Telescope Optics and Their Functions
1/21
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
22 Terms
Earth's Atmosphere
Transparent to visible light and radio waves only.
Optical Telescope
Uses visible light to form images of celestial objects.
Radio Telescope
Detects radio waves from astronomical sources.
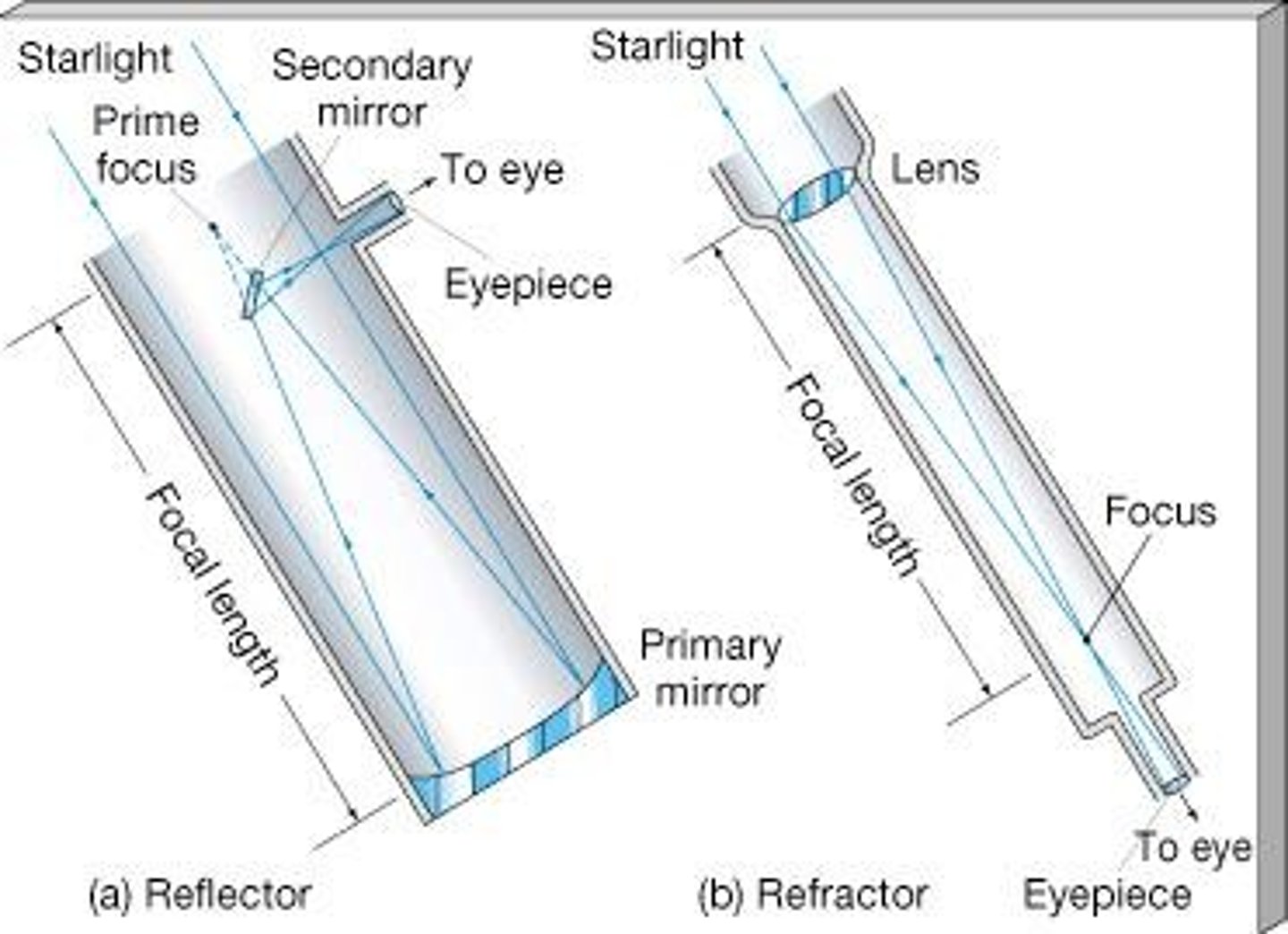
Refracting Telescope
Uses lenses to bend light for image formation.
