Chapter 4&5 Study Guide - Ethan
1/41
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
42 Terms
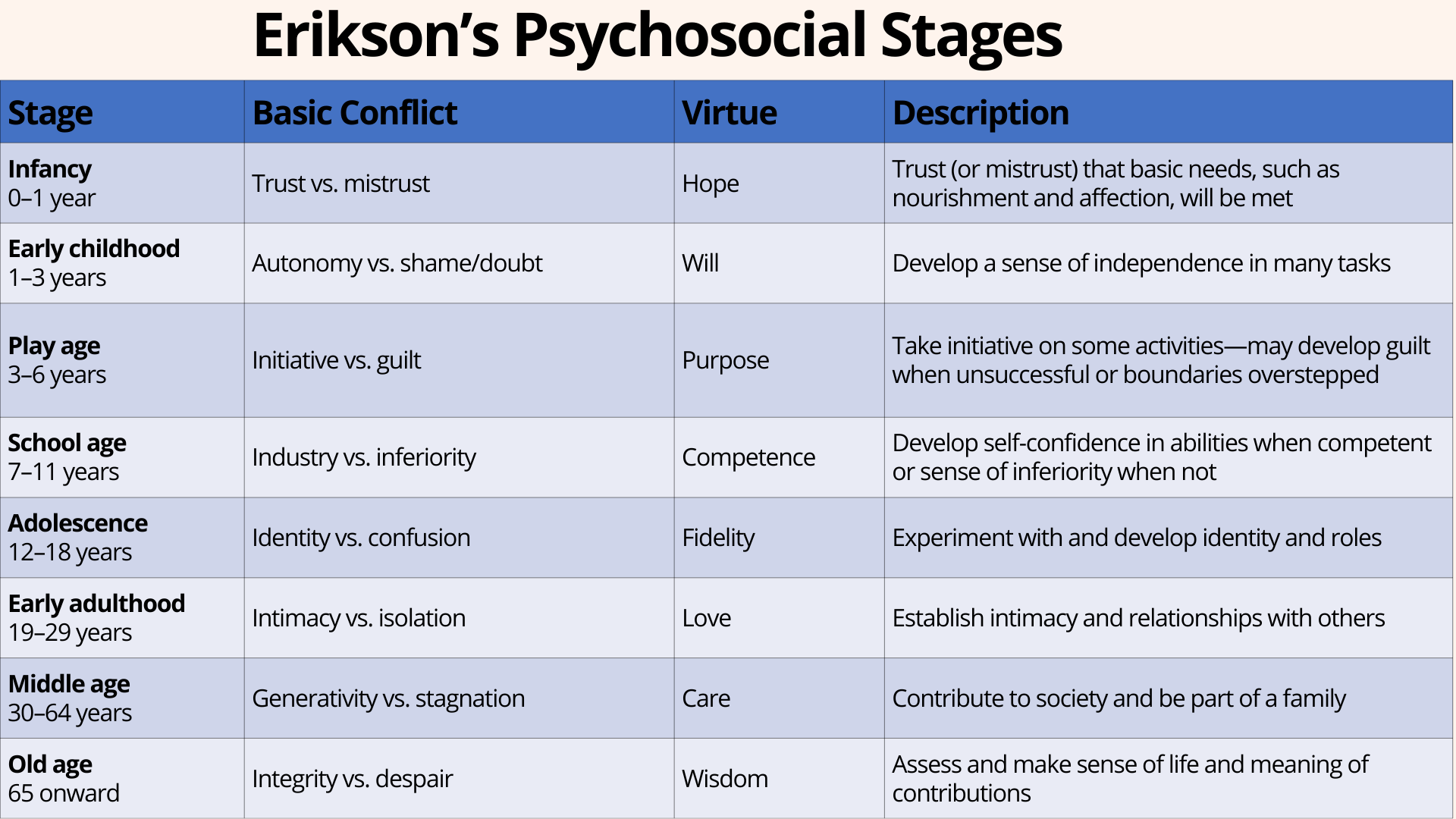
Erickson’s Theory
8 stages of psychosocial development - conflicts & virtues
1: Infancy
2: Early Childhood
3: Play Age
4: School Age
5: Adolescence
6: Early Adulthood
7: Middle Age
8: Old Age
Infancy (Stage 1)
Age: 0-1 year
Basic Conflict: trust vs mistrust
Virtue: hope
Description: trust/mistrust that basic needs will be met
Early Childhood (Stage 2)
Age: 1-3 years
Basic Conflict: autonomy vs shame/doubt
Virtue: will
Description: develop a sense of independence in many tasks
Play Age (Stage 3)
Age: 3-6 years
Basic Conflict: initiative vs guilt
Virtue: purpose
Description: take initiative on some activities - may develop guilt when unsuccessful or boundaries overstepped
School Age (Stage 4)
Age: 7-11 years
Basic Conflict: industry vs inferiority
Virtue: competence
Description: develop self confidence in abilities when competent or sense of inferiority when not
Adolescence (Stage 5)
Age: 12-18 years
Basic Conflict: identity vs confusion
Virtue: fidelity
Description: experiment with and develop identity and roles
Early Adulthood (Stage 6)
Age: 19-29 years
Basic Conflict: intimacy vs isolation
Virtue: love
Description: establish intimacy and relationships with others
Middle Age (Stage 7)
Age: 30-64 years
Basic Conflict: generativity vs stagnation
Virtue: care
Description: contribute to society and be part of a family
Old Age (Stage 8)
Age: 65+
Basic Conflict: integrity vs despair
Virtue: wisdom
Description: assess and make sense of life and meaning of contributions
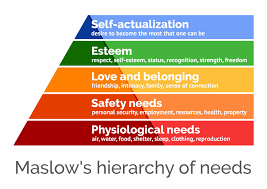
Maslow’s Hierarchy of Needs
suggests that individuals must satisfy lower-level needs before they can focus on fulfilling higher-level ones
self actualization: desire to become the most that one can be - highest level
esteem: respect, self-esteem, status, recognition, strength, and focus
love and belonging: friendship, intimacy, family, sense of connection
safety needs: personal security, employment, resources, health, and property
