Chapter 12 Japanese Art before 1333
1/25
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
26 Terms
Japan has some of the oldest what?
Some of oldest pottery in the world
earlier than 10,000BCE.
human habitant 30,000 yrs ago
Kasuga Shrine Mandala
buddhist deities hover on top of hill and trees and diagrammatic birds eye views of religious compoound. Known as kami from shinto religious. Family shrine for aristocratic clan in Japan(Fujiwara). Surrounded around kami who believed to decend from heaven from majestic places. Kami(give and protect life, embody renewable life sustaining forces of nature). Deer are sacred messengers of Kami even now roaming freely there.
End of Heian period, interaction for Shinto and Buddhist lead to believe buddhist dieties were original forms of kami. When buddhism first came to Japan(6th cent) tried to intergrate with kami which later became Shinto. Later goverment seperated 2 religions and elevated shinto and buddhism and shinto became intertwines as complementary systems.
Shinto-explain origin of japanese ppl and deities
Buddhsim-slavation after death.
Early and medival art and culture shown in painting. Art made to embody religious teachings and belief, Reverance for natural world informed informed religious practices and vocab and shows buddhism intergration into indiginous belief without sacraficing either.
Describe Jomon period
The early potters lived during the Jomon period named for pattern of pottery.
They made functional earthenware vessels and humanoid figures known as dogu
Describe the Yayoi Period
Immigrants from Korea during the Yayoi period (400 BCE–300 CE) helped Japan become an agricultural nation through rice cultivation.
Korean settlers also brought metal technology.
Bronze was used to create weapons and bells.
Japan thrived in early period because of Koreon immigrants, Korean were responsible for teahing Japanese how to make stuff and agriculture practices
HANIWA
Kyoto. Kofun period, 6th century CE. Earthenware
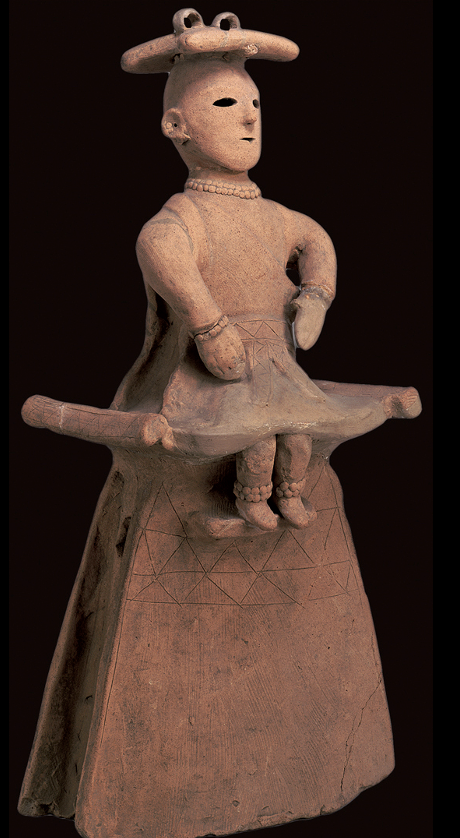

Centralized govermnet formed durig Kofun period named after “old tombs”Emperor.empress descended from Shinto deities
When emperor dies chambers followed korean examples, potter put to pacif spirit of dead and aid into next life .started high-fire ceramic ware . Not allowed to see tombs. Tombs resemblre keyhole. Artificail hills on tombs, on top of hills sculptures of HANIWA/.
First HANIWA cylindrical to hold jars for offerings, then 5th cent made in shapes of ceromonial objects, house, boats. Them animals were added. 6th cent HANIWA became human shape.
not glazed, no showing if of technical virtuosity. Simple and bold. never symmetrical so mimic individualty.
Describe Shinto during Kofun period
Shinto is a religious belief system centered around the worship of kami (deities), became after buddhism in 6th cent,
Shinto became more systematized after Buddhism was introduced to Japan, with shrines, a hierarchy of deities, and regulated ceremonies.
MAIN HALL, INNER SHRINE, ISE
Mie Prefecture. Last rebuilt 1993. Photograph by Watanabe Yoshio (1907-2000), 1953.10th cent
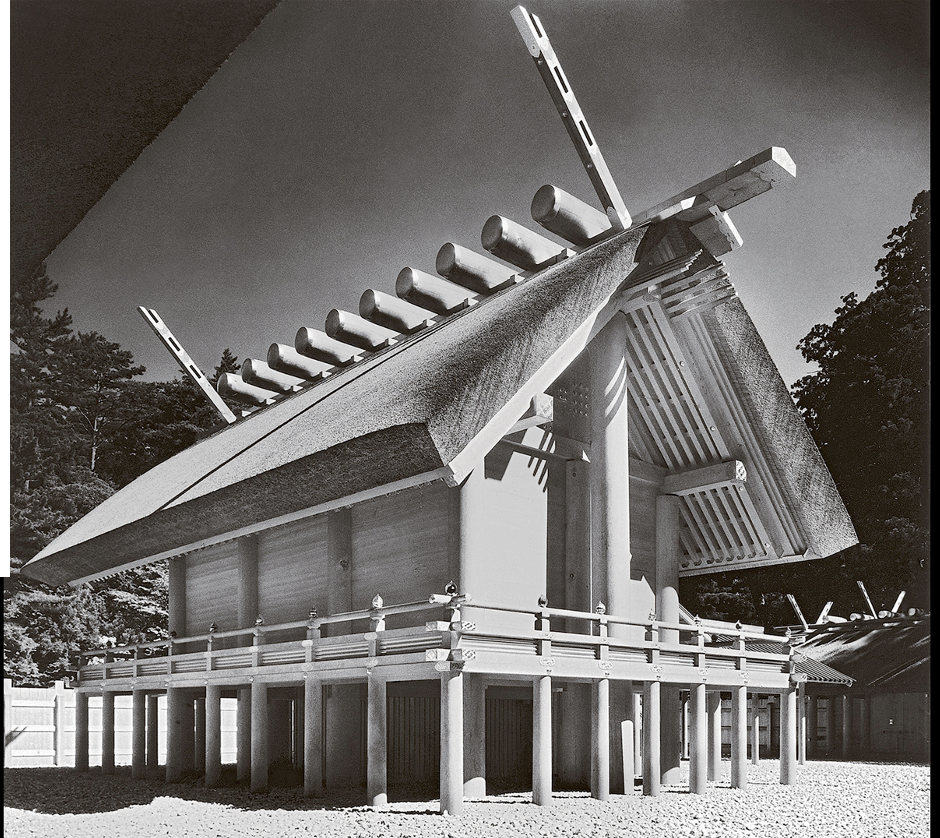

