Cell & Immune Based Assays
1/35
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
36 Terms
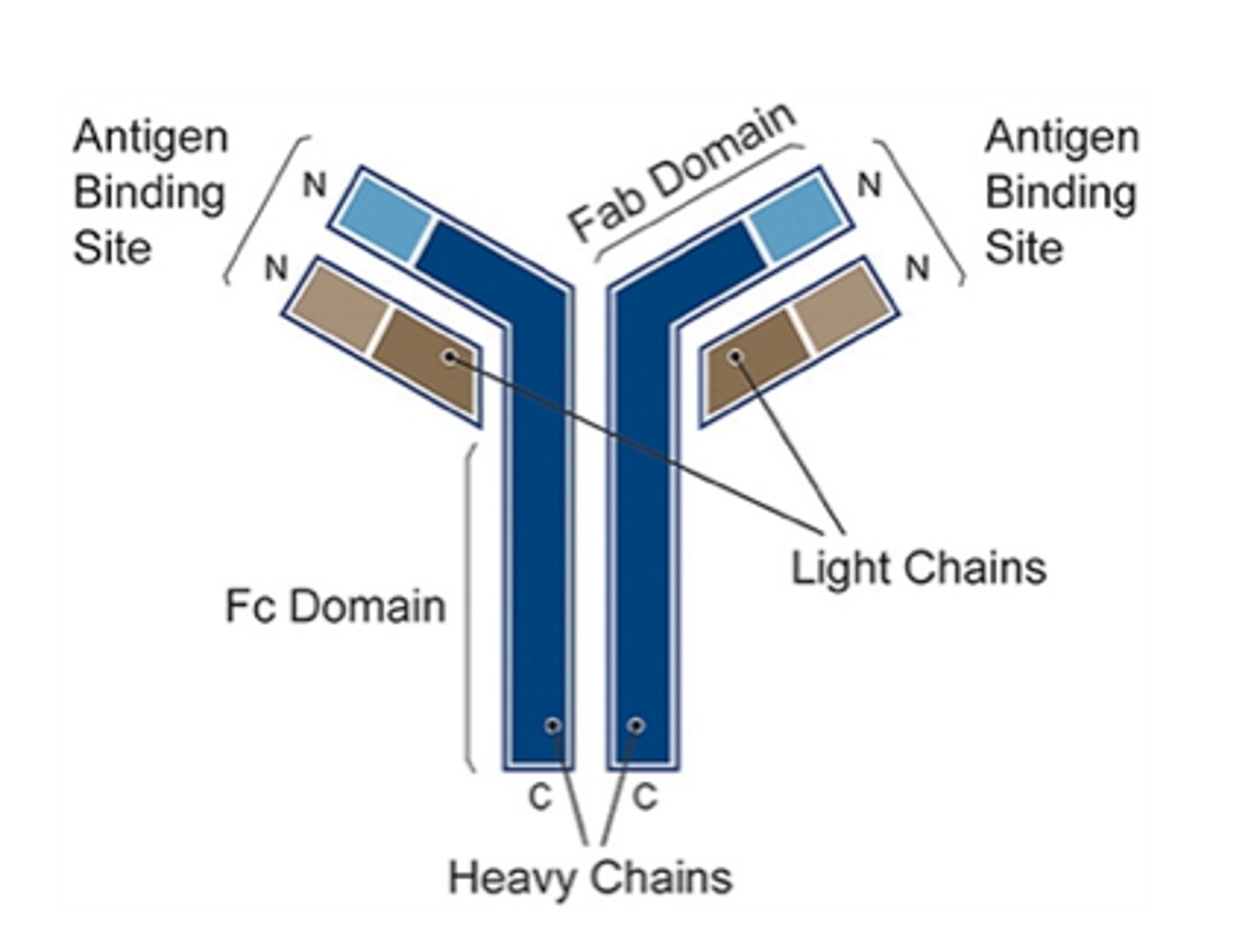
Fc region of antibody
constant region that binds other cells of the immune system
- determines the isotype
- limited variability
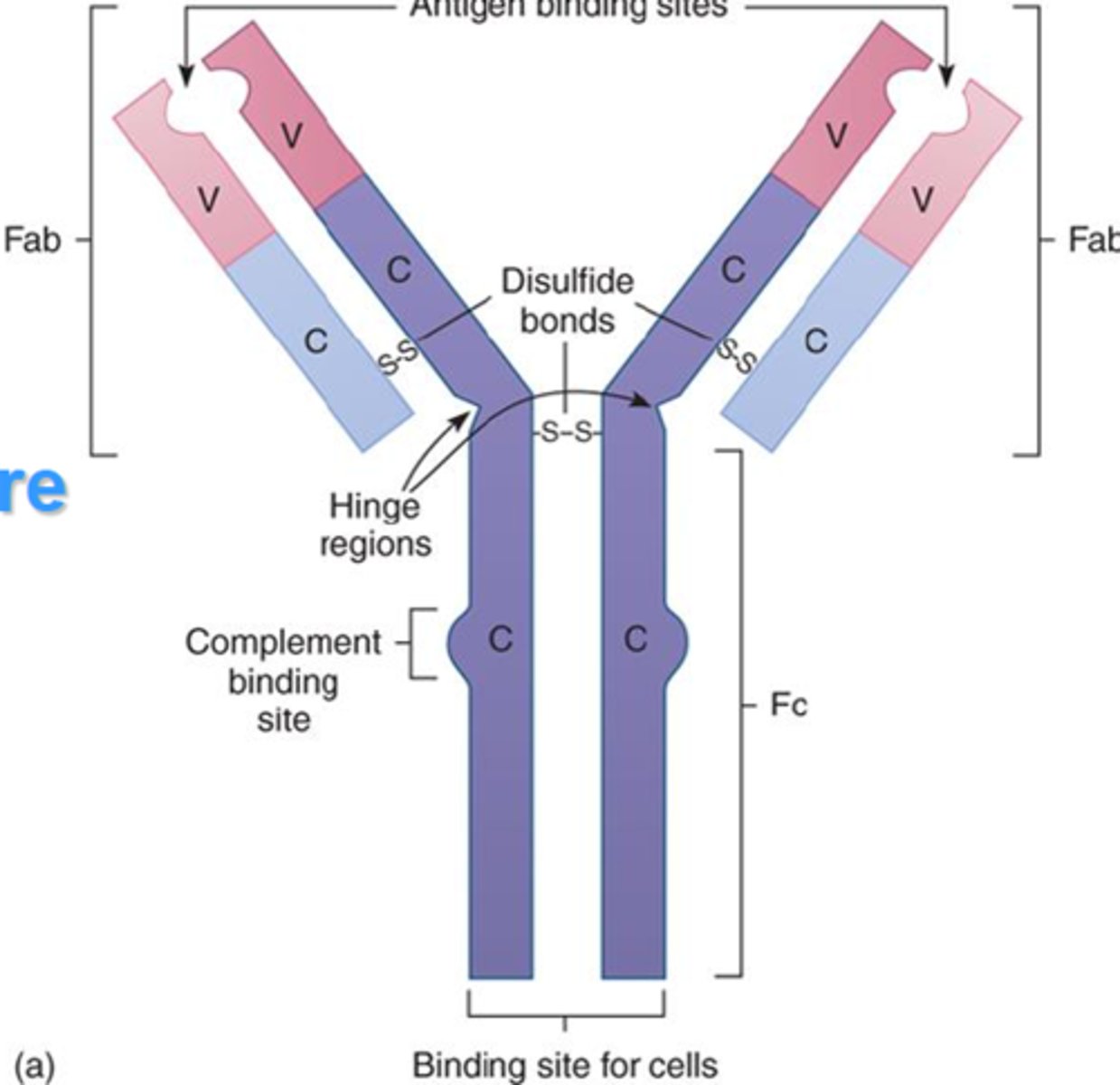
Fab region
determines the specificity of antigen binding
antibody
A protein that acts against a specific antigen
antigen
a toxin or other foreign substance that induces an immune response in the body, especially the production of antibodies.
fluorochrome
momentary excitation and emission of wavelengths (color) are functions of fluorochrome identity
different fluorochromes are excited by different wavelengths, and thus emit different wavelengths
direct immunofluorescence
- fluorochrome conjugated to a primary antibody, antibody directly attaches to a cell-specific surface molecule
- applications: fluorescence microscopy, flow cytometry
--> cons: need much more fluorochrome primary antibodies
indirect immunofluorescence
- primary antibody: specific for surface molecule
- fluorochrome-conjugated secondary antibody: specific for Fc portion of primary antibody
- applications: fluorescence microscopy, flow cytometry
--> cons: potential for more background noise, takes longer
--> pros: more economical
why use flow cytometry?
