Exam 3
1/39
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
40 Terms
Cilia and flagella (match the type of movement with the responsible motor protein)
Axonemal Dynein
Muscle Contraction (match the type of movement with the responsible motor protein)
Myosin
Organelle trafficking (match the type of movement with the responsible motor protein)
Cytoplasmic Dynein and Kinesin
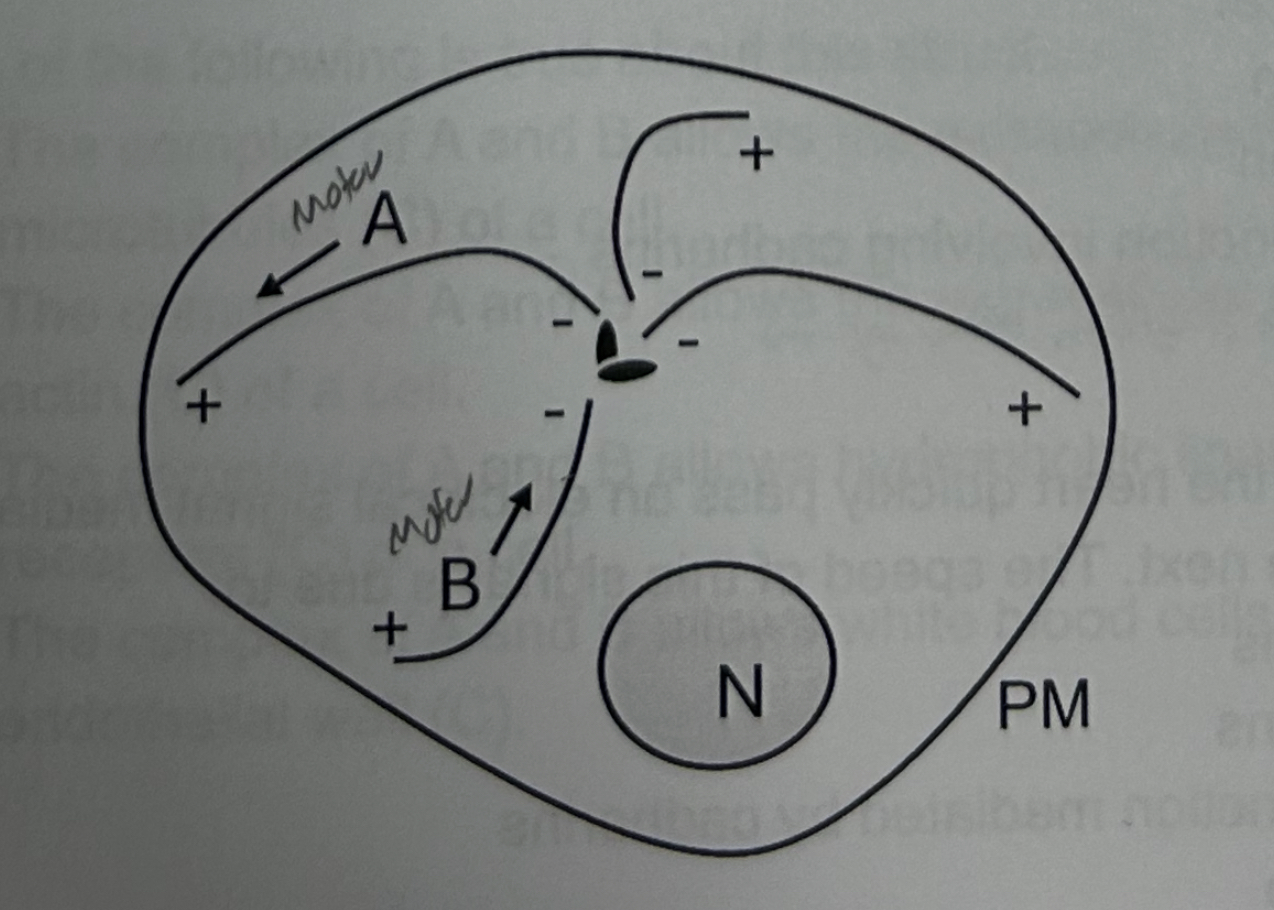
Which of these protein movements requires ATP hydrolysis?
Both A and B
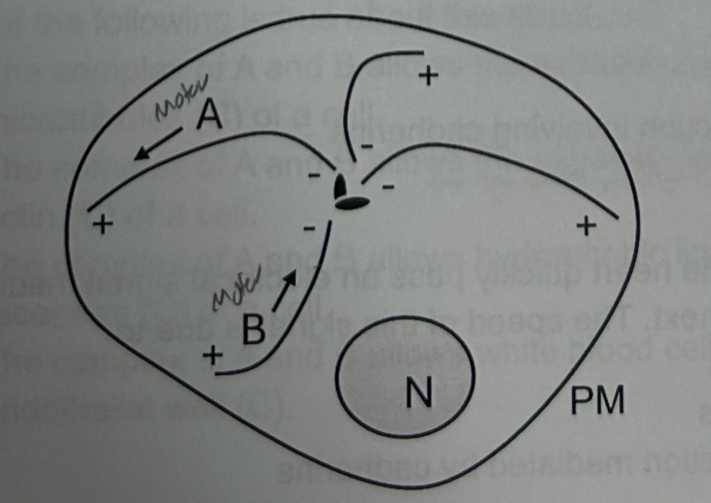
Protein “A” is likely
a Kinesin
Research shows that high sugar can lower transcription of the protein ZO-1, which can lead to increased permeability between epithelial cells in the gut.
Sugar likely compromises which kind of cell-cell junction?
Tight Junction
What kind of protein would make up tight junctions?
