Unit 5A.6: EARS Assessment | Eyes, Ears, Nose & Sinuses, Mouth & Pharynx, Neck
1/62
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
63 Terms
Size, shape, and position of the auricle, tragus, and lobule
Lesions, discolorations, and discharge of the auricle, tragus, and lobule
External auditory canal
Color and consistency of the ear canal walls and inspect character of nodules
Whisper test
Watch tick test
Weber’s test
Rinne test
8 Steps of the Ears Assessment
Size, shape, and position of the auricle, tragus, and lobule
First Step of the Ears Assessment
Ears are equal in size bilaterally (4-10 cm)
Auricle aligns with corner of each eye and within a 10-degree angle of the vertical position
Earlobes either free, attached, or soldered
Normal Finding for 1. Size, shape, and position of the auricle, tragus, and lobule
Soldered
Identify the earlobe shape.

Attached
Identify the earlobe shape.
Free
Identify the earlobe shape.
Malaligned or low-set ears (may indicate chromosomal defects, like down syndrome)
Abnormal Finding for 1. Size, shape, and position of the auricle, tragus, and lobule
Low Set Ears
May indicate down syndrome
Lower pinna than lateral canthus

Lesions, discolorations, and discharge of the auricle, tragus, and lobule
Second Step for Ear Assessment
Skin is smooth with no lesions, lumps, or nodules
Color is consistent with facial color
Darwin’s tubercle
No discharge
Normal findings for 2. Lesions, discolorations, and discharge of the auricle, tragus, and lobule
Darwin’s Tubercle
Normal findings for 2. Lesions, discolorations, and discharge of the auricle, tragus, and lobule
Clinically insignificant projection that may be seen on the auricle
Enlarged Preauricular & Postauricular Lymph Nodes
Tophi
Postauricular Cysts
Ulcerated, crusted nodules
Otitis Externa
Frostbite
Abnormal Findings for 2. Lesions, discolorations, and discharge of the auricle, tragus, and lobule
Enlarged Preauricular & Postauricular Lymph Nodes
Abnormal Findings for 2. Lesions, discolorations, and discharge of the auricle, tragus, and lobule
Indicate infection
Tophi
Abnormal Findings for 2. Lesions, discolorations, and discharge of the auricle, tragus, and lobule
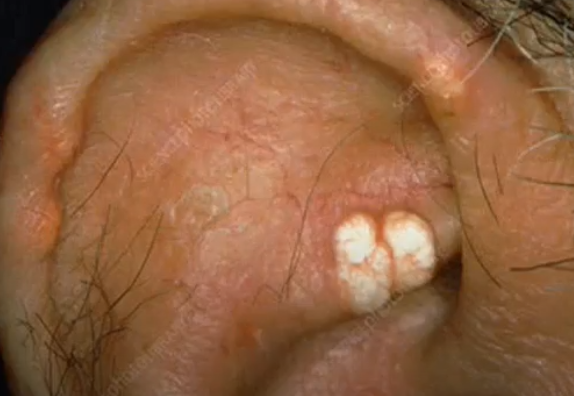
Nontender, hard, cream-colored nodules on the helix or antihelix, containing uric acid crystals
Indicate gout
Deposits of monosodium urate in crystal form
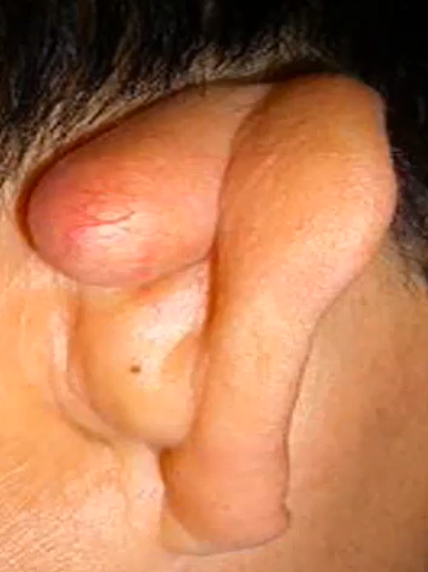
Postauricular Cysts
Abnormal Findings for 2. Lesions, discolorations, and discharge of the auricle, tragus, and lobule
Rare, unilateral asymptomatic, extracranial swellings that are associated with a delay in seeking medical intervention, due to blocked sebaceous gland behind the ear
Blocked sebaceous glands
Malignant Lesions
Mass or lump of abnormal cells
Some ear tumors are cancerous
Ulcerated, crusted nodules
Abnormal Findings for 2. Lesions, discolorations, and discharge of the auricle, tragus, and lobule
Bleed
Skin cancer
Most often seen on helix due to skin exposure
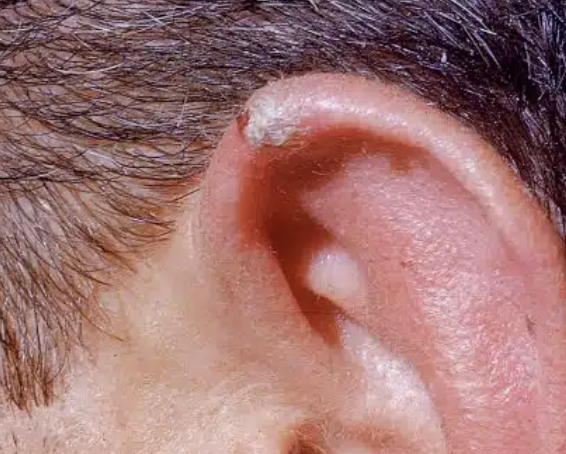
Otitis Externa
Abnormal Findings for 2. Lesions, discolorations, and discharge of the auricle, tragus, and lobule
“Swimmer’s Ear”
Redness, pain, swelling, scaling, or itching, conductive hearing loss due to swelling
Usually caused by pseudomonas bacteria
Frostbite
Abnormal Findings for 2. Lesions, discolorations, and discharge of the auricle, tragus, and lobule
Pale blue ear color
External auditory canal
Third Step of Ears Assessment
Pull out, up, and back the patient’s auricle
How to assess 3. External auditory canal?