- before flow, microscope was major tool to examine cells, but it has limitations
- counts of specific cell populations and ratios are major factors in the diagnosis of disease
--> greater # cells = more accurate estimate of the size of target population
- flow cyto allows for the rapid quantitative analysis of characteristics of large numbers of cells
the absence of proof
absence of evidence is not evidence of absence
limitations of microscopy
- labor intensive and time-consuming
- practical limitations of # of cells analyzed
- in some cases qualitative, semi-quantitative at best
- accuracy is highly operator dependent
flow cytometer components
- fluidics system - sample delivery (cells are analyzed in suspension)
- optical system - measurement of cell characteristics
- electronics - signal detection, data processing, automation
- computer interface - control of cytometer, data collection, display, and storage
how do cells flow through a flow cytometer?
via bernoulli effect
-> move from high pressure to lower pressure
- cells are forced into a single file stream
interrogation point
exact point where the laser intercepts the cells, one at a time
why use lasers in flow cytometry?
Laser: Light Amplification by Stimulated Emission of Radiation
lasers are:
- spatially coherent: beam is in phase, emitted as a narrow, low divergence beam
- monochromatic: single wavelength
side scatter
right angle scatter
- cell complexity: nucleus size, nucleus morphology, organelle content, granularity
Forward Scatter (FSC)
indicator of cell size
photo-cathode
converts photon energy into electrons
photomultiplier tube
An apparatus that converts a photon of visible light into an electrical signal
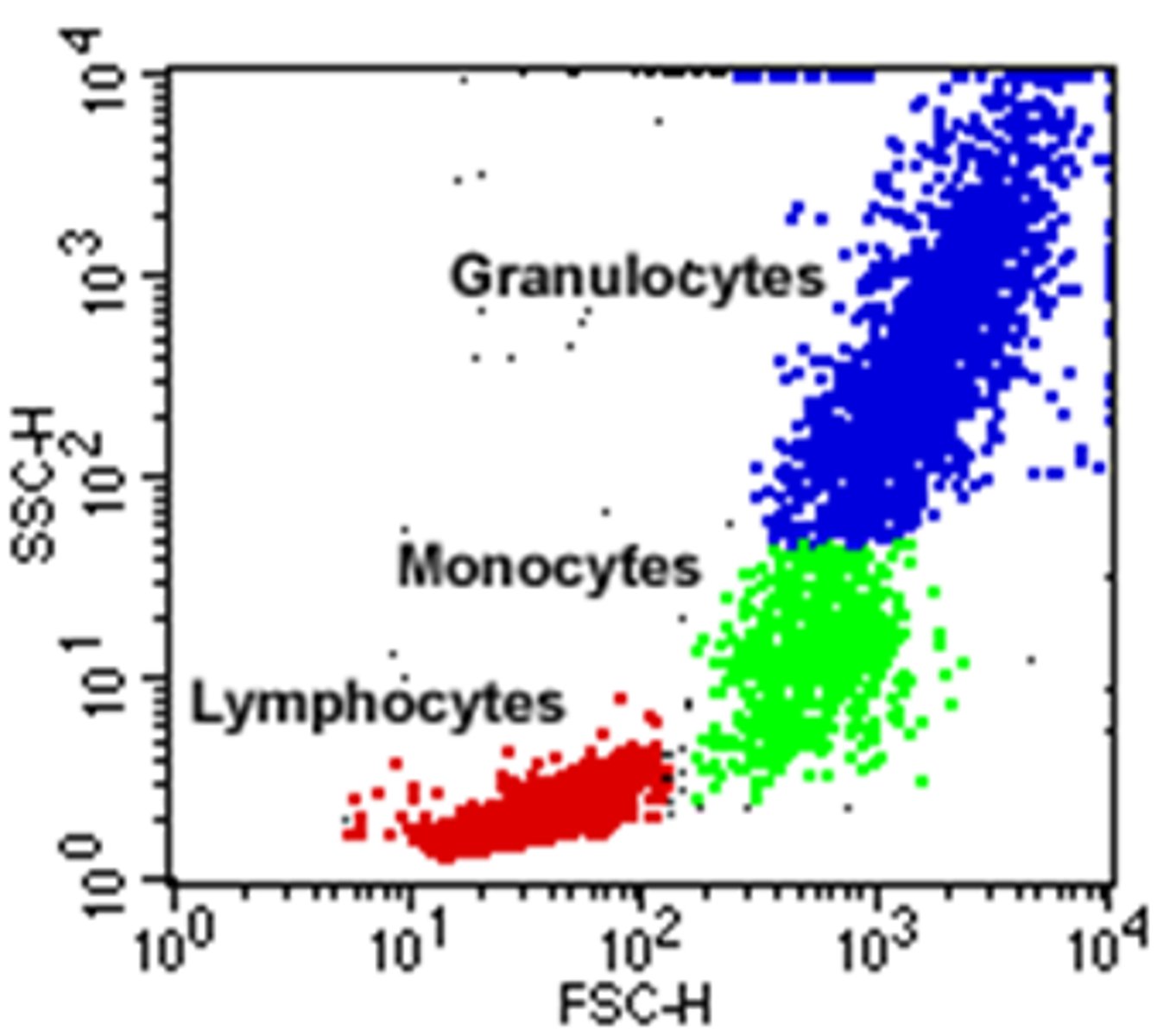
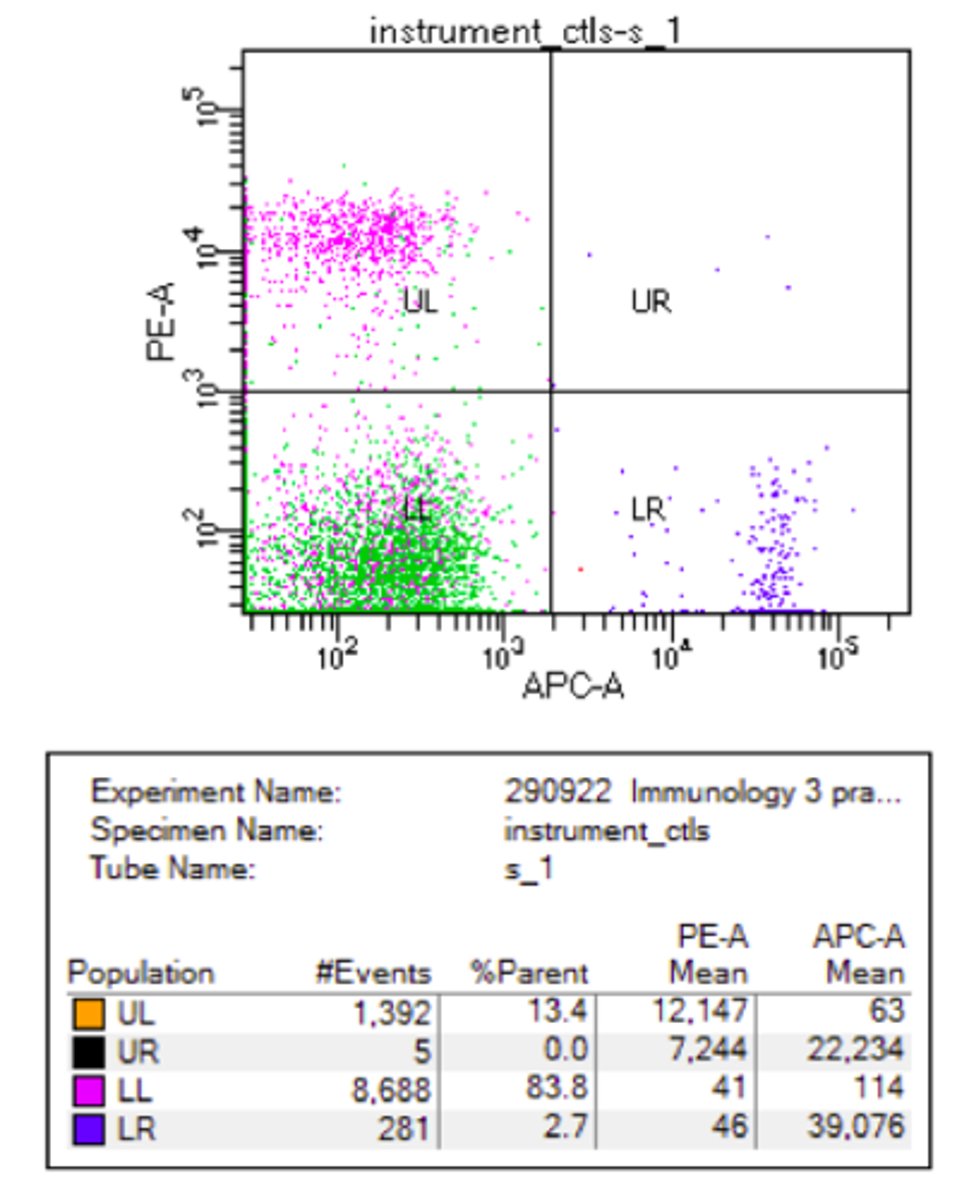
scatter plot of physical characteristics of cells
x = SSC (granularity)
y = FSC (cell size)
fluorescence histogram
LFL (fluorescence intensity) on x axis, log scale
Count (relative to cell number) on y axis
fluorescence histogram: high cell count, low LFL
- cells expressing minimal fluorescence
- negative for target antigen
fluorescence histogram: high cell count, moderate LFL
- 100% positive for target antigen
- moderately stron fluorescence
- relatively homogenous population with respect to quantity of antigen per cell
fluorescence histogram: high cell count, high LFL
- very strong fluorescence; greater quantity of antigen per cell
- 100% positive for taget antigen