The Ise Shrine.
Shinto monument.
-worshiped is sun goddess Amaterasu-o-mi-kami, the legendary progenitor of Japan’ imperia family.
-japan’s earliest written historical texte recorded by imperial court in 8th cent claim that Ise Shrine dates to the 1st cent CE, unsure if true.
-Ritually rebuilt , two adjoining sites at 20 year interval with few breaks since 690, when imperial family was solidifying hegemony. Recent rebuilt in 2013.
After kami is moved from one shrine the old shrine is dissmantled, like japanese culture is both ancient and constantly renewed. Embodies Shinto faith(Ritual purification), respect for cycle of seasons where pure life emerges in spring time and death j winter and reborn following year.
-few members of imperial family and shinto priests allowed within enclosure that surrounds shrine. Dates back to 10th cent but wasn’t allowed phtos until 1953
typical of Shinto architecture L wooden piles that elevate buildings above ground; thatched roof held in place by horizontal logs; unpainted cypress wood, feeling of natural simplicity . building shape comparable to early raised granaries known from drawing of bronze artifact from Yayoi period. Use of unornamented natural material suggest an early origin for japanese taste and still today.
Describe Writing , language and culture of Japanse.

-chinese writing used in japan such as Buddhist sutras, philosophical and legal texts, chinese poetry, into 19th cent. Japan initially borrowed chines writing or called kanji.
difference in writing were unwidely therefore developed 2 syllabaries/kana from simplifies chinese.
syllabary=each symbol stand for syllabe
Katakan- angular symbols made to aid chines buddhist text and now foreign words.
Hiragana -graceful, cursive symbols, used by japanese for native poetry and prose, eventually only grammatical portions of written japanes elanguage in conjuction with chinese character that convey meaning- Hiragana “women’s hand” because of feminity, during Heing eriod used for large bodies of literature, by women or for women by men.
Poem in Heian period to teach new writing system, 4 line each, uses almost all syllable sounds of spoken japanese and almost all kana symbol. Memorized like our ABC’. Katakan, stanza, hiragana, kanji an hiragana.
written in columns top to bottom and right to left like hand-scrolls.
Describe Asuka and Nara Periods.
-single cent of Asuka period (552-645 ce) new everything came to Japan from Korea and China at fast pace.
Most significant was buddhism, -centralized government and writing system, each adopted to suit japanese. Reached Japan in Mahayana form with buddhas and bodhisattvas. Adopted as stae religion. Diff gods then Shinto and new religion. Worshit in temples close to imperial cities. Chines influence buildings loooked nothing like previous Japanese buildings, they house anthropomorphic and buddhsi icons when Kami was not represented in human form.
-buddhism attracted followers because it offered a cosmology with meditation and enlightenment. Protective powers of deities justifies elites an their own power and called upon deities to nurture and protect populace.
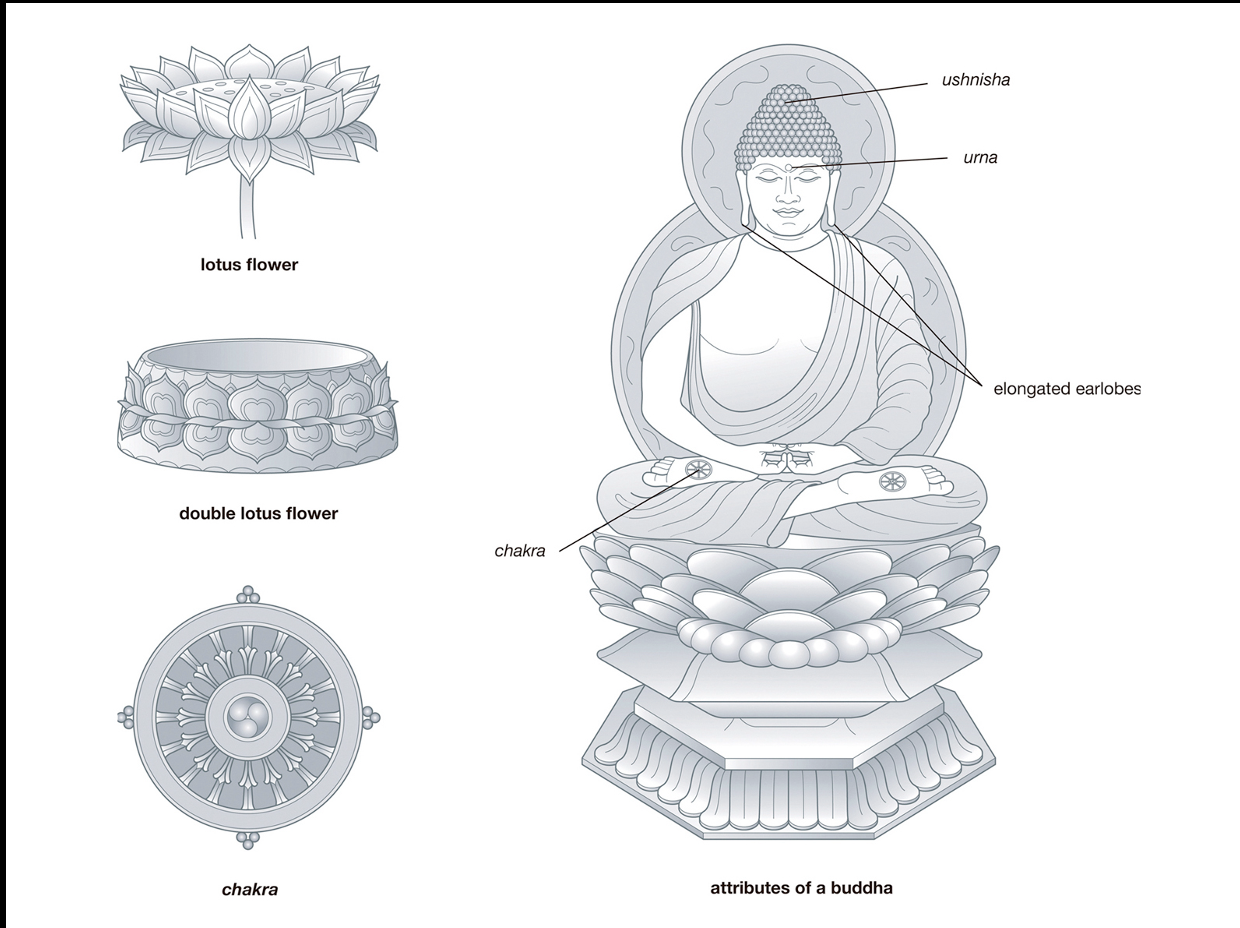
important Buddhist symbols:
The lotus flower symbolizes spiritual purity, t
Lotus throne-nirvana
Chakra symbolize both the various states of existence (the Wheel of Life) and the Buddhist doctrine (the Wheel of the Law).meaning depends on spokes
Marks of a buddha are distinguished by 32 physical attributes(lakashanas) including ushnisha, urna, elongated earlobes, and chakras on the soles of the feet.
Mandalas represent order and meaning within the spiritual universe.A diagram of cosmic realms.
Describe the Horyuji
-on Japan’s central plaines . Founded in 697 by prince Shotoku, who ruled Japan and was the most influential proponent of buddhism.
Oldest wooden temple in the world.
-Main compound: rectangular courtyard with corridors. Within compound 2 buildings; A Kondo(main hall) and 5-story pagoda. Asymmetrical layout. Kondo balances the Pagoda. Kondo filled with buddhist images for worship while the pagoda serves as. Reliquary and is not entered. Monasteries outside of main compound with outer gate, lecture hall, dormitories for monks, belfry, repository.
-Has portable shrine with lacquer paintings, the Tamamushi shrine names after the beetle who wings paint the glitter for painting, and architestural form replicate building older than Horyuji.
HUNGRY TIGRESS JATAKA
Panel of the Tamamushi Shrine, Horyuji. Asuka period, c. 650 CE.
Lacquer on wood, height of shrine

