IB BIOLOGY TOPIC 1
1/99
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
100 Terms
cell theory
- all living things are composed of cells
- the cell is the smallest unit of life
- cells only arise from pre-existing cells
challenges to the cell theory
- striated muscle challenges the idea that a cell has one nucleus
- giant algae challenges the idea that cells must be simple in structure & small in size
- aseptate fungal hyphae challenges the idea that a cell is a single unit
functions of life
- metabolism
- response
- homeostasis
- growth
- reproduction
- excretion
- nutrition
explain why small cells are more efficient than big cells
- larger surface area to volume ratio can act more efficiently
- diffusion pathways are shorter (takes less time & energy)
- concentration gradients are easier to generate
advantages of cells differentiating
- makes it possible to complete functions that individual cells can't do alone
- functions are performed faster
- the cell uses less energy because they only have to do one specific job
describe how new formed cells become specialized
Newly form cells get signals that tell them to deactivate (or activate) certain genes. Active genes are packages in an expanded form while inactive genes are condensed.
how many different distinct highly specialized cell types have been recognized by humans?
220
stem cell
is an unspecialized cell that can continuously divide & replicate, & have the ability to differientate into specialized cell types
totipotent
can differentiate into any type of cell
(ex: first divisions of embryonic stem cells)
pluripotent
can differentiate into many types of cells
(ex: embryonic stem cells)
multipotent
can differentiate into a few closely-related types of cell
(ex: adult stem cells, cord blood stem cell)
unipotent
can generate but only differentiate into their associated cell type
(ex: skin cell)
Stargardt's macular dystrophy
problem: causes progressive & eventually total loss of central vision
treatment: embryonic stem cells are treated to become retinal cells, & retinal cells are injected into the retina
benefit: stem cells are currently the only viable treatment for this condition
therapeutic cloning
for
- may lead to discoveries, beneficial technologies, cures
- transplants are less likely to be rejected
- does not require death of another human being
against
- involves destruction of human embryos