physiological needs: air, water, food, shelter, sleep, clothing, and reproduction - lowest level
Spirituality & Culture
S: individual's search for meaning and connection to something larger than themselves - expressed through various cultural practices
C: shared beliefs, customs, and practices of a group - traditions often reflect spiritual beliefs
PTSD
PTSD develops in some people after they experience or witness an event that threatens their life or safety, or that of others around them.
Symptoms include vivid memories, feeling constantly on edge and avoiding reminders of the event.
It is common for people to have some of the symptoms of PTSD in the first few days after the traumatic event. Most will recover by themselves or with the support of family and friends. Others may need professional help.
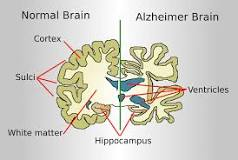
Alzheimers
brain disorder that gradually destroys memory and thinking skills, and eventually, the ability to carry out simple tasks
common type of dementia: broader term for conditions that cause a decline in cognitive abilities
Alzheimer's is characterized by the buildup of abnormal proteins in the brain, which disrupt nerve cell communication and lead to cell death
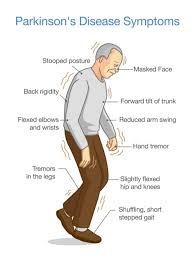
Parkinsons
progressive nervous system disorder that primarily affects movement
occurs when nerve cells in the brain that produce dopamine - a chemical crucial for movement coordination, are damaged or die
symptoms: tremors, stiffness, slowness of movement, and problems with balance and coordination - often impacting daily activities
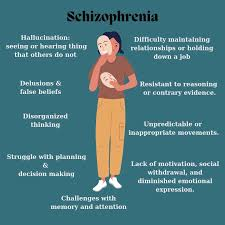
Schizophrenia
Schizophrenia is a mental disorder characterized by disruptions in thought processes, perceptions, emotional responsiveness, and social interactions
Symptoms: hallucinations, delusions, and thought disorder (unusual ways of thinking), as well as reduced expression of emotions, reduced motivation to accomplish goals, difficulty in social relationships, motor impairment, and cognitive impairment