Claudins
A cell-cell interaction involves intermediate filaments to provide maximal adhesion between two cells subject to frequent mechanical forces. This interaction is likely a:
Desmosome
Myocardial cells in the heart quickly pass an electrical signal mediated by ions from one cell to the next. The speed of this signal is due to:
Gap junction
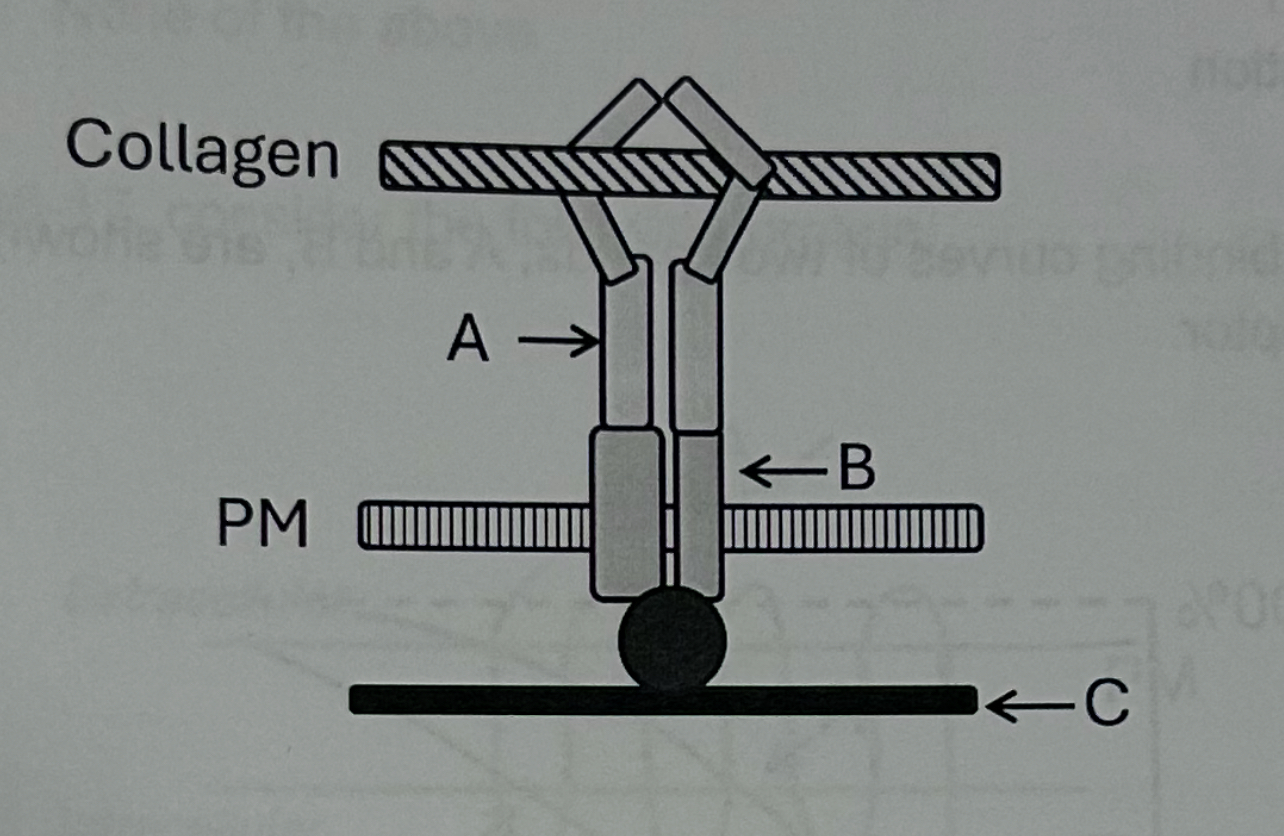
The structure “A” ______
Has an RGD amino acid sequence that binds a site in "B."
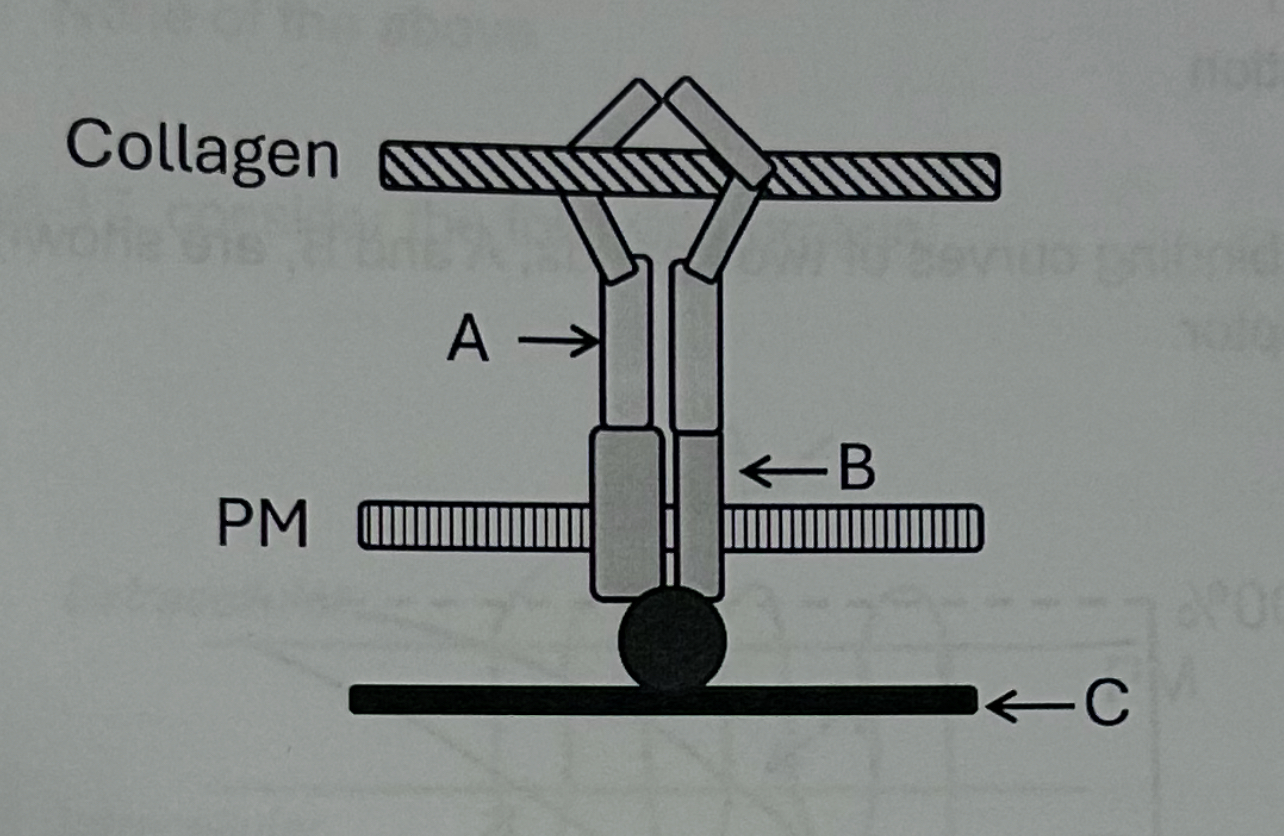
Which of the following is true about this structure
The complex of A and B allows the extracellular matrix to interact with the actin (C) of a cell.
