Hematology Test 2 practice
1/76
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
77 Terms
The laboratory base definition of anemia is a reduced concentration of _____ compared to a reference value.
A. hemoglobin
B. leukocytes
C. packed erythrocytes
D. either A or C
D. either A or C
Functional anemia…
A. results in hypoxia
B. is a decrease in ability of RBCs to carry oxygen
C. has inadequate stored body iron
D. both A and B
D. both A and B
The steady-state total erythrocytes mass is…
A. a balance between new and old erythrocytes
B. the reference value for leukocytes in peripheral blood
C. homeostasis of erythrocytes
D. both A and C
D. both A and C
If the survival time of an erythrocyte is decreased,
bone marrow must increase erythropoiesis
The clinical signs and symptoms of anemia can result from…
diminished delivery of oxygen to the tissues
Anemia can be categorized into…
A. hemolytic types
B. blood loss types
C. impaired production types
D. all of the above
D. all of the above
Which of the following is a significant laboratory finding in anemia?
Decreased hemoglobin
The adult reference range for MCV is…
80 to 96 fL
The adult reference range for MCH is…
27.5 to 33.2 pg
The adult reference range for MCHC is…
33% to 36% (32 to 36 g/dL)
Disorders of the GI system or heavy menstruation can cause…
chronic blood loss
Traumatic conditions can cause…
acute blood loss
Results in an iron deficiency and a hypochromic/microcytic erythrocytes morphology on a peripheral blood smear.
chronic blood loss
Anemia caused by chronic blood loss is characterized by…
hypochromic, microcytic erythrocytes
The sudden appearance of aplastic anemia or pure red cell aplasia is often caused by…
an immune process
Aplastic anemia can occur years before a diagnosis of ____ is made.
A. paroxysmal nocturnal hemoglobinuria
B. myelodysplasia
C. acute myeloid leukemia
D. all of the above
D. all of the above
If a patient with aplastic anemia is referred to as exhibiting pancytopenia, which cell lines are affected?
A. Erythrocytes
B. Leukocytes
C. Thrombocytes
D. All of the above
D. All of the above
A characteristic of Fanconi’s anemia is…
the best-described congenital form of aplastic anemia
A characteristic of familial aplastic anemia is…
a subset of Fanconi’s anemia
Most operational iron is human being is found in…
heme portion of hemoglobin and myoglobin
The etiology of Iron Deficiency Anemia (IDA) is…
A. nutritional deficiency
B. faulty iron deficiency
C. excessive loss of iron
D. all of the above
D. all of the above
Iron deficiency is still common in…
A. toddlers
B. adolescent girls
C. women of childbearing age
D. all of the above
D. all of the above
Decreased iron intake can be result of…
red meat-deficient diet
Faulty iron absorption can result from…
celiac disease
Pathological iron loss can be caused by…
colon cancer
Physiological iron loss can be caused by…
heavy menstruation
Increased iron utilization can be the result of…
adolescent growth spurt
The cytochemical stain that can demonstrate iron, hemosiderin, and ferritin is…
Prussian Blue
Transferrin represents a…
A. storage form of iron
B. beta globulin
B. beta globulin
In stage 3 IDA, the erythrocytic indices are typically…
MCV decreased, MCH decreased, and MCHC decreased
The peripheral blood smear demonstrates ___ red blood cells in Iron Deficiency Anemia (IDA).
Microcytic, Hypotonic
The most common cause of nonmegaloblastic macrocytic anemia is…
alcoholism
Megaloblastic anemias can be caused by…
A. tapeworm infestation
B. gastric resection
C. nutritional deficiency
D. all of the above
D. all of the above
Megaloblastic anemia related to folic acid deficiency is associated with…
A. abnormal absorption
B. increased utilization
C. nutritional deficiency
D. all of the above
D. all of the above
In megaloblastic anemia, the typical erythrocytic indices are…
MCV increased, MCH increased, and MCHC normal
In a case of classic pernicious anemia, the patient has…
A. leukopenia
B. hyperseqmented neutrophils
C. ovalo-macrocytes
D. all of the above
D. all of the above
The reticulocyte count in a patient with untreated pernicious anemia is characteristically…
<1.0%
In untreated pernicious anemia, peripheral blood smears display…
pancytopenia
In pernicious anemia, serum B12 is…
decreased
In pernicious anemia, folate is…
normal
In pernicious anemia, serum iron is…
increased
Hemolytic disruption of the erythrocyte involves…
an alteration in the erythrocyte membrane
Intravascular hemolysis is…
destruction of RBCs within the circulatory blood
Extravascular hemolysis is…
destruction of RBCs outside the circulatory blood
Which of the following tests is not useful in determining increased erythrocytes destruction?
