PEE
1/227
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Sun bleached flies sitting in the windowsill Waiting for the day they escape They talk all about that money and how their babies are always changing While they're breathing in the poison of the paint What I wouldn't give to be in Church this Sunday Listening to the choir, so heartfelt, all singing God loves you, but not enough to save you So, baby girl, good luck taking care of yourself So I said fine, 'cause that's how my daddy raised me If they strike once then you just hit 'em twice as hard But in the end, if I bend under the weight that they gave me Then this heart would break and fall as twice as far We all know how it goes The more it hurts, the less it shows But I still feel like they all know, and that's why I can never go back home And I spend my life watching it go by from the sidelines And God, I've tried, but I think it's about time I put up a fight But I don't mind 'cause that's how my daddy raised me (how my daddy raised me) If they strike once then you just hit 'em twice as hard But I always knew that in the end no one was coming to save me So I just prayed and I keep praying and praying and praying If it's meant to be then it will be So I met him there and told him I believe Singing if it's meant to be then it'll be I forgive it all as it comes back to me (back to me) If it's meant to be then it will be So I met him there and told him I believe (I believe, yeah) Singing if it's meant to be then it will be (oh, oh) I forgive it all as it comes back to me (it comes back to me) If it's meant to be then it'll be (it'll be, it'll be, it'll be) So I met him there and told him I believe (yeah) Singing if it's meant to be then it will be I forgive it all as it comes back to me (oh) I'm still praying for that house in Nebraska By the highway, out on the edge of town Dancing with the windows open I can't let go when something's broken It's all I know and it's all I want now
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
228 Terms
Design Process Flowchart
Define Problem
Generate Concepts
Develop a Solution
Construct and Test Prototype
Evaluate Solution
Present Solution
Vector
quantities that have both magnitude and direction
Magnitude: length of vector
Direction: angle between vector and reference axis
Sense: way the arrow is facing (ex. Upwards to the right, downwards to the left)
Ex: velocity, force, acceleration
Position
vector value
place where something is located
displacement
distance from starting point (final position - starting position)
velocity
speed and direction an object is moving; v = d/t
contact forces
forces that require physical contact
Applied: push or pull
Friction: resisting motion
Air Resistance: friction force due to air molecules
Tension: forces in ropes, cables, chains, strings, etc.
Spring: F=kx, force in spring
Normal: contact force that is perpendicular to the surface that an object contacts
action-at-a-distance forces
Forces that can still exert push and pull while not being in physical contact
Gravitational Force: force due to object’s mass
Electrical Force: attractive or repulsive force between electrically charged objects
Magnetic Force: force due to motion of electrically charged particles
Strong and Weak Nuclear Forces: force within atoms
Strong: neutrons and protons
Weak: electrons and antineutrinos
Scalar
quantities that only have magnitude
Ex: volume, density, speed, energy, time, temperature
Mechanical Advantage
output/input
1 hp = 550 ft-lb/s = 1714 gpm-psi
Inexhuastible Resource
resource that are unlikely or impossible to deplete
Nonrenewable resources
resources with a finite supply that cannot be easily replenished
Renewable Resource
resources that can replenish themselves over time
Wind energy
Inexhaustible
unlimited supply of kinetic energy from wind (air travels from areas of high to low pressure)
Created using turbines
The wind blows past turbines → blades on turbine spin → kinetic energy is transferred to mechanical energy → rotation spins generator → generator produces electricity