Which of the following is NOT one of the four stages of intracellular signaling?
ligand Binds to receptor
Signal transduction/Amplification
Deactivation
DNA replication
DNA replication
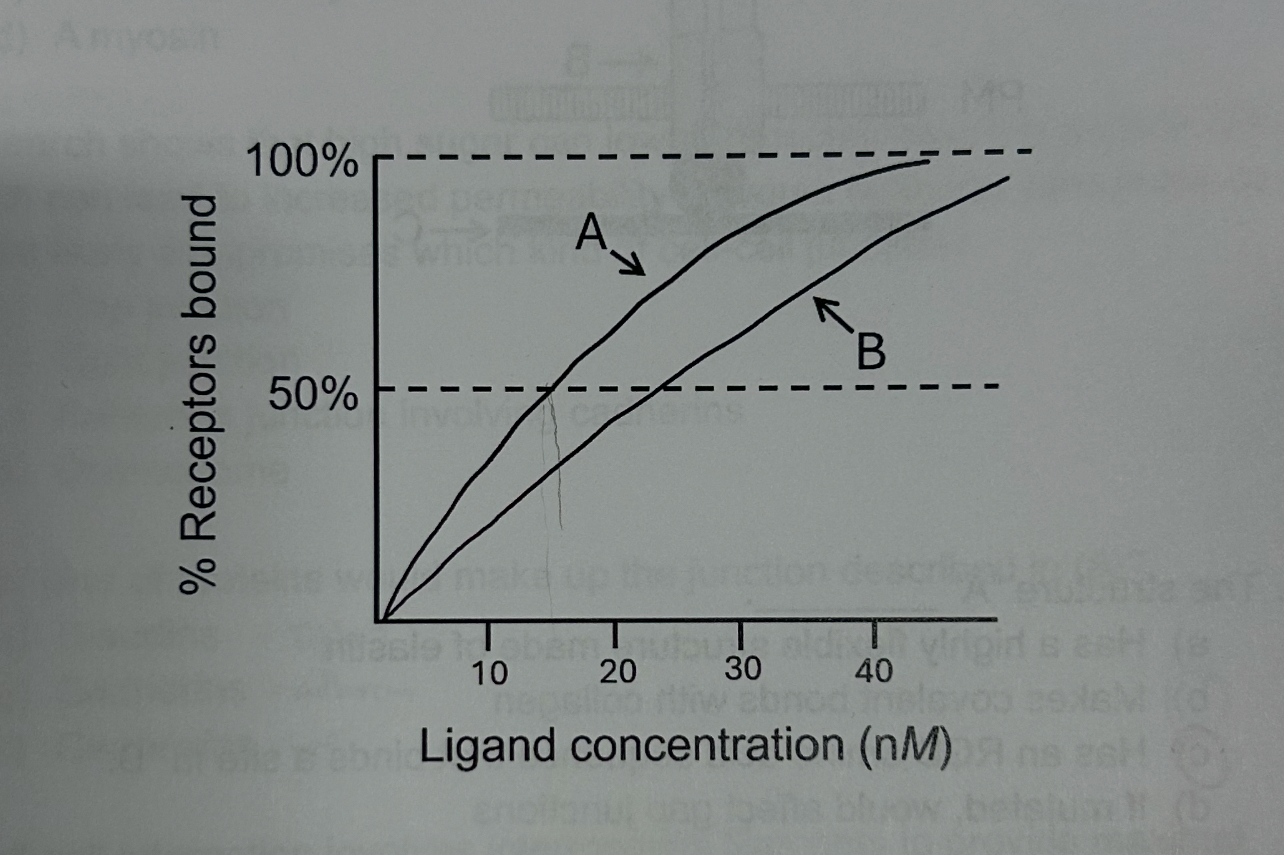
The Kd of Ligand A is roughly
15nM
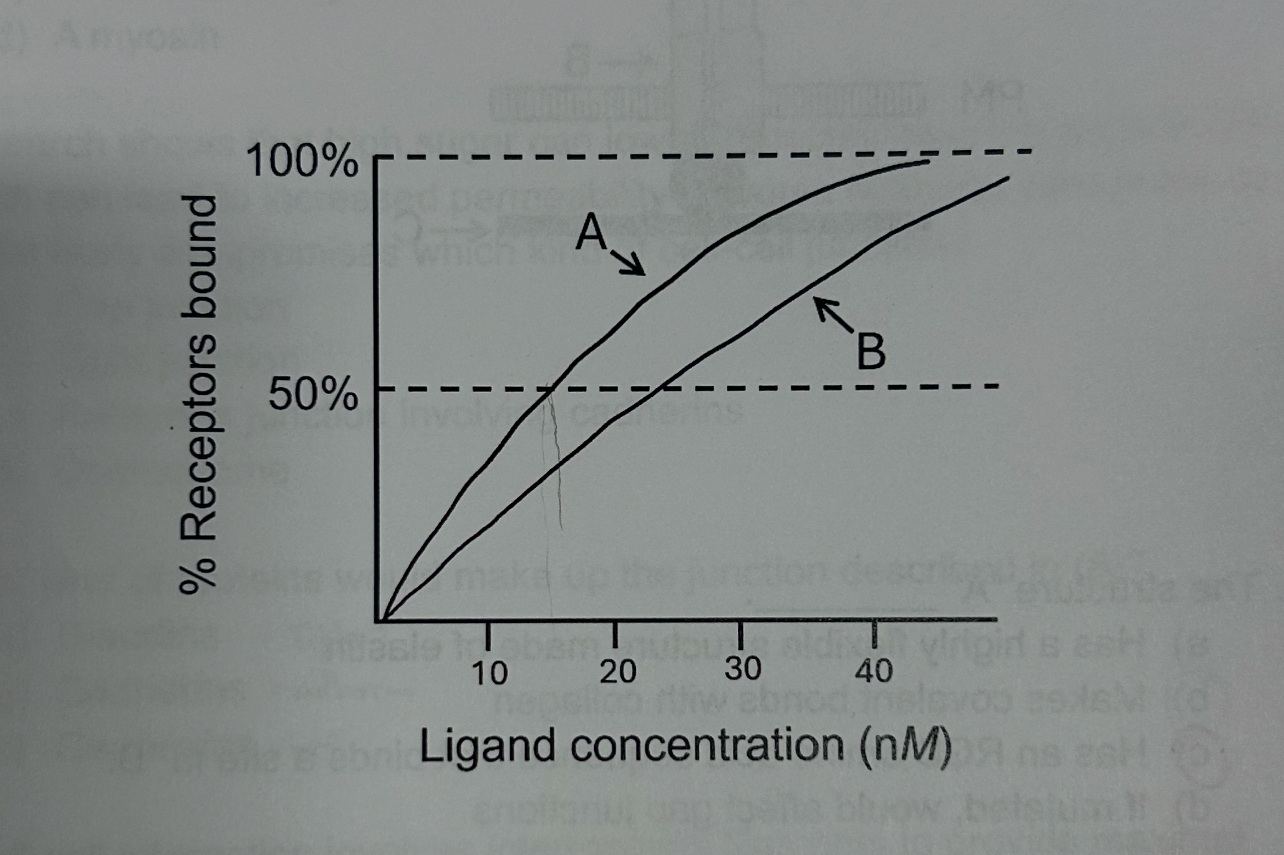
Which ligand has higher affinity for the receptor?
Ligand A
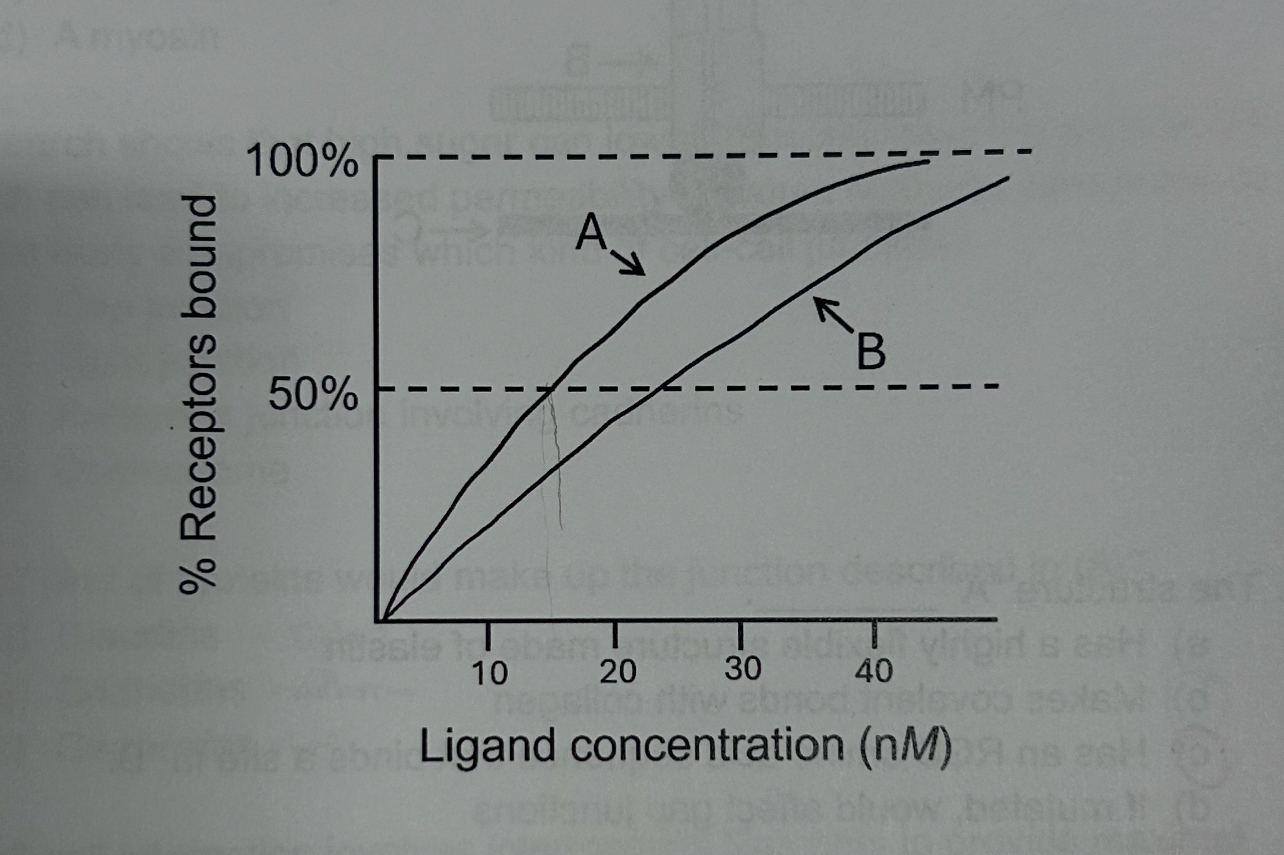
These ligands do not make covalent bonds with the receptor because ____
It is important that signals are temporary
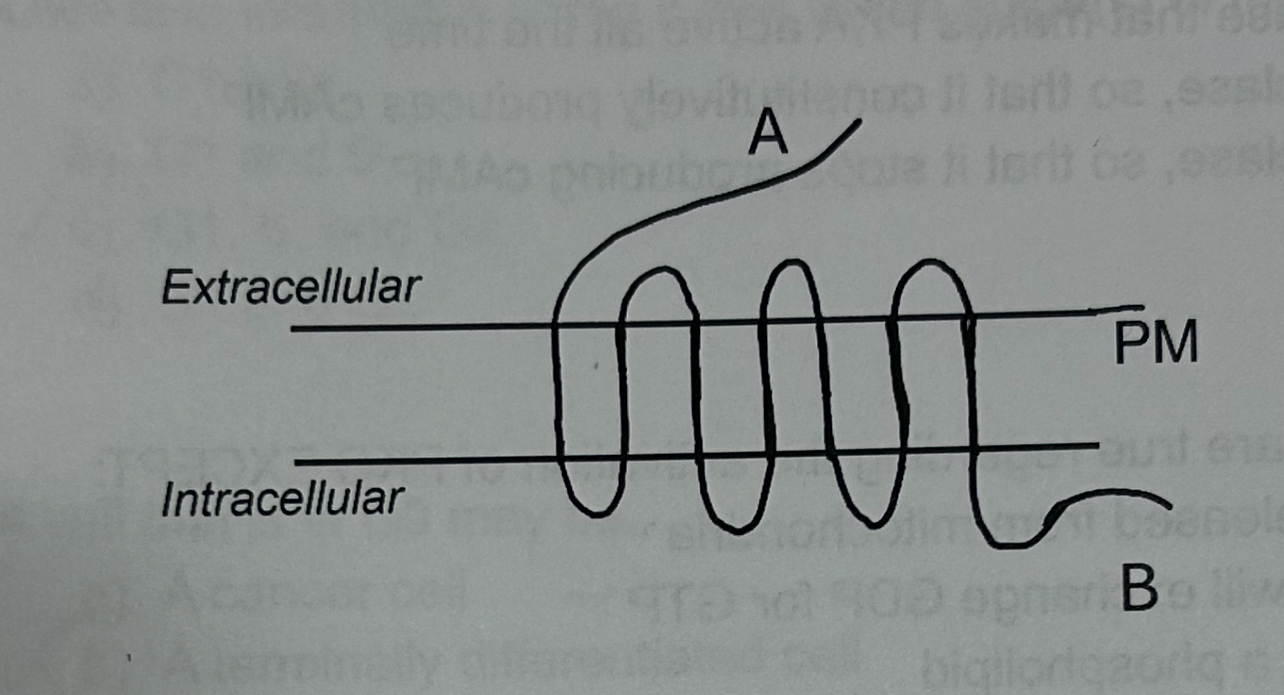
The following are true regarding this structure EXCEPT:
The protein will interact with heterotrimeric G proteins at "B"
