Cell Structure and Cell Diversity
1/50
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
51 Terms
What stain is used on a plant cell?
iodine
What stain is used on a animal cell?
Methylene blue
Plant cell example
Onion
Plant cell structure + Organelles
Cell wall
Cell membrane
Cytoplasm
Nucleus
Chloroplast
Ribosome
Mitochondria
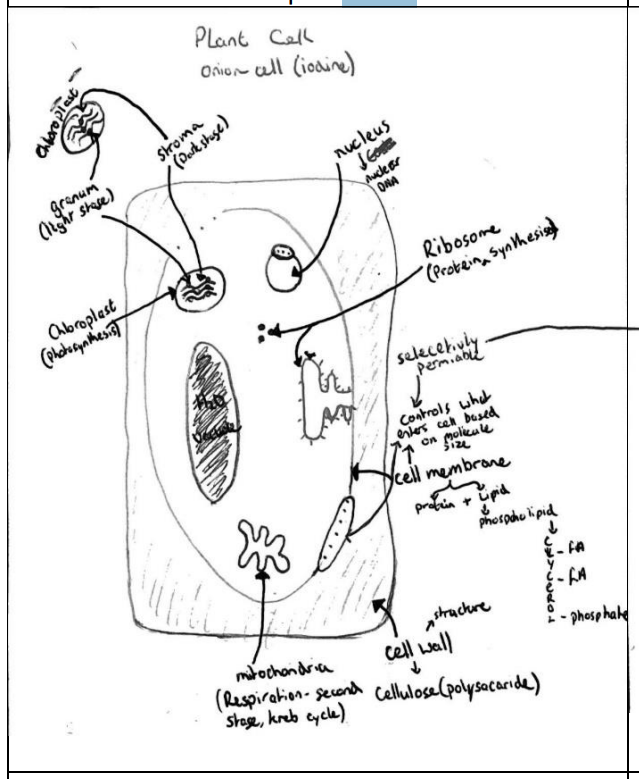
Cell wall
Made of cellulose (polysaccharide). Gives structure and support to cell.
Cell membrane
Made of lipids (phospholipids) and protein. Controls what enters the cell; selectively permeable. (Need to know structure of cell membrane).
Cytoplasm
Liquid medium composed of water (70-95%) in which cell organelles are suspended. Stage 1 (glycolysis) of respiration occurs here.
Nucleus
Brain of cell. Controls activities of cell and contains genetic material in the form of DNA (nuclear DNA) located on structures called chromosomes. Nucleolus is part of nucleus that makes ribosome.
Chloroplast
Contains chlorophyll (gives plants its green colour). Location for photosynthesis. Contains DNA (non-nuclear DNA).
Ribosome
Location for protein synthesis. Does not contain DNA BUT contains RNA.
Mitochondria
Respiration occurs here (2nd stage-Krebs cycle). Contains DNA (non-nuclear DNA).
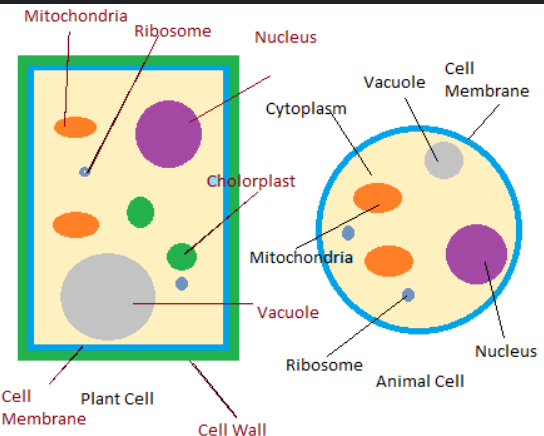
Animal cell structure + Organelles- e.g. cheek cell
Cell membrane
Cytoplasm
Nucleus
Mitochondria
Ribosome
What two organelles are missing from an animal cell compared to a plant cell?
Chloroplasts and cell wall.
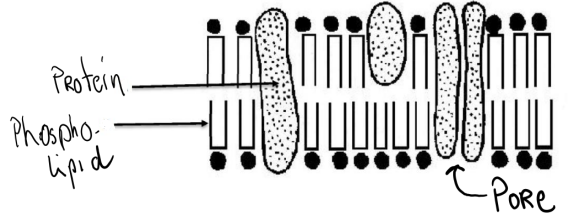
Cell Membrane Structure
• Composed of protein and phospholipids
• The selectively permeable gaps in the membrane of a cell or nucleus are called pores.
Eukaryotic Organisms
Organism that has a nucleus and has membrane enclosed cell organelles, e.g. Fungi.
Prokaryotic Organisms
Organism that does not have a nucleus or does not have membrane enclosed cell organelles, e.g. Bacteria.
Parts of the microscope
Eyepiece/Objective lens
Stage
Light/Mirror
Coarse Focus Wheel
Fine Focus Wheel
Diaphragm/condenser
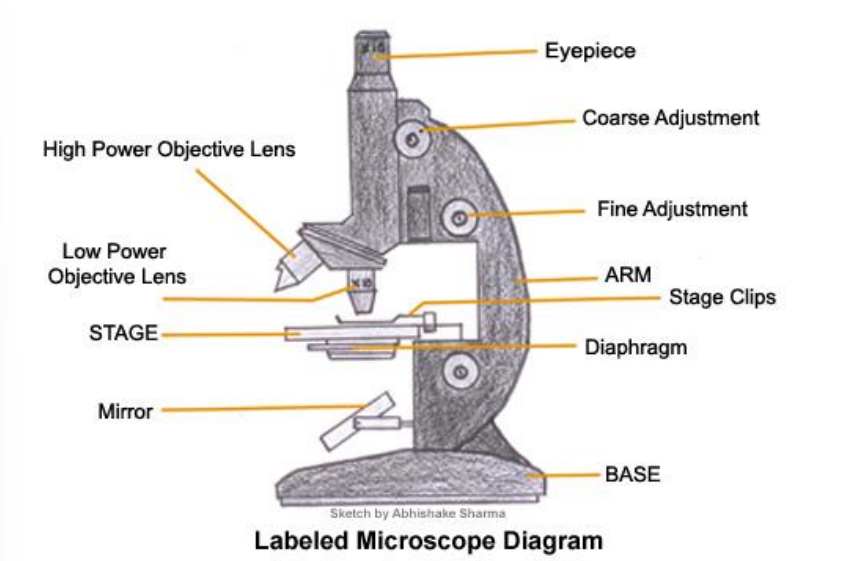
Eyepiece/Objective lens
Magnification of the image to be viewed.