Reflecting Telescope
Uses mirrors to reflect light and form images.
Primary Lens
First lens that light hits in a telescope.
Primary Mirror
First mirror that light hits in a telescope.
Eyepiece
Magnifies the image for easier viewing.
Focal Length
Distance from lens/mirror to formed image.
Chromatic Aberration
Color distortion in refracting telescopes' images.
Achromatic Lenses
Reduce chromatic aberration but are costly.
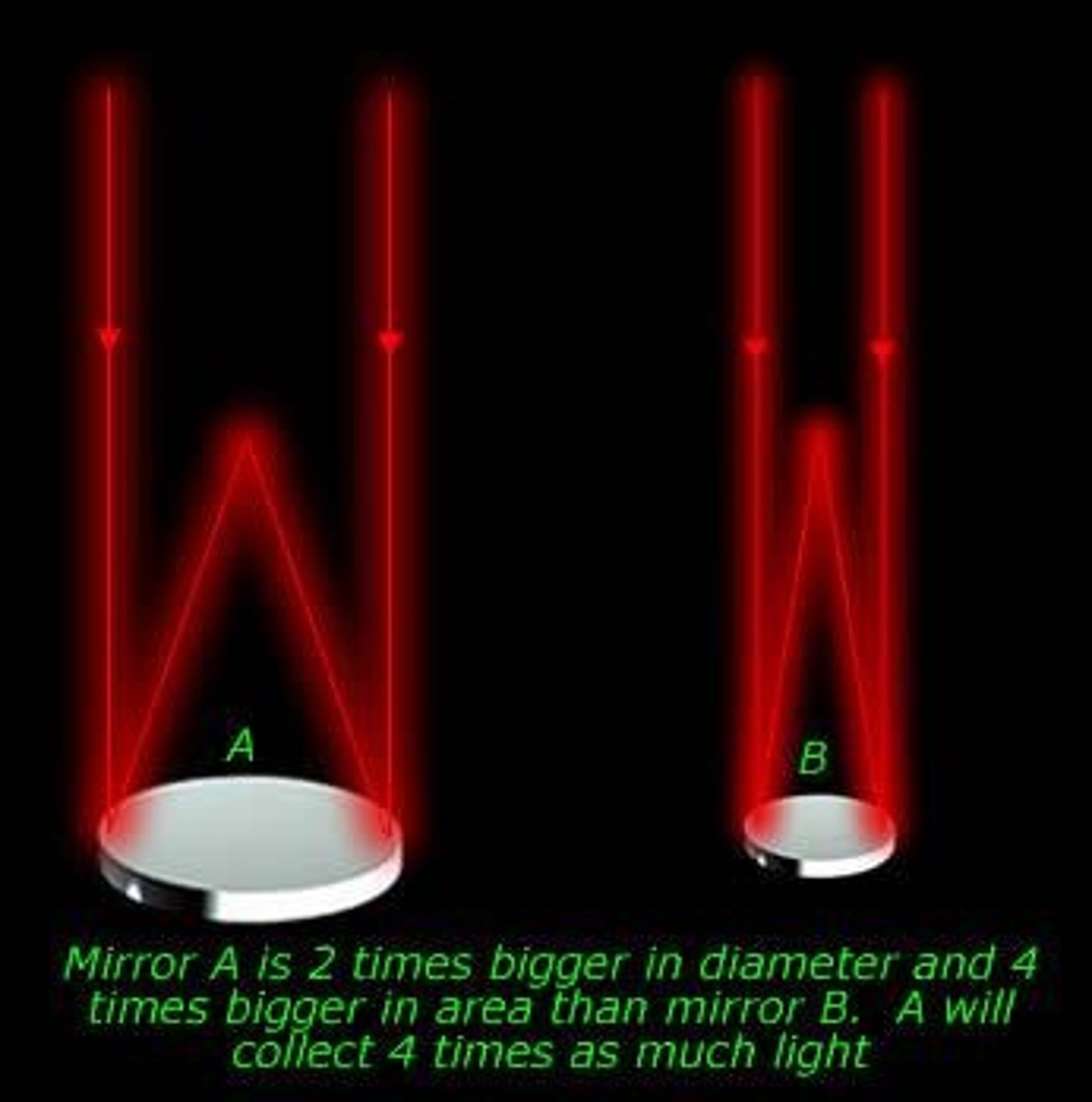
Light-Gathering Power
Telescope's ability to collect light effectively.