Small amount of odorless cerumen (earwax)
Cerumen may be yellow, orange, red, brown, gray or black. Consistency soft, moist, dry, flaky, or even hard
Normal Finding for 3. External auditory canal
Foul-smellling, sticky, yellow discharge
Bloody, purulent discharge
Blood or watery drainage
Impacted cerumen blocking external ear canal
Foreign Bodies
Abnormal Finding for 3. External auditory canal
Foul-smelling, sticky, yellow discharge
Abnormal Finding for 3. External auditory canal
Caused by Otitis Externa or Impacted Foreign Body
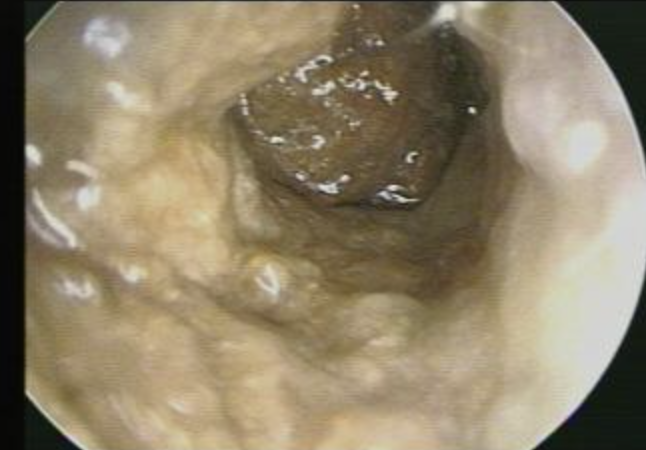
Bloody, purulent discharge
Abnormal Finding for 3. External auditory canal
Otitis Media with Ruptured Tympanic Membrane
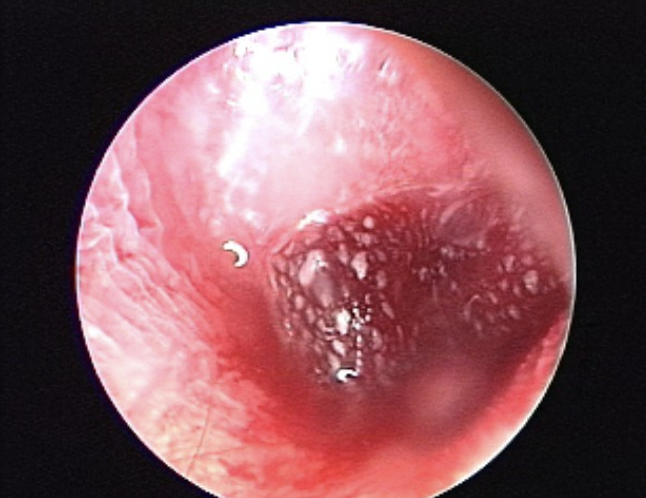
Blood or watery drainage (CSF)
Abnormal Finding for 3. External auditory canal
Skull trauma
Impacted cerumen blocking view of external ear canal
Abnormal Finding for 3. External auditory canal
Conductive hearing loss
Foreign Body Occlusion
Abnormal Finding for 3. External auditory canal
Presence of bugs, plants, food, et for prompt removal due to possible swelling and infection
Button-type batteries need urgent medical attention as leaking chemicals can burn and damage the ear canal
Cerumen Impaction
Accumulation of wax in the ear canal which can affect the flow of sound to the tympanic membrane
Excessive cerumen can cause problems with hearing and balance
Color and consistency of the ear canal walls and inspect character of nodules
Fourth Step of Ear Assessment
Canal walls pink and smooth, without nodules