- embryonic cells may develop into cancerous cells
- alternative technologies may fulfill similar roles
- religious/moral objections
magnification
drawing size ÷ actual size
actual size
drawing size ÷ magnification
drawing size
actual size × magnification
resolution
the shortest distance between two points that can be distinguished
explain why electron microscopes have a better resolution than light microscopes
electrons have a shorter wavelength
ultrastructure
all the structures of a biological specimen that are at least 0.1 nm in their actual dimension
what's one thing that electron microscopes can see, but light microscopes cannot
viruses
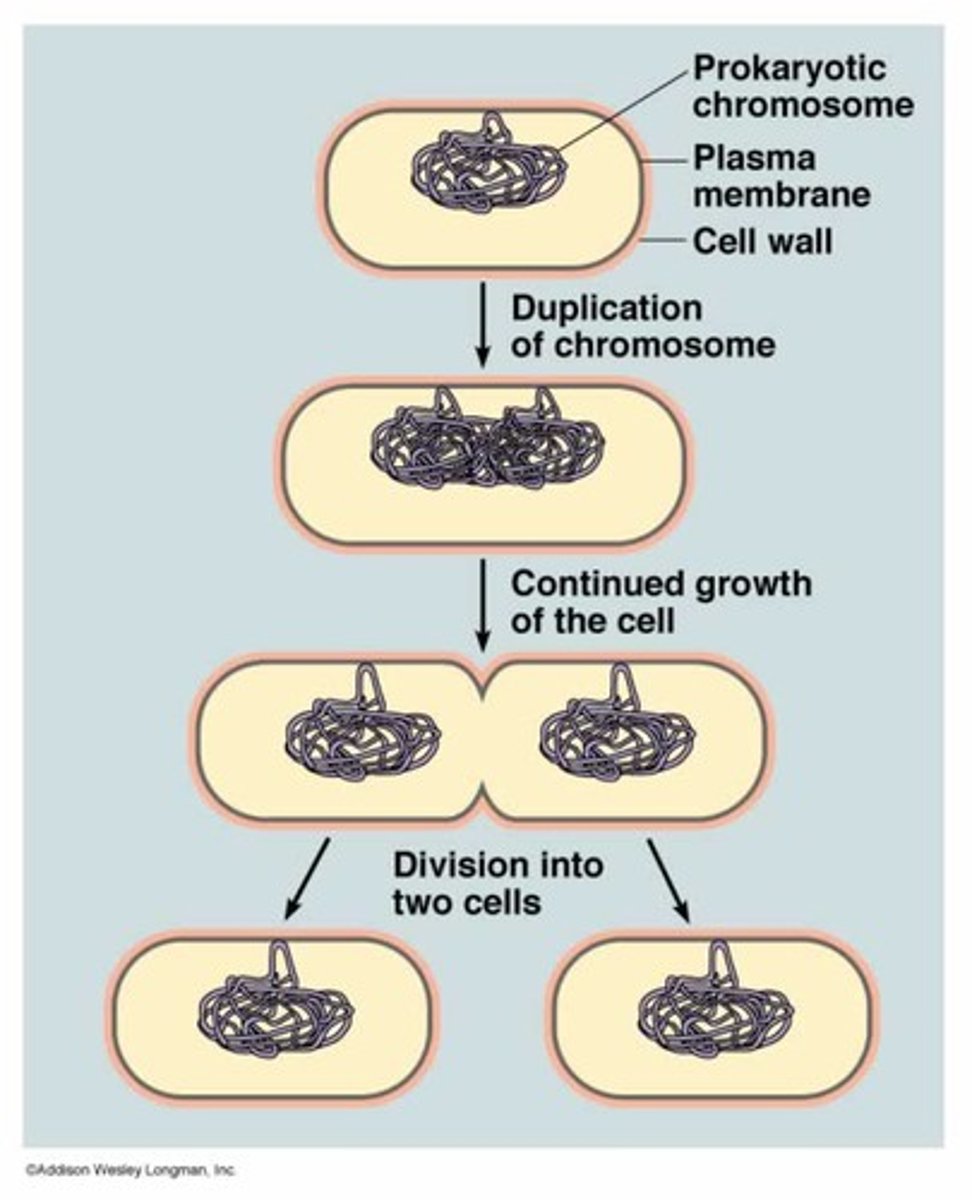
prokaryote
a single-celled organism that doesn't have a distinct nucleus with a membrane or specialized orgnanelles
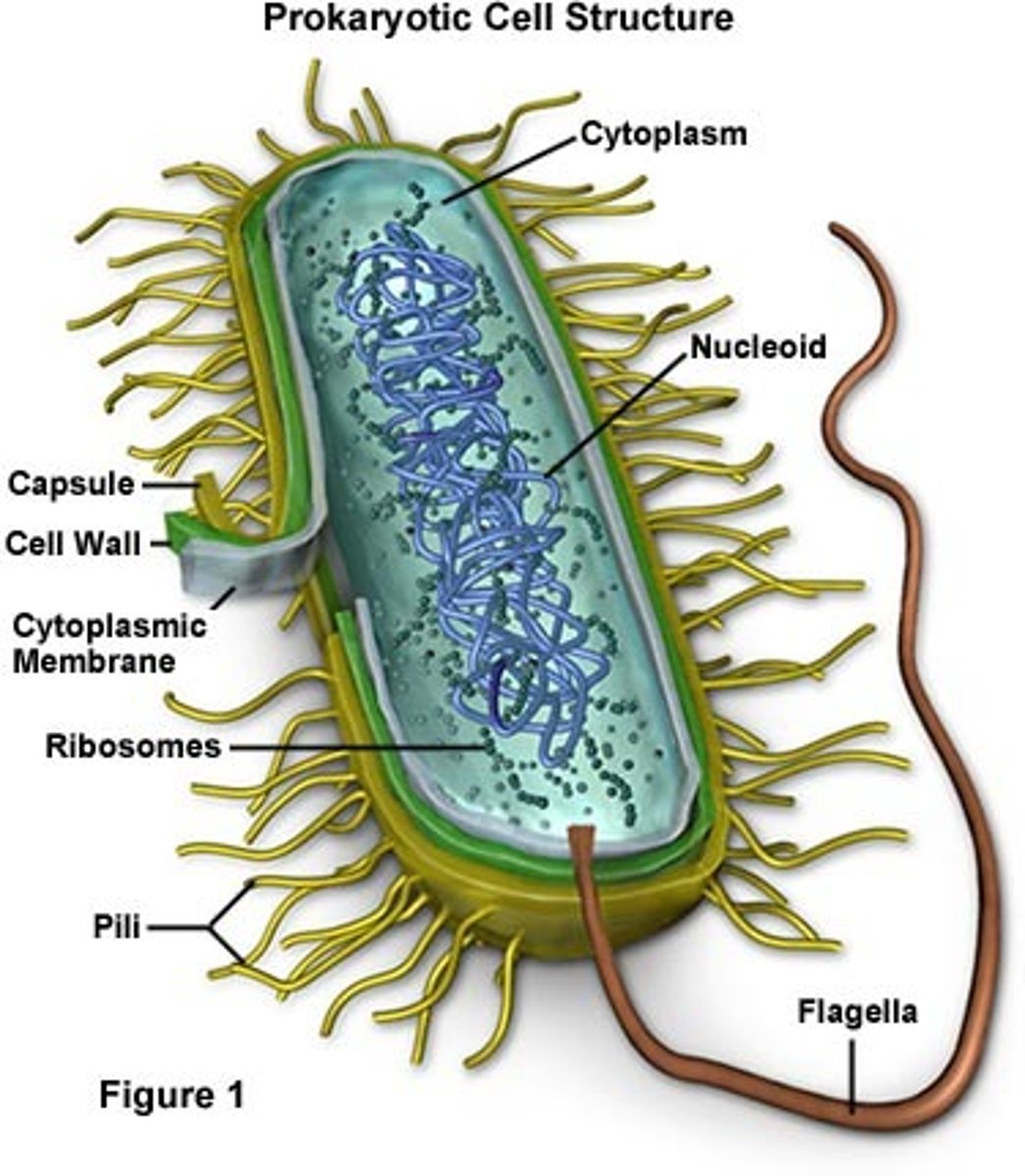
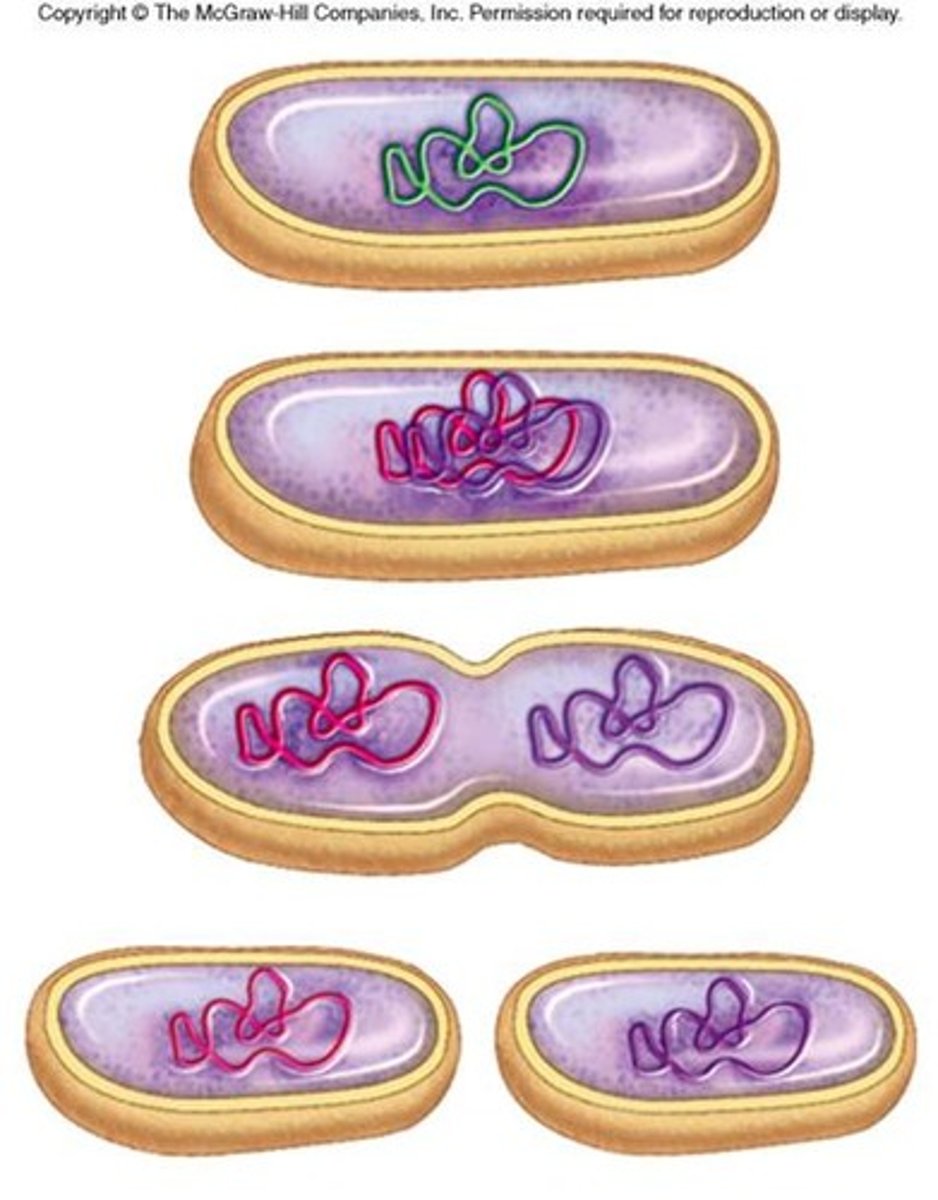
binary fission (process)
- DNA is replicated semi-conservatively
- 2 DNA loops attach to the membrane
- membrane elongates & pinches off
eukaryote
a cell which DNA is in the form of chromosomes contained within a distinct nucleus
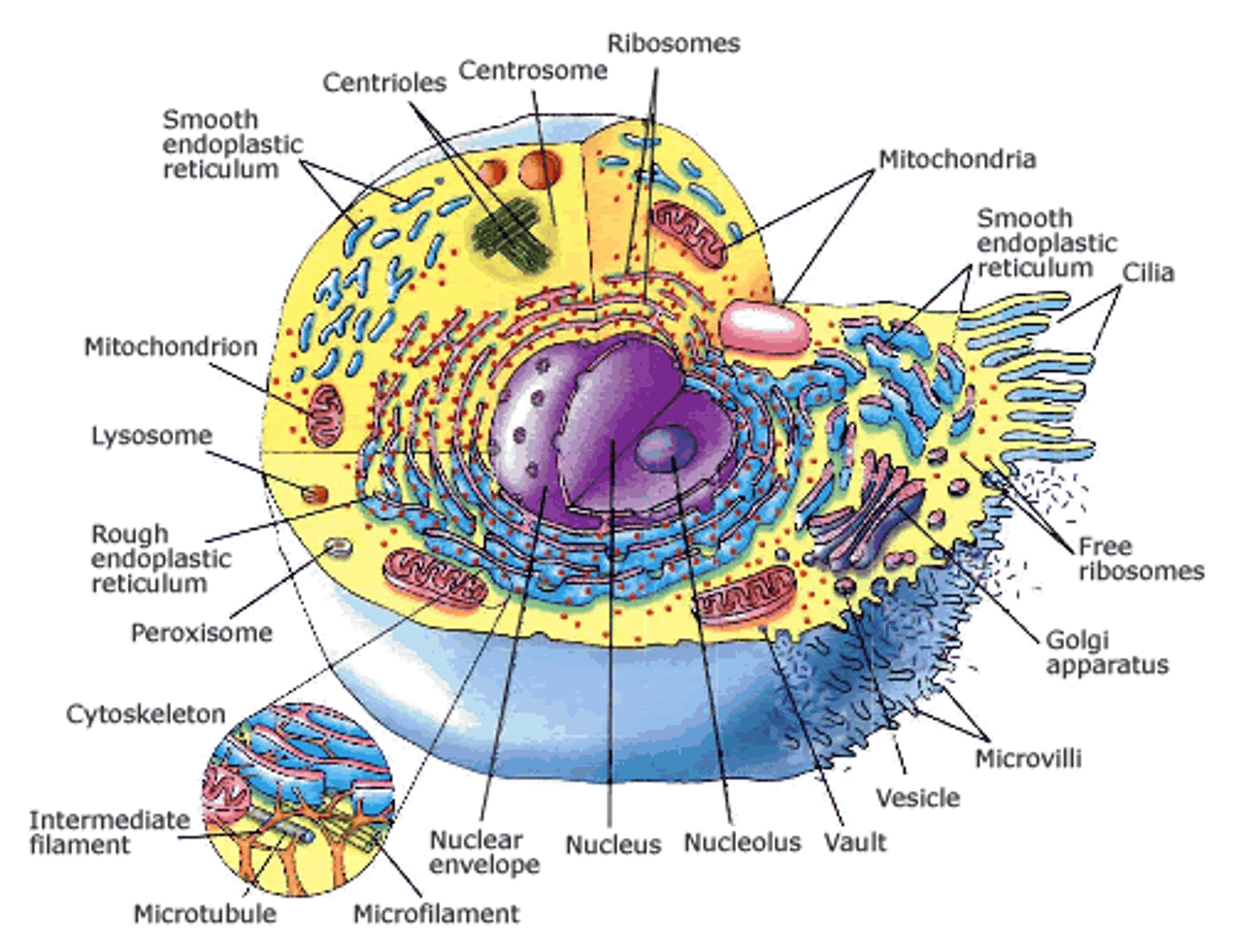
benefits of compartmentalization
- efficiency of metabolism
