Dental Terminology Ch. 9
1/135
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Radiography
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
136 Terms
X-rays
Radiant energy waves that are produced, charged and emitted from a common center in the dental radiation tube, charged electrons are tiny energy bundles or waves of photons with extremely short wavelengths that are used to penetrate matter and expose photographic film surfaces, discovered by Wilhelm Conrad Roentgen, and sometimes called Roentgen waves
X-ray tube
AKA Vacuum tube, produces X-rays
Cathode
(negative pole) Electrode in the vacuum tube that serves as the electron source
Filament
(fine thread) Tungsten coil in the cathode focusing cup thhat generates the electrons
Anode
(positive pole) The target for the electron barrage to convert thte electron force into photons
Focal spot
Target area where rays are projected to make the primary beam, or central beam; the smaller focal spot produces a better image
Collimator
(to align) A device used to regulate the size of the beam leaving the tube in parallel rays, helping to avoid stray radiation, also termed a diaphragm, it is usually shaped similar to a lead washer on the connecting end of the PID that also has lined walls to assist collimation
PID
Position indicating device
Aperture
(Opening or port) Opening in the lead collimator disk that regulates the size of the primary beam
Filter
Aluminum disks that are placed between the collimator attachment and the exit window of the tube to absorb weak radiation
Three types of filtration
Inherent, added, and total filtration
Inherent filtration
All filtration (tube wall, insulating oil, aluminum disks) devices that filter weak, longer wavelength X-rays
Added filtration system
Filtration placed outside the tube head to meet safety standards
Total filtration
The sum of the inherent and added filtration, expressed in millimeters of aluminum equivalent
Milliampere control
(mA) AKA milliampere; an increase in milliamperage increases the number of electrons available and darkens the radiograph
Kilovolt Power
(kVp) Controls the force that attracts the electrons to the anode; helps to determine the penetrating power and the quality/energy of the radiation rays
Exposure time
Duration of the interval during which current will passthrough the X-ray tube; this period may be stated as fractions of a second or impulses, (50 pulses to a second) the amount of exposure that a patient actually receives is measured in milliampere seconds
(mAs) (mA x exposure time = mAs)
Target film distance
(source-film distance, or focus-film distance) distance of the film surface from the source of radiation
Target-object distance
(source-object distance or focus-object distance) distance between the anode target and the object to be radiographed
Film speed
A (slowest) to F (fastest) speed; faster speed film requires less radiation exposure time for the patient
Different types of X-ray radiation
Are generated during radiography
Primary radiation
Central ray of radiation emitting from the tube head and PID. Primary radiation is the desired radiation and is used to expose radiographic film
Secondary radiation
Radiation given off from other matter that is exposed to the primary beam
Scattered radiation
Radiation deflected from its path during its passage through matter; may be deflected or diffused in all directions, becoming attenuated (weakened) or another form of secondary radiation
Stray radiation
Aka leakage, any radiation other than the useful beam produced from the tube head, a faulty or broken tube head may be the source of stray radiation
Remnant radiation
Radiation rays that reach the film target after passing through the subject part being radiographed, these rays form the latent image on the film emulsion
Sensitivity
Ability of X-rays to penetrate and possibly ionize, reproductive cells are more radiosensitive than the radioresistant body tissues (somatic) cells, younger cells are more sensitive than other, thicker cells
Cumulative effect
Long-term outcome of radiation, Repetition increases and intensifies the ionizing effect on cells for a buildup of damage, the latent period of exposure is the time interval between the exposure and the effect or detection
Mutation effect