-few 2 dimensional painting from asuka period, Former lives of buddha,
one depict future buddha sacrificing his life to feed body to a starving tigress and he cubs. Tigers to weak to eat him so he jumps off a cliff to open his flesh.
Full narrative. Buddha appears 3 times anf 3 sequential stages, harmonized by cliffs and bamboos. First hangs short on tree, then dives down into rocks then animals eat his body. The figure and styl represent an international buddha style that was transmitted by china and Korea. This take helped popularize Buddhism in Japan.
Tori Busshi BUDDHA SHAKA AND ATTENDANT BODHISATTVAS IN THE HORYUJI KONDO
Asuka period
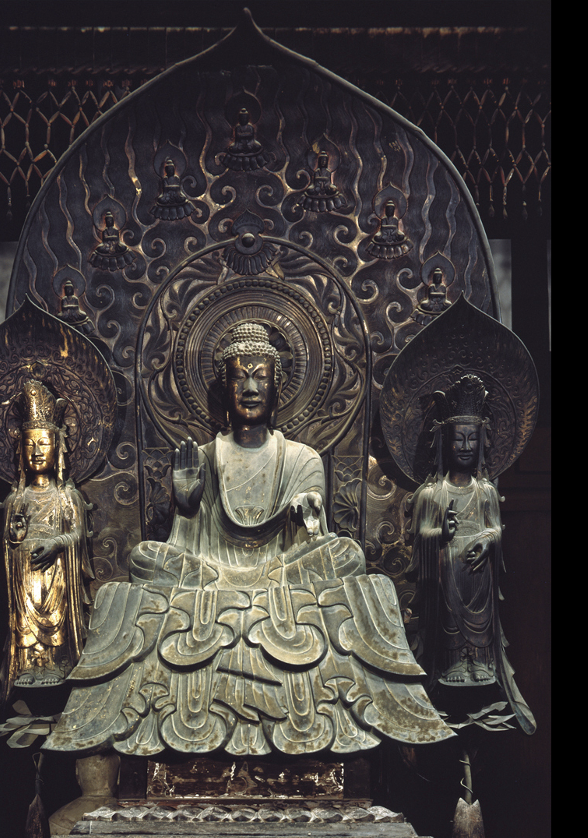