Infrastructure
Challenges
Takes up a lot of space
Noisy
Difficult to transport wind turbines
Cannot take certain roads and make certain turns
Equipment
Towers, blades, hub components, nacelle assemblies
nacelle assemblies: generator, gearbox
nacelle assemblies are domestically obtained
Internal components are imported
Emerging Technologies
flexible blades
self-adjusting blades
3D modeling
Tidal Energy
Inexhaustible
Energy harnessed from the natural rise and fall of ocean tides
Moon’s gravity causes tides
Process to make it usable
Tidal streams
Turbines are placed in tidal streams (created by tides)
Convert kinetic energy of moving water into electricity
Most effective in shallow waters
Turbines move slowly to not disturb marine life
Tidal barrages
Large dams built across tidal rivers, bays, and estuaries
Tide rises → gates open
High tide → gates close
Water levels between high tide and low tide drive turbines
Water released through turbines at controlled rate
Tidal lagoons
Large, enclosed body of water
Turbines capture energy from the rise and fall of water levels
Generate energy as lagoon is emptied or filled
Minimal environmental impacts
Less common since it does not generate a lot of power
Infrastructure
Hydroelectric dam
Ideally located on river with steep drop
Steeper drop = more energy produced
Energy from water is created by gravity moving water down a hill
Flow of water controlled by dams and tunnels
Water behind dam flows through an intake → pushes against turbine blades → water’s kinetic energy converted to mechanical energy → drivers generator → produces electricity → electric energy transmitted to electrical power grid
Bulb turbines
Turbine on horizontal axis, parallel to flow of water
Emerging technologies
Environmental protection
Make hydropower turbines more fish-friendly
Replace larger blades with more smaller blades
Decrease turbine speed
Efficiency
water can be run through multiple rounds of smaller turbines
Biodiversity
replacing the sharp edges of the turbine for extremely rounded edges
Solar Energy
Inexhaustible
Source of most energy
Process
Light and heat from the Sun is harnessed
Sunlight → electricity using photovoltaic cells
Sun gives off PV cells → light strikes semi-conductive material → material absorbs photons and releases electrons (photovoltaic effect) → electrons react → creates small voltage → electrons pushed to conductive metal → becomes current → direct current to alternating current
Infrastructure
Solar panel
Semi-conductive material
Gets energy from the Sun
Energy from Sun is transferred to conductive metal
Controller
Regulates electrical flow by controlling voltage and amps
Sends electricity to solar battery
Battery bank
Uses stored energy
Activates when little solar energy is available (cloudy day, at night, etc.)
Inverter
Converts direct current to alternating current
Allows current to be more efficient and usable for home appliances
Meter
Determines the kilowatts per hrs of solar powers
Emerging technologies
Perovskites
Unstable, degrades quickly in wet environments
Reacts to different solar colors
Can deliver more power when combined with other material
High efficiency
Quantum dots
Toxic, degrades in UV and water
Can be used to make artificial atoms
Energy levels are controlled
Size of atom represents colors on solar spectrum absorbed
Night solar
Generates little energy
Solar panels for night
Uses a diode from night vision goggles
Inverse of solar cells
No need for collar battery
Nuclear Fusion
Inexhaustible
still in development
Energy from light atoms
Hydrogen - deuterium and tritium
Natural tritium is rare and on high demand = expensive
Tritium needs to be artificially produced
Waste production
Needs high temperatures and pressures
Process
Thermonuclear - nuclear reactions occur at high temperatures
Electrons stripped from atoms → electrons separated from nuclei → nuclei repel each other and mov incredibly fast → temperature rises → two light nuclei fuse together → heavy nuclei → energy