Abnormal growth or development due to radiation causing a genetic change
2 types of X-radiation exposure that will damage the body cells are
Acute and chronic radiation exposure
Acute radiation exposure
Radiation occurring from a massive short-term ionizing dose, such as an accidental exposure or explosion of radiation material
Chronic radiation exposure
Accumulated radiation cell damage from continual or frequent small exposures absorbed over a period of time (thus the need for questioning the patient as to when the last X-ray was taken)
Roentgen (R)
The basic unit of exposure to radiation; the amount of X-radiation or gamma radiation needed to ionize 1 cc of air at standard pressure and temperature conditions
Rad (radiation absorbed does)
The basic unit of absorbed radiation does equal to 100 ergs per gram of tissue or 1 gad = cGy
Rem (roentgen equivalent measure
The unit of ionizing radiation needed to produce the same biological effect as 1 roentgen of radiation
rbe (relative biological effectiveness)
Unit of measurement used to determine amount of biological absorption effects on body tissues by different types of radiation energy
Coulomb
International electromagnetic measurement abbreviated as C; 1 C per kilogram (C/kg) is equal to 3880 roentgens
Maximum permissible dose (MPD)
Highest rate of exposure permissible for the occupationally exposed person, formula is (5 rem per year) - {age-18} X 5 rem per year + MPD
Erythema dose
Radiation overdose that produces temporary redness of the skin
ALARA
(as low as reasonably achievable) A policy of using the lowest amount of radiation exposure possible, measures to accomplish this include proper exposure and protection aids, use of fast films, good techniques in exposure and developing, questioning the patient regarding recent exposure, and the correct calculations or control settings
Dosimeter
(giving measure) operator’s radiation-monitoring device with ionizing chamber or a device to indicate exposure and measure accumulated doses of radiation, available in the form of a film badge, pen, ring, and so on
Lead apron/tyrocervical collar
Patient apparel with lead protection for genetic cells in the torso and the thyroid glands in the cervical area
Lead barriers, shields
Devices used by operators to block out scattered radiation
Phantom
Practice mannequin containing tooth and head structures to imitate the actual condition, a popular model is DXTTR, aka dexter
Periapical Film packet
Size 0 (pedodontic size), 1 (adult anterior), or 2 (adult anterior and posterior); used for the intraoral periapical view of the entire tooth or teeth in a given area along with adjacent tissues and oral structures, this film may also be placed in a device or loop to expose an intraoral bitewing view and may be ordered in a double film packet, if desired
Bitewing film packet
(aka interproximal radiograph, size 3): film used to record crown and interproximal views of both arches while in occlusion; used intraorally with attached bite tab, other film sizes may be adapted to accomplish this task
Film speeds
Film are rated A to F according to the amount of exposure needed, with A needing the most time, aka D-Ultra-speed, E-Ektavision, and F-Insight
Occlusal film packet
Size 4; film that may be used intraorally or extra orally to expose large areas, these film packets may contain more than 1 film and are marked and color-coded to identify the amount of film enclosed
Extraoral films
Radiographs exposed outside the oral cavity; larger in size and loaded in a film cassette or wrapped for protection from light rays
Cephalometric films
Aka headplates, these extraoral radiographs of the head are used in orthodontic, oral surgery, and sometimes in prosthodontic dentistry
Cephalostat
A device used to stabilize the patient’s head in a plane parallel to the film and tat right angles to the central ray of the X-ray beam, it is used for large radiographs of the head
Panoramic radiograph
A special radiograph capturing a view of the entire dentition with the surrounding structures on one film, the extraoral film is placed in the machine’s cassette and rotates around the patient at the same speed as the tube head rotation, providing a panoramic view, popular in orthodontics and oral surgery
What do panoramic and cephalographs have in common?
