PSYB20 - Midterm 1
1/201
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
202 Terms
development
systematic changes and continuities in the individual that occur between conception and death
developmental continuities
ways in which we remain stable over time or continue to reflect our past
maturation
developmental changes in the body or behavior that result from the aging process rather than from learning, injury, illness, or some other life experience
biological unfolding of inheritance
ie. seeds to plants
2 critical developmental processes
maturation and learning
learning
A process through which experience produces lasting change in behavior or mental processes.
ie. practice basketball become better
Development is a joint function of...
maturation, learning, and the active individual (reacting to situations differently)
normative development
developmental changes that characterize most or all members of a species; typical patterns of development
ie. baby to adult
ideographic development
individual variations in the rate, extent, or direction of development
ie. identical twins differing
Goals of developmentalists
describe: normative or ideographic
explain: why does it occur in a certain way
optomize: how can this info be used to optimize development (practical)
The goal of optimization depends on
the larger culture the developmentslists are placed in.
ie. gender roles may define optimal female development
To be plastic means
the capacity to change in response to positive and negative life events
developments from ___________ are particularly important
birth to age 12
characteristics of development
lifelong process - across lifespan
holistic - physical growth, cognitive growth, and psychosocial growth all work together
plasticity - capacity to change in response to positive and negative life events
Historical/Cultural Context - development is influenced by society, culture, and societal events such as social movements and wars
Thomas Hobbes Original Sin
children are inherently selfish egoists that much be restrained by society and taught to channel their selfish interests into socially acceptable outlets
parents should control their kids to channel selfish interests
Jean-Jacques Rousseau innate purity
Children are born with an intuitive sense of right and wrong that society often corrupts
parents should give kids freedom to follow inherently positive inclinations
John Locke Tabula Rasa
Mind of a child is a blank slate written on by experiences
children have no in born tendencies
Parental discipline child to encourage good habits and prevent bad habits
baby biography
a detailed record of an infant's growth and development over a period of time
first systematic studies of development
Biased by authors assumptions and often found what they were looking for
Darwin views on development
young, untrained infant's share traits with non human ancestors
studied his son
Theory
a set of concepts and propositions designed to organize, describe, and explain an existing set of observations
hypothesis
predictions about some aspect of experience
reliability
consistency
similar results across measurements
validity
accuracy
measures what is it supposed to measure
structured interview/questionnaire
a research procedure in which all participants are asked to answer the same questions
can't be used with very young children
clinical method
participants response to each question determines what the investigator will ask next
more flexible than structured interview. Researchers may be biased to which questions they ask, it may also be hard to make comparisons
naturalistic observation
observing people as they engage in everyday activities or natural habitats
limitations of naturalistic observation
some behaviors are rare or socially undesirable and hars to view in natural environments
observer influence
the tendency of participants to react to an observer's presence by behaving in unnatural ways
mitigating observer influence
videotaping from concealed location
gettung participants accustomed to being observed before testing
time sampling
a measurement of the presence or absence of behavior within specific time intervals
structured observation
a method that involves presenting an identical situation to each child and recording the child's behavior
allows for more control than naturalistic observation
may not correlate with everyday life due to unnatural environment
case study
an observation technique in which one person is studied in depth in the hope of revealing universal principles
analyze individuals life events and history
may lack generizability
Ethnography
the scientific description of the customs of individual peoples and cultures.
may live amongst culture to make extensive observations
highly subjective to researchers own cultural values
psychophysical methods
research that focuses on the relationship between physiological processes and behavior
can study perceptions, cognition and emotional responses.
affected by mood, fatigue, etc so can be inaccurate at times
correlational research
studies the strength of association between variables
Developmentalist
any scholar, regardless of discipline, who seeks to understand the developmental process
can be historians, sociologists, anthropologists, etc.
cross-sectional study
subjects from different age groups studied at same point in time.
cohort
A group of individuals of the same age who are exposed to similar culture and history growing up.
cohort effect
age-related difference among cohorts that is attributable to cultural/historical differences in cohorts' growing-up experiences rather than to true developmental change
longitudinal study
research in which the same people are restudied and retested over a long period
drawbacks of longitudinal research
practice effects
selective attentions
nonrepresenatative sample
practice effects
Improvements in performance resulting from opportunities to perform a behavior repeatedly so that baseline measures can be obtained.
can occur with longitudinal studies
selective attrition
nonrandom loss of participants in study resulting in nonrepresentative sample
nonrepresentative sample
subgroup that differs from larger popular of interest.
cross-generational problem
the fact that long-term changes in the environment may limit conclusions of a longitudinal project to that generation of children who were growing up while the study was in progress
sequential design
Combination of cross-sectional and longitudinal designs involving repeated study of different cohorts over time.