Total leukocyte count
G6PD deficiency is a disorder with a/n…
erythrocytic enzyme defect
Hereditary spherocytosis is a disorder with a/n…
structural membrane defect
Pyruvate kinase (PK) deficiency is a disorder with an…
erythrocytic enzyme defect
Hereditary spherocytosis is…
the most common prevalent hereditary hemolytic anemia among people of Northern European descent
Hereditary elliptocytosis is…
an overabundance of oval-shaped red cells
Heinz Bodies are associated with the congenital hemolytic anemia…
G6PD deficiency
What is the most common glycoytic enzyme deficiency associated with the aerobic pathway of erythrocyte metabolism?
Glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase (G6PD)
What is the most common glycolytic enzyme deficiency associated with the anaerobic pathway of erythrocyte metabolism?
Pyruvate kinase (PK)
What laboratory assay would specifically indicate a deficiency of G6PD enzyme?
Heinz bodies on peripheral blood smears
What enzyme deficiency causes methemoglobinemia?
NADH-methemoglobin reductase
Paroxysmal nocturnal hemoglobinuria episodes are usually associated with…
Sleep
The defect in PNH probably is an (an) associated defect of the red cell membrane…
structural protein
Which of the following is a significant laboratory finding in anemia?
Decreased hemoglobin
Disorders of the gastrointestinal system or heavy menstruation can case…
chronic blood loss
If a patient with aplastic anemia is referred to as exhibiting pancytopenia, which cell lines are affected?
A. erythrocytes
B. leukocytes
C. Thrombocytes
D. all of these
E. none of these
D. all of these
Fanconi’s anemia is:
A rare congenital form of red cell aplasia
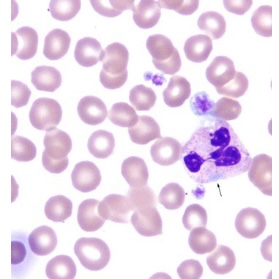
Inclusions in the cytoplasm of neutrophils as shown in this picture are known as:
Dohle bodies
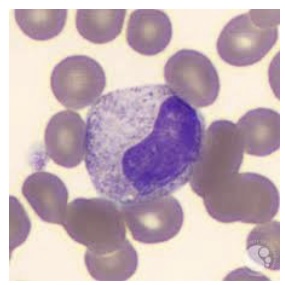
The neutrophil stage shown in this picture is the most common myeloid cell found in normal adult bone marrow:
Metamyelocyte
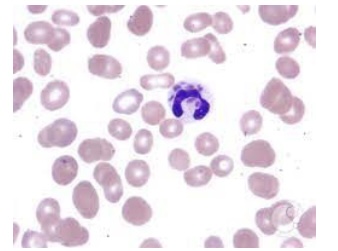
Which of the following diseases is most closely associated with cytoplasmic granule fusion as seen in this picture:
Chediak-Higashi Syndrome
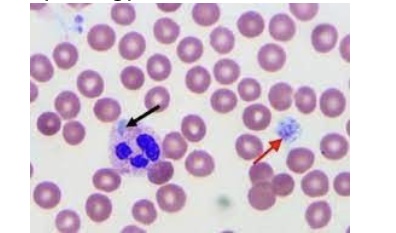
Which of the following diseases is an autosomal dominant disorder characterized by these pale blue inclusions and platelet morphology?
May-Hegglin Anomaly
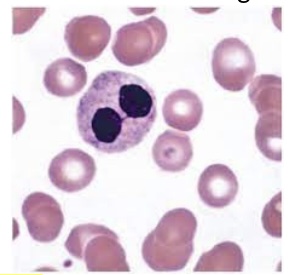
The disease most closely associated with the granulocytic morphology shown here is:
Pelger-Huet Anomaly
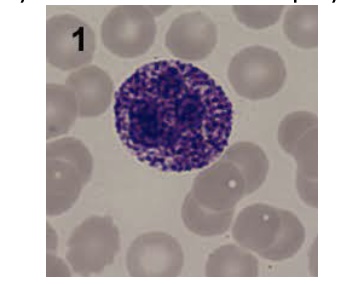
The disease most closely associated with mucopolysaccharidosis in the lysosomes as shown here is:
Alder-Reilly Anomaly
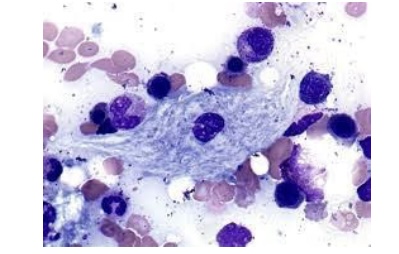
Of the following, the disease most closely associated with glucocerebrosidase deficiency and characterized by the cell type shown here is:
Gaucher Disease
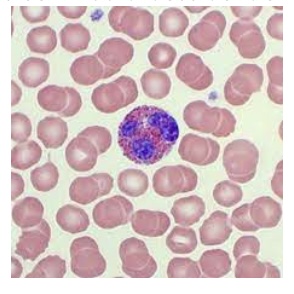
This cell would best be identified as:
eosinophil
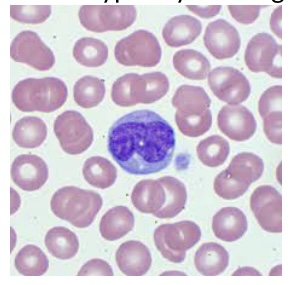
This cell is typically the largest mature peripheral blood cell:
Monocyte
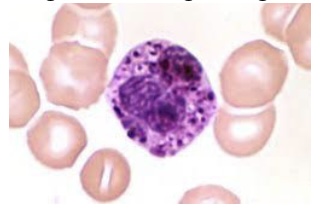
Which of the following is TRUE regarding these cells?