Infrastructure
Magnetic confinement (tokamak)
Plasma in donut-shaped chamber is squeezed using magnetic field
Plasma movement confined
Generates stable continuous plasma → nuclear fusion occurs
Inertial confinement
Uses pulses from powerful lasers to heat surface of fuel pellet
Pellet fuses when hot and dense
Nuclear fusion occurs → pulses of energy
Emerging technologies
ITER
Multinational collaboration
World’s largest tokamak
Aims to achieve net energy gain
More output than input
500 MW from 50 MW
In-vessel tritium production
NIF
Laser-based inertial confinement
Aims to achieve net energy gain
Laser beams → amplifier of mirrors and optics → beam converges at holruam → shock wave → heat → fusion reactions
Nuclear Fission
Nonrenewable
Splitting atoms of neutrons to release energy in form of heat and radiation
Uranium ore is finite → cannot be replenished once mined
Small amounts of uranium can generate a lot of energy
Process
Mills
Transport uranium ore → crush to fine particles → leach
In-situ leaching
Dissolve uranium ore using leaching solution → pump up desired minerals
Uranium chain reaction
Fission of atom → release of neutrons → split other atoms → release neutrons
Uranium
235 - less common, fissile
238 - fertile
Infrastructure
Nuclear power plant
Fuel rods
Steel rods with radioactive pellets
Reactor
Inside rods
Fission occurs in atoms → release heat
Rods lowered in water → steam created
Turbine
steam → turbine → powers generator → produces electricity
Condenser
Steam turned back to water → water can be reused
Cooling tower releases excess steam
Emerging technologies
Thorium fuel
More abundant in Earth’s crust
Cleaner than uranium
Not fissile → requires processing
Small modular reactors (SMRs)
Safer
Smaller carbon footprint
Constructed in rural areas
Efficient
3D printing and AI
Available
Safer
Needs less onsite workers
Natural Gas
Nonrenewable
Made from hydrocarbons
Formed by remains of organisms through pressure and heat over time
Used in electricity, heating, transportation
Process
Extraction
Conversion
Infrastructure
Wells
Processing plants
Pipelines
Storage facilities
Hydroelectric Energy
Inexhaustible
Running water
Hydropower - energy transferred from water to generator
Water cycle is unending → powered by sun
Process
Something diverts flow of water
gravity → water from higher to lower elevation → water flows through penstock (pipe) → turns turbine → generator → mechanical energy to electrical energy
Infrastructure
Needs reservoir/lake, river, change in elevation
Water diversion
Dam with penstock
Power plant
For processing
Generator, turbine, pump
Power grid
Distributes power
Emerging technologies
Archimedes screw
Fish friendly
Efficient - operates in rivers with low flow speed
High cost
Composite materials could be used to lower cost
Hydropower digitization
Capture production values
Faster fix time
Can quickly assess unexpected behavior
hydEA (hydro, efficiency, analysis)
Hydro-clone (RTSM)
Hybrid power
Combination of many renewable systems in one area
Hydropower
Ow cost for generators and transmission systems
Pumped storage
Geothermal Energy
Inexhaustible
Energy using heat stored in Earth
Continuously replenished by decay of radioactive elements
Captures heat from Earth’s crust from geothermal plants
Direct use or electricity generation
Direct use - direct heating purposes
Process
Need to identify and explore potential geothermal sites
Power plants
Drills into reservoirs of underground water and steam → hot water brought to surface → produces steam → drives turbines for electricity → steam condenses water → water re-injected into surface again
Dry steam power plants
Hot, pressurized steam → electricity
Flash steam power plants
water → steam and water → electricity
Binary steam power plants
Heat from water → liquid → steam
Infrastructure
Power generation - well pads, drilling rigs, production well, turbine, generatore, injection well, heat exchanger
Environmental mitigation - injection system, environmental monitoring