HORYUJI—INTERNATINAL STYE OF EARLY BUDDHISM, Sculptor Tori Busshi. Shaka comes from Shakyamuni the historical buddha. Tori Busshi mean buddha maker, descendant or Korea ppl and immigrated to Japan as part of influx of buddhist and artisans from Japan.
reflect strong of art from Wei dynasty, frontal pose, face and hands, linear drapery show that artisans were well aware of earlier continental models and fine bronze casting show advances skills.
Describe Nara period

The Nara period is named for Japan’s first permanent imperial capital.
Divisions of the imperial bureaucracy grew as did the city’s population.
Grand Buddhist temples and Shinto shrines were built in Nara, including the Shinto Kasuga Shrine and Todaiji. Giant gilt-bronze image of buddha inspired by chinese rock cut out. Ceremony infront of hall presided by illistartion of Indian monk and sutra chanting over 10000 japanese buddhist monks and sacred performances of musicians and dancer. Numerous ritual objects used in ceremony come form Exotic Asian and Near Eastern Lands. Nara held eatserns terminus of the central silk road.
oBJECT PRESERVED AT tODAIJI
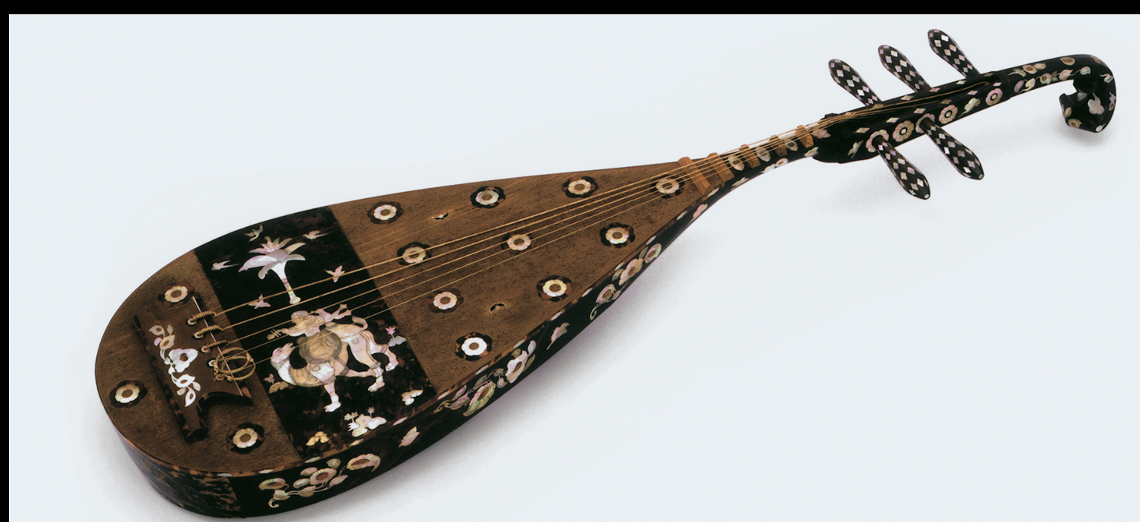
The Shosoin came to be year 756 when Shosu died and his wife donated object used for the great Buddhas’ consercration ceremony. Objects from Shomu’s collection came form many places demonstrating the vast trade network happening.
Wife(empress Komyo) donated in 756 is a crafted 5-stringed lute(biwa) made of lacquered red sandle wood and chest nut and inlaid with mother of pearl and amber and tortoise shell. Asian musician portrayed sitting on camel and playing lute.
-Only example of 5- stringed lute, made in India and transmitted to China the Japan via silk road ,
From china to Japan for consercration ceremony or could be made in japanese/chinise mad eit in Japan using imported material. Craftmenship like today.
Buddhist faith permeated all aspect of Nara court society, influence by Shomu. 49 shomu left throne to be monk and his daughter took throne but other didn’t like how empowering buddhism was so move to Kyoto where few buddhist temples allowed.
Heian Period
Generally peaceful conditions and a sever with the Chinese government lent an air of self-reliance to Japan in this period.
During this time, an efficient method of writing was developed, spurring literary masterpieces such as The Tale of Genji.
2 stream of Buddhism emerged , esoteric sects and Buddha Amida
Describe Esoteric Buddhist art and an example of a mandala
(heian period)
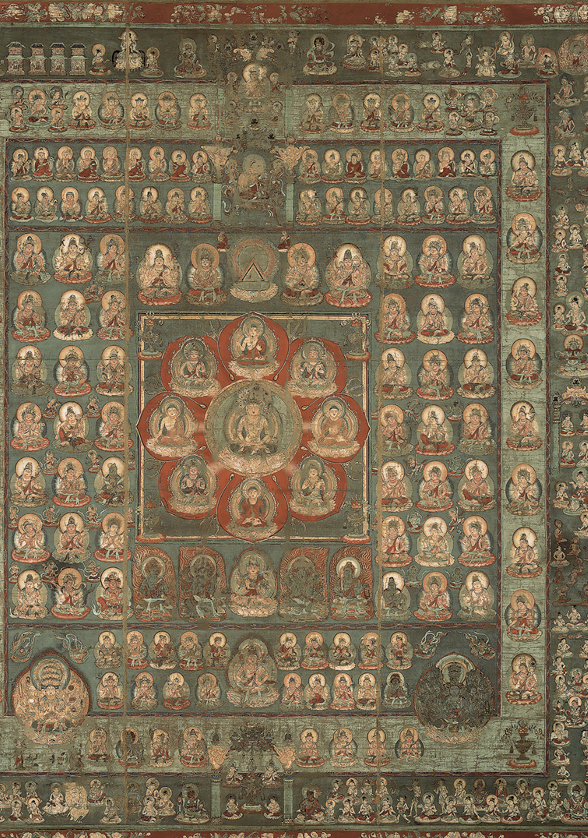
WOMB WORLD MANDALA
Heian period, late 9th century CE.
Hanging scroll with colors on silk