Stage
Holds the slide.

Light/Mirror
Illuminate the content of the slide. The light intensity maybe changed by adjusting the condenser or diaphragm.

Coarse Focus Wheel
To move the stage and roughly focus the image.

Fine Focus Wheel
Improve the clarity of the image.

Diaphragm/condenser
Alters the light intensity reaching the sample on the stage.

Total magnification formula?
= eyepiece x objective lens.
E.g. 500 = 10 × 50
Types of Microscopes
Light + Electron
Light
Found in most school labs. This type of microscope will magnify the object and allow basic detail to be observed such as cell membrane and the nucleus. It will not allow cell organelles such as ribosome and mitochondria to be observed.
Electron
Provides far greater magnification than the light microscope and far more expensive. Will allow cell organelles such as mitochondria and ribosome to be observed.
Expt: Preparation and examination of a plant/animal cell under the microscope.
Apparatus:
Onion, saliva, glass slide X2, dropper, water, iodine, methylene blue, cover slip, microscope.
Method
1. Peel a thin layer (to allow light to pass through) of onion (or rub finger/ swab inside cheek) and place on a glass slide.
2. Add two drops of water (to prevent cells drying out).
3. Place a cover slip over the cells; add to the glass slide slowly at a 45o angle using a mounted needle (cover slip holds cells in place/ protects objective lens of microscope and by adding it at a 45o angle will prevent the formation of air bubbles).
4. Add drops of iodine (plant) or methylene blue (animal) stain using a dropper around the edges of the cover slip. The stain will travel towards the cells naturally (stain helps to highlight cell organelles from cytoplasm especially nucleus).
5. Place glass slide on stage of microscope and turn on light of microscope.
6. Observe under low magnification objective lens using coarse and fine focus wheel to adjust the image.
7. Move to a higher magnification objective lens and improve the clarity of the image using the fine focus (do not use coarse focus wheel at this stage as it will damage the lens).
8. Draw an image of what was observed under microscope.
Results: (Image of cells)
Tissue
Group of similar cells working together to carry out a specific function.
Example in Plants
Vascular tissue (Xylem, phloem), dermal tissue, ground tissue.
Adaptation in Plants
Xylem has adapted by having walls reinforced with lignin and the vessels lie end-to-end.
Phloem: contain sieve plates which allow food to pass through.
Example in animals
Epidermis (part of skin)
blood
blood vessels
bone
nerves
muscles
Adaptation in Animal
Muscles have adapted for cellular respiration by having a large surface area.
Nervous tissue adapted by having a layer of insulation (myelin sheath) to ensure continuous transmission of electrical messages.
Organ
Group of tissues working together to carry out a function.
Example in Plants
Leaf
Adaptation in Plants
-Large surface area (photosynthesis)
-Waxy cuticle (waterproofs top layer of leaf)
-Stomata (openings in the leaf for gaseous exchange)
Example in animals
Liver
Kidney
Heart
Adaptation in Animal
Heart has thick muscle wall to pump blood around entire body.
System
Group of different organs working together to carry out a specific function.
Example in Plants
Transport system (xylem and phloem).
Adaptation in Plants
-Attraction between water molecules allow water to travel to great heights against the force of gravity
-Roots have a large surface area to facilitate the uptake of a large volume of water
Example in animals
Digestive system
Circulatory system
Respiratory system
Nervous system
Excretory system
Adaptation in Animal (Digestive system)
Digestive System
- Large surface area (many villi)
-walls of villi one cell thick (rapid exchange between cells and blood)
-good blood supply (transport)
Tissue culture
Is the growth of cells on a sterile (free from all microorganisms) nutrient medium outside of a living organism-on glassware. Type of cell division involved is mitosis.
In-vitro
Grown on glass ware.
Asepsis
Free from harmful or disease causing microorganisms (Pathogens).
Conditions necessary for tissue culturing
• Suitable nutrients present
• Suitable pH
• Suitable temperature
• Sterile
Uses of tissue culture
Micropropagation of plants (carrots)
-Produces large quantities of carrots very rapidly
Cancer research
Skin graft
IVF
Advantages of Tissue culturing
Fast
Large quantities of cells produced
Allows for advancement of medicine or treatment of illness.