Geothermal vents
Deep well drilled into Earth
Obtain heat or pump liquid
Turbines
Pump steam from vents → turn turbines → electric generator
Transmission lines
Carried electric energy from one point to another
Condensers
Condenses steam → liquid water → pumped into Earth
Emerging technologies
Enhanced geothermal systems (EGS)
Man-made reservoirs
Increase permeability of subsurface
Fluid injected → reopens pre-existing fractures
Liquid circulate and heat up
Advanced geothermal systems (AGS)
Closed loop systems
Fluid kept inside wells → exposed to heat
Reduces water consumption
Risks inducing earthquakes
Can be applied anywhere
Advanced drilling techniques
Potential carbon-free geothermal energy
Hydraulic fracturing techniques
Fracking - creating fractures in rocks and rock formations by injecting specialized fluid into cracks to force them to open further
Fracking hot rocks
Related to EGS
Oil/Petroleum
Nonrenewable
Limited supply due to time to replenish - needs millions of years, no replacement
Algae, bacteria, sediment → heat and pressure over millions of years → created sedimentary basins → compressed into erogen → hydrocarbons
Process
Petroleum extracted as crude oil
Oil rigs and oil platforms
Air rotary drilling rig
Refining process for crude oil
Distillation towers → heated
Different components of crude oil → condense on different layers
Oil prepared for future use
Infrastructure
Oil rigs and platforms
Pipelines
Refinery plant
oil → fuel
Electrical plant
fuel → electricity
Electrical grid
Power → people
Emerging technologies
Safety
Robotics
Drones
Efficiency
AI
Cloud computing
Sustainability
Carbon capture
Storage systems
Coal
Nonrenewable
Sedimentary rock with carbons and hydrocarbons
Slow process, slowly replenished
Organisms die → buried under earth → heat and pressure → chemical and physical change → coal
Process
Surface mining
Electric + hydraulic shovels, drills, bulldozers
Remove overburden
Cheaper option
Torn landscapes, habitats and ecosystems destroyed
Underground (longwall) mining
Thick and large panels of coal are sliced off by longwall shearers → panels moved by a conveyor belt + shuttle cars back to the surface
Processing in power plants
Coal combustion → heat production → high-pressure steam → drives a turbine → produces electricity → electric current transmitted through power lines → homes, buildings
Biomass
Renewable
Living or recently dead organisms or organism byproducts
Biofuel - liquid resultant from biomass, can be used as fuel, emits less carbon
Process
Can be burned directly for heating and electricity
Pyrolysis
heating organic material without oxygen → start chemical reactions in biomass → turn to biofuel (bio-oil, bio-char, synthetic gas)
Gasification
Heating solid waste with small amounts of oxygen
Produces syngas and slag
Syngas - used in transportation and fertilizer
Slag - used in cement and asphalt
Fermentation
Anaerobic process → converts sugars in organic matter to alcohols and acids → creates ethanol
Dehydrate ethanol → high concentrations of alcohol
Infrastructure
Facilities to support feedstock production, biomass, transportation, biofuel production, and biofuel transportation
Feedstock - growing crops and livestock for waste
Transportation - large energy input
Biofuel production - various technologies
Biorefineries - costly, does all work in converting biomass into resources
Biofuel transportation - similar to traditional gasoline and diesel engines
Atom
smallest unit of a chemical element; made of protons, neutrons, electrons
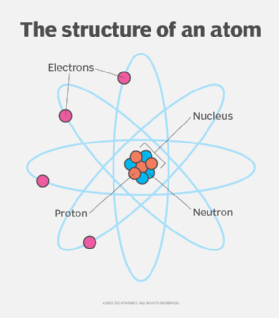
Protons
positively charged particles
Electron
negatively charged particle
Element
Substance made up of atoms of the same type and cannot be broken down
Isotope: different number of neutrons
Ion: different number of electrons
Bohr Model vs. Electron Shell Model
Bohr (planetary) model uses simple drawings of rings to showcase energy levels
Electron Shell Model has electron shells (more accurate since electrons don’t just go in a flat orbit)