The protein was translated on a free ribosome in the cytosol
A structurally similar protein is involved in activation of PKA and PKC
B-arrestin binding at "B" will decrease signaling by this protein
The protein was translated on a free ribosome in the cytosol
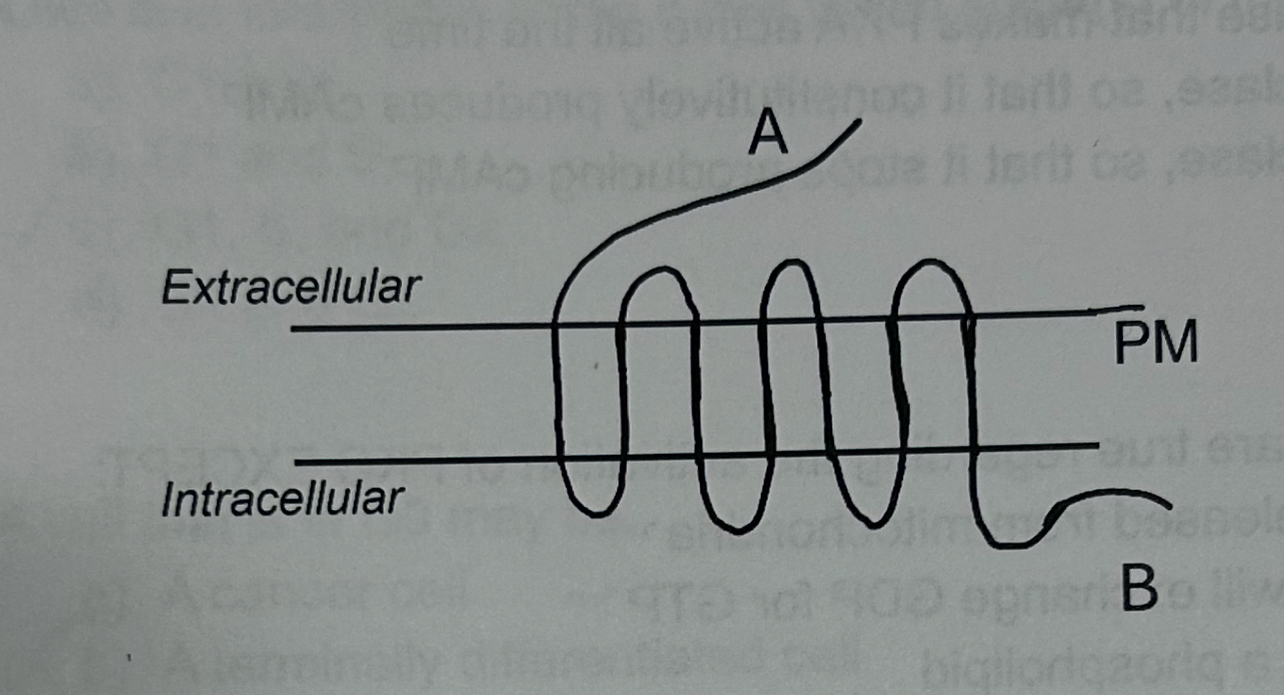
A mutation in “A” could
prevent ligand from binding
Decrease activation of downstream second messengers
Increase phosphorylation at the C-terminus
A and B
A and B
Cells are treated with growth factors that cause them to divide rapidly. The cells also have receptors that bind epinephrine, which activates adenylyl cyclase. In these cells, PKA inhibits the protein Raf. In these cells, epinephrine will:
Slow cell division
A cell has a mutation where PKA activation is 100X higher than normal cells, even in the absence of adrenaline. This mutation is likely in:
Adenylyl Cyclase, so that is constitutively produced cAMP
All of the following are true regarding the activation of PKC EXCEPT:
- Calcium is released from mitochondria
- Gq protein will exchange GDP for GTP
- PLC cleaves a phospholipid
- DAG is hydrophobic and remains in the plasma membrane
Calcium is released from the mitochondria
The type 2 mAch receptor activates Gi G proteins to inhibit adenylyl cyclase. Ach binding this receptor in the heart will _ the effect of epinephrine binding the
B adrenergic receptor.