- localized conditions
- toxic/damaging substances can be isolated
cell wall
protects the cells, maintains its shape, & prevents excessive water uptake
plasma membrane
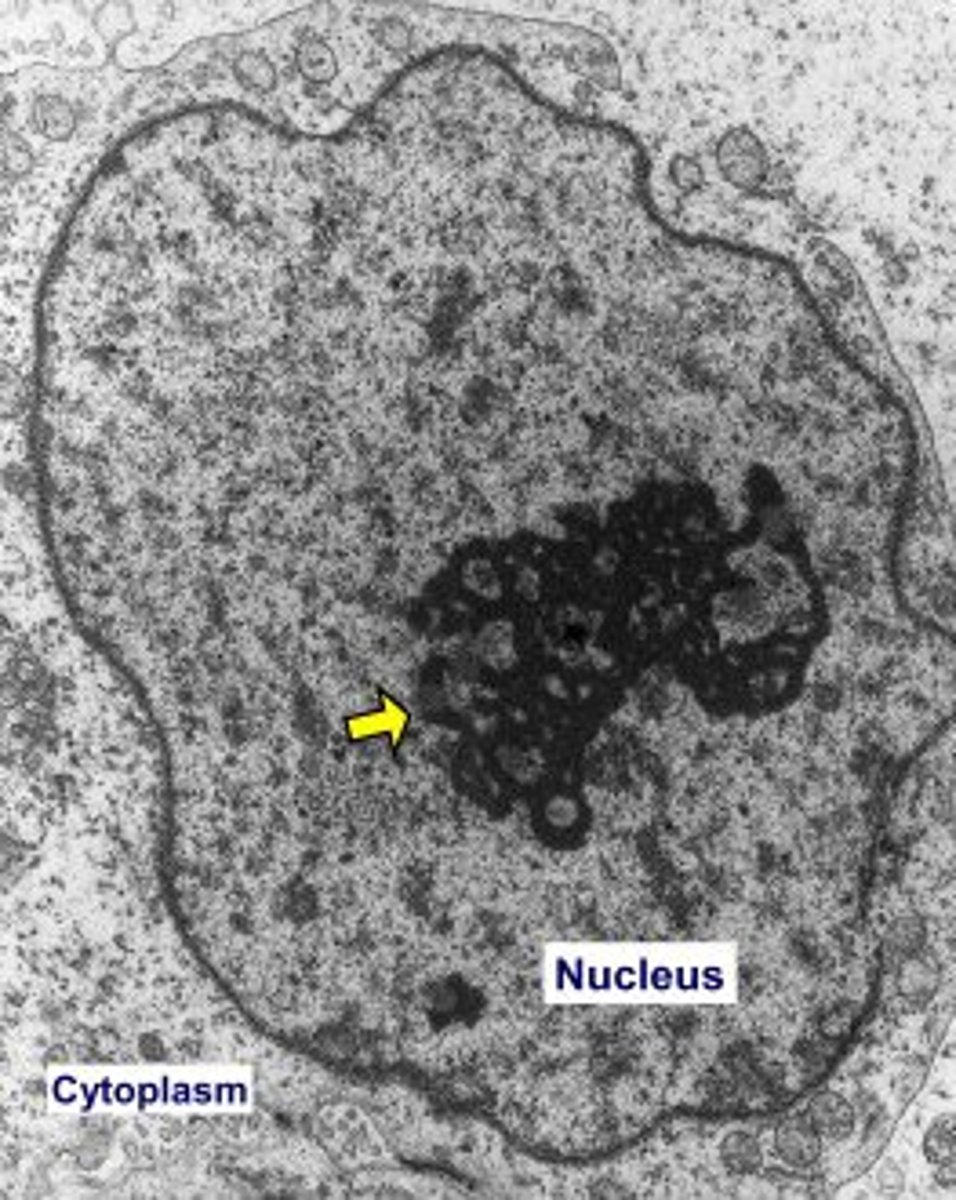
nucleus
- contains genetic info
- mRNA is transcribed here
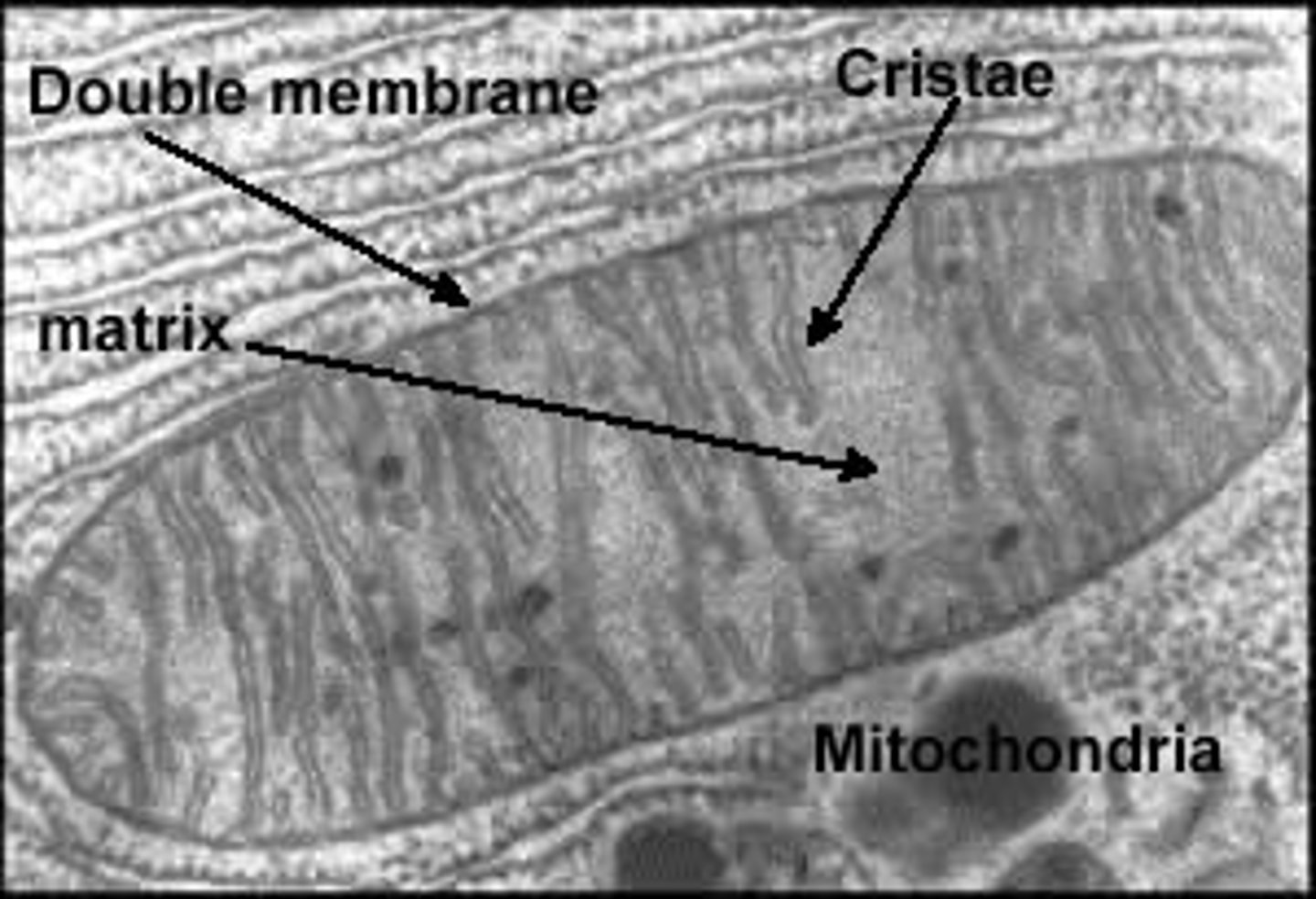
mitochondrion
- site of ATP production
- powerhouse of the cell
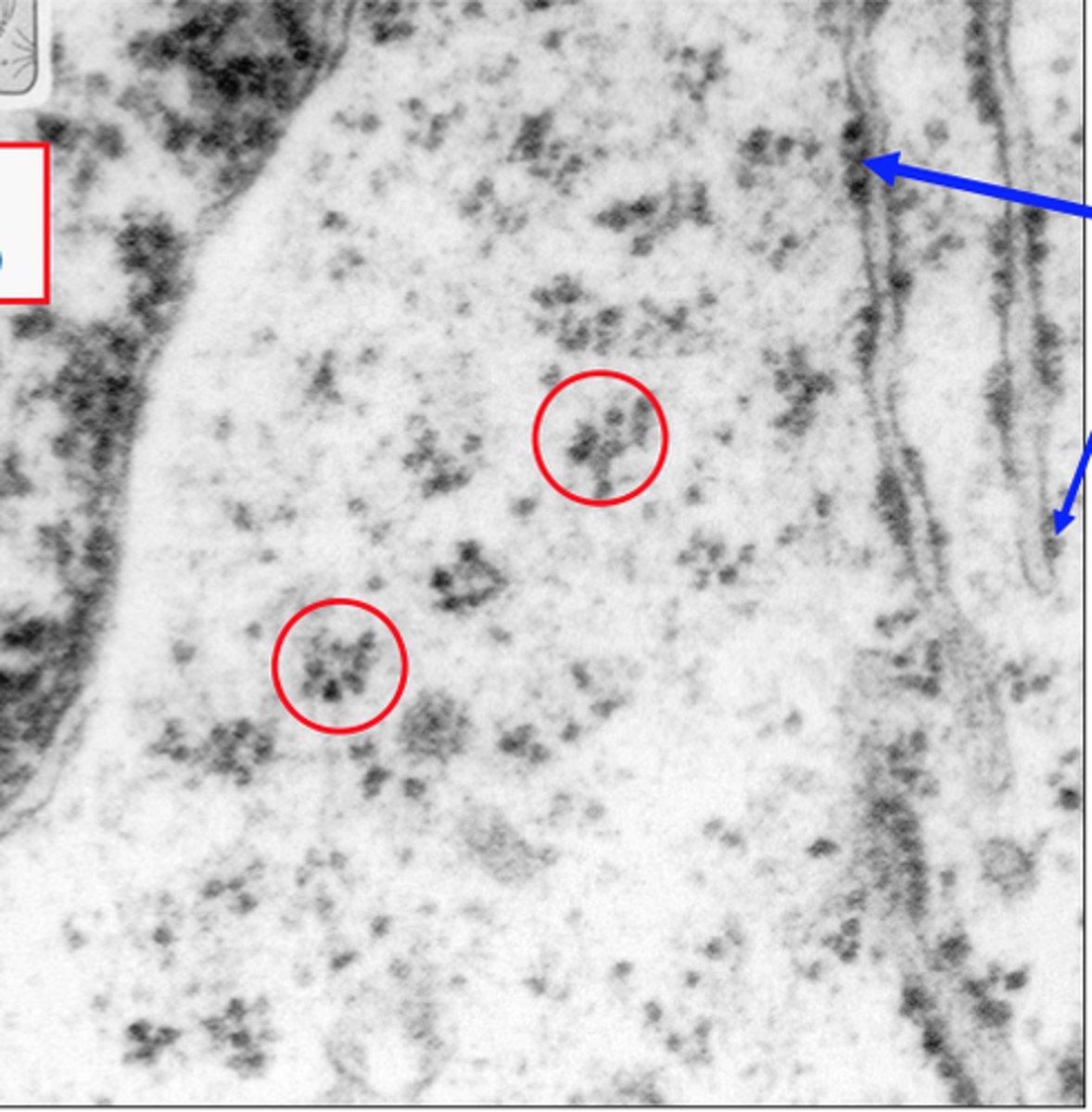
free ribosomes
synthesizes proteins to function in the cytoplasm
rough endoplasmic reticulum
synthesizes proteins which are to be transported to the Golgi for modification before secretion outside the cell
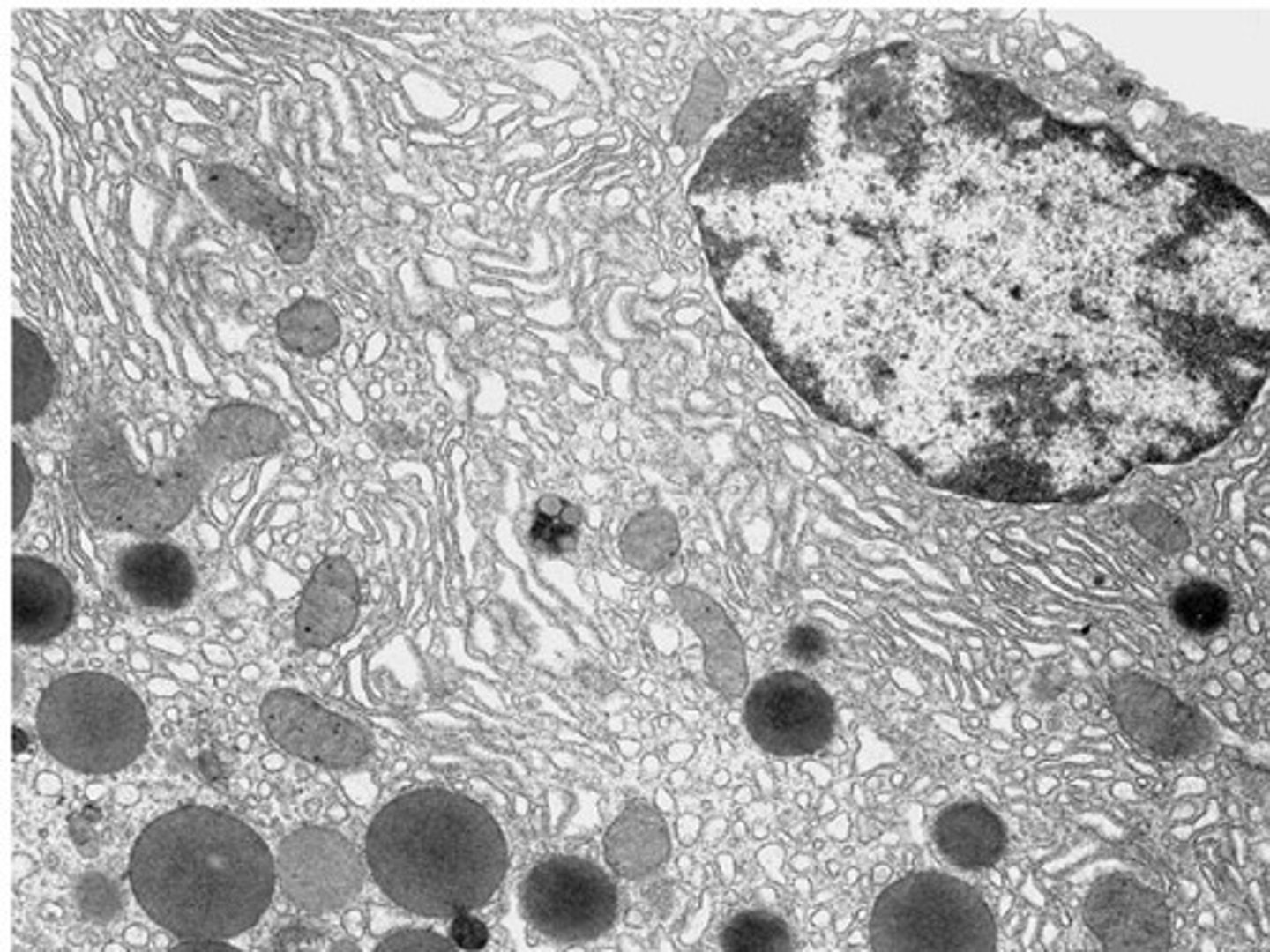
Golgi apparatus
- processes/modifies proteins from the rER
vesicles
- transport materials inside the cell
- proteins are repackaged here
lysosomes
break down ingested food in vesicles, unwanted/damaged organelles, & the cell itself
vacuoles
absorb & digest food
flagellum
used to move the cell
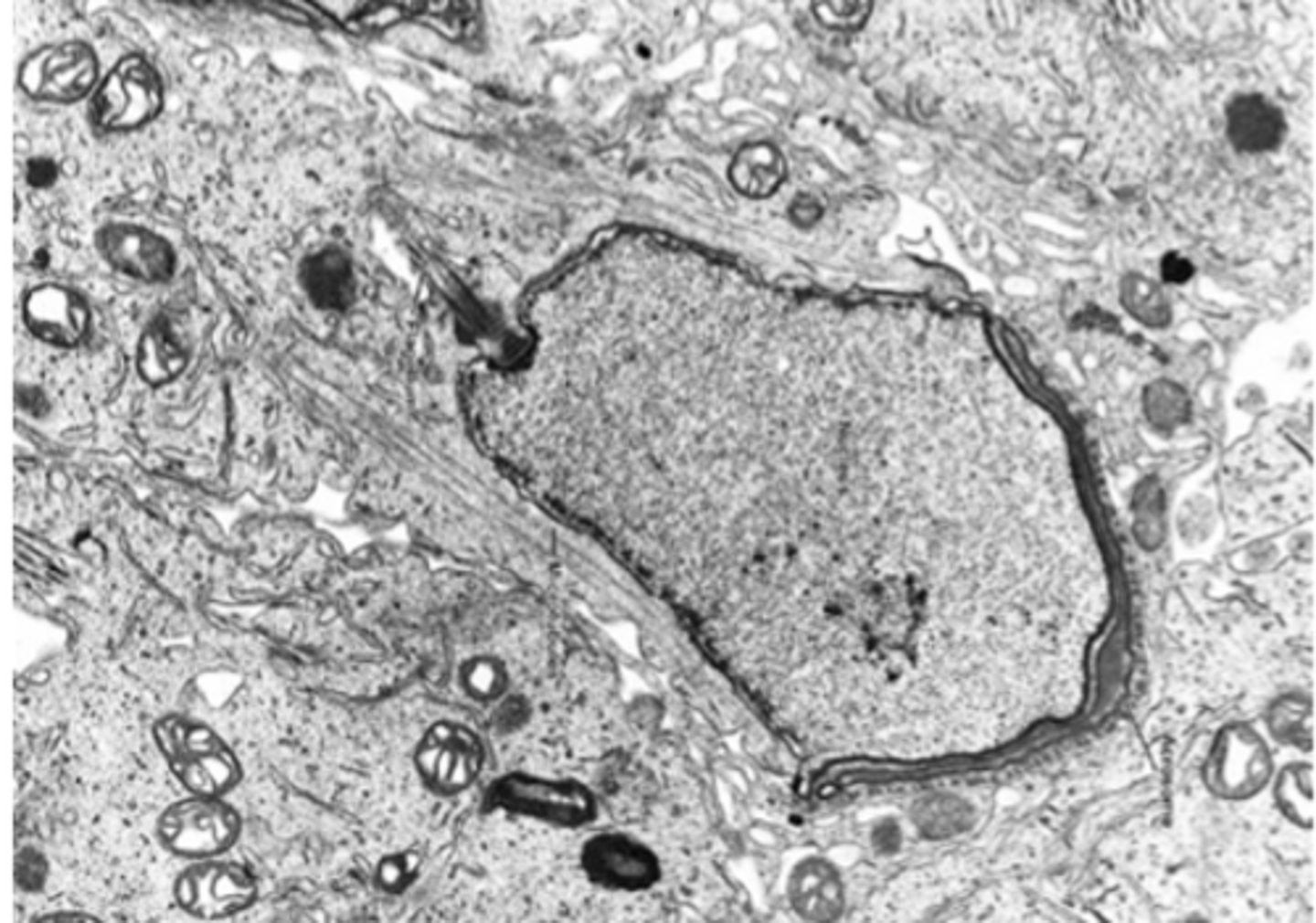
cilia
used to either move the cell or move the fluids next to the cell
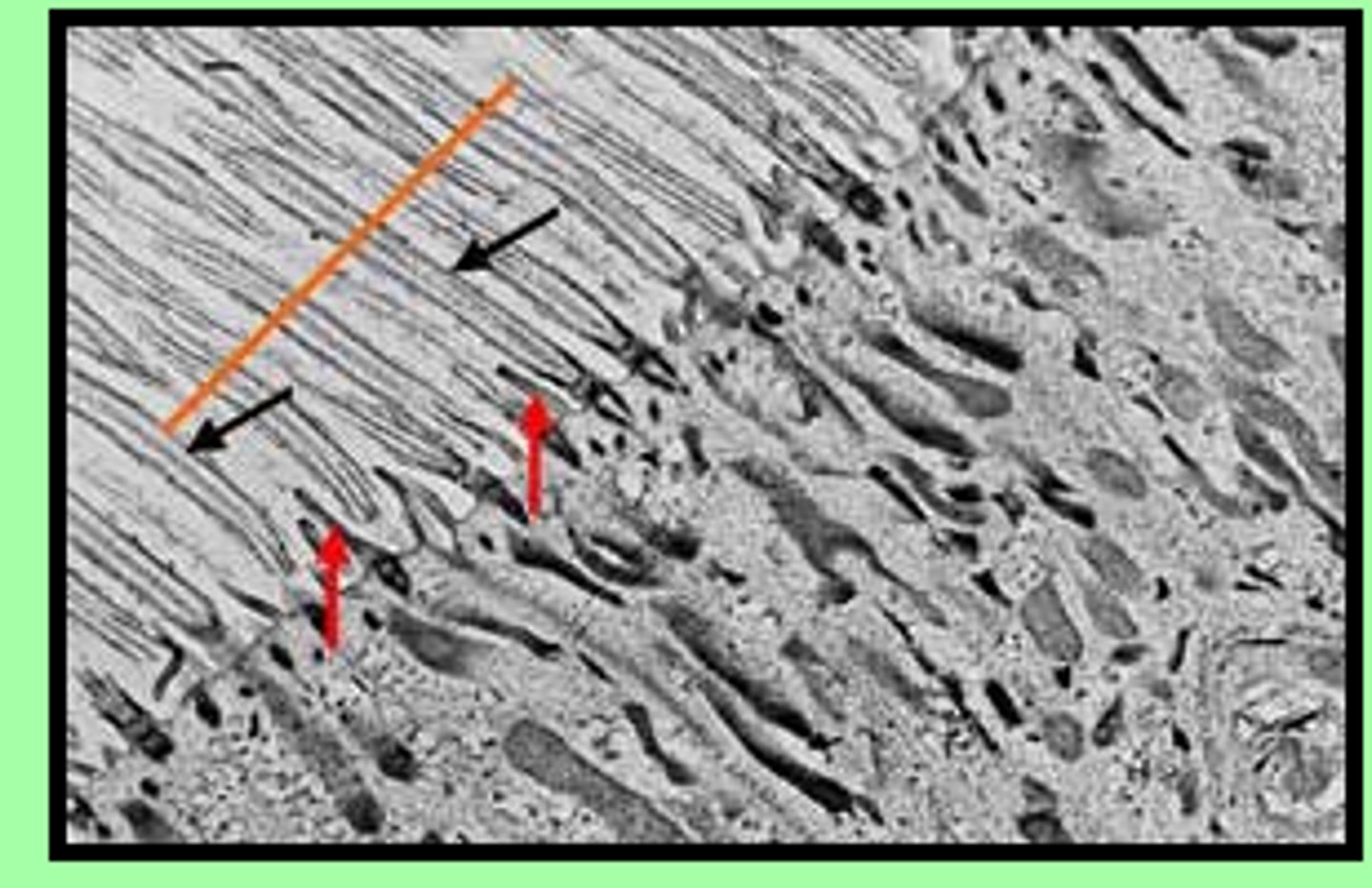

microtubules & centrioles
- part of the structure of flagella
- role in cell division