What does having more electrons on the valence shell indicate?
More electrons on valence shell means more stable (each shell can hold a certain number of electrons, but valence shell can only hold max of 8 electrons)
Coulomb’s Law
Attractive force (electrostatic force) between 2 charges in inversely proportional to the distance between them
as distance between nucleus and valence electrons increase, less ionization is needed to move electrons
Explains why certain atoms with same number of valence electrons have different conductivities
Ex. silver is a better conductor than copper because silver’s valence shell is further from nucleus, even though they both have the same number of valence electrons
Electricity
Flow of electric charge
Can occur naturally (ex. lightning) can be controlled using circuits
Conductance
Property that describes a material’s ability to allow flow of electric charge
Ionization Energy
Amount of energy needed to remove an electron from the valence shell
Conductors
A material with high conductance
Electrons flow easily between atoms
1-3 valence electrons in outer orbit
Low ionization energy
Ex. silver, copper, gold, aluminum, platinum
Insulators
A material with low conductance
Electron flow is difficult between atoms
5-8 valence electron in outer orbit
High ionization energy
Ex. Mica, glass, quartz, sulfur
Quartz is also piezoelectric (can generate AC voltage when subjected to mechanical stress or vibration)
Current
Flow rate of electric charge in a circuit
Amount of charge (Q) per unit time unit that passes through an imaginary surface that is perpendicular to the motion of the charges
Measured in Coulombs/sec = amps
Atoms do not move → electrons jump from valence shell to valence shell
Resistance
Measure of how difficult it is to pass amount through a wire/component (Ω)
Depends on resistivity, length, and cross sectional area
R=ρL/A
Increase length = increase friction
Designers have control over components
Resistivity
Measure of a material’s ability to resist the flow of charge (Ωm)
ρ=E/J
E = electric field (N/C or V/m): physical field that surrounds electrically charged particles
J = Current Density (per unit area): current that flows per unit area of chosen cross section
J=I/A
Intrinsic material property and reciprocal of conductivity
Meanwhile, resistance takes into account length of component
Direct Current
One direction
Anode → circuit → cathode
Useful, portable, can be converted to AC
Voltage and current can vary but direction is constant
Alternating Current
Electrons alternate directions
Current moves along rotating wire
Direction of current periodically changes
Generates sinusoidal graph
Conventional Current Model
Assumes positive charge flows from cathode through circuit and into anode
Same result as electrons flow
+ sign corresponds with high electric potential energy
use this one
Electron Flow
Electrons flow from anode (high energy state/electric potential) to cathode (low energy state/electric potential)
Field
Physical quantity represented by number, array of numbers or function that value can be assigned to at every point in space-time
Spread over large region
Interact with objects in field
Electric Field
Originate from electric charge or time-varying magnetic field
Shows direction positively charged particles will move when placed in field
Electric fields act with on other electric charges placed in field - attract or repel
Vector quantity
Describes electrical force exerted by charge
Voltage
Change in work required per unit charge to move charge from point A to point B in circuit
ΔV = W/q
Measured in joules/Coulomb → volts
Δv measured by voltmeter represents voltage drop or rise across circuit component
Drop - voltage lost, resistance
Rise - voltage gain, power source
Drops = rises
More voltage = more electron flow
If two points are at same EPE, no work
EPEB = EPEA
WAB = 0
Batteries
use DC
anode: negative end
cathode: positive end
idk what else
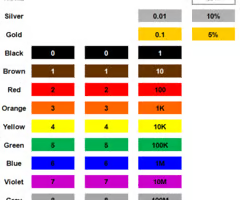
Reading Resistor Values