Decrease
A Receptor Tyrosine Kinase (RTK) is mutated such that tyrosine residues are replaced with phenylalanine residues. This receptor will not be functional in the most part because:
It will not be able to undergo autophosphorylation
For a cell to respond to a ligand, it must:
Have a receptor that binds that ligand
A cell is in interphase when it is in which stage(s) of the cell cycle?
G1, S, and G2
A cell that is in G0 may be
A terminally differentiated cell
During prophase to metaphase, microtubules attach to chromosomes at the kinetochore and move them to the middle of the cell to form the metaphase plate. These congressions are mediated by
Motor proteins
DNA viruses need to use a host cell's DNA replication machinery. To do so, it must push a cell into which phase of the cell cycle?
S phase
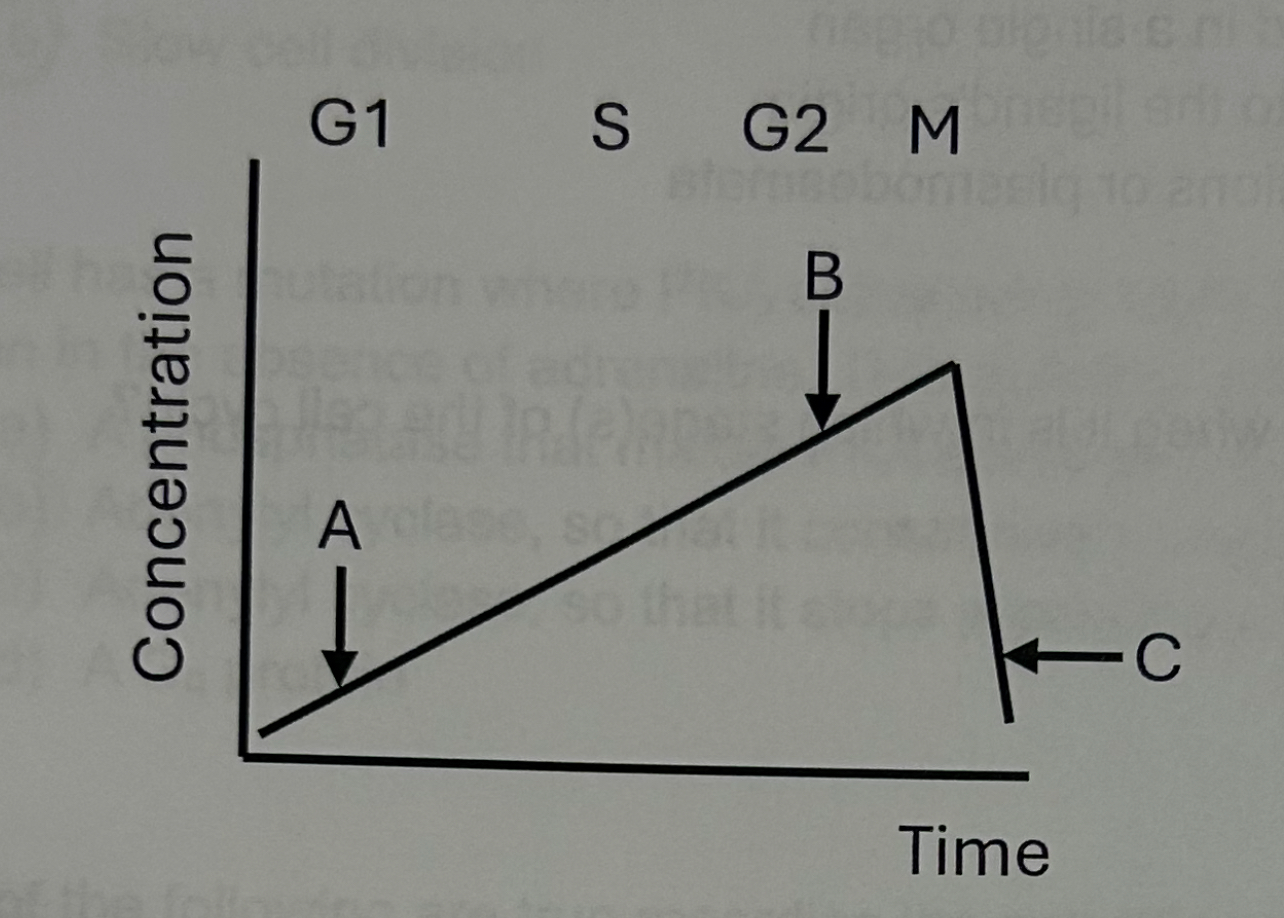
This curve likely represents the expression of _ during the cell cycle.