a. Their granules contain anti-histamine
b. They are identified as eosinophils
c. They fight parasitic infections
d. Their normal peripheral blood range is 0-1%
d. Their normal peripheral blood range is 0-1%
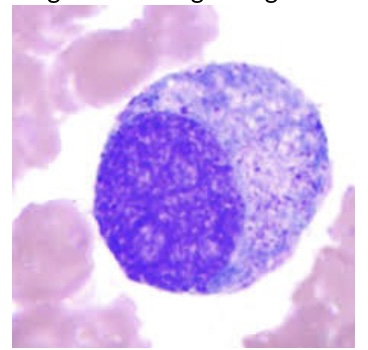
Which of the following is FALSE regarding this cell type:
a. Has azurophilic (primary) granules in the cytoplasm
b. Has secondary (specific) granules in the cytoplasm
c. Is the stage of neutrophil development after the blast stage - identified as promyelocyte
d. May be larger than the blast stage
b. Has secondary (specific) granules in the cytoplasm
What are the six stages of neutrophilic maturation?
Myeloblast, Promyelocyte, Myelocyte, Metamyleocyte, Band, Segmented neutrophil
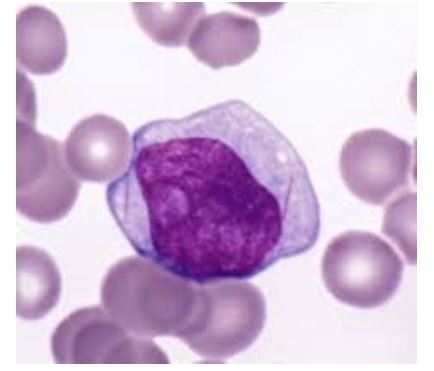
Which of the following is FALSE about this stage of myeloid development?
a. They may contain Auer rods in the cytoplasm
b. They typically have no nucleoli present in the nucleus
c. They have a delicate chromatin pattern
d. They are classified as myeloblasts
b. They typically have no nucleoli present in the nucleus
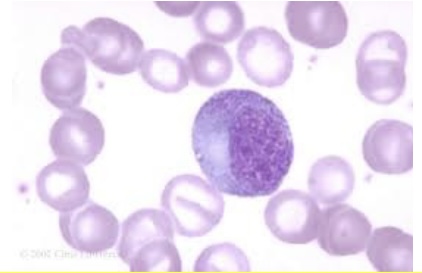
Which of the following is TRUE regarding this myelocytic development stage?
a. This is the stage in which the cell will be identified as a neutrophil, basophil, or eosinophil
b. This stage is not able to divide
c.This is the metamyelocyte stage
d. This stage has only primary granules
a. This is the stage in which the cell will be identified as a neutrophil, basophil, or eosinophil
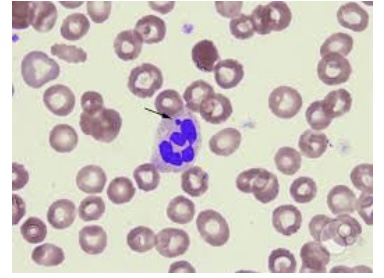
Which of the following is FALSE regarding the small projection indicated on this neutrophil?
a. It is a Barr body
b. It is a normal finding in patients with an inactive X chromosome
c. It is found only in disease states
d. It is typically seen in 2-3% of neutrophils when present
c. It is found only in disease states
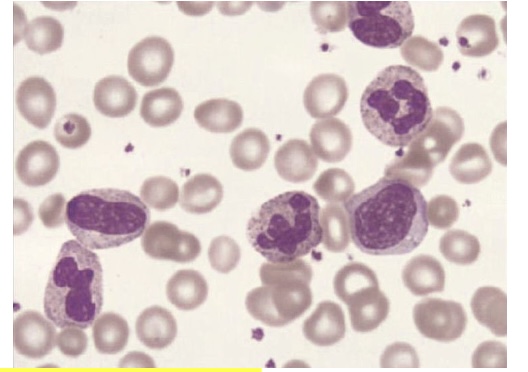
How would you describe this peripheral blood finding?
a. Neutrophilic leukemoid reaction
b. Normal blood picture
c. Found with viral infections
d. Typical in patients with allergies
a. Neutrophilic leukemoid reaction