first band + second band (at face value) * multiplier ± tolerance
Example: first band: 1, second band: 0, multiplier: 100, tolerance: 5%
10*100 Ω ± 5%
1000 Ω ± 5%
Cell Circuit symbol
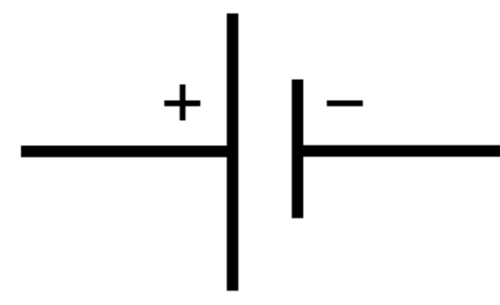
Battery Symbol
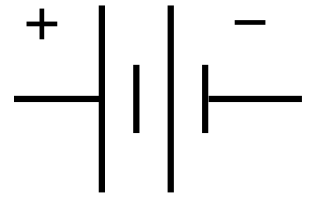
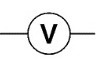
Voltage Source Symbol
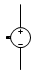
Switch Circuit Symbol
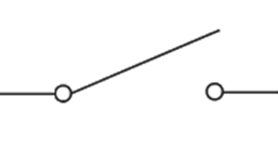
Voltmeter Symbol
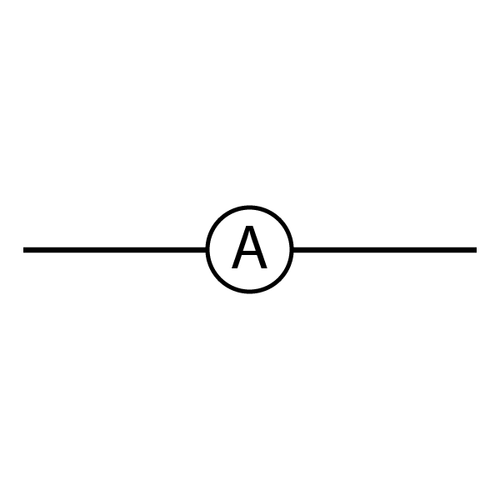
Ammeter Symbol
Resistor Symbol

Variable Resistor (Potentiometer) Symbol
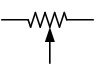
Inductor Symbol
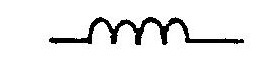
Capacitor Symbol
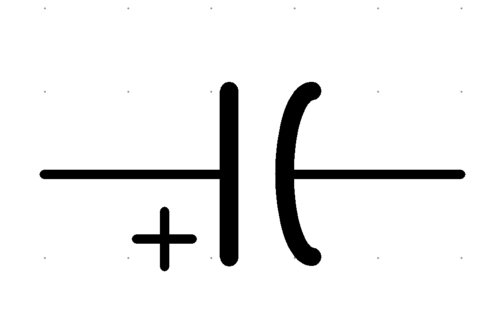
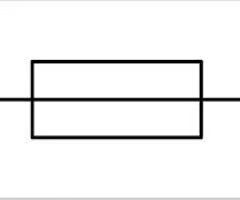
Fuse Symbol
Diode Symbol
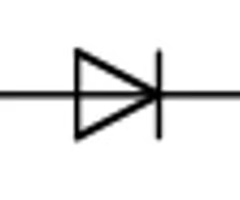
Light Emitting Diode (LED) Symbol
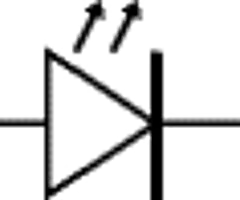
Earth Ground Symbol
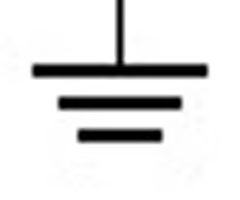
Chassis Ground Symbol
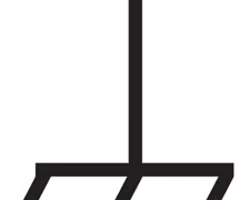
Pushbutton Switch Symbol
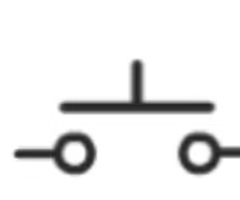
Electric Wire Symbol

Motor Symbol

Circuit Diagram
line represents wires
no current flows if the lines (connecting devices) do NOT form a closed loop
Circuit’s Ground
Additional path for electrical current to return safely to Earth (ground) without danger in the event of a short circuit
circuit breaker will trip to protect circuit is fuse blows out
Multimeter
device used to measure the various attributes of an electrical circuit (current, resistance, voltage)
display
buttons
dial for measurement section (voltage, resistance, current, continuity, etc.)
Red probe: measuring lead (+)
Black probe stays in "COM" port
move red probe depending on what is being measured

Voltmeter
A device used to measure voltage, or electrical potential energy difference
place voltmeter PARALLEL with component to measure voltage, drop/gain across component
do not place in series with components
red probe on high potential side (+)
black probe on low potential side (-)
Ammeter
a device used to measure current
place in SERIES with components
do not place in parallel with component → creates shirt circuit and increased total current in circuit → blows out fuse
has zero resistance
negligible affect on total resistance in circuit
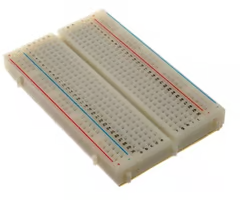
Breadboards
Reusable platform that allows you to temporarily build and then disassemble electrical circuits
power rails: red and blue (black) columns located at A and D
red column: current enters circuit from power supply
blue (black): current leaves circuit and returns to power supply
provides ability to quickly modify components during development and testing
no soldering needed to make circuit connections
Electrical Polarity
refers to whether a circuit component is symmetric or not
Non-Polarized
symmetric component where current can flow through it in either direction (wire, resistor, etc,)
no correct input or output side (two-way street)
current flows in either direction
Polarized
component with polarity, allowing current flow in one direction
Ohmmeter
disconnect power supply from circuit
switch to ohmmeter mode
place in PARALLEL with resistor
Open Circuit
An incomplete circuit due to an opening or gap that prevents direct current (DC) flow
Short Circuit
When a path of lower than intended resistance is provided for the current, usually as the result of some sort of accidental contact (shortcut for the current)
Resistance of Circuits in Series
Rt = R1 + R2 + … + Rn
Current of Circuits in Series
It = I1 = I2 = … = In
Resistance of Circuits in Parallel
1/Rt = 1/R1 + 1/R2 + … + 1/Rn
Current of Circuits in Parallel
It = I1 + I2 + … + In
How to decrease system efficiency
increasing time
decreasing force
increasing current
How to find mechanical system efficiency
find work output (W = Fd)
find power output (Pout = Wout/t)
find power input (Pin = IV)
find efficiency (Pout/Pin * 100)
When is maximum motor power delivers?