Resolving Power
Ability to reveal fine details in images.
Magnifying Power
Telescope's ability to enlarge images.
Diameter Importance
LGP and RP depend on telescope diameter.
Diffraction Fringes
Light wave interference around distant star images.
Telescope RP Calculation
RP = 13.8 / diameter in cm.
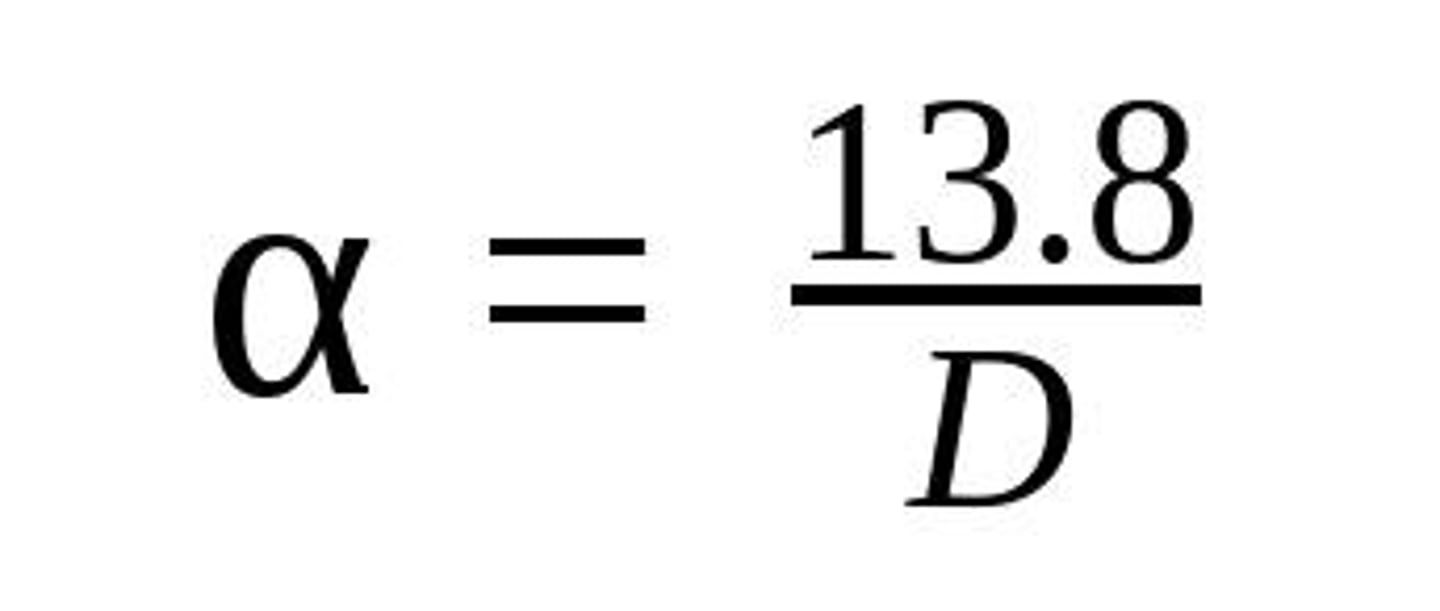
Magnifying Power Formula
Calculated by dividing objective focal length by eyepiece.
Light Pollution
Artificial light brightening the night sky.