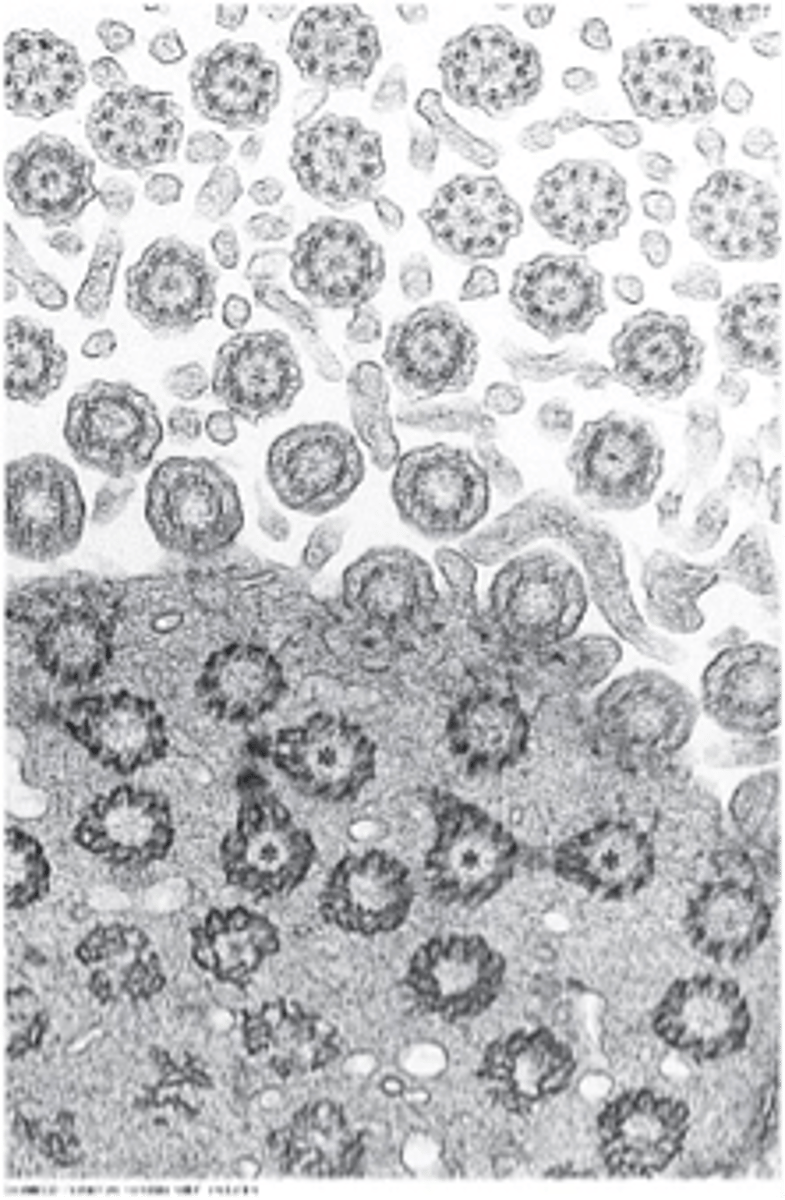
chloroplast
site of photosynthesis
cytoplasm
is made of water, proteins, salt & sugar
disproving Davson-Daniella Model
- freeze-etched micrographs (freezing & fracturing cells ➟ showed globular structures scattered in the center of the membrane)
- protein extraction (proteins varied in size & were globular ➟ unfit to form on surface of the membrane)
- fluorescent antibody tagging (markers are attached to antibodies that bind to membrane proteins ➟ cells fuse together ➟ red & green markers are mixed)
general functions of membrane
- sites of hormone-binding
- enzymatic action
- cell adhesion
- cell-to-cell communication
- channels for passive transport
- pumps for active transport
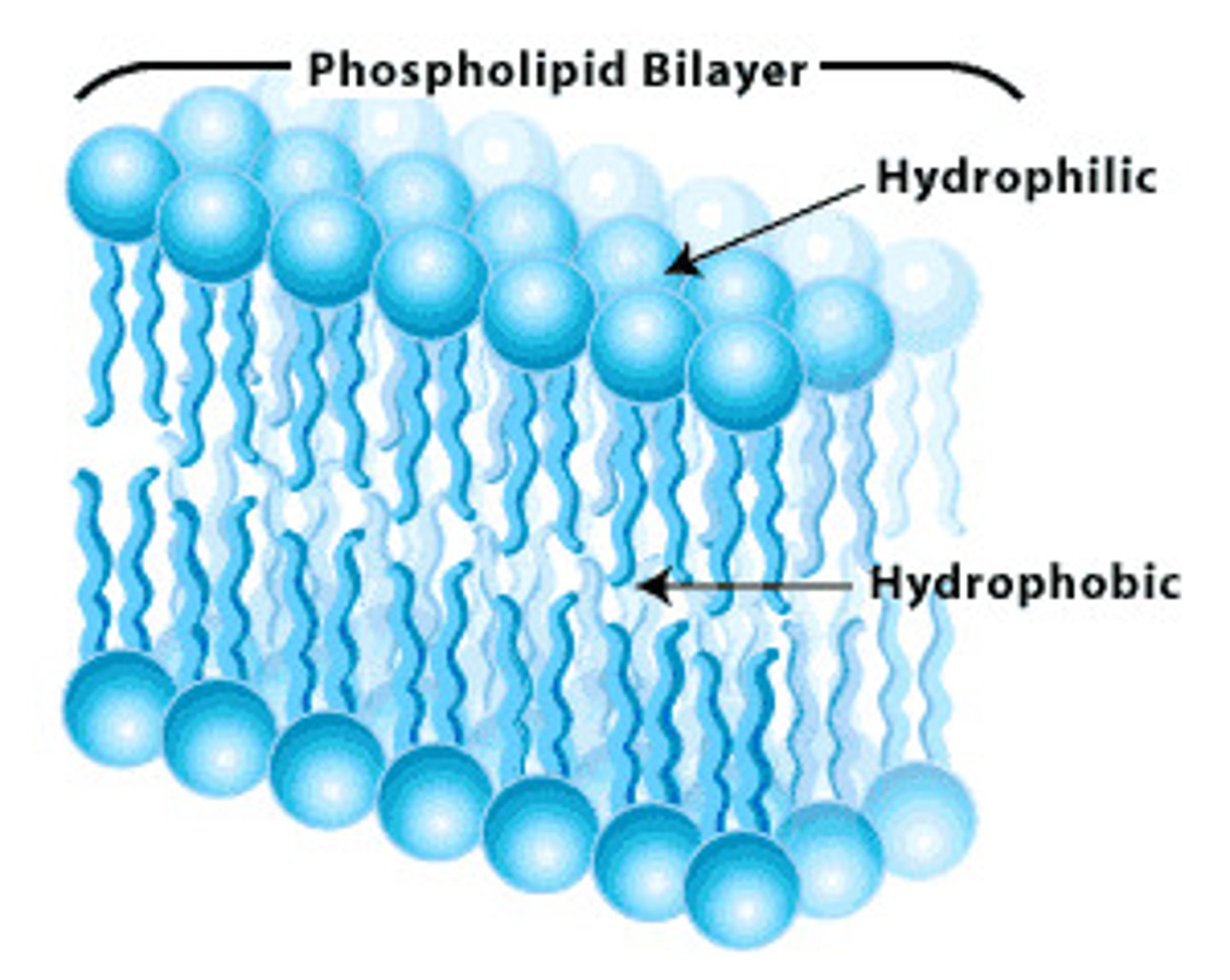
phospholipid bilayer
- composed of glycerol
- hydrophobic & hydrophilic regions cause the phospholipids to align as a bilayer if there is water present
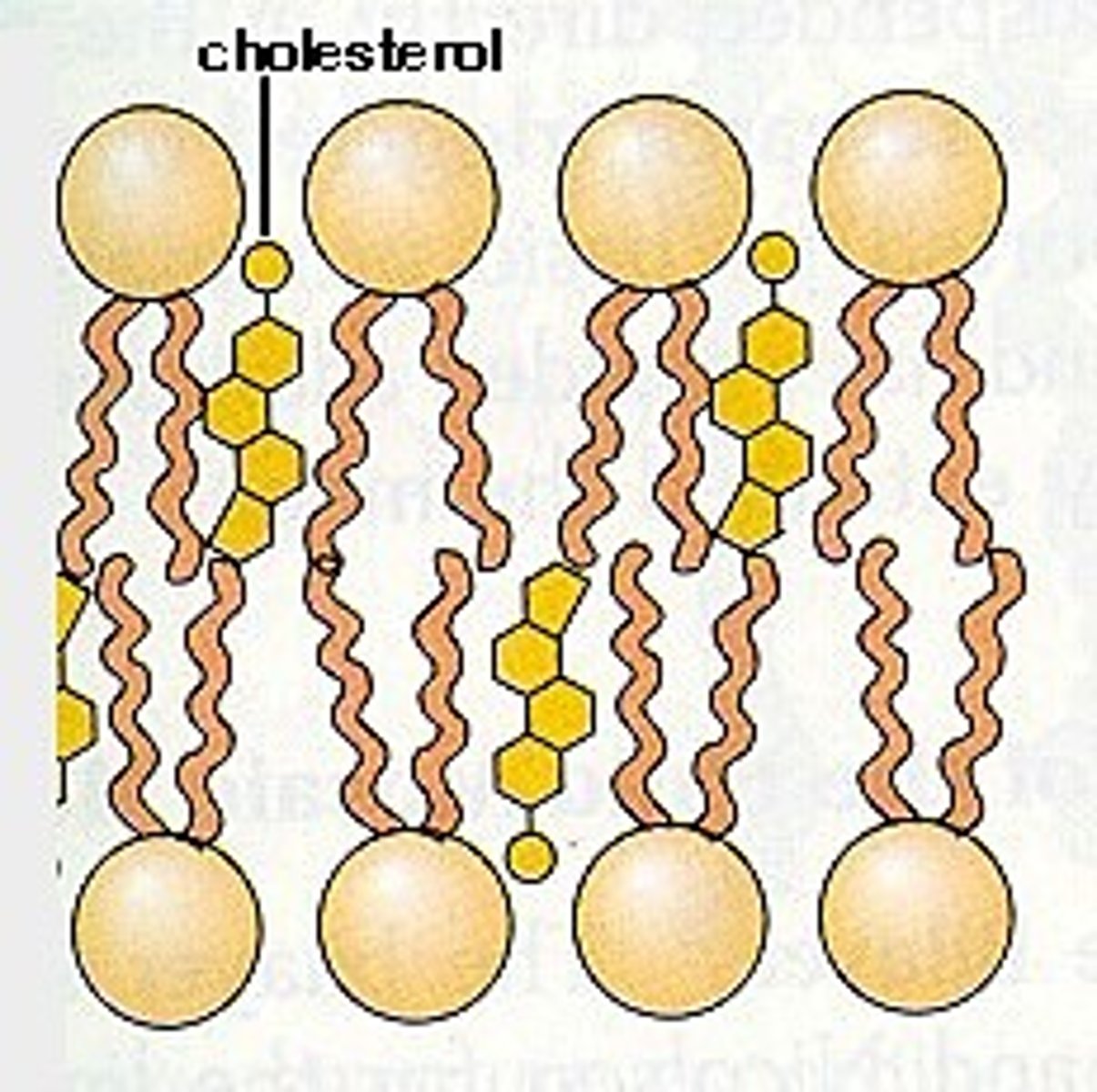
cholesterol
helps regulate membrane fluidity/flexibility & is important for membrane stability
integral proteins
= membrane proteins
- control the entry & removal of specific molecules from the cell
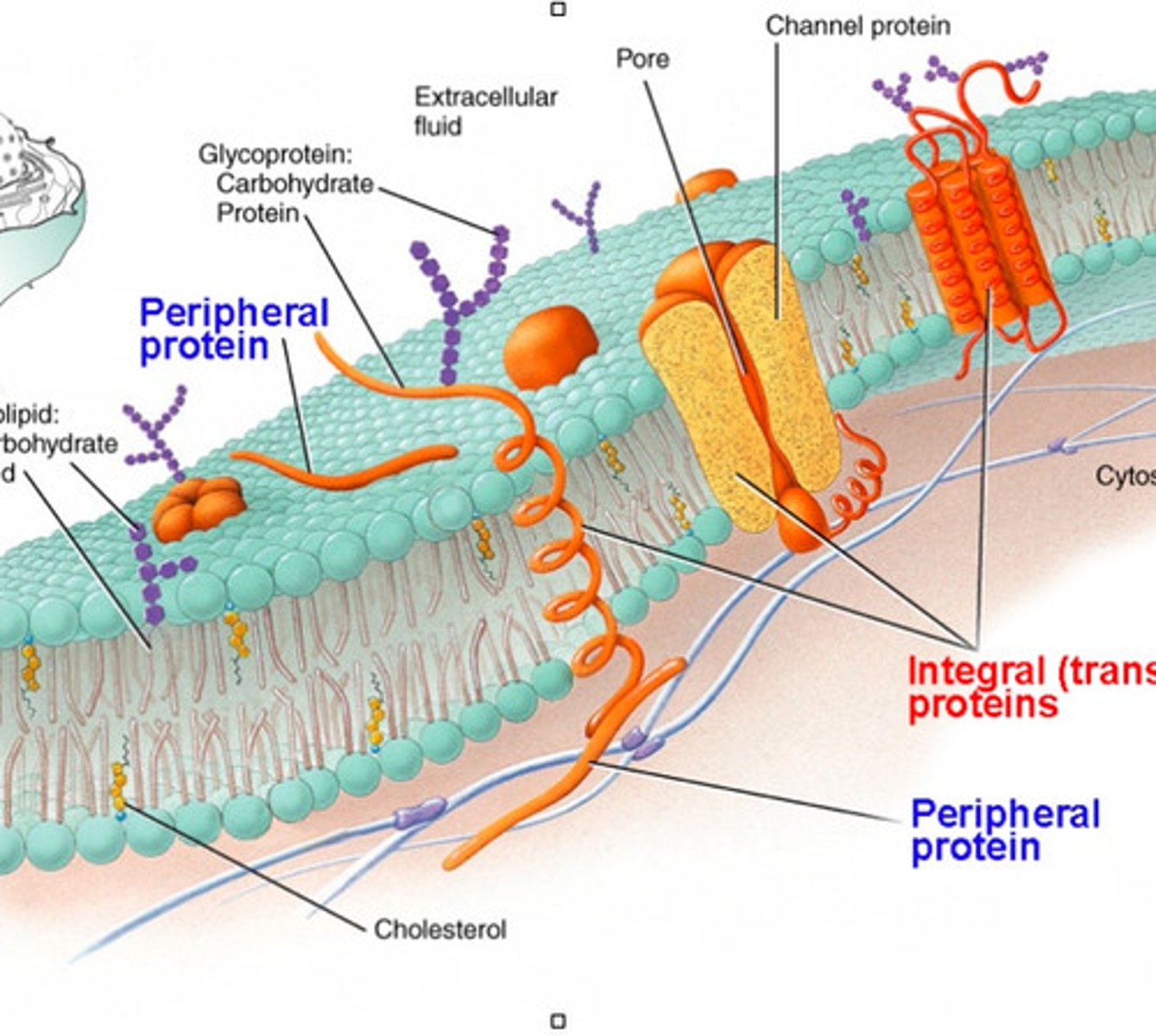
