THE ROLE OF COENZYMES IN BIOCHEMICAL PATHWAYS
1/28
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
29 Terms
ATP, NADH, NADPH, CoA AND FADH2 roles
- ATP: Carries useable energy
- NADH: Electron carrier; transfers electrons to electron transport chain.
- NADPH: Reducing agent; used in biosynthesis of molecules.
- CoA (Coenzyme A): Carrier of acetyl groups
- FADH2: To transfer protons/electrons to the site of the ETC Or accepts ions during Krebs cycle
Define cofactors
additional non-protein molecules needed for enzyme activity and stability
Define coenzymes
organic cofactors needed for enzyme activity and stability, such as those used in cellular respiration and photosynthesis
What are the major coenzymes involved in photosynthesis and cellular respiration?
NAD (nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide)
NADP (nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate)
FAD (flavin adenine dinucleotide)
ATP (adenosine triphosphate)
CoenzymeA (CoA)
What can cofactors also be other than organic?
Inorganic
Define inorganic
Do not contain carbon
Include metal ions
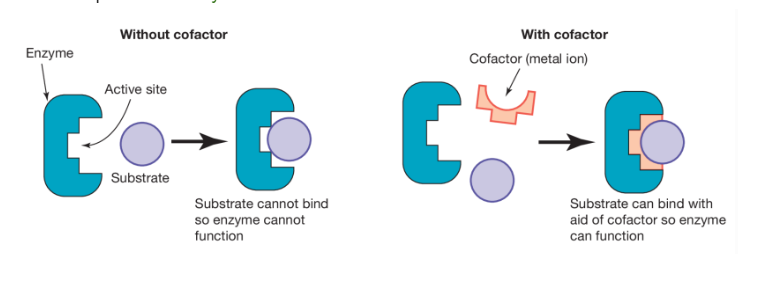
What do some enzymes include to aid the substrates binding?
What does this do?
Many enzymes include a metal cofactor
Form bonds at the active site of their enzyme and also bond with the substrate
As a result, the substrate is temporarily held (with help from the cofactor) in the position required for enzyme action
Diagram with cofactor?
Define organic factors?
Small non-protein organic molecules that are essential for the function of particular enzymes.
What do organic cofactors comprise of?
Prosthetic groups
Coenzymes
Define prosthetic groups
cofactors that are tightly bound to an enzyme and are essential for it to function as a catalyst
Define coenzymes
cofactors that are loosely bound to their enzymes only when the enzyme is acting on a substrate
What is the role of coenzymes in biochemical pathways?
Assist some enzymes to perform their catalytic actions
What are the specific roles of coenzymes in biochemical pathways?
Transferring of atoms or groups of atoms, such as hydrogens, phosphate groups and acetyl groups.
Energy transfers.
What two forms do coenzymes exist in?
a high energy form that is loaded with a group that can be transferred
a lower energy form that is unloaded
Unloaded vs unloaded form of nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (NAD) - which assists other enzymes crucial for cellular respiration
UNLOADED FORM:
NAD+
It accepts hydrogen ions and their associated electrons (receiver)
Energy level is low
Its redox state is oxidised
LOADED FORM:
NADH
It can donate hydrogen ions and electrons and transfer energy
Energy level is high - Unloads electrons so that the energy released is used in the production of ATP
Its redox state is reduced
What is the role of coenzymes involved in cellular respiration (ATP)?
transferring energy within cells
transfer of its energy to drive endergonic reactions in biochemical pathways
How is ATP removed/used in cellular respiration?
The third phosphate group is removed creating ADP (lower energy level).
How is ATP regenerated from cellular respiration?
ATP can be regenerated from ADP with the addition of a phosphate (Pi).
Endergonic reactions and ATP interaction
Coenzyme ATP transfers both energy and a phosphate group to assist the action of the hexokinase enzyme on its substrate
Glucose to form glucose-6-phosphate
Exergonic reactions and ATP interaction
Pyruvate kinase enzyme is assisted by an ADP coenzyme that accepts a phosphate group and energy from PEP, allowing pyruvate and ATP to be formed
What is a coenzyme involved in cellular respiration and what are its two forms?
FAD⁺ (flavin adenine)
An unloaded FAD⁺ and a loaded FADH2
What does FAD⁺ do?
Carries protons and electrons from one location to another within the mitochondria
What is the coenzyme involved in photosynthesis? What is its two forms?
NADP (nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate)
An unloaded NADP+ and a loaded NADPH.
Coenzyme use for cellular respiration vs photosynthesis
CELLULAR RESPIRATION
NAD+
FAD+
PHOTOSYNTHESIS
NADP+
Both
ATP
What does the photosynthesis pathway involve?
Adding hydrogen to form glucose
How is NADPH formed?
Formed from NADP+ using high-energy electrons produced by uptake of the radiant energy of sunlight.
NADPH formation equation
NADP+ + H+ + 2e- (double squiggle) NADPH
Each coenzyme exists in…
two forms