-older Nara temples lost temples.
-two sects od Esoteric: Shingon and tendai. Influence by polytheistic religions. No longer historical buddha but now the universal buddha Dainichi(great sun) who was believed to preside over the universe. Surrounded by deities.
-hierarchical, deities have complex relationship with each-other. Learning their relationship was assisted by mandalas(cosmic diagrams of the universe that portray deities in schematic order)
-dainichi in center surrounded by buddhas, other dieties branch out with diff symbols and diff level of potential worshippers. Mandal represents ultimate reality beyond the visible world.
Many Esoteric buddhist images have sense of spiritual force and potency especially in warthful deities. Religion for educated aristocracy not for masses. Religions network paralleled in social division of the Heain court.
describe Pure land Buddhist art during Heian period
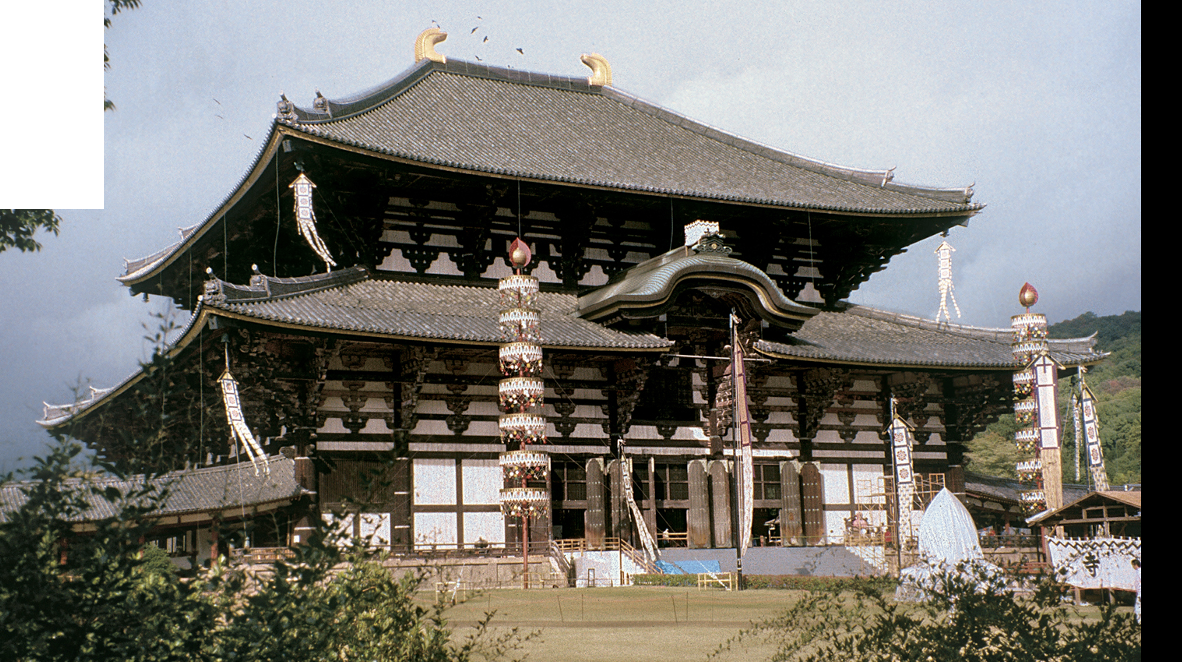
GREAT BUDDHA HALL (DAIBUTSUDEN), TODAIJI, NARA
Original structure completed in 752 CE; twice destroyed; rebuilt in 1707; extensively restored 1906-1913, 1973-1980.

Jocho AMIDA BUDDHA
Phoenix Hall, Byodoin. Heian period, c. 1053 CE.
Gold leaf and lacquer on wood,
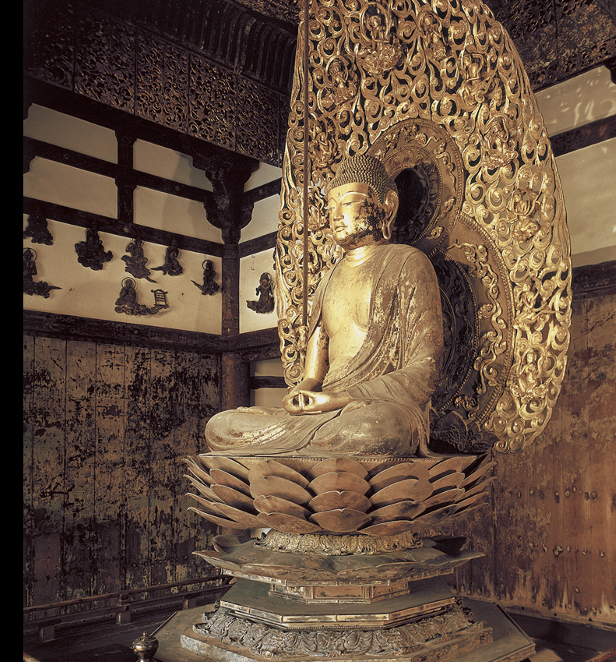