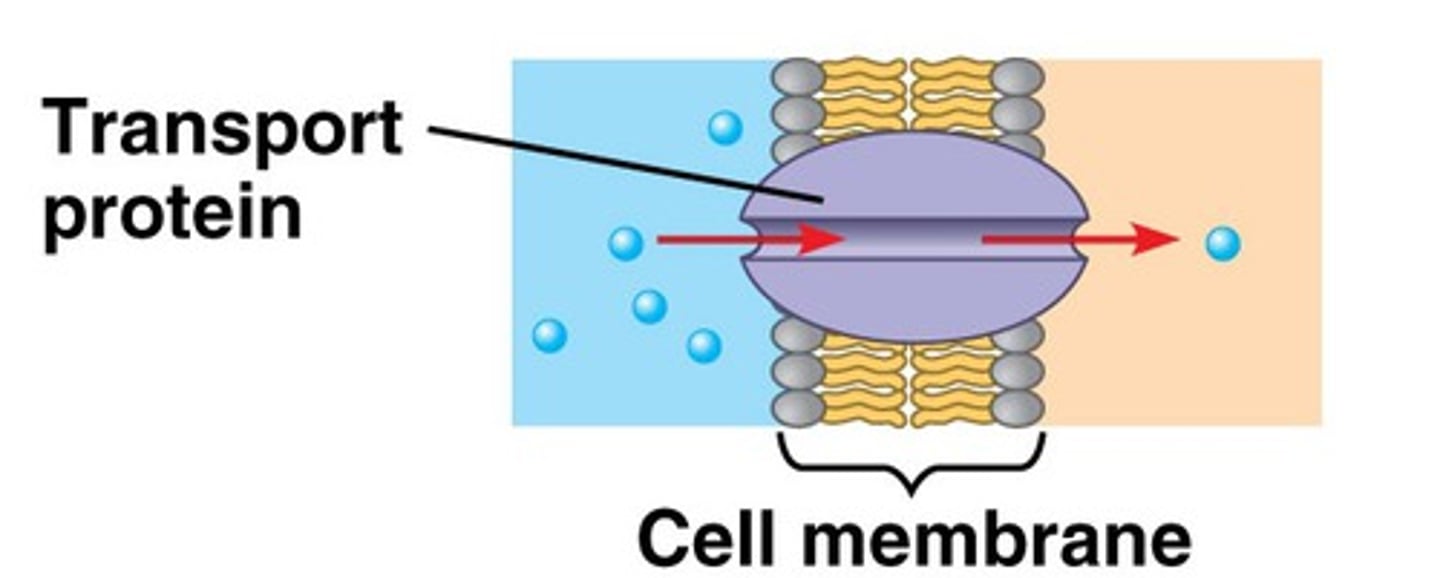
transport proteins
go all the way through the bilayer
peripheral proteins
remain bound to the surface of the membrane & are often anchored to an integral protein
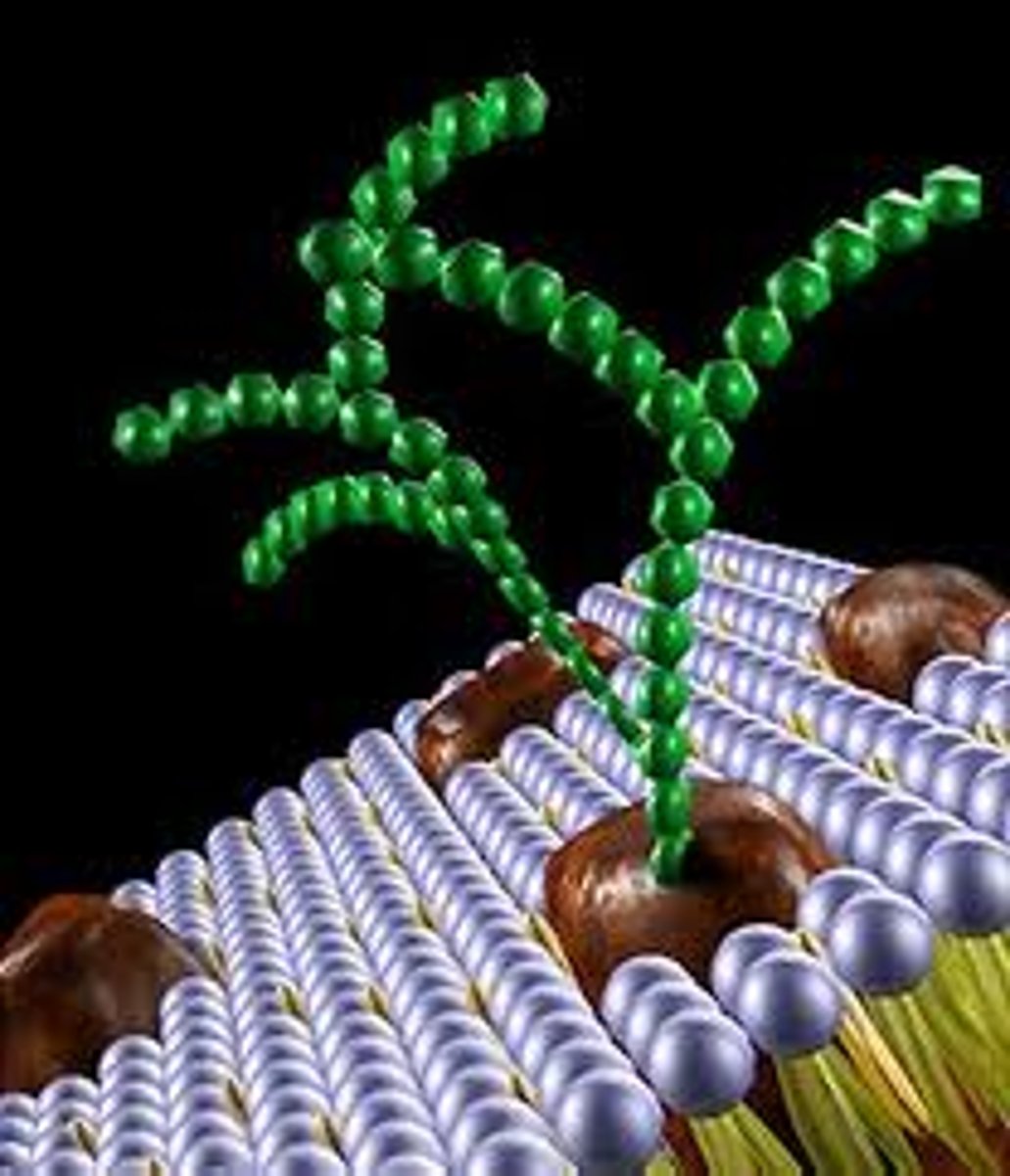
glycoproteins
are composed of carbohydrate chains attached to peripheral proteins
- plays a role in recognition of like-cells
- involved in immune responses
passive transports
occurs in high-to-low concentrations
- movement occurs along the concentration gradient
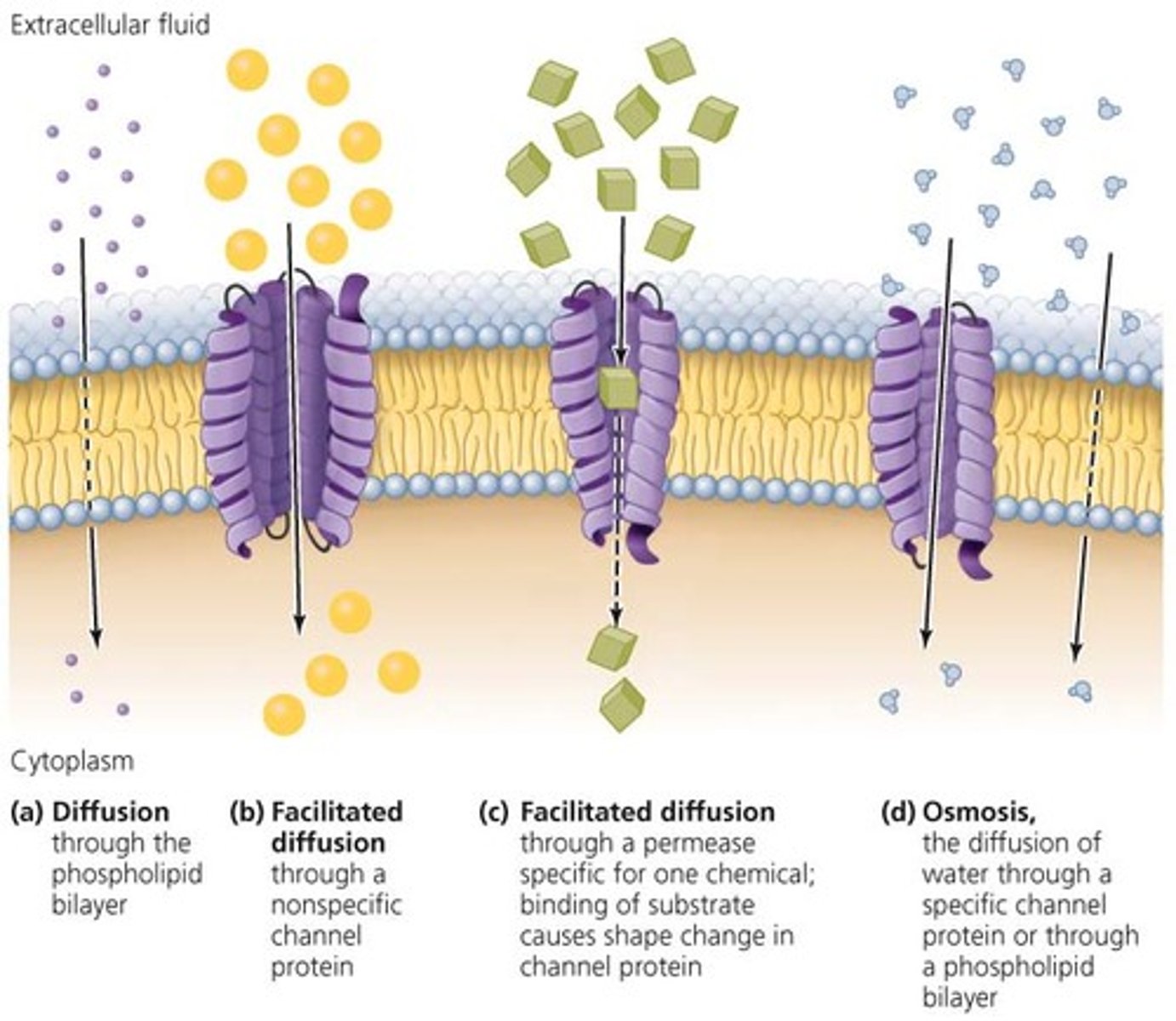
diffusion
substances move between phospholipd molecules/proteins that possess channels
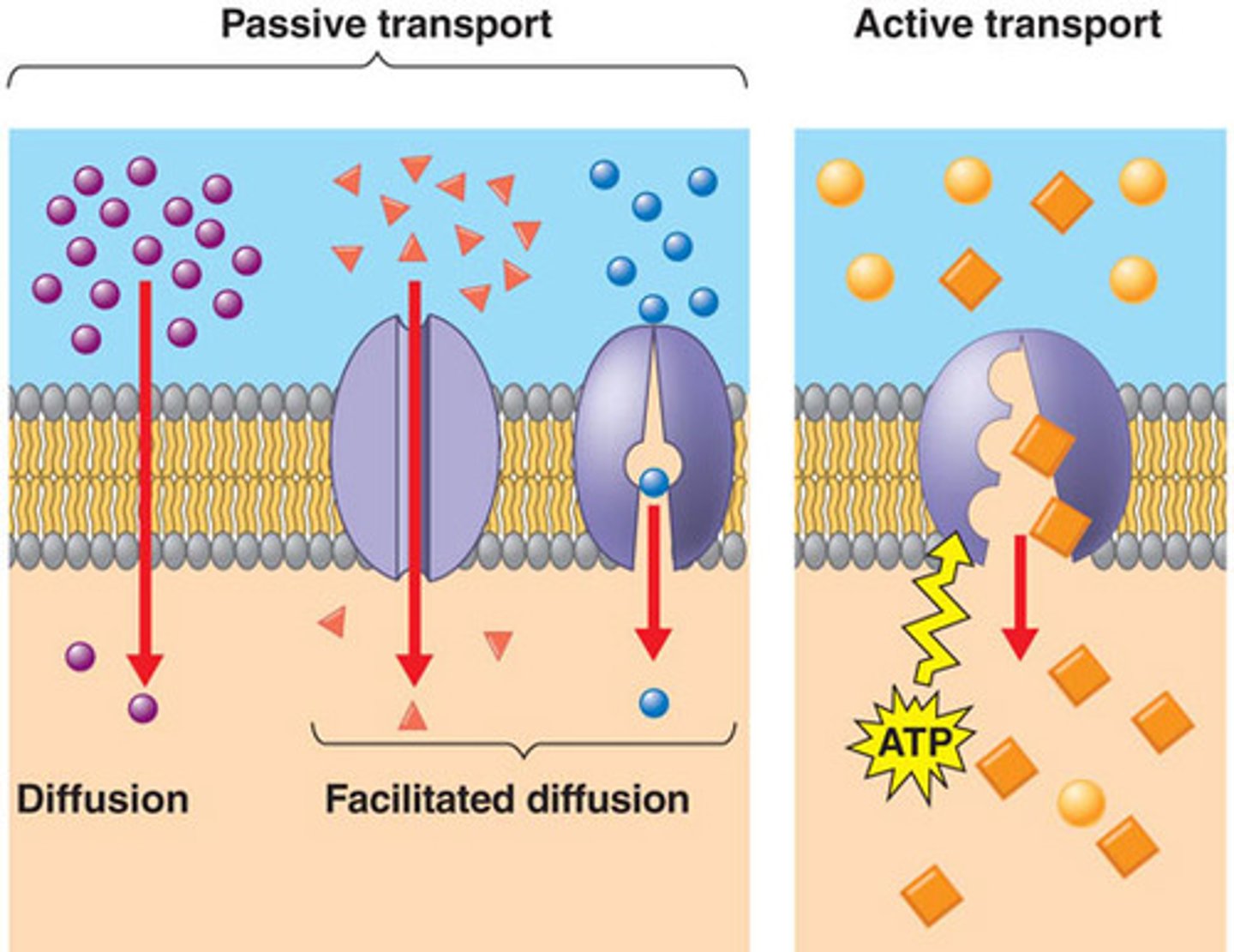
facilitated diffusion
non-channel protein carriers change shape to allow movement of substances other than water
osmosis
the diffusion of water
isotonic
equal concentration of solute
- cell has normal shape
hypertonic
lesser concentration of solute
- cell shrinks
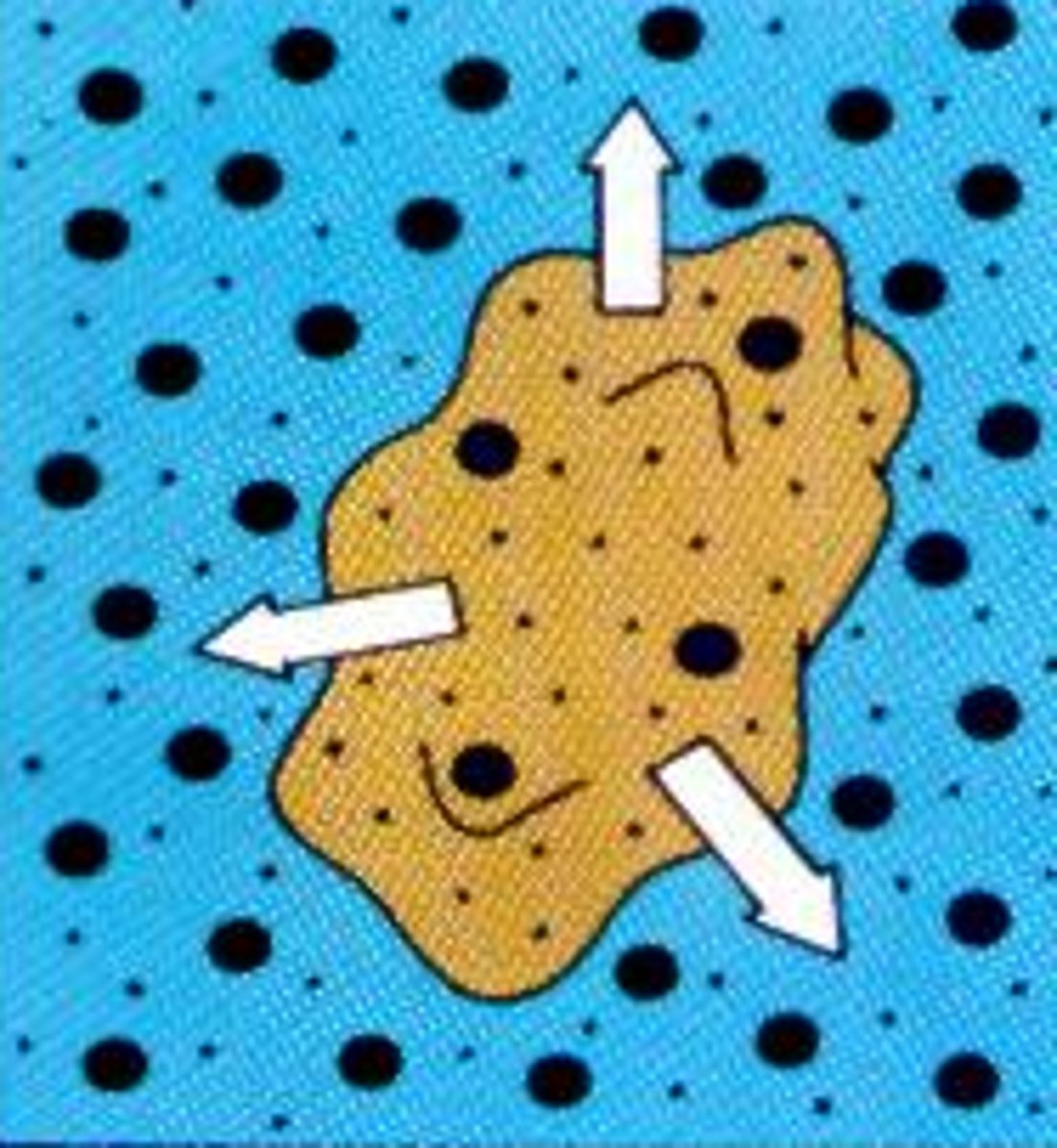

hypotonic
higher concentration of solute
- cell can burst from being too big
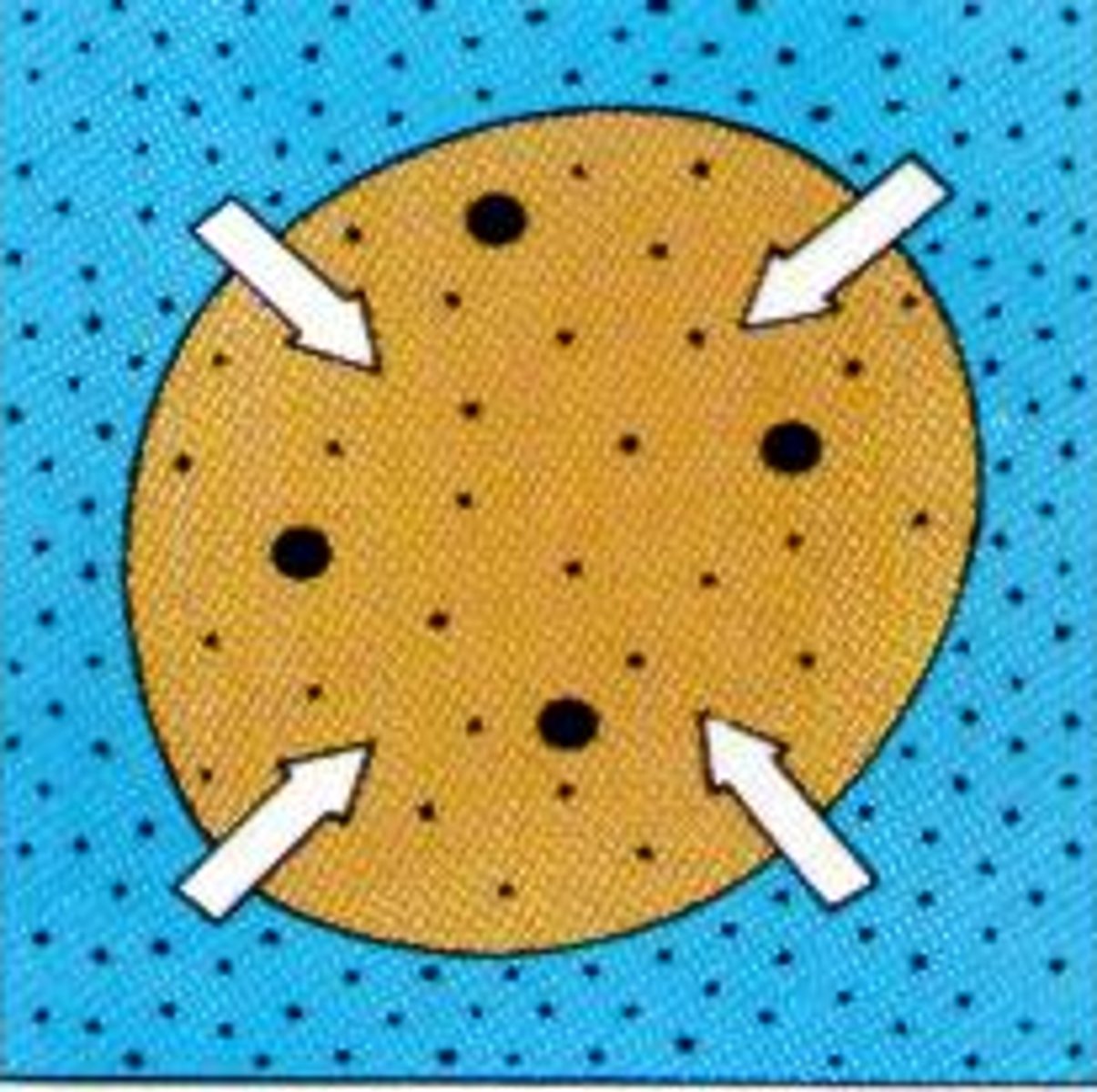
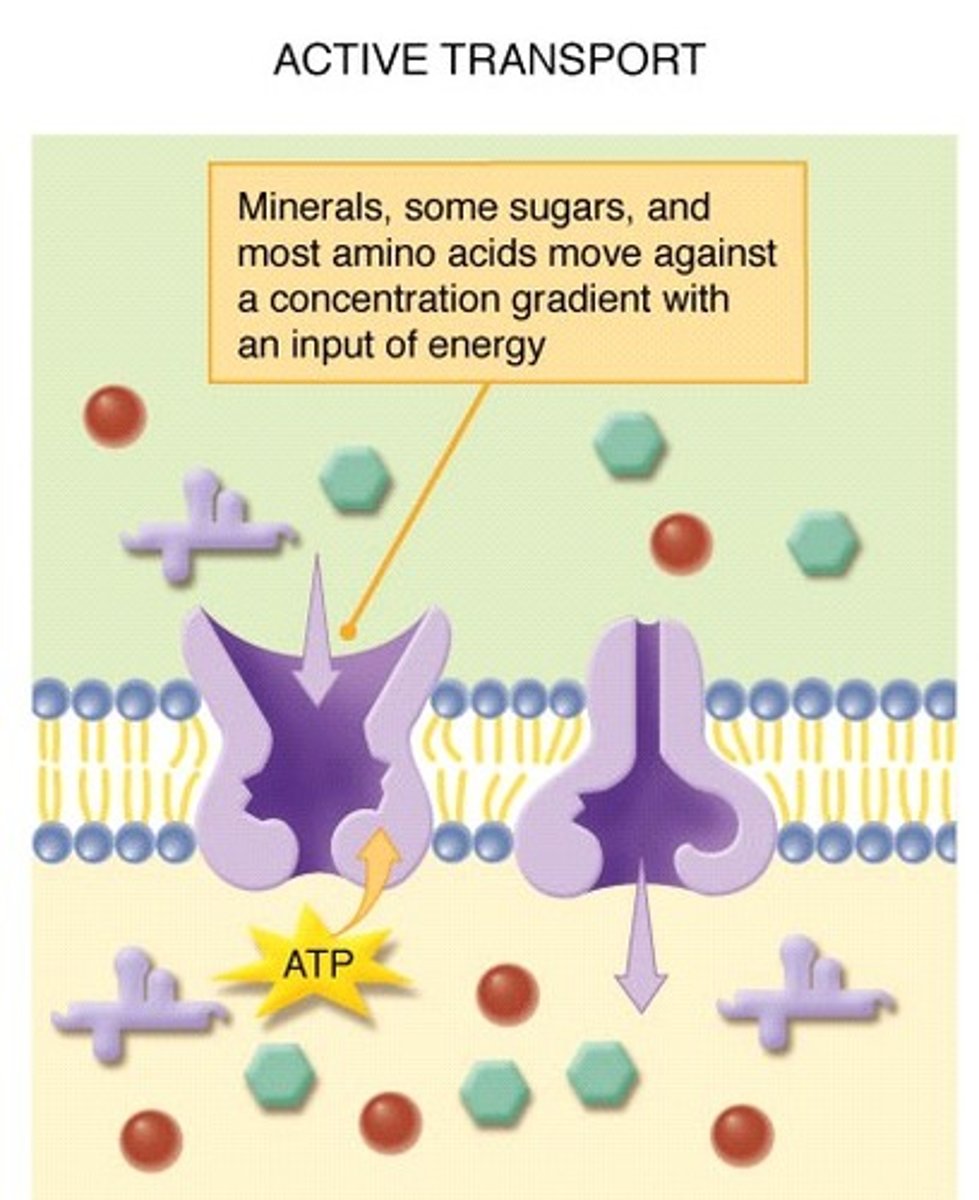
active transport
requires ATP; involves the movement of substances against a concentration gradient
