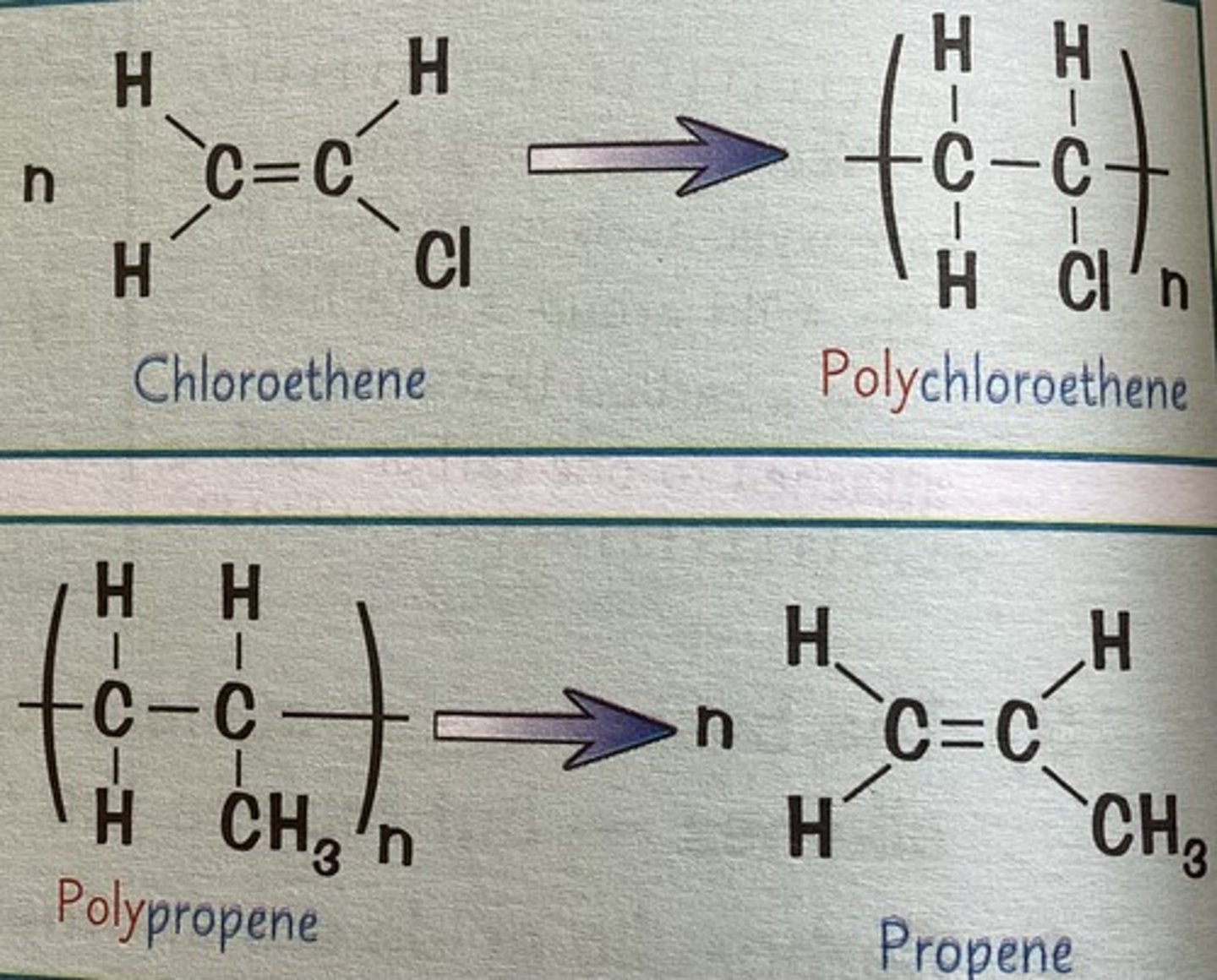
how do u draw the displayed formula of the monomer from the polymer
- draw out the repeating bit of the polymer
- get rid of the two bonds going out through the brackets
- put a double bond between the carbons
- put an n on the left of the displayed formula
why are most addition polymers inert (don't react easily)
- their carbon-carbon double bonds in the polymer chain
- are very strong and are not easily broken
what does the fact that most addition polymers are inert mean
- it takes a really long time for addition polymers to biodegrade
- so if u bury them in a landfill site they will still be there years later
biodegrade meaning
be broken down by bacteria or other organisms
why is burning a bad way of disposing of addition polymers
because this releases toxic gases
why is it difficult to dispose of addition polymers
- their inertness and inability to biodegrade
- the production of toxic gases when they are burned
what does chloroethene look like
like ethene with one H swapped for Cl
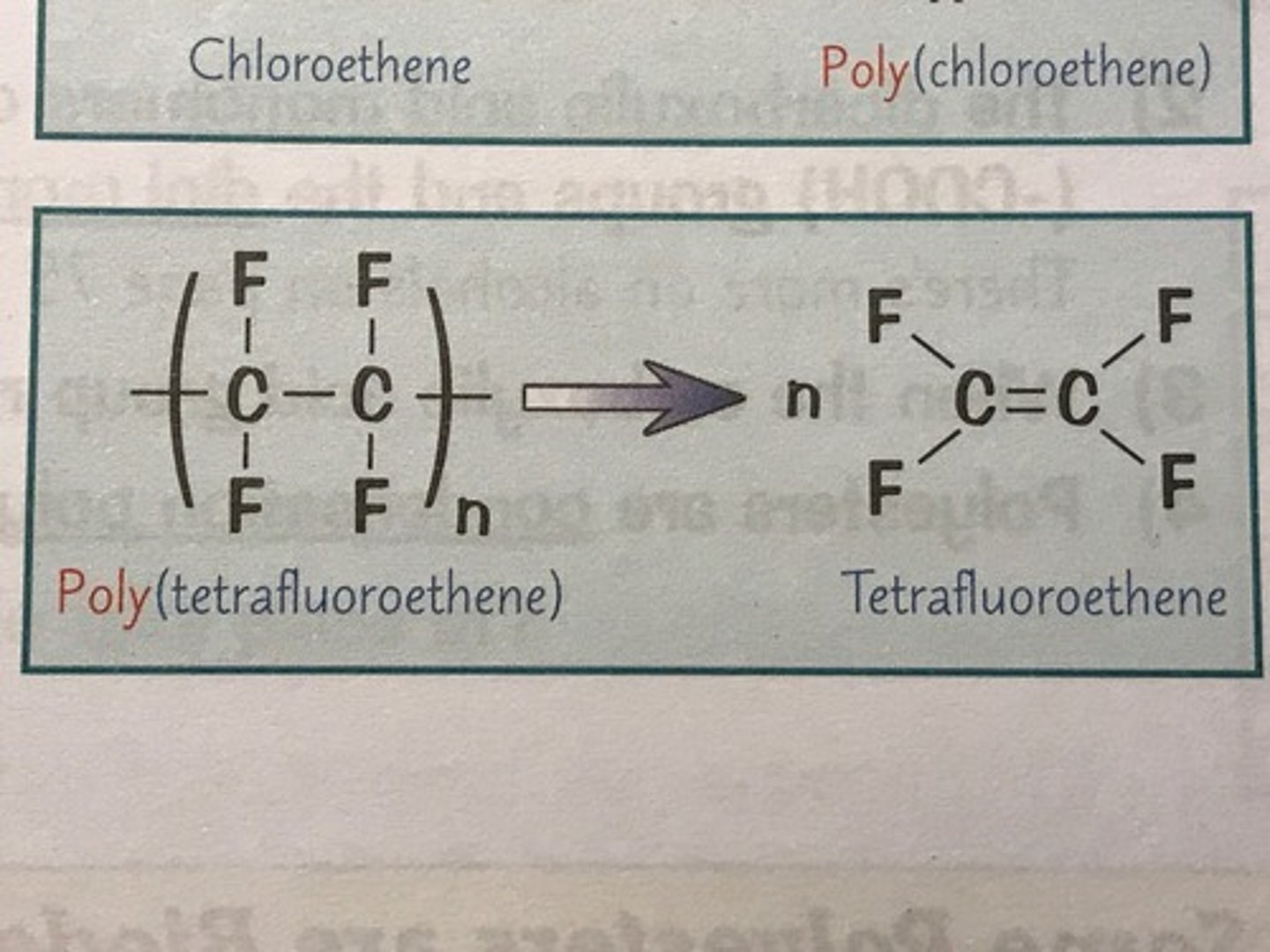
what does tetrafluoroethene look like
ethene but with all the Hs swapped for Fs
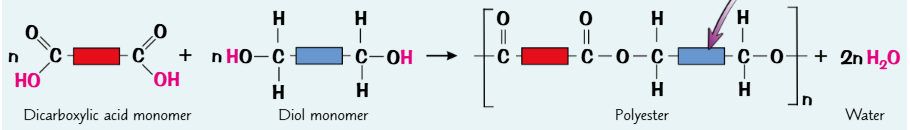
polyesters
- polymers that contain ester links that join together repeating units
- example of a condensation polymer
how cna polymers be made
by condensation polymerisation
what does condensation polymerisation usually involve
2 diff types of monomer
what do the monomers involved in condensation polymerisation have to contain
each monomer has to contain at least 2 functional groups (one on each end of the molecule)
how does condensation polymerisation occur
- monomers react together + bonds form between them
- making polymer chains
- each functional group can react with the functional group of another monomer
- creating long chains of alternating monomers
describe condensation polymerisation
monomers react together
and ester links form between them to make a polymer chain
a small molecule/ water is lost for every ester link that forms
in condesnation polymerisation, what is lost for every new bond that fomrs
a small molecule e.g water is lost
what is produced when a dicarboxylic acid reacts with a diol
polyester and water
what happens when the carboxylic acid functional group reacts with the alcohol functional group
it forms an ester link
what happens each time an ester link is formed
a molecule of water is lostd
drawing polyesters
add diagram
what are biopolyesters
- biodegradable polyesters
- they can be broken down by bacteria and other living organisms in the environment over time
why do biopolyesters reduce the polymers' pollutant effect
bc they decompose + don't stay in landfill forever
dicarboxylic acid, diol and polyester name examples
ethanedioic acid, ethanediol, poly (ethyl ethanoate)
naming polyesters
1st part of name = diol
2nd part of name = dicarboxylic acid