-rising turbulence marked start of 11th cent, ppl though Mappo was coming a buddhist concept spiritual degeneration. Turned to salvation after death toward the buddhist realm of western paradise of the pure land, with music and flowers, Amida and bodhisattvas are protecters to submit to them. Spread to japan from china from korea. More immediate way of salvation than esoteric in rituals. If you chanted”namu amida butsu” faithful would reborn in the paradise.
-most beautiful pureland temple is the Byodoin,
originally a secualr villa to represent palatial residenc of Amida. Build for member of Fujiwara family, leading couselor to emperor, after his death temple was converted into a memorial temple to honour spirit. Called phoenix hall because of comparable shape and two phoenix on roof. thin columns give airness as if it could rise up. Hall infron to A shaped pond for Amida.
Byodoin’s central image is Amida carved by Jocho. Looking into pond Amida shimmers in reflection. Around are Bodhisattvas and angels, some playing music. Simulate appearenceof paradise that await believer after death. well preserved.
carved in joined black method(carved from several blocks and joint together)
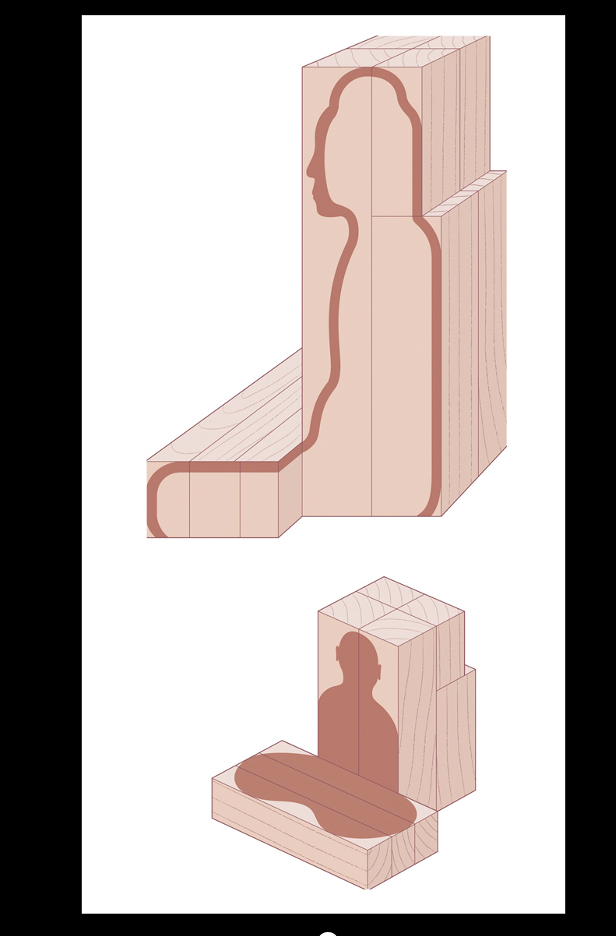
Describe the Joined-block wood sculpture technique
used on the Amida statue by Jocho
-wood is a tempermental material because it absorbes and swells/shrinks. Cut from sap tree and dried for years. Inside dries slowly. Wood with thinner cross section and few irregularities is less susceptible to crack because it dires evenly
methodes reduces cracking in heavy wooden stautues
4 blocks vertically 2 infront and 2 in back for main body, then added block horizontal for lap or knees. assemble and hollowed out.