M-cyclin
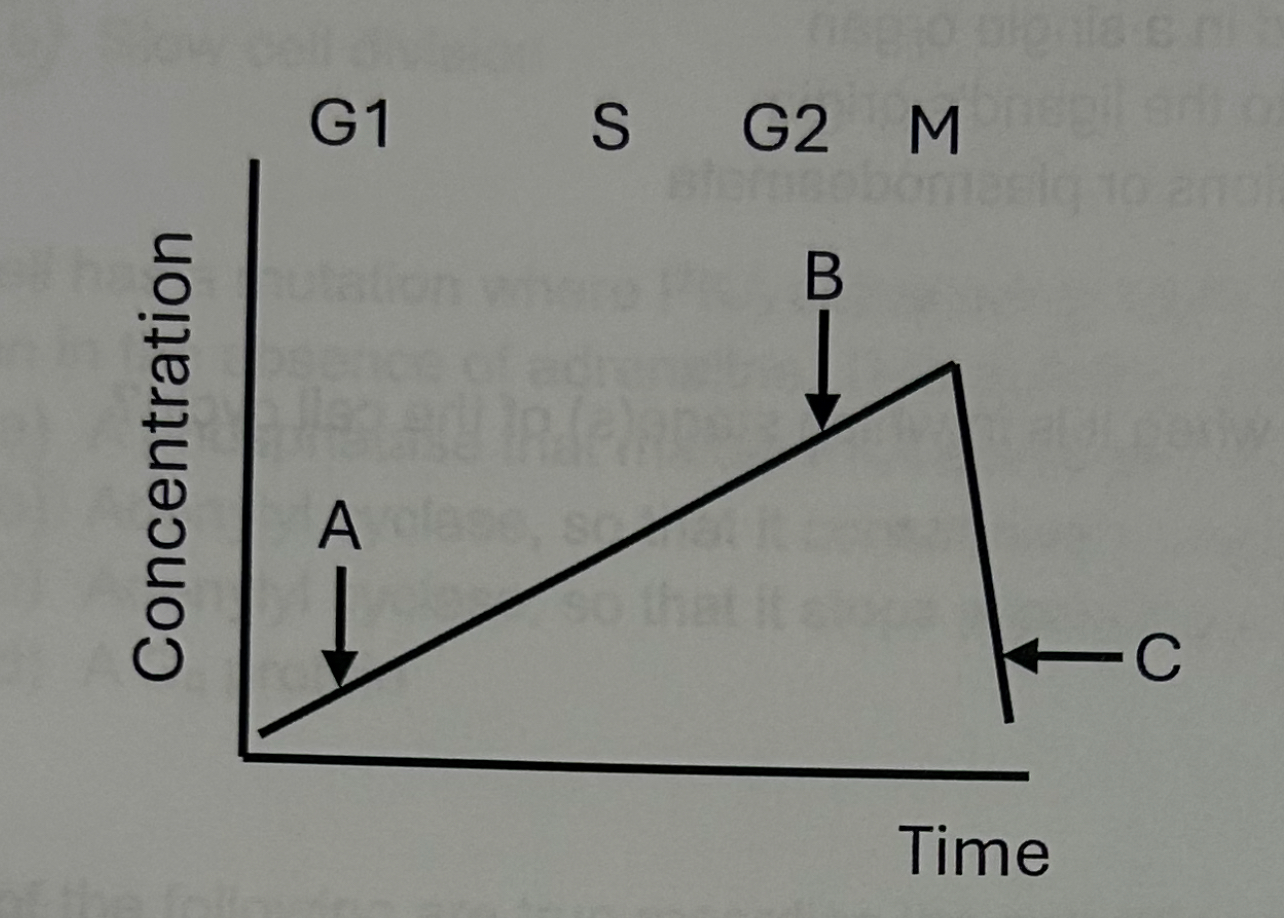
The mitotic promoting factor (MPF) approaches peak activity at which of the labeled points?
B
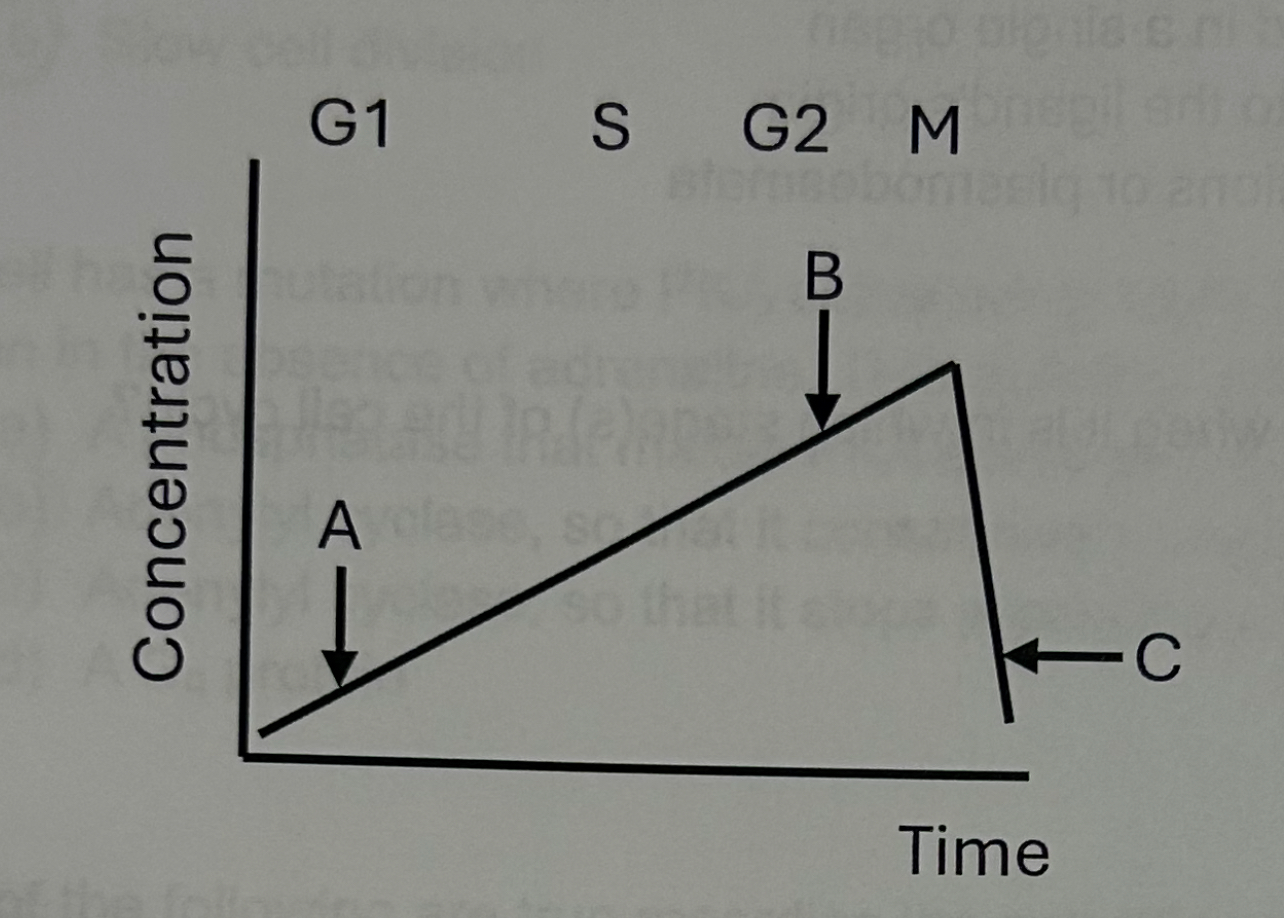
What would need to be true for division to move past this checkpoint (not including previous checkpoints)?