Completed using special mounted machines
Intensifying screen
A lining of calcium tungstate phosphors or rare earth within the cassette that gives off a bluish light (calcium tungstate) or green glow (rare earth) when exposed to radiation
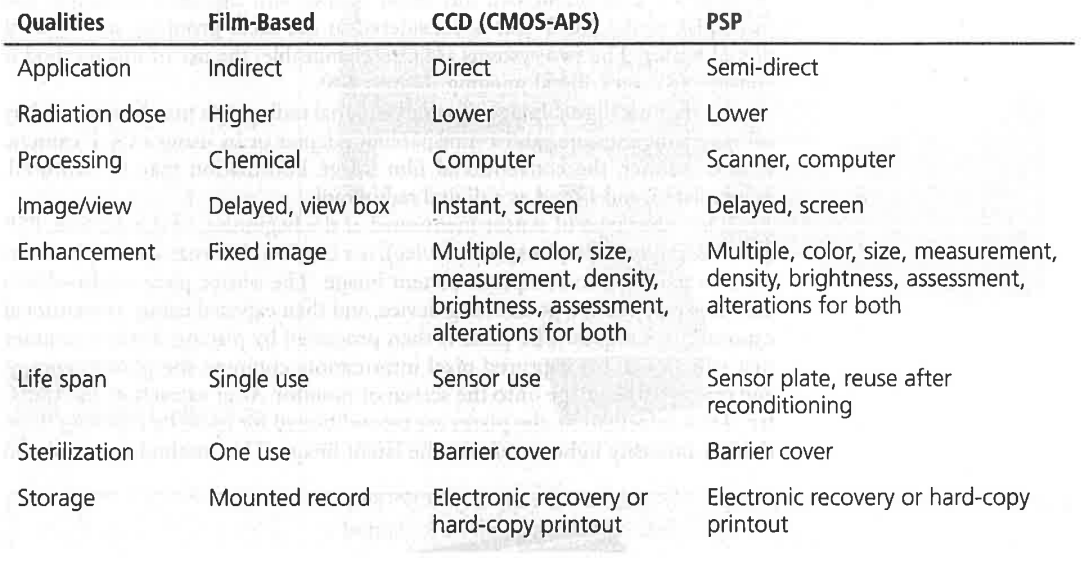
CCD
(charge coupled device) sensor that is a solid-state sensor that may or may not be wired to the computer workstation, the sensor and sensor wire are barrier wrapped and inserted into a positioning device for insertion and exposure in the mouth, the same placement and alignment technique used for conventional film exposure are applied
PSP
(photostimulable phosphor device) Is a cordless, indirect sensor plate that absorbs radiation to complete a latent image
Radiograph Image Receptor Comparison
Contrast radiography
Variations in shades from black to white, a radiograph exhibiting many variations in shades is considered to possess long-scale contrast, increased kilovoltage helps to produce this effect
Density/brightness radiography
amount of film blackening associated with the percentage of light transmitted through a film, an increase or decrease in density is accomplished by an increase or decrease in milliamperage and exposure time (mA/second)
Detail radiographysmoothness
Point-to-point delineation or view of tiny structures in a radiograph image, proper exposure, handling factors, and kVp selection provide good detail
Definition/smoothness
Outline sharpness and clarity of image exhibited on a radiograph, movement of the film, patient, or tube head is the most common cause of poor definition or fuzzy outline called Penumbra (nearly shadow) proper digital machine filtration of electronic noise can improve the sharpness and smoothing of the digital image
Radiolucent
(ray shine) describes a radiograph that appears dark, or the ability of a substance to permit passage of X-rays, thereby causing the radiographic film to darken
Radiopaque
(ray dark) The portion of the radiograph that appears light, or the ability of a substance to resist X-ray penetration, thereby causing a light area on the film
Two basic techniques used by conventional and digital methods for exposure of intraoral radiographs
Bisecting angle and paralleling
Bisecting angle
The central X-ray beam is directly perpendicular with an imaginary bisecting line of the angle formed by the plane of the film and long axis of the tooth, aka the short cone technique
Paralleling
The film packet is placed parallel to the long axis of the tooth and at a right angle to the central X-ray beam, aka the extension cone or tight-angle technique
Sagittal plane
AKA midsagittal plane; imaginary vertical line bisecting the face into a right and left half
Ala-tragus line
Imaginary line from the ala (wing) of the nose to the tragus, center of ear, this line is important for positioning the patient in the bisecting-angle technique
Frankfort Plane
Imaginary line from the tragus of the ear to the floor of the orbit that is used to align the maxillary arch parallel to the floor; used mostly for extraoral films, many machines that expose large extraoral films and digital images have a stabilizing chin rest or an aiming light to ensure this directional position.