Describe Heian painting and Calligraphy

Chinese in aristocratic society gave ride to new Japanese developments. Women became vital for the expression of human love, and contributed great to art. Men and women wrote prose and poetry using Kana script, use kana on small scale paintings.
begining of 11th cent lady Murasaki turned the lifestyle of Heian aristocrats into fiction fro amusement and it became the Tale of Genji, some consider to be the 1st novel.Pinnacle of literary achievement. About love and affair of prince Genji and his companions is the Heian conception of fleeting pleasure and ultimate sadness echo of buddhist view.
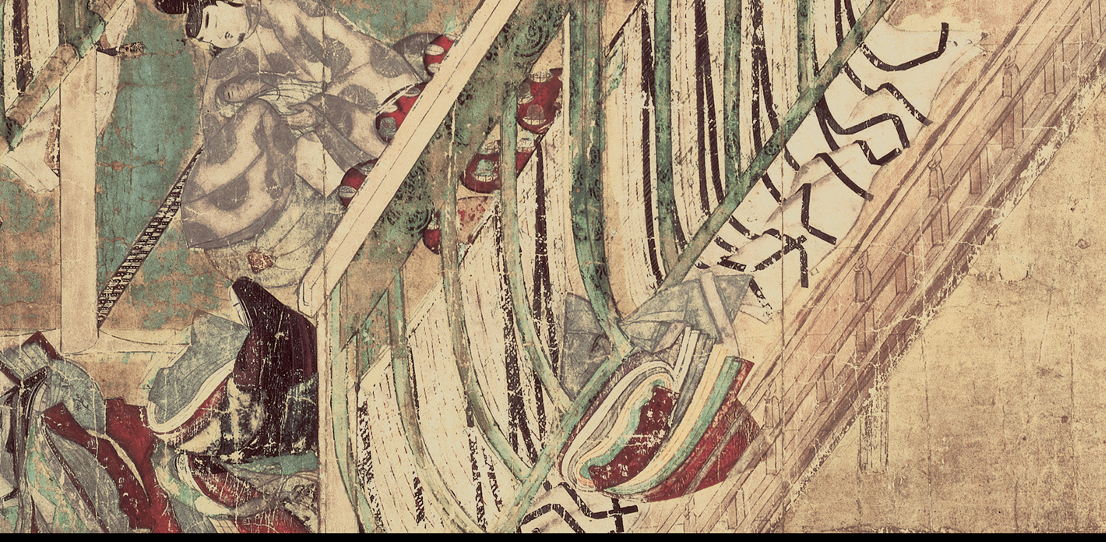
new secular painting style called yamato-e, old word for Japan. From tale of Genji. Alternate between words and pictures. Hand-scroll. Usually court figures in architectural setting and natural elements to help set the mood. Emotion not shown through face but composition of scenes. Bout genji visiting women that he couldn’t marry, they are very small in images but the outside scenes depict their feelings.
nature and human a common theme in japanese art.54 capter , 100 pcitures. In kana writing
BOOK PAGE FROM THE ISHIYAMA-GIRE (DISPERSED VOLUMES, ONCE OWNED BY THE ISHIYAMA TEMPLE, OF THE ANTHOLOGY OF THE THIRTY-SIX IMMORTAL POETS)
Heian period, early 12th century CE.
Ink with gold and silver on decorated and collaged paper
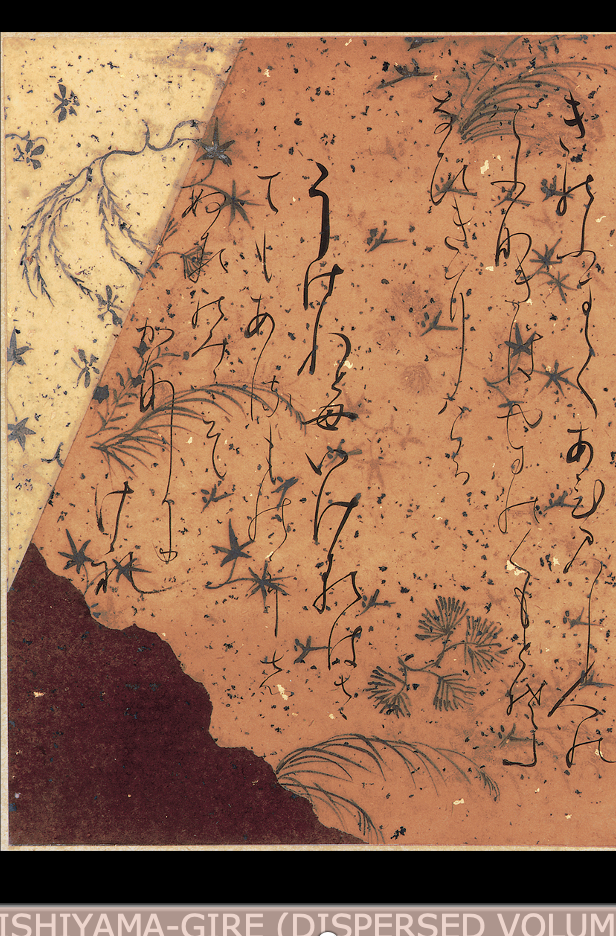
in waka writing , most significant form of poetry was Waka, in heian period finest waka writing from writers and collected for albums known as 36 immortalpoets, an antgology, originally had 39 volums then 2 were taken out, seprate volums know as Ishiyamagire
simple flowing letters, float elegently
shows 2 verses by 8th cent courtier Ki nno Tsurayuki esxpressing melancholy emotions , calligraphy mathed elegance of poetry.
Attributed to Toba Sojo SCENE FROM FROLICKING ANIMALS
Heian period, 12th century CE.
Handscroll with ink on paper
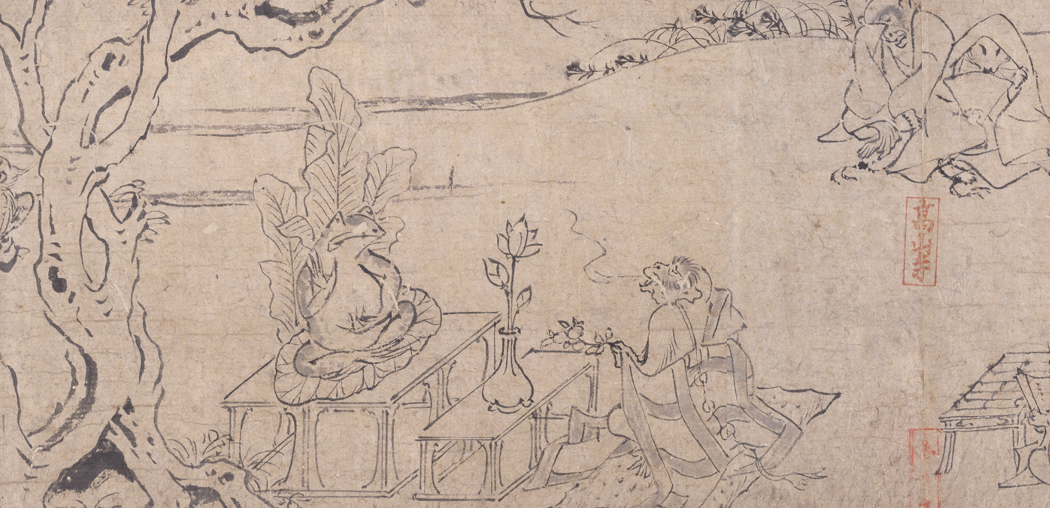

another style of native painting Bold and confident and engaged in stories outside teh court. Human behavious through animal antics. Attributes to Tobba Sojo , abbot of a buddhist monestary.
monkey in monk rob offers peach to. afrog that is posed like. A buddha and enthroned on a lotus flower. Around monkey other animals for monastic and secular worshiper. No accompying text so unsure what it means but is still humorous.
describe the Kamakura Period
Courtiers became so engrossed in their own refinement that they neglected their responsibilities.
The Taira and Minamoto clans took opposing sides to the imperial conflict.
Eventually Yoritomo Minamoto prevailed, establishing a military capital at Kamakura but residing in Kyoto.
The shogunate endured until 1868.
SECTION OF NIGHT ATTACK ON THE SANJO PALACE
Kamakura period, late 13th century CE.
Handscroll with ink and colors on paper,