Normal findings for 4. Color and consistency of the ear canal walls and inspect character of nodules
Otitis Externa
Nonmalignant Nodular Swellings
Polyps
Abnormal findings for 4. Color and consistency of the ear canal walls and inspect character of nodules
Otitis Externa
Abnormal findings for 4. Color and consistency of the ear canal walls and inspect character of nodules
Reddened, swollen canals
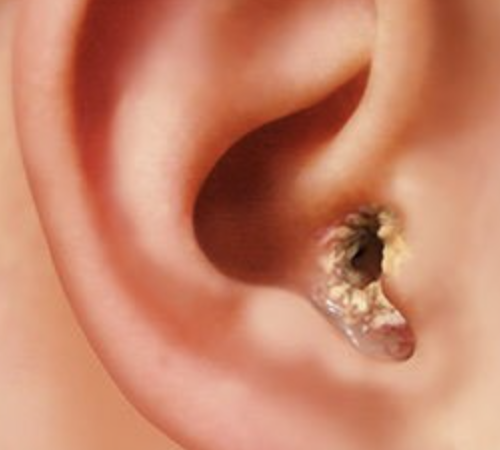
Exostoses
Abnormal findings for 4. Color and consistency of the ear canal walls and inspect character of nodules
Benign, bony growths covered by skin
Often seen in those who have been repeatedly exposed to cold water (i.e. swimmers)
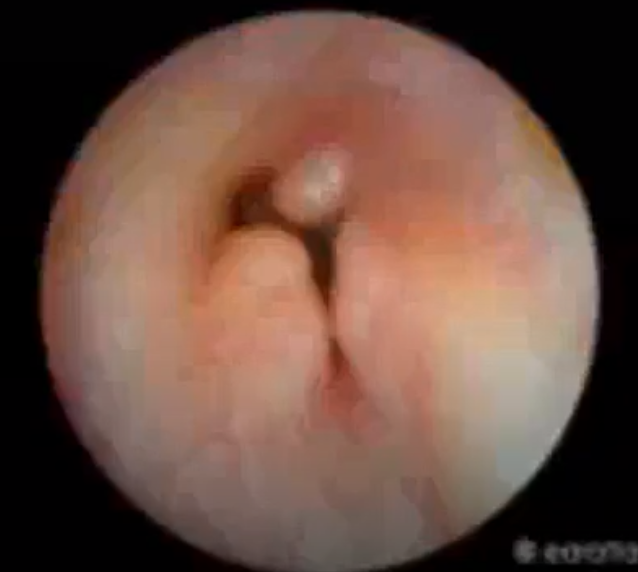
Polyps
Abnormal findings for 4. Color and consistency of the ear canal walls and inspect character of nodules
May block the view of the eardrum
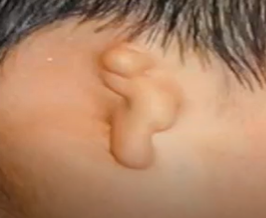
Microtia
Congenital deformity wherein the pinna is either small, abnormally shaped, or absent
Can occur on just one side or on both
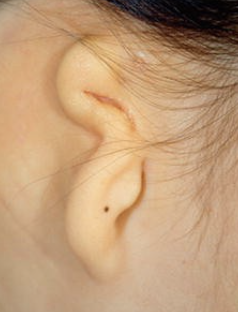
Aural Atresia
Malformation of the external ear canal
Usually on just one side and can be a complete or partial closure.
Extent of the closure directly affects that person’s conductive hearing loss.
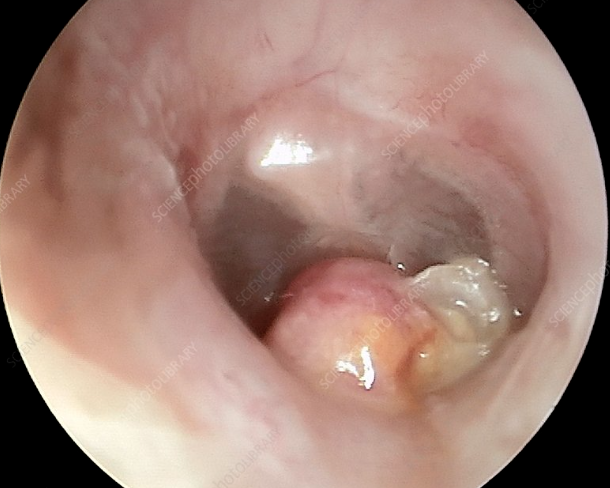
Acute Otitis Media
Serous Otitis Media
Chronic Otitis Media
Abnormalities of the Tympanic Membrane
Acute Otitis Media
Abnormality of the Tympanic Membrane
Bacteria or viral infection of the middle ear, usually accompanying an upper respiratory infection.