DNA must not be damaged and DNA replication must be complete
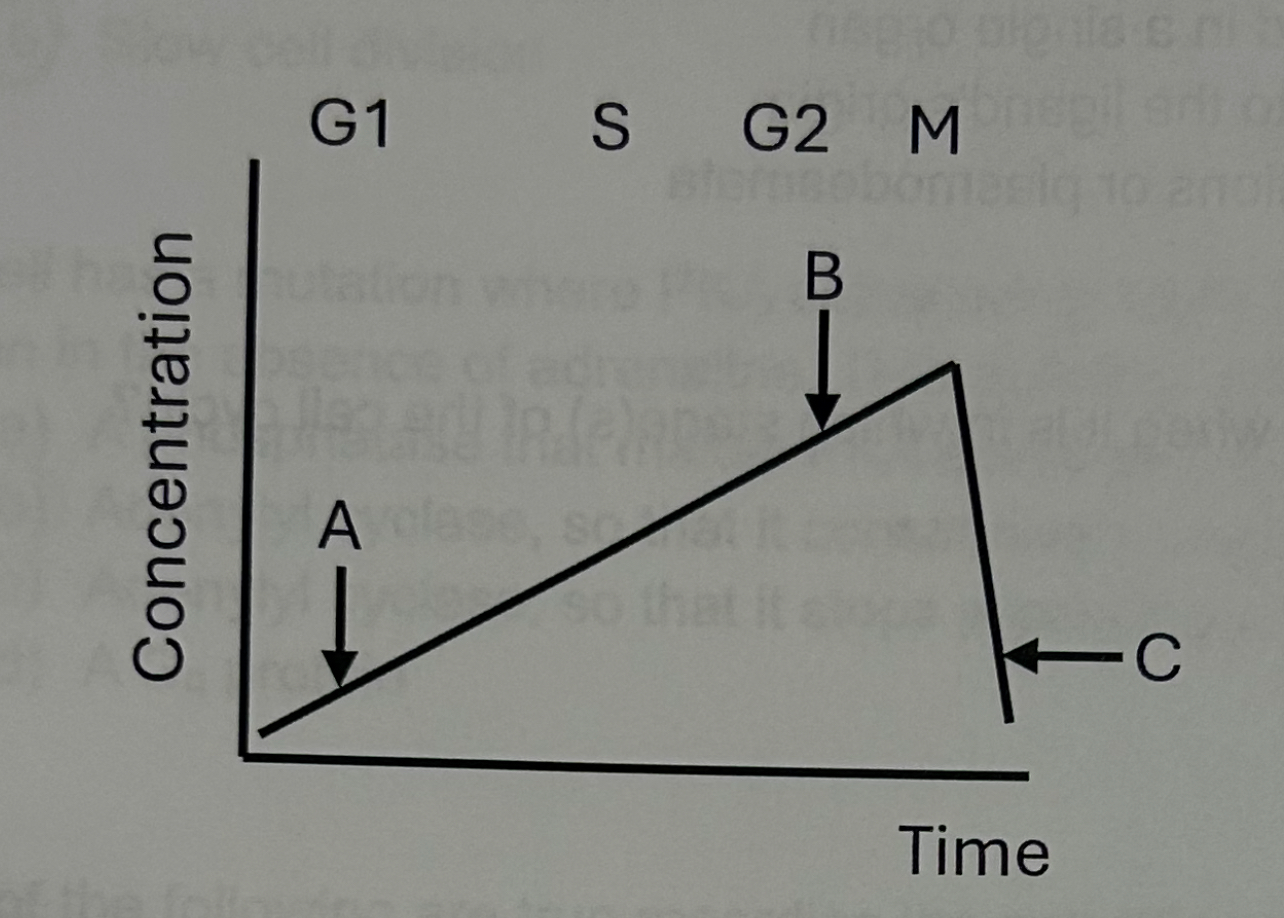
What might happen to the cell if levels of this protein did not fall, as in “C”
Cell might stay arrested in mitosis
Oncogenic DNA viruses require host cell's replication machinery to replicate their own DNA. Which of these genes would the virus target for destruction?
cytochrome C
Retinoblastoma (Rb) protein
Bcl-2
Securin
Retinoblastoma (Rb) protein
A T-lymphocyte ligand binds the CD95 death receptor of a cell. The cell likely
Has been infected
Which of the following are characteristics of malignant cancer cells?
Can survive without anchoring and are resistant to apoptosis
Retain the ability to divide independent of growth factors Will complete mitosis at a faster rate than normal cells
A and B
All of the above
A and B
During indirect apoptosis, cytochrome C is released from
Mitochondria
P53 cannot be phosphorylated (match the mutation with the expected result on cell function)
Cell division occurs despite DNA damage
Ras that does not hydrolyze GTP (match the mutation with the expected result on cell function)
Cell enters the cell cycle in the absence of growth factors
Securin no longer binds Seperase (match the mutation with the expected result on cell function)
Anaphase proceeds without chromosomes attached to microtubules
Procaspase-3 cannot be cleaved (match the mutation with the expected result on cell function)
Cell is resistant to both direct and indirect apoptosis
Overexpression of Bcl-2 (match the mutation with the expected result on cell function)
Cell is resistant to indirect apoptosis