- allows cell to maintain different interior & exterior concentrations
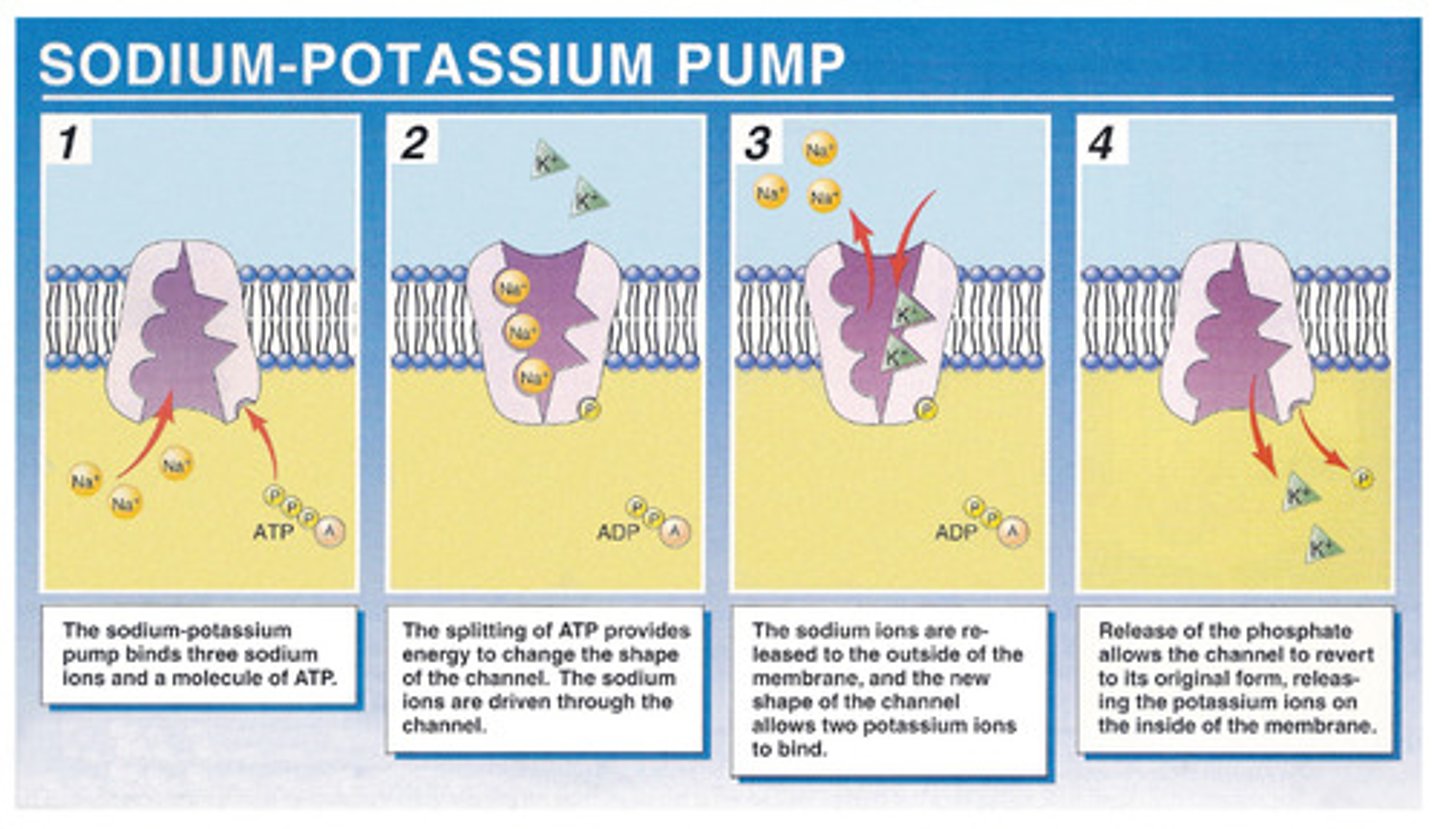
sodium-potassium pump
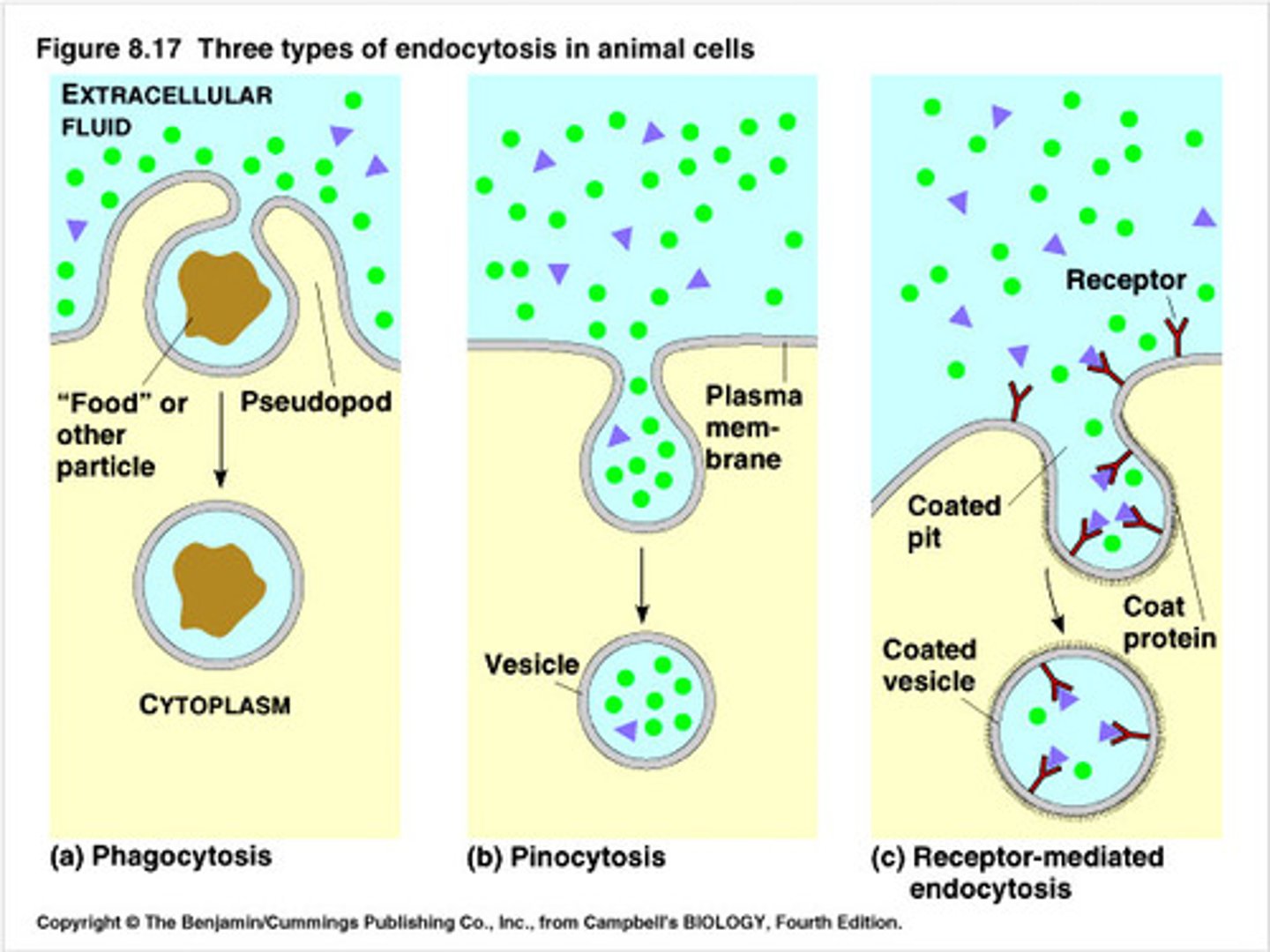
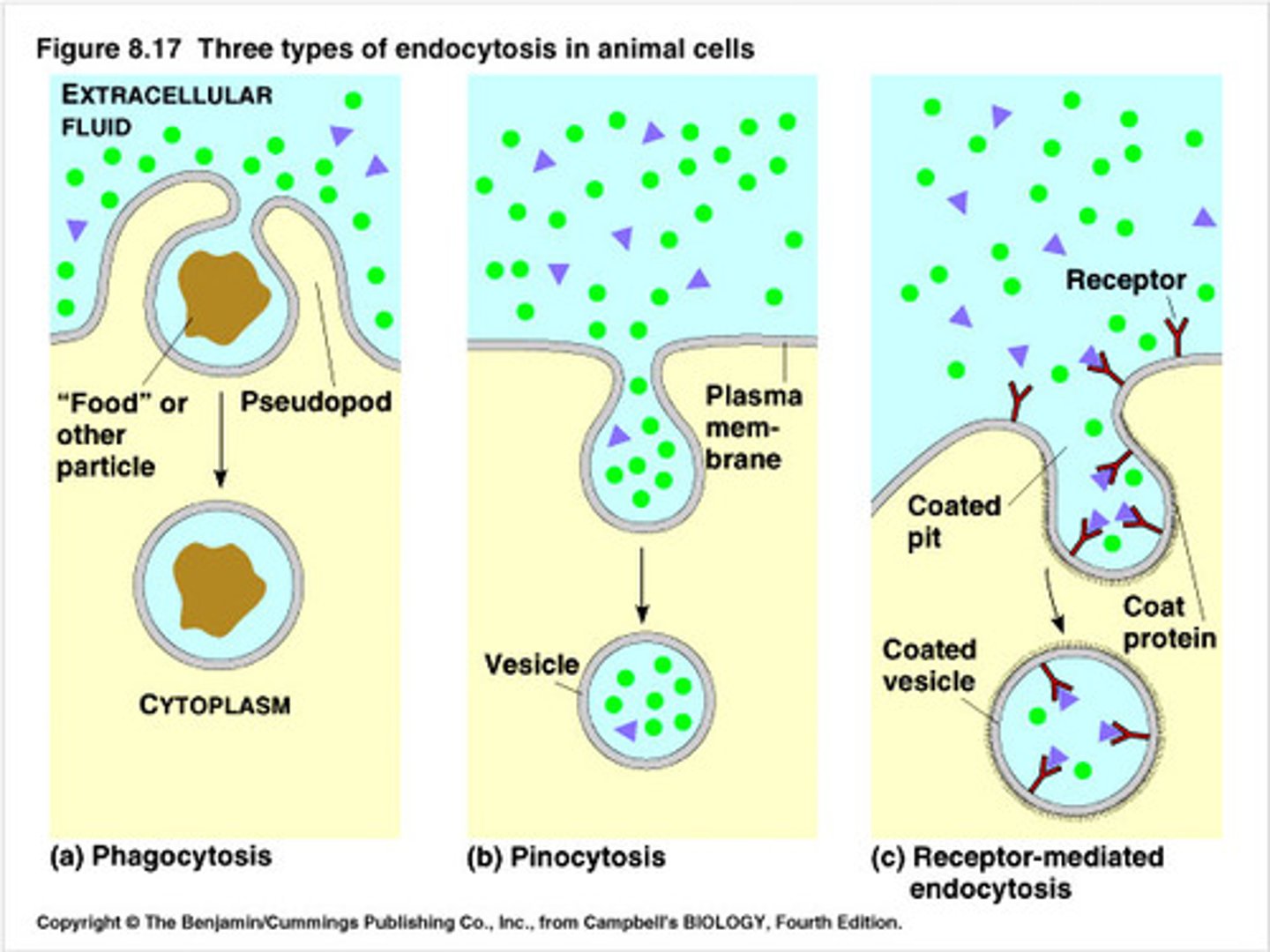
endocytosis
allows macromolecules to enter the cell
- portion of plasma membrane is pinched off to enclose macromolecules ➟ formation of a vesicle
exocytosis
allows molecules to leave
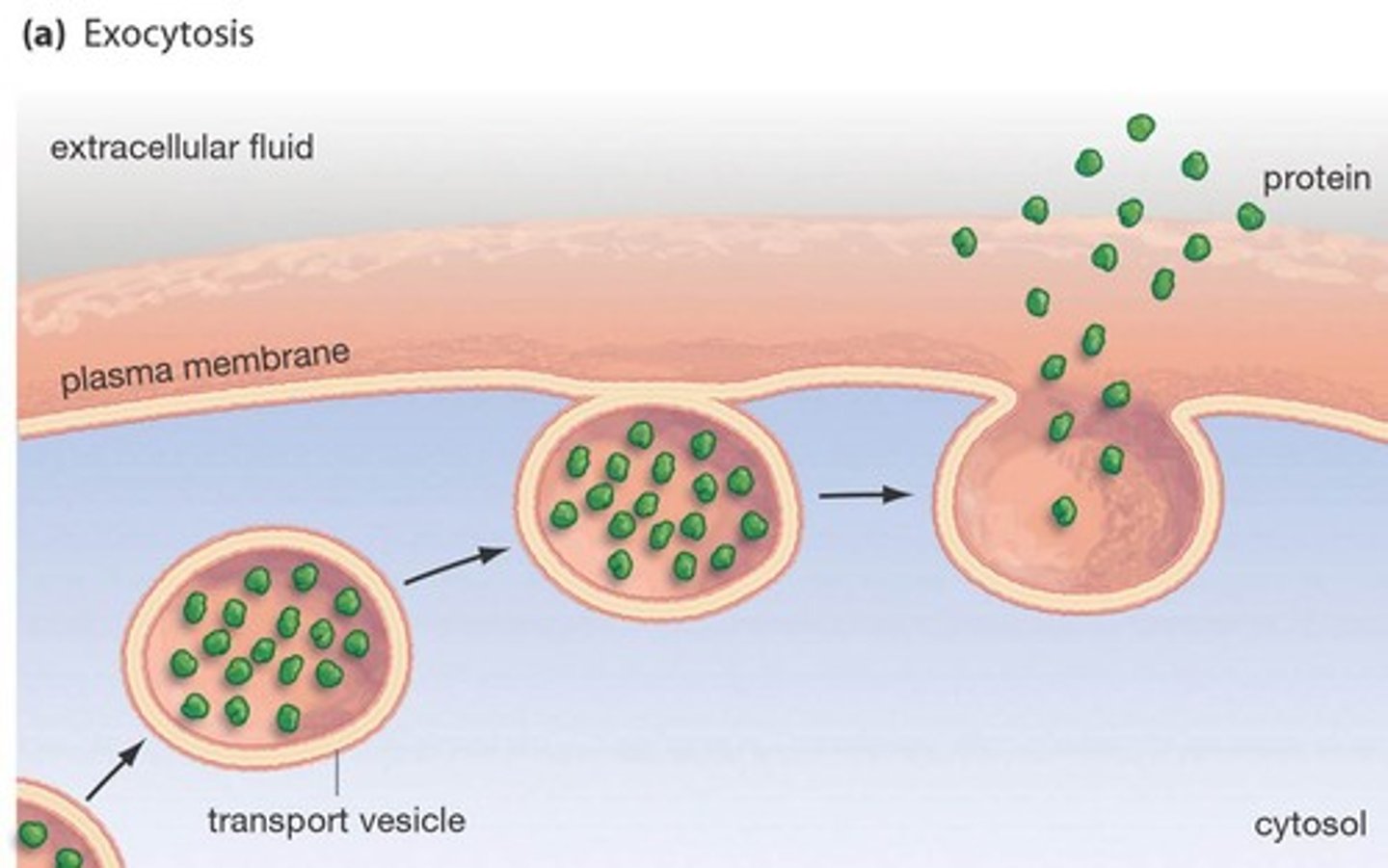
describe how the plasma membrane breaks & reforms during exocytosis & endocytosis.
1. vesicle approaches plasma membrane
2. membrane fuses
3. there's a single phospholipid bilayer at the point of contact (temporary)
4. membrane pore opens ➟ allows content to pass through
phagocytosis
intake of food/solids
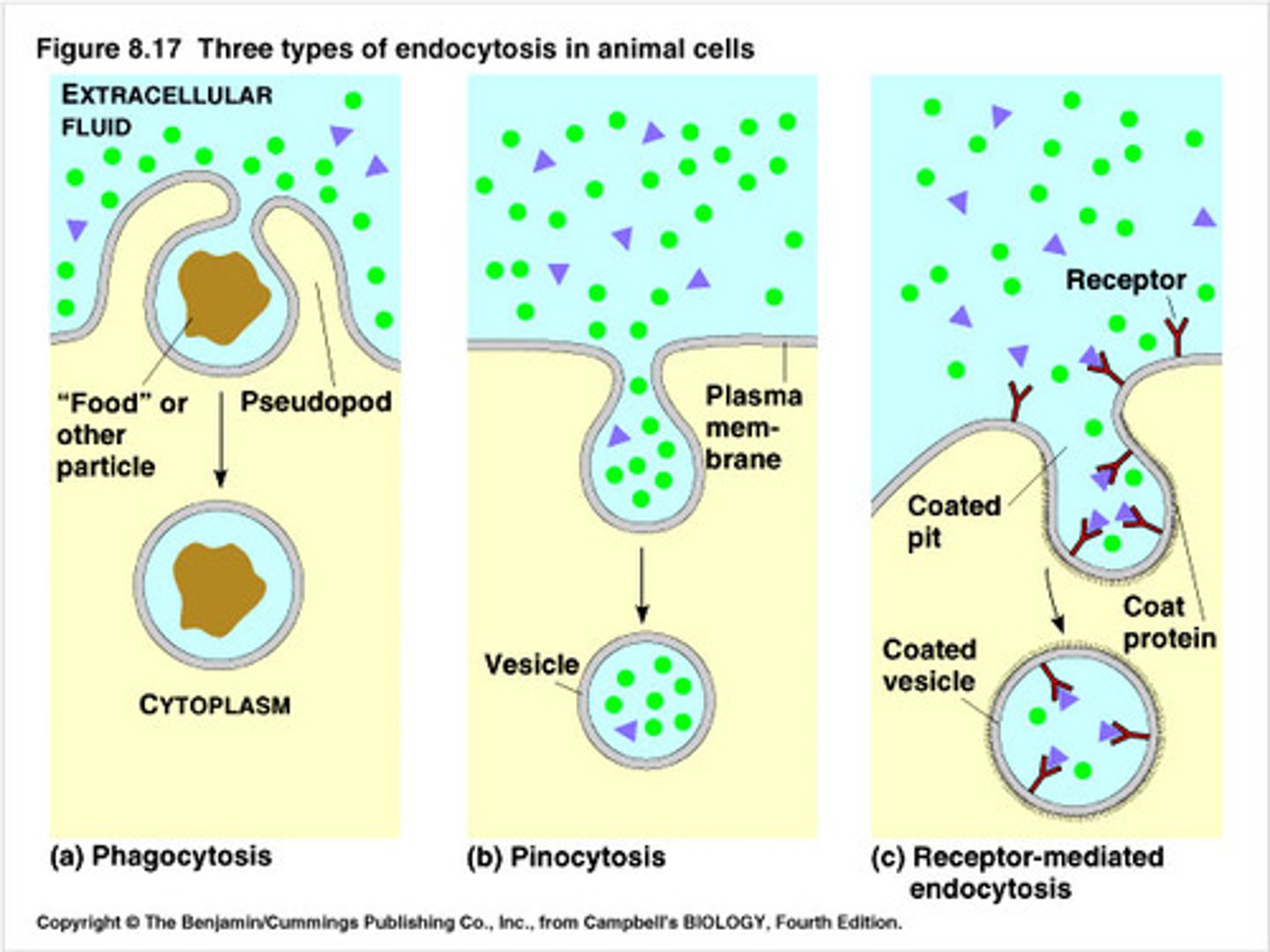
pinocytosis
intake of liquids
primary active transport
direct ATP
secondary active transport
energy is derived from built up concentration from previous ATP
binary fission
cell cycle
all stages in the life cycle of a cell
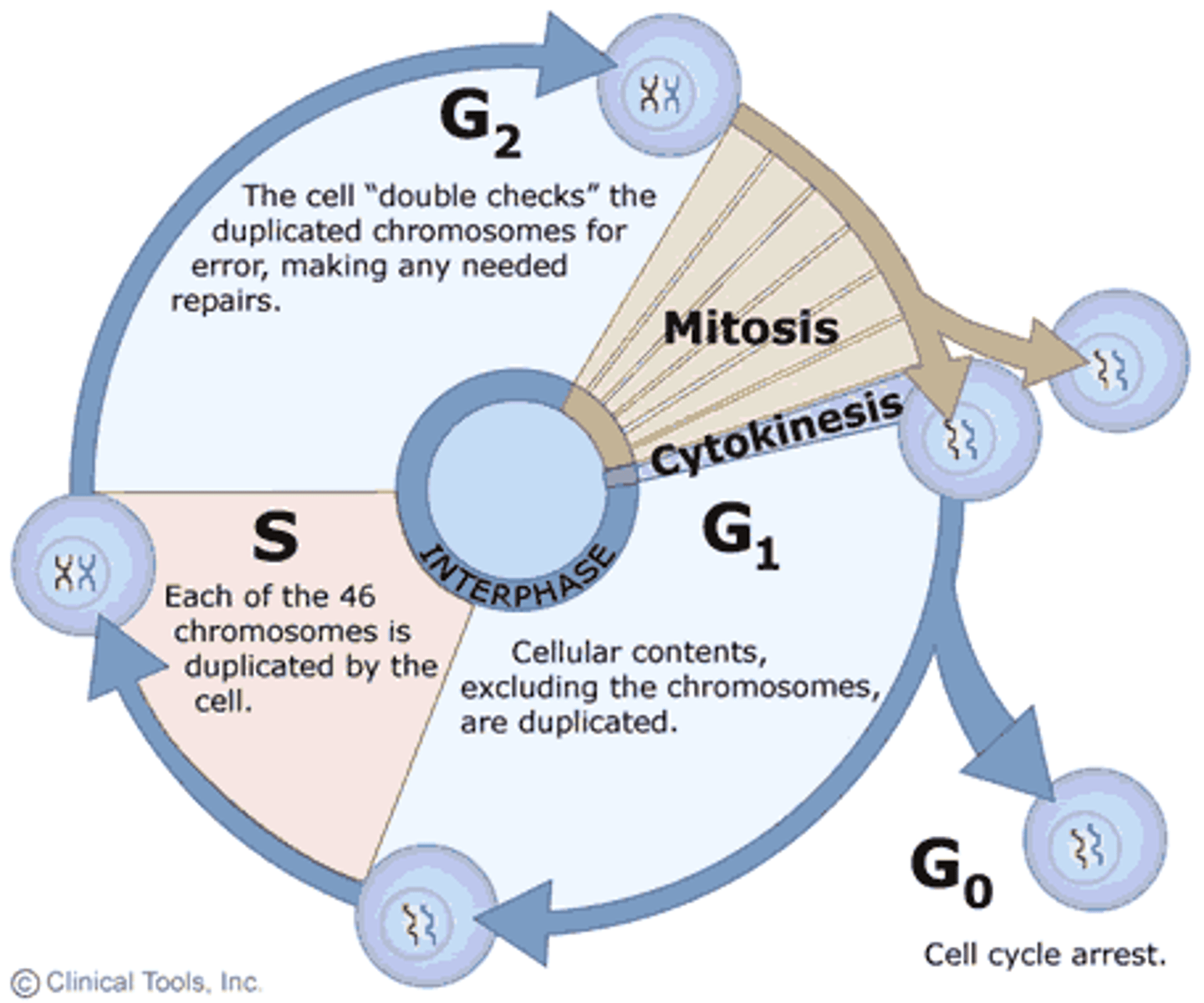
interphase
composed of G1, S, & G2
- by the end of interphase, an individual cell has two full sets of DNA/chromosomes, & is large enough to divide