Selects participants of different cohorts over time
benefits of sequential design
more efficient - requires less time for full data set
can determine if cohort effects are present between cohorts - ie compare 8 years olds now vs 6 years olds 2 years later.
make longitudinal and cross secrional comparisons
microgenetic study
Participants studied intensively over a short period of time as developmental changes occur
attempts to see how or why changes occur
ie. going through puberty
cross cultural comparison
a study that compares the behavior and development of people from different cultural or subcultures backgrounds
guards against overgeneralization
informed consent
an ethical principle that research participants be told enough to enable them to choose whether they wish to participate
Protection from harm
the right of research participants to be protected from physical or psychological harm
benefits to risks ratio
a comparison of the possible benefits of a study for advancing knowledge and optimizing life conditions versus its costs to participants in terms of inconvenience and possible harm
minimal risk
term used when assessing risk in ethics reviews that refers to risks that are no greater than those one would encounter in daily life
ie. bodily harm vs boredom
Characteristics of good theories
parsimonious - concise, few assumptions
falsifiable- generate predictions that can be disconfirmed
heuristic - theory that continues to build on existing knowledge
what does it mean for a theory to be heuristic
build on existing knowledge by generating new testable hypotheses
psychosexual theory
Freud said maturation of the sex instincts underlies stages of personality development
manner in which parents manage children's instinctual impulses determines traits of child
issues with freud
no evidence, just waffled
when do id, ego, and super ego emerge?
id - birth, basic desires
ego - 1 year, compromise
super ego - 3-6, moral compass
psychosocial theory
Erikson's proposal that personality development is determined by the interaction of an internal maturational plan and external societal demands
revised version of Freuds theory
issues with Eriksons psychosocial theory
explains the what, but not the how or why
just describes conflict, not mechanism or relevance
Karen Horney
Neo-Freudian; offered feminist critique of Freud's theory
Behaviorism
the science of behavior that focuses on observable behavior only
rather than speculation about unconsious drives and unobservable phenomena
habits
well-learned associations between stimuli and responses that represent the stable aspects of one's personality
core of behaviorism - baby albert conditioned to fear rat
skinner
operant conditioning
bandura
Observational learning; Bobo dolls; social learning theory
social learning theory
we learn social behavior by observing and imitating and by being rewarded or punished
Bandura
observational learning
learning by observing others; also called social learning
we observe models
information processing theory
a perspective that compares human thinking processes, by analogy, to computer analysis of data, including sensory input, connections, stored memories, and output
cognitive development is continuous and not in stages
Konrad Lorenz
ethology perspective; studied imprinting and critical periods in geese
Ethology
the study of the evolutionary bases of behavior and development
belief in critical period
Classic Ethology
behaviors are programmed by genes and serve an evolutionary purpose
focus on responses all members of species share and may steer them along simar paths
sensitive period
a point in development when organisms are particularly susceptible to certain kinds of stimuli in their environments, but the absence of those stimuli does not always produce irreversible consequences
ie. language development
Evolutionary Theory
the study of the evolutionary bases of behavior and development, with more focus on genes than the individual
evolutionary Theory vs ethology
evolutionary Theory says adaptations occur to ensure safety of genes not individual.
explains why parents will sacrifice life for child
Nature vs. Nurture
name for a controversy in which it is debated whether genetics or environment is responsible for driving behavior
Active/Passive issue
a debate among developmental theorists about whether children are active contributors to their own development or, rather, passive recipients of environmental influence
Hobbe is active
Rousseau is passive
continuity-discontinuity issue
the debate about the extent to which development involves gradual, cumulative change (continuity) or distinct stages (discontinuity).
positional stability
stability of an individual's relative position in a group of people with regard to a psychological characteristic
ie. babies who cry a lot being emotionally stable adults
position terms of emotionality is stable as the develop, even though they change.
absolute stability
no change in a person's attribute over the course of development
quantitative changes
changes in degree, or amount. Individual is fundamentally same
ie. height
qualitative changes
transformations that fundamentally change being.
Ie. tadpole to frog, infant learning language
holistic nature of development
awareness that development is a holistic process even when being studied as a segmented, separate process.