Hallucination
sensory experiences that appear real but are created by the mind, meaning they occur without an external stimulus
involve any of the five senses (sight, sound, smell, taste, and touch)
caused by various factors: mental health conditions, neurological disorders, substance use, and even medication side effects
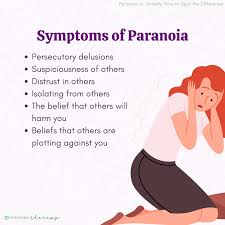
Paranoia
psychological state characterized by persistent and irrational distrust and suspicion of others, often with the belief that they are being threatened or harmed
can manifest as a symptom of various mental health conditions or as a standalone issue

Depression
(major depressive disorder) is a common and serious medical illness that negatively affects how you feel, the way you think and how you act

Mental Adjustment Disorder
mental health condition triggered by a stressful life event, causing emotional or behavioral symptoms that are out of proportion to the stressor itself
reactions, which occur within three months of the event, can significantly impact daily functioning, including work, school, and relationships
Symptoms: depressed mood, anxiety, conduct disturbance, or a combination of these

Substance Abuse
harmful or hazardous use of psychoactive substances, including alcohol, prescription drugs, and illegal drugs
involves using substances in ways that cause social, physical, emotional, or job-related problems, and can lead to addiction or dependence

Addiction
chronic, relapsing disorder characterized by compulsive engagement in behaviors or use of substances despite harmful consequences
considered a disease of the brain, impacting reward, motivation, memory, and related brain circuits
key elements: loss of control over the behavior, preoccupation with it, and continued engagement despite negative consequences
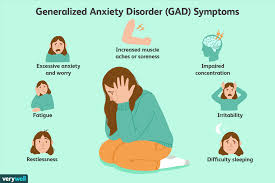
Anxiety
normal human emotion characterized by feelings of worry, nervousness, or unease, typically about an event with an uncertain outcome
when these feelings become excessive, persistent, and interfere with daily life, they can indicate an anxiety disorder
disorders involve repeated episodes of sudden feelings of intense anxiety and fear or terror that reach a peak within minutes (panic attacks)

Delusions
false beliefs that persist despite evidence to the contrary
key symptom of various mental illnesses, including schizophrenia and delusional disorder
distinct from false beliefs based on misinformation or misinterpretations; they are held with strong conviction and are resistant to reason or evidence

Bipolar Disorder
mental health condition that causes unusual shifts in mood, energy, activity levels, concentration, and the ability to carry out day-to-day tasks
shifts can range from periods of extreme highs (mania or hypomania) to lows (depression)
mood episodes last days to months at a time and may also be associated with suicidal thoughts
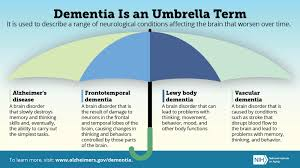
Dementia
general term for a decline in mental ability severe enough to interfere with daily life, affecting memory, thinking, and behavior
not a specific disease but rather a syndrome caused by various underlying conditions, with Alzheimer's disease being the most common type
What is nonpharmacological?
healthcare interventions that do not involve the use of medications
methods focus on other approaches like lifestyle changes, physical therapies, psychological therapies, and other techniques to manage health conditions, improve well-being, or address pain

Acute vs Chronic
A: develop suddenly and are usually short-term
common cold, flu, broken bones, and sudden injuries
treatable with medication or other therapies, and the body can often heal on its own
C: develop slowly and persist for a long time, often months or even years
asthma, diabetes, arthritis, heart disease, and osteoporosis
may require ongoing management, medication, lifestyle adjustments, and regular monitoring
Protective Oversight
24 hour awareness of the location of a resident and the ability to intervene and supervise the nutrition, medication, and care of the resident

Delirium
sudden and temporary state of confusion and altered awareness, often marked by rapid changes in brain function and mental status
can manifest in various ways, including disorientation, memory problems, and changes in behavior and mood
often linked to underlying medical conditions, medication side effects, or withdrawal from substances like alcohol
crucial to recognize delirium as a medical emergency that requires prompt attention and treatment, as it can lead to serious complications and even long-term cognitive damage