Serous Otitis Media
Abnormality of the Tympanic Membrane
___ ___ with effusion
Fluid in the ear, middle ear effusion (MEE), or secretory otitis media
Fluid resides in the middle ear
Chronic Otitis Media
Abnormality of the Tympanic Membrane
Describes a variety of signs, symptoms, physical findings that result from the long-term damage to the middle ear by infection and inflammation
Includes:
Severe retraction or perforation of the eardrum (a
hole in the eardrum)
Scarring or erosion of the small, sound conducting bones of the middle ear
Chronic or recurring drainage from the ear
Inflammation causing erosion of the bony cover or the facial nerve, balance canals, or cochlea (hearing organ)
Erosion of the bony borders of the middle ear or mastoid, resulting infection spreading the meninges (the coverings of the brain) or brain
Presence of cholesteatoma
Persistence of fluid behind an intact eardrum
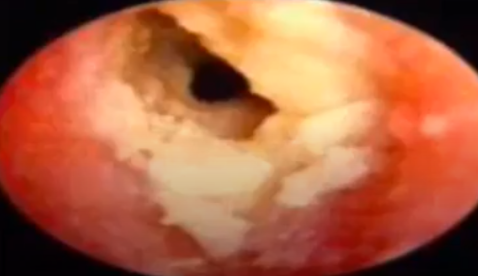
Tympanic Membrane Perforation
When there is a tear in the tympanic membrane leading to a connection between the external auditory canal and the middle ear
Whisper Test
Fifth Step of Ear Assessment
Ask client to rub tragus of opposite ear then occlude it.
Stand 2 feet behind the client
Whisper a two-syllable word
Ask client to repeat.
Needs to repeat 3-6 words to pass the test
How does 5. Whisper Test work?
Able to correctly repeat at least 3-6 two syllable words at two feet distance whispered
Normal Finding for 5. Whisper Test
Unable to repeat two-syllable word after two tries indicates hearing loss
Abnormal Finding for 5. Whisper Test
Watch Tick Test
Sixth Step of the Ear Assessment
Hold ticking watch approximately 5 in away from one of the client’s ears.
Ask client to cover opposite ear.
Slowly move watch closer after every inch not hear
How does the 6. Watch Tick Test work?
Reports hearing watch tick within 5 inches from the ear
Normal Finding for 6. Watch Tick Test
Conductive Hearing Loss
Sensorineural Hearing Loss
Abnormal Findings for 6. Watch Tick Test
Conductive Hearing Loss
Abnormal Findings for 6. Watch Tick Test
Sound is heard better in one ear than the other, or there is a significant reduction in hearing ability
May indicate conditions affecting the outer or middle ear, like earwax impaction, middle ear infections, or otosclerosis
Sensorineural Hearing Loss
Abnormal Findings for 6. Watch Tick Test
Client is unable to hear the ticking sound at all or hears it less clearly in one ear
May indicate damage to the inner ear or auditory nerve commonly seen in presbycusis
Weber’s Test
Seventh Step for Ear Assessment
Conduction of sound waves through bone to help distinguish between conductive hearing and sensorineural hearing
What does 7. Weber’s Test help evaluate?
Strike tuning fork and place it at the center of the client’s head
Ask client if they hear the sound better or same in the ears
How to conduct 7. Weber’s Test?
Vibrations heard equally well in both ears; no lateralization of sound to either ear
Normal Findings for 7. Weber’s Test
Conductive Hearing Loss
Sensorineural Hearing Loss
Abnormal Findings for 7. Weber’s Test
Conductive Hearing Loss
Abnormal Findings for 7. Weber’s Test
Lateralization of sound to the poor ear, “hearing” the sounds in the poor ear
Good ear is distracted by background noise and conducted air, which the poor ear has trouble hearing
Sensorineural Hearing Loss
Abnormal Findings for 7. Weber’s Test
Lateralization of sound to the good ear
Limited perception of the sound due to nerve damage in the bad ear, making sound seem louder in the unaffected ear
Rinne Test
Eighth Step of Ears Assessment
Air and Bone conduction sounds
What does 8. Rinne Test compare?
Air conduction sound is normally heard longer than bone conduction sound (AC > BC).
Normal Finding for 8. Rinne Test
Sensorineural Hearing Loss
Abnormal finding for 8. Rinne Test
Air conduction sound is heard longer than bone conduction sound (AC>BC) if anything is heard at all
Occurs with damage to the inner ear or to the nerve pathays between the inner ear and brain
Most common type of permanent hearing loss