Even though we may study, social development and cognitive development separately, they are interconnected processes
critical period vs sensitive period
Critical period: a specific time during which development of a skill must occur or else that skill might never develop.
ie. geese imprinting
Sensitive Period: a specific time during which development of a skill occurs more easily. The developmental of that skill can occur later though it might be harder later.
ie. language development
simple dominant-recessive inheritance
a pattern of inheritance in which one allele dominates another so that only its phenotype is expressed
ie. Aa, shows only A phenotype
Codoninance
situation in which both alleles of a gene contribute to the phenotype of the organism
ie. red + white = red + white
incomplete dominance
Situation in which one allele is not completely dominant over another allele
ie. red + white = pink
polygenic inheritance
combined effect of two or more genes on a single character
ie. height and weight
Epigenetics
the study of influences on gene expression that occur without a DNA change
Ie. methylation
prenatal development
development from conception to birth
period of the Zygote (geminal period)
conception to implantation
anout 14 days
period of the embryo
organs form, heart beats
3 cell layers
weeks 3-8
3 cell layers
ectoderm - skin, hair, NS
mesoderm - bones, muscles, circulatory
endoderm - digestive, urinary, vital organs, lungs
period of the fetus
organ function and growth
9th week to birth
amnion
Innermost membranous sac surrounding the developing fetus
cushions
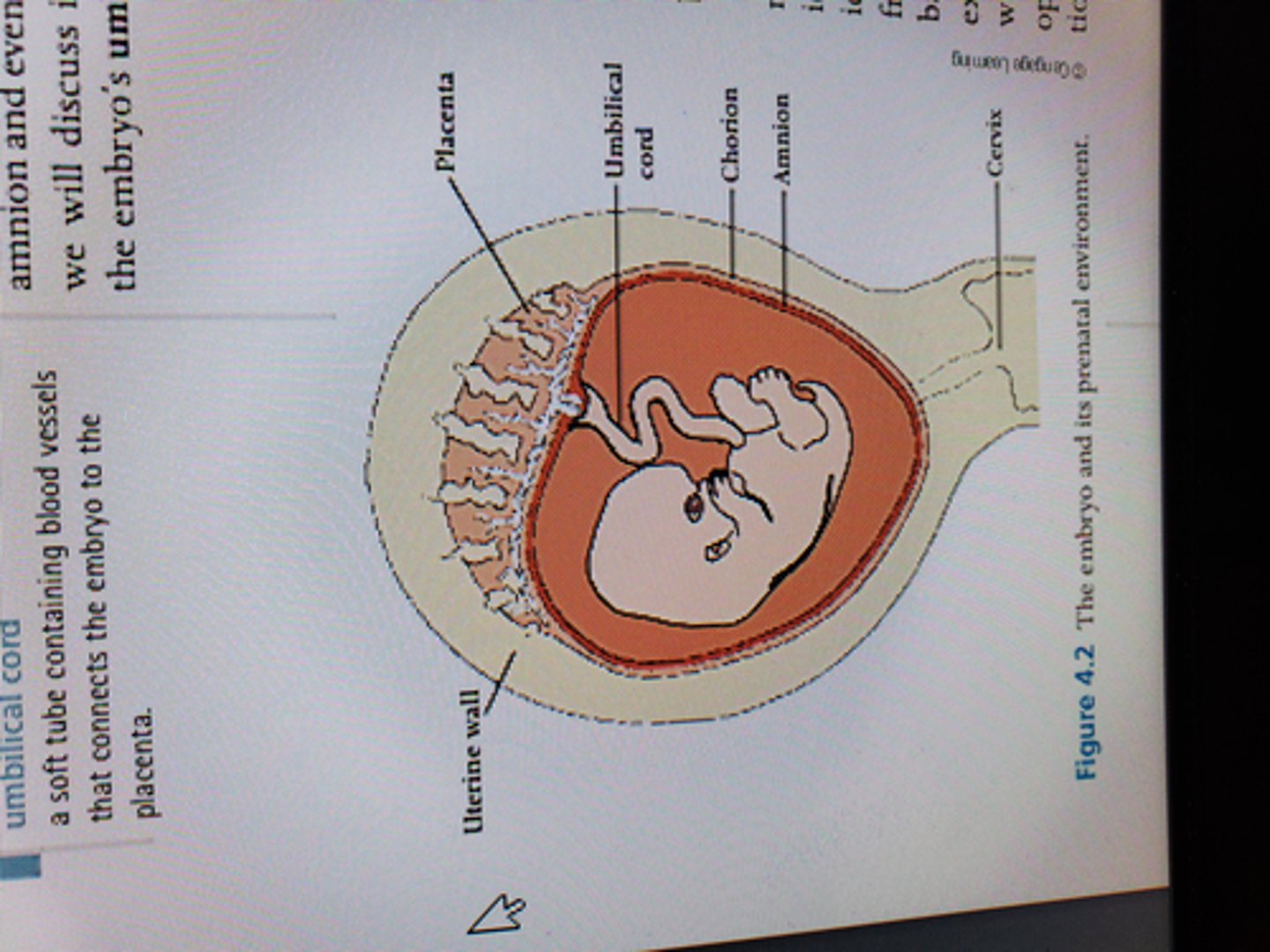
chorion
Outermost layer of the two membranes surrounding the embryo; it forms the fetal part of the placenta.