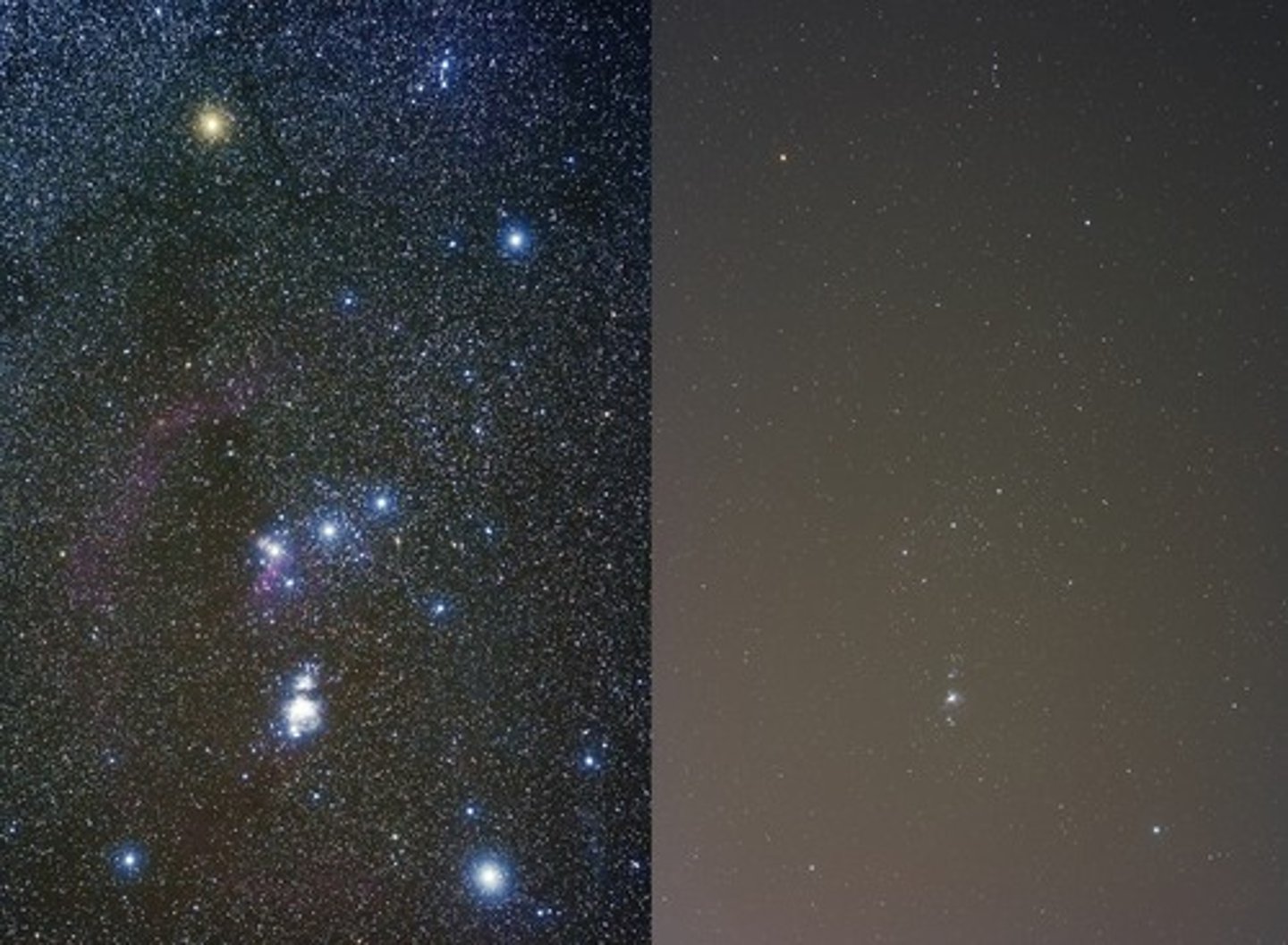

Optimal Telescope Placement
Far from civilization to minimize light pollution.
Good Optics
Prefer glass lenses over plastic for quality.
Solid Mounting
Essential for effective telescope performance.