- relatively homogenous population with respect to quantity of antigen per cell
fluorescence histogram: moderate cell count, broad LFL
- lower quantity of antigen per cell
- relatively heterogenous population with respect to quantity of antigen per cell
gating
only show cell type of interest
do fluorochromes emit one λ ?
no - emission values listed are usually their peak λ values, but fluoreochromes have an emission spectra
what are dichroic and band pass filters ?
used in spectral flow cytometer - enable the labeling of cell populations with multiple fluorochromes with narrowly separated λ;
multi-color fluorescence emitted by cells bearing 4 different fluorochromes is λ-fractionated by dichroic and band pass filters
MFI
Mean fluorescence intensity - indication of mean antigen density per cell
dichroic filters
some of the source light is deflected off the filter while some of it passes through the filter
- Isolates the PEAK colors/wavelength
band pass filters
a band of frequencies passes through amplified or unchanged, while frequencies higher and lower are attenuated
flow cytometry: advantages
- rapid analysis of large populations of cells
- quantitative multi-parametric data
- accuracy is operator-independent
flow cytometry: disadvantages
- no information on induvidual cells
- new high-end ctometers can produce images of each cell
- high tech - more things prone to go wrong
- high cost
Enzyme-Linked ImmunoSorbent Assay
Quantification of specific proteins (ex. cytokines, antibodies) in solution
works by linking an antibody to an enzyme, then adding the sample to a plate coated with the antibody. If the sample contains the target substance, the enzyme will react with a substrate to produce a color change
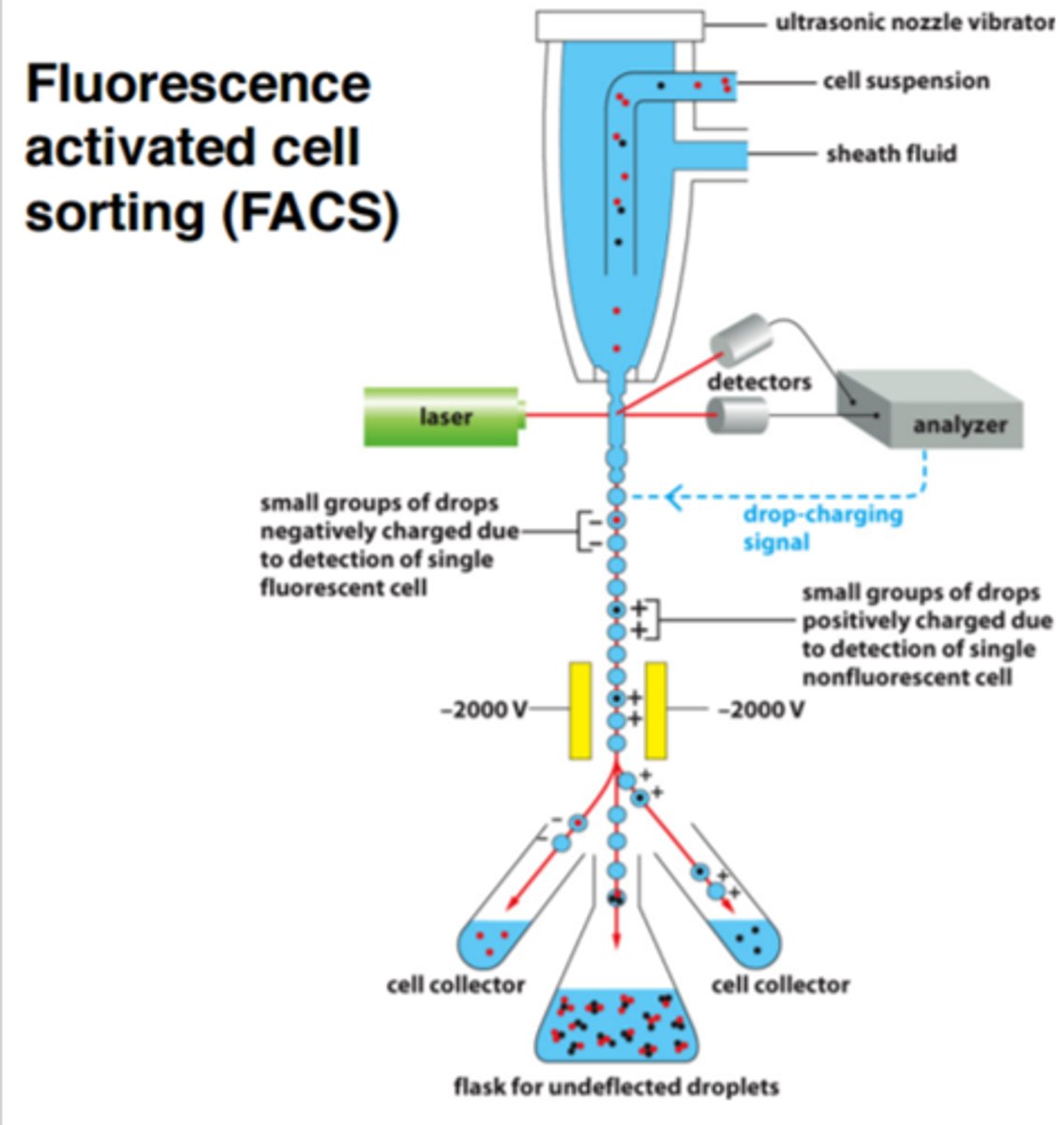
Fluorescence-Activated Cell Sorting (FACS)
- cells stained with fluorochrome-conjugated antibodies specific for cells of interest (different fluorochrome for each cell type)
- droplets containing cells given electrical charge (+ or -) based upon fluorochrome emission wavelength
- cells directed into separate receiving vessels by positively or negatively-charged electrons
ELISpot
a modified ELISA technique that detects the frequency of cultured cells that secrete a particular cytokine
ELISA vs. ELISpot
ELISA:
- quantitation of soluble factors in solution. NO information regarding number of cells producing such factors
ELISpot
- quantitation of cells producing soluble factors. NO information regarding quantity of soluble factors produced