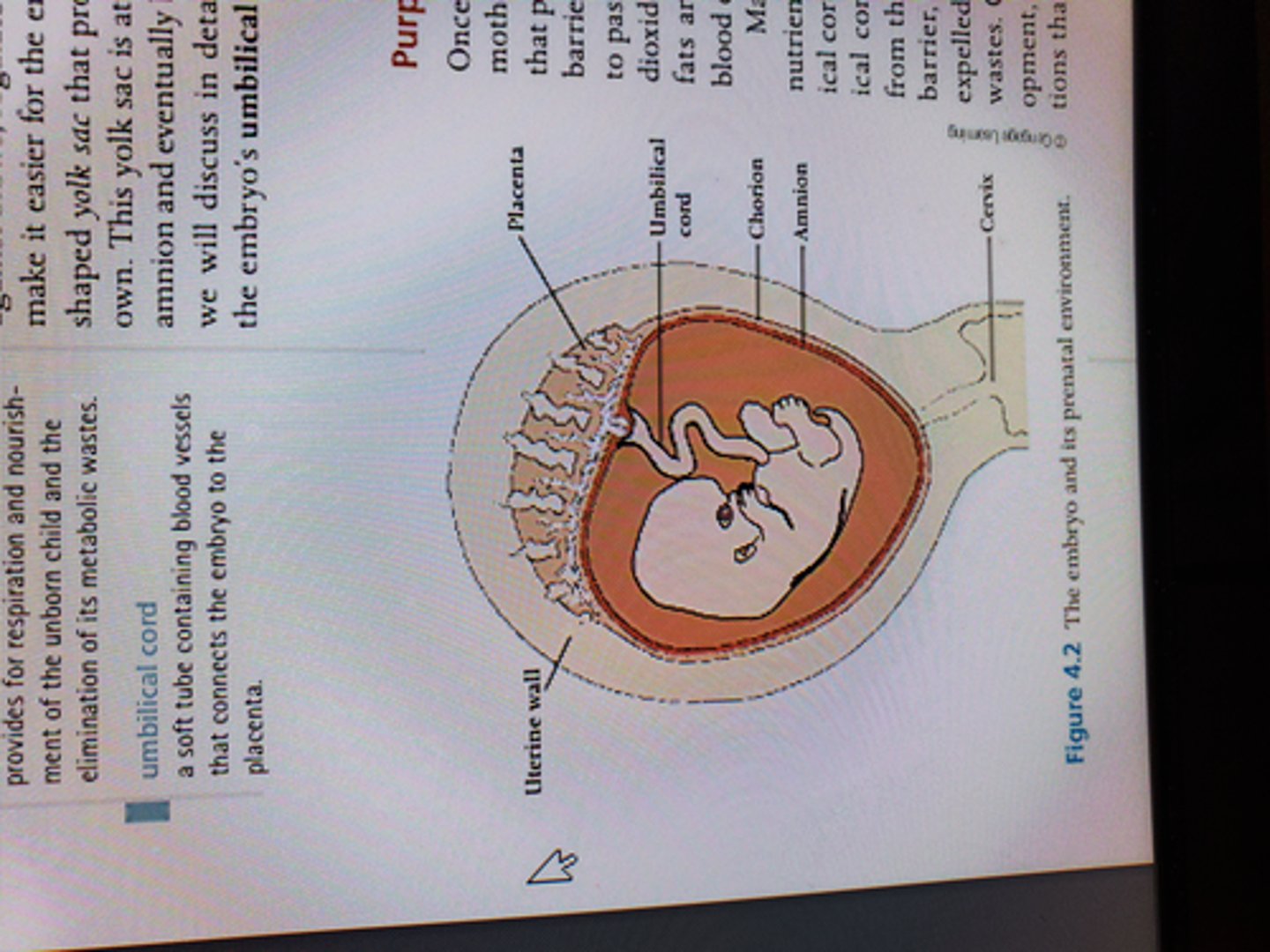
placenta
organ that nourishes the fetus
formed from chorion and uteral lining
gas and nutrient exchange
neural tube
a groove formed in the top layer of differentiated cells in the embryo that eventually becomes the brain and spinal cord
forms from ectoderm in first month
indifferent gonads
the undifferentiated gonads of the early mammalian fetus, which will eventually develop into either testes or ovaries
presence of Y chromosome triggers male at 7th week
first month of pregnancy
neural tube formation
heart beat
facial structures
arms and legs bud
second month of pregnancy (week 5-8)
ears form
rudimentary skeleton
limbs
brain develops
indifferent gonads