battle of Minamoto and Taira became historical and muse for art.Painting a century after event, conveyed from eye witness and verbal Description. Style is brisk and lively like the frolicking animals and colour and birds eye view similar to genji scroll. full of action violence and energy no trace of poetic refinemnet, samjrai is dominating secular arts. Minamoto destroyed Taira clan in 1185. Used swords an arrows and wore armour.
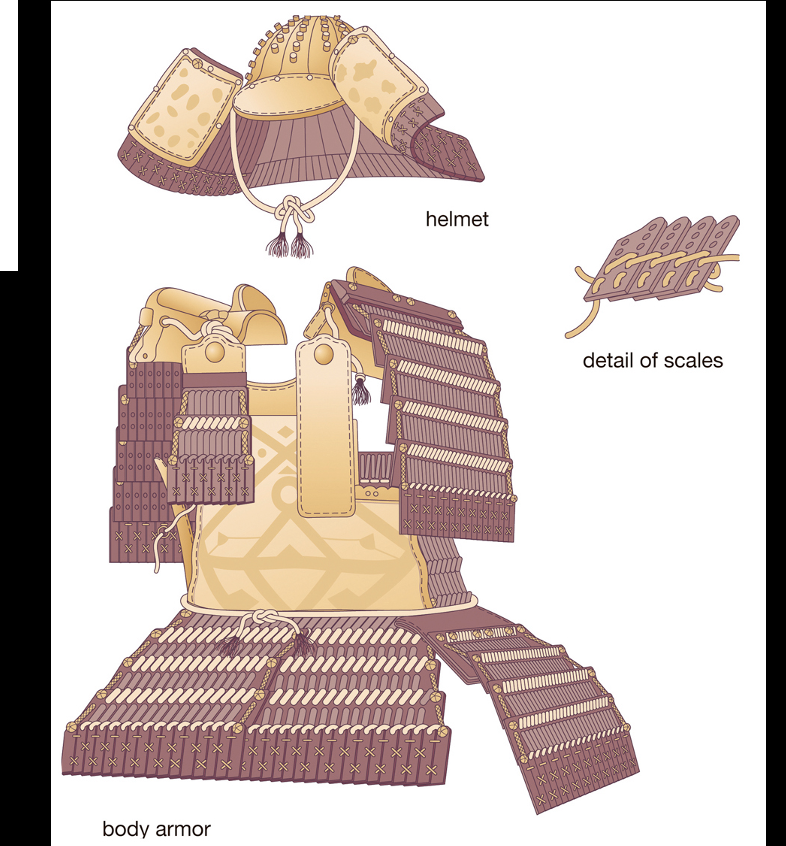
fought by archers on horse bac. fORGED A BLADE WHICH LAMINATED A HARD CUTTING EDGE WITHING LESS BRITTLE SUPPORT LLAYERS.
EARLIEST SAMURAI ARMOR WAS YOROI, MADE FOMR IRON AND LACQURED LEATHER SCALES, HELMET FROM IRON PLATES RIVETED TOGETHER.Made from wood, leather, jade(ceremonial/burial)
describe pure land buddhist art during the Kamakura period
pure land became so popular it still remains the most popular.
Courtiers became so engrossed in their own refinement that they neglected their responsibilities.
The Taira and Minamoto clans took opposing sides to the imperial conflict.
Eventually Yoritomo Minamoto prevailed, establishing a military capital at Kamakura but residing in Kyoto.
The shogunate endured until 1868.
popular painting called raigo (welcoming approach), depicts Amida buddha with bodhisattvas coming down to welcome soul of dying believer. Differ from mandal paintings, found on walls and doors of Byodin. Made in numbers. One ex is the decent of Amida and the 25 bodhisattvas. , gold and silver for deities. Cut gold technique known as “kirikane” is achievement of early Japan, seen glissering under lamp, taken form chinese and refines.
sensitve rendering of landscape, shinto pictures portraying landcscape first appeared during Kamakura period as pure land was growing. Kamakura art combined buddhism and shinto.
Zen buddhist art during Kamakura period
from china to Japan and already highly developped known as cHAN. MONKS WHO WENT TO CHINA TO STUDY buddhsim CAME BACK WITH ZEN. secluded in monestaries.
chan(zen) monks modeled form buddhist sage Druma who taught chan patriach.
earliest surviving zen paintings
Zen monk a top a rick meditating, incscription by Yishan Yining and early chan master. Stayed in Japan taught chan.
DARUMA
Artist unknown, inscription by Chinese Chan (Zen) master Yishan Yining (1247-1317). Kamakura period, early 14th century CE.
Hanging scroll with ink and colors on silk,

PORTRAIT OF THE CHINESE CHAN MASTER LANXI DAOLONG.Inscription by Lanxi Daolong. Kamakura period, dated 1271 CE.Hanging scroll with colors on silk,

Kenchoji founded in 1253 by another emi grant chan master, Lanxi Daolonh, first chan to travel to Japan, greeted by the 5th Minamoto shotgun which helped him built Kenchoji in which th first time authetin chines chan buddhism was taught, one of the most important zen monasteries in Japan.
PortraiT of founder. Known as cHINSO. GIVEN BY MASTER WHEN DISCIPLES FINSIHED TRAINING AND MOVE TO OTHER TEMPLES. Like a diploma. Dedicated inscription to samurai official
zen comparable to origin tecahing of buddha, enlightenment through meditation with no help. Zen was last form of buddhism to reach Japan.