Quality of Life
subjective measure of an individual's overall well-being, encompassing physical, mental, and social aspects, as well as their perception of their position in life within their cultural and societal context
dynamic concept, influenced by various factors like health, relationships, work, and personal values, and is often used to assess the impact of illness, treatment, or social conditions on a person's life
STOP AND WATCH
early warning tool
STOP
S: seems to be acting differently - symptoms of new illness
T: talks or communicates less
O: overall needs more help
P: pain - new development or participated in fewer activities
AND
A: ate less
N: no bowel movements in 3+ days/diarrhea
D: drank less
WATCH
W: weight change - swollen legs/feet
A: agitated/nervous more than usual
T: tired/weak/confused/drowsy
C: change in skin color/condition
H: help with walking/transferring/bathroom more than usual
Body Systems
Skeletal: provides support, protection, and movement through bones, ligaments, and tendons - BONES
Muscular: enables movement through the contraction and relaxation of muscles - MUSCLES
Nervous: controls and coordinates body functions through electrical impulses, using the brain, spinal cord, and nerves - NERVES + BRAIN
Endocrine: regulates body functions through hormones produced by glands - PITUITARY/THYROID/ADRENAL/ETC
Cardiovascular: transfers oxygen, nutrients, hormones, and waste products through the heart and blood vessels - HEART + BLOOD VESSELS + ARTERIES + VEINS
Lymphatic: supports the immune system by filtering fluid and returning it to the bloodstream - LYMPHNODES + BONE MARROW + SPLEEN
Respiratory: facilitates gas exchange (oxygen and carbon dioxide) between the body and the environment - LUNGS + AIRWAYS
Digestive: breaks down food into nutrients for absorption and eliminates waste - STOMACH + MOUTH + LARGE/SMALL INTESTINE + COLON
Urinary: filters waste from the blood and eliminates it as urine - BLADDER + KIDNEYS + LIVER
Integumentary: protects the body - SKIN + HAIR + NAILS
Reproductive: enables reproduction through specialized organs in males and females
Infectious Process
Exposure:
The pathogen comes into contact with the host through various portals of entry like the respiratory tract, skin, or gastrointestinal tract.
Colonization:
The pathogen attaches to the host's cells and begins to multiply.
Invasion:
The pathogen penetrates deeper into the body's tissues, potentially spreading through the bloodstream or lymphatic system.
Infection:
The pathogen successfully establishes itself within the host and causes harm, leading to a disruption in normal bodily functions.
Disease:
If the infection causes significant damage and symptoms become apparent, it is considered a disease.
Spread (Transmission):
The pathogen may be released from the host and transmitted to another susceptible individual, continuing the cycle.
Body Systems Responses to Infection
Fever: A common response to infection, possibly helping to inactivate viruses and activate immune cells.
Malaise, headache, muscle aches: General symptoms resulting from the immune response.
Rash: Can be caused by various pathogens, including viruses, bacteria, and fungi.
Swelling: A hallmark of bacterial infections, especially localized ones.
Pus: A collection of dead white blood cells at the site of infection, indicating the body's attempt to eliminate bacteria.
Infection Effects on Body Systems
Localized infections: These infections are confined to a specific part or organ system of the body, such as a skin boil or an ear infection
Systemic infections: These infections spread throughout the body, typically through the bloodstream, potentially affecting multiple organ systems
Chain of Infection
Infectious Agent:
This is the pathogen (like bacteria, virus, fungus, or parasite) that causes the disease.
Reservoir:
This is where the pathogen lives and multiplies. It could be a person, animal, insect, or even an inanimate object like contaminated equipment or soil.
Portal of Exit:
This is how the pathogen leaves the reservoir. For example, through respiratory secretions (coughing, sneezing), open wounds, or bodily fluids.
Mode of Transmission:
This is how the pathogen travels from the reservoir to a new host. It can be direct contact (person-to-person), indirect contact (through a contaminated object), or airborne (through respiratory droplets).
Portal of Entry:
This is how the pathogen enters the new host. It can be through the respiratory tract, mucous membranes, broken skin, or ingestion.
Susceptible Host:
This is a person who is vulnerable to infection, often due to factors like age, health status, or weakened immune system.
Mode of Transmission
This is how the pathogen travels from the reservoir to a new host. It can be direct contact (person-to-person), indirect contact (through a contaminated object), or airborne (through respiratory droplets)
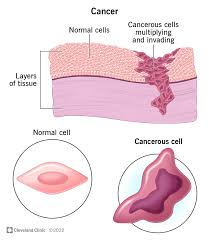
Cancer
disease where cells grow out of control and can invade nearby tissues or spread to other parts of the body
not a single disease, but rather a group of over 100 different diseases, each with unique characteristics
develops due to changes in a cell's DNA, leading to uncontrolled growth and division
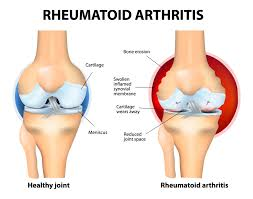
Arthritis
group of conditions characterized by inflammation and pain in the joints and surrounding tissues
over 100 different types
common symptoms include joint pain, stiffness, swelling, and limited movement
no cure for many forms of arthritis, various treatments can help manage symptoms and improve quality of life
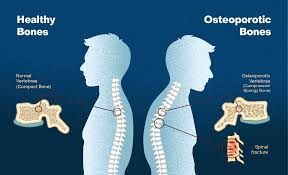
Osteoporosis
OSTEO = BONE & POROSIS = HOLES/PORES
disease that weakens bones, making them more susceptible to fractures
often called a "silent disease" because it can progress without noticeable symptoms until a fracture occurs
common fracture sites include the hip, spine, and wrist
Women are more likely to develop osteoporosis than men
The risk increases with age, especially after menopause for women
Family history of osteoporosis or hip fractures can increase risk
People with certain medical conditions or who take specific medications may also be at higher risk

Orthostatic Hypotension
drop in blood pressure that occurs when standing up from a sitting or lying down position
can lead to symptoms like dizziness, lightheadedness, and blurred vision
often caused by a failure of the body's autonomic nervous system to quickly adjust blood pressure when standing, and it's more common in older adults and those with certain medical conditions
Hyperglycemia
condition where there's too much glucose in the blood
often occurs in people with diabetes when the body doesn't produce enough insulin or can't properly use the insulin it produces, leading to glucose buildup in the bloodstream
can also occur in individuals without diabetes, particularly in hospital settings due to stress, infections, or certain medications