half the stall torque
Convert RPM → rad/s
#rev/min * 2pi rad/60 seconds
How many times is the function “setUp()” ran?
once
Which function begins the serial monitor?
Serial.begin()
If a button is being pushed, what does digitalRead(pushButton) return?
1
What is a duty cycle?
% of time signal is HIGH
What symbol indicates that a pin has PWM capabilities?
~
How is the color violence made using the RGB LED?
violet = red + blue
(255, 0, 255)
How to import library into C
DHT11 → #include <DHT.h>
PWM
A technique that allows you to simulate an analog signal using digital means
PWM values range
[0, 255]
potentiometer values range
[0, 1023]
Wire color conventions
Black: ground
Red: 5V
Orange: 3.3V
Other colors for signal wires
digital pins
allows you to connect digital sensors and other integrated circuits
allow you to read digital inputs and control outputs
digital signals are either HIGH (1) or LOW (0)
pins 0-13 for GPIO
digital pins 3, 5, 6, 9, 10, 11 have a ~
allows you to perform PWM
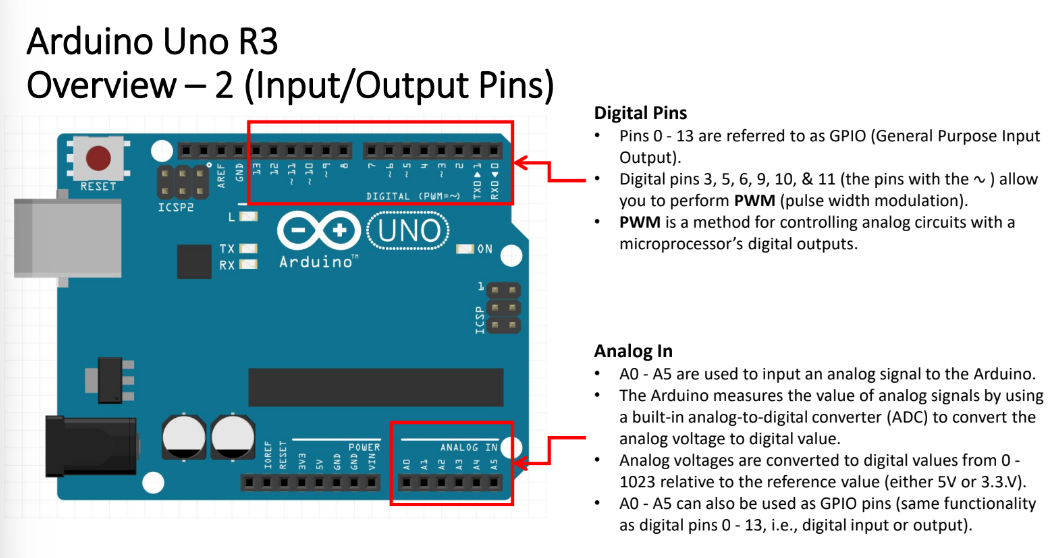
Analog In
used to read analog inputs
analog signals can take an infinite number of values within a range of values
A0 - A5 used to input analog signal from Arduino
Arduino measures the value of analog signals by using ___, which converts ___ to ___
analog-to-digital converter (ADC); analog voltage; digital value
Analog voltages are converted to digital values from the range __
[0, 1023]