Positive angulation
Angulation achieved by positioning the PID downward; also called plus angulation, maxillary exposures are incisors (+40 degrees), cuspids (+45 degrees), bicuspids/premolars (+30 degrees), and molars (+20 degrees)
Negative angulation
Angulation achieved by positioning the PID upward; aka minus angulation, mandibular exposures are incisors (-15 degrees), cuspids (-20 degrees), bicuspids/premolars (-10 degrees), and molars (-5 degrees)
Zero angulation
Angulation achieved by PID placement parallel to the floor
Horizontal angulation
Direction of the central X-ray beam in a horizontal plane, the central beam must be placed perpendicular to the film front and teeth alignment, the error observed with improper horizontal angulation is called overlapping or cone cutting
Vertical angulation
Direction of the central X-ray beam in an up or down position, improper vertical angulation results in foreshortening or elongation errors.
PID
Position indicated device, formerly called a cone; may be a long cone (12-16 in) or a short cone (8 in); may be a round or rectangular, open-ended tube
Film-holding instrument
Device used to place and retain the film or sensor in the oral cavity during exposure,
VIP
Versatile Intraoral Positioner, by UpRad
Rinn BAI
For the bisecting angle technique
XCP
Extension Cone Paralleling device
Rinn XCP-DS
for sensor use
Rinn XCP
For endodontic views
Colors for locator or aiming rings
blue, yellow, red, green
Blue for locator or aiming rings
anterior placement
Yellow locator or aiming rings
Posterior placement
Red locator or aiming rings
Bitewing placement
Green locator or aiming rings
Endodontic placement
Biteblock
A device inserted between the teeth to hold the film during exposure; made of foam, wood or plastic
Individual film holder
A grip device that will hold 1 film or 1 sensor for exposure in the mouth, mostly used in a small mouth or difficult areas, the loaded film holder is put into position and help by the patient’s bit or finger pressure
Bite loop/tab
Paper tab or a celluloid circle placed around periapical film, enabling the film to be used in a bitewing position, this combination is used in place of a commercially manufactured interproximal film, some bite loops are constructed to assist with stabilizing and holding the digital sensors in the film-holding device
Film-safe container
A lead-lined container used to hold exposed films until processing; protects the film from exposure to scattered or secondary rays during exposure of films
Full mouth survey (FMS or FMX)
Multiple exposures of the oral cavity showing crown and root area in a series of radiographic views, when arranged in proper sequence, these films or images give a survey or view of the condition of the entire mouth
Bitewing survey (BWS or BWX)
Two or four film exposures of the posterior view to observe the crowns of maxillary and mandibular posterior teeth, anterior bitewing exposure is also possible
Edentulous survey
Radiographic survey of a patient without teeth
Radiograph processing
A procedure for bringing out the latent image on a film and making the exposure permanent, involves developing, rinsing, fixing, washing, and drying
Developing in film processing
Chemical process using the chemical elon to bring out contrast and another chemical, hydroquinone, to show contrast in films, developing brings out the latent image on the film’s silver halines that were affected or darkened by radiation
Accelerator in film processing
Solution used to swell the film emulsion during the processing
Activator in film processing
Solution used to aid other chemicals in the processing activity
Replenisher solution in film processing
Super-concentrated developing solution that is added to the developing tank to restore fluid levels
Rinsing in film processing
Water bath used to remove chemical liquids from films during solution exchanges
Fixing in film processing
Chemical process that stops the developer action and “fixes” the image, making it permanently visible