G1
- DNA transcription
- protein synthesis (centrioles)
- cell respiration (produces energy)
- growth of cell volume
- organelles double (mitochondria & chloroplast)
- increase in energy stored
G0
the stage where cells are unlikely to divide (ex: neurons)
S
- synthesis of genetic material
- DNA replication
- duplication of chromosomes into sister chromatids
G2
- growth & production of components needed for cell division (mitosis & cytokinesis)
3 metabolic reactions that occur during interphase
- protein synthesis
- DNA replication
- increase in the number of mitochondria and/or chloroplast
mitosis
= nuclear division;
split into 4 parts: prophase, metaphase, anaphase, & telaphase
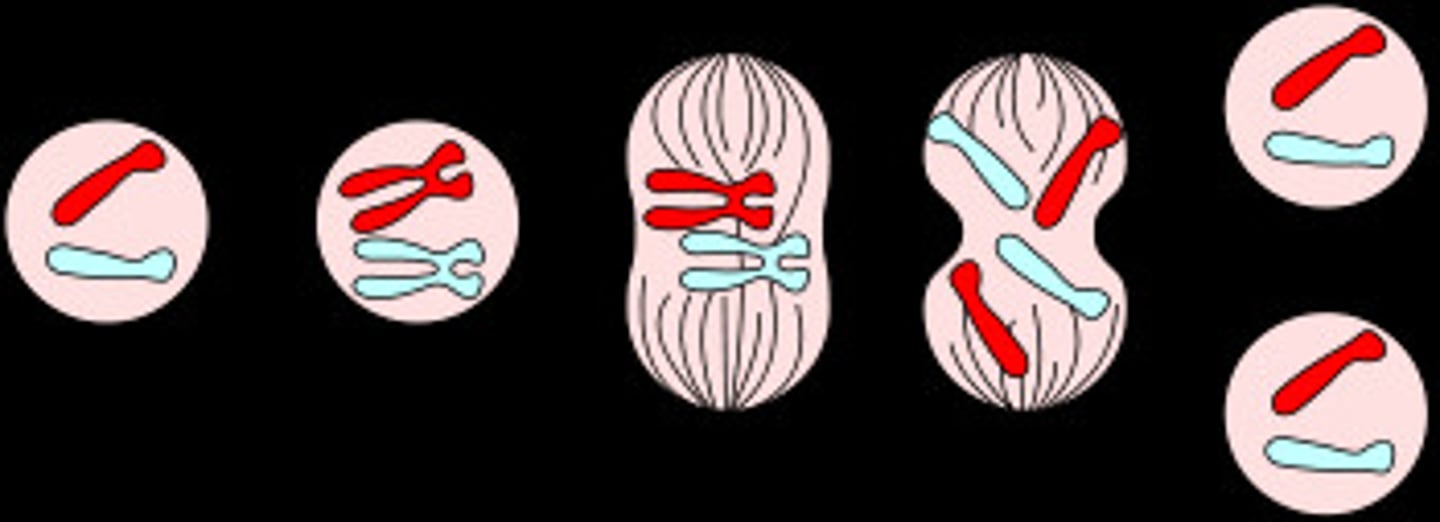
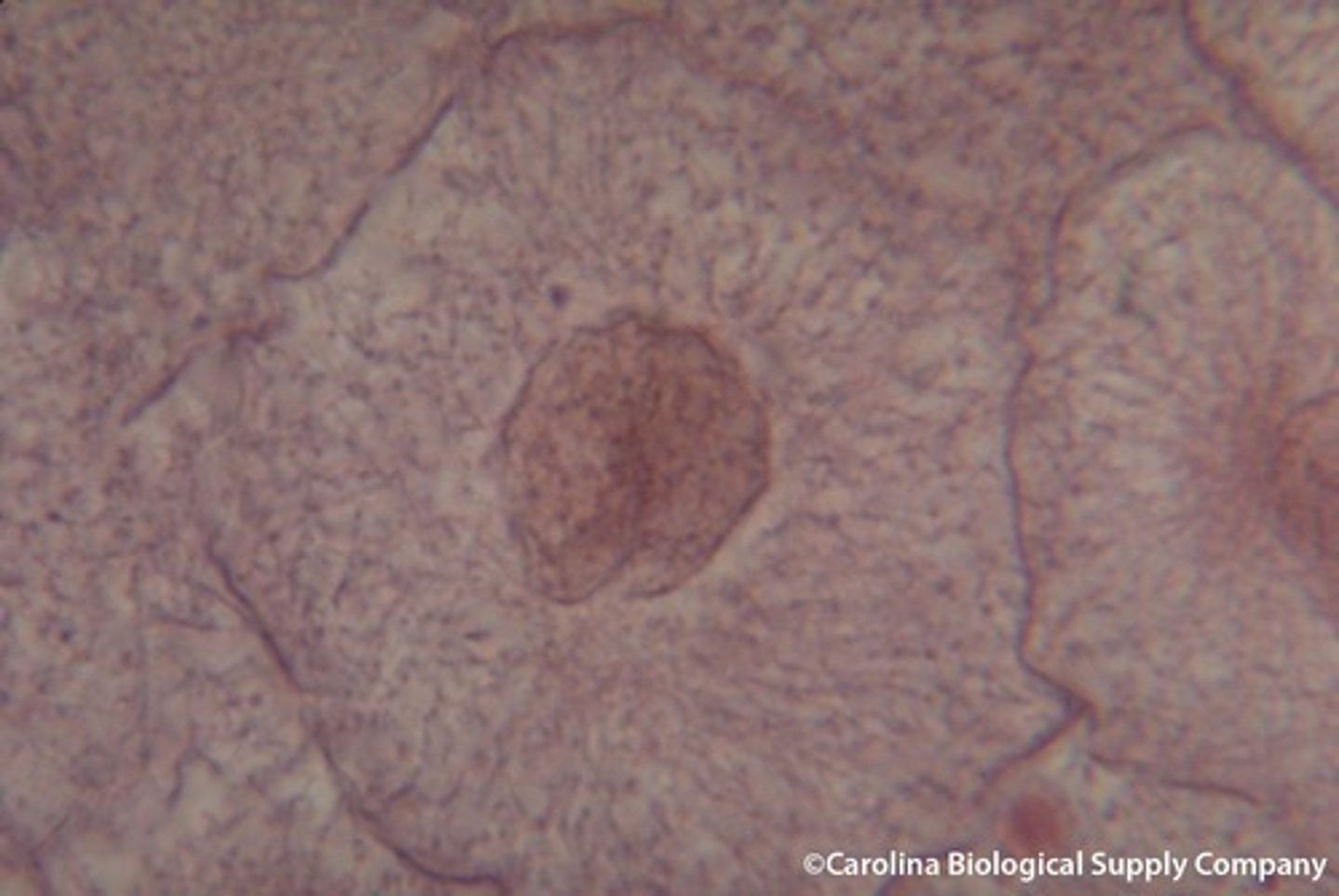
prophase
- DNA and proteins condense into tightly coiled chromosomes (& become 2 sister chromatids)
- nuclear envelope breaks down
- centrioles begin to move to opposite poles
- spindle fibers form between 2 centrosomes
- chromosomes become attached to the spindle fibers at their centromeres
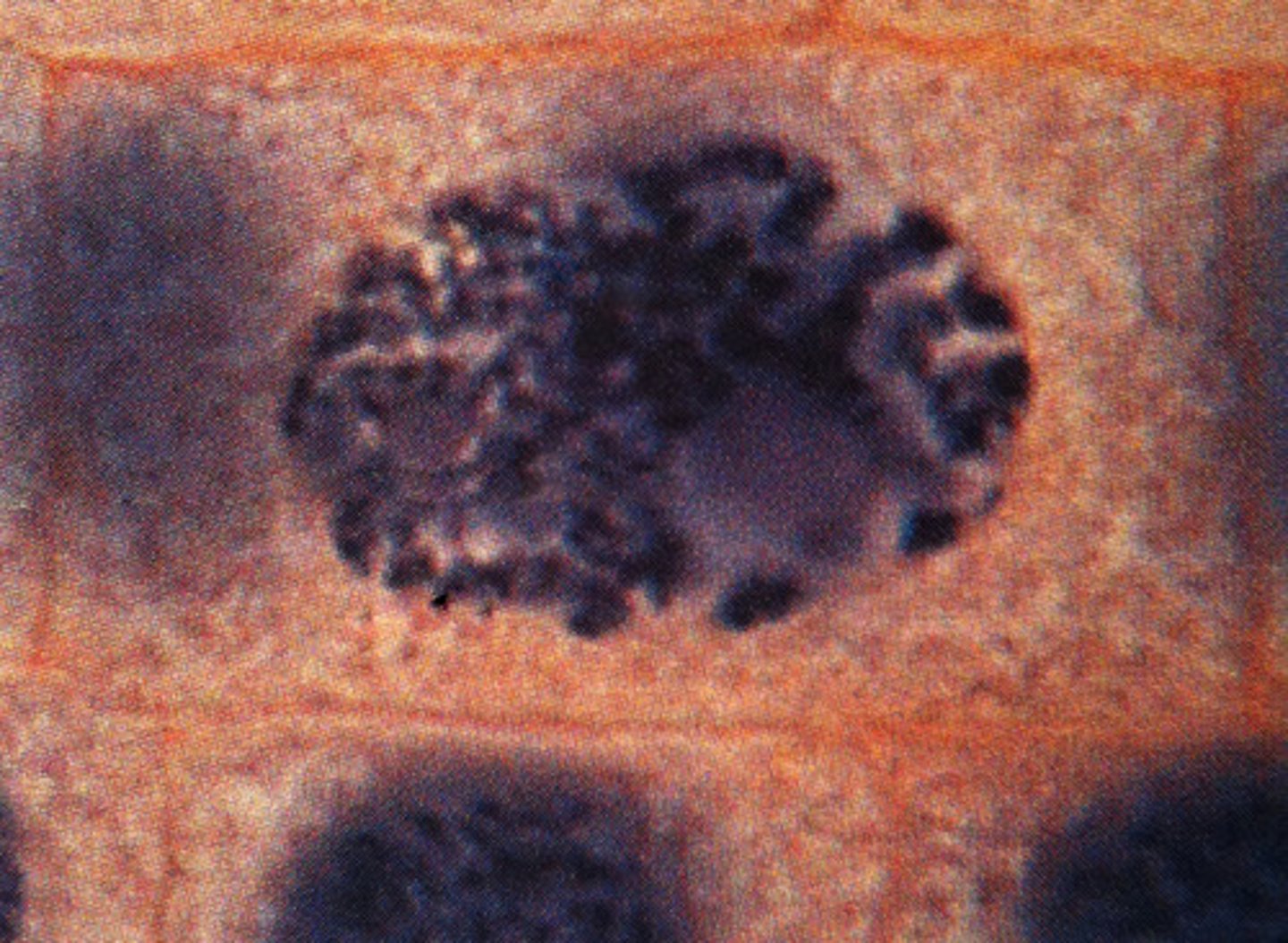
metaphase
- spindle fibers attach to each chromosome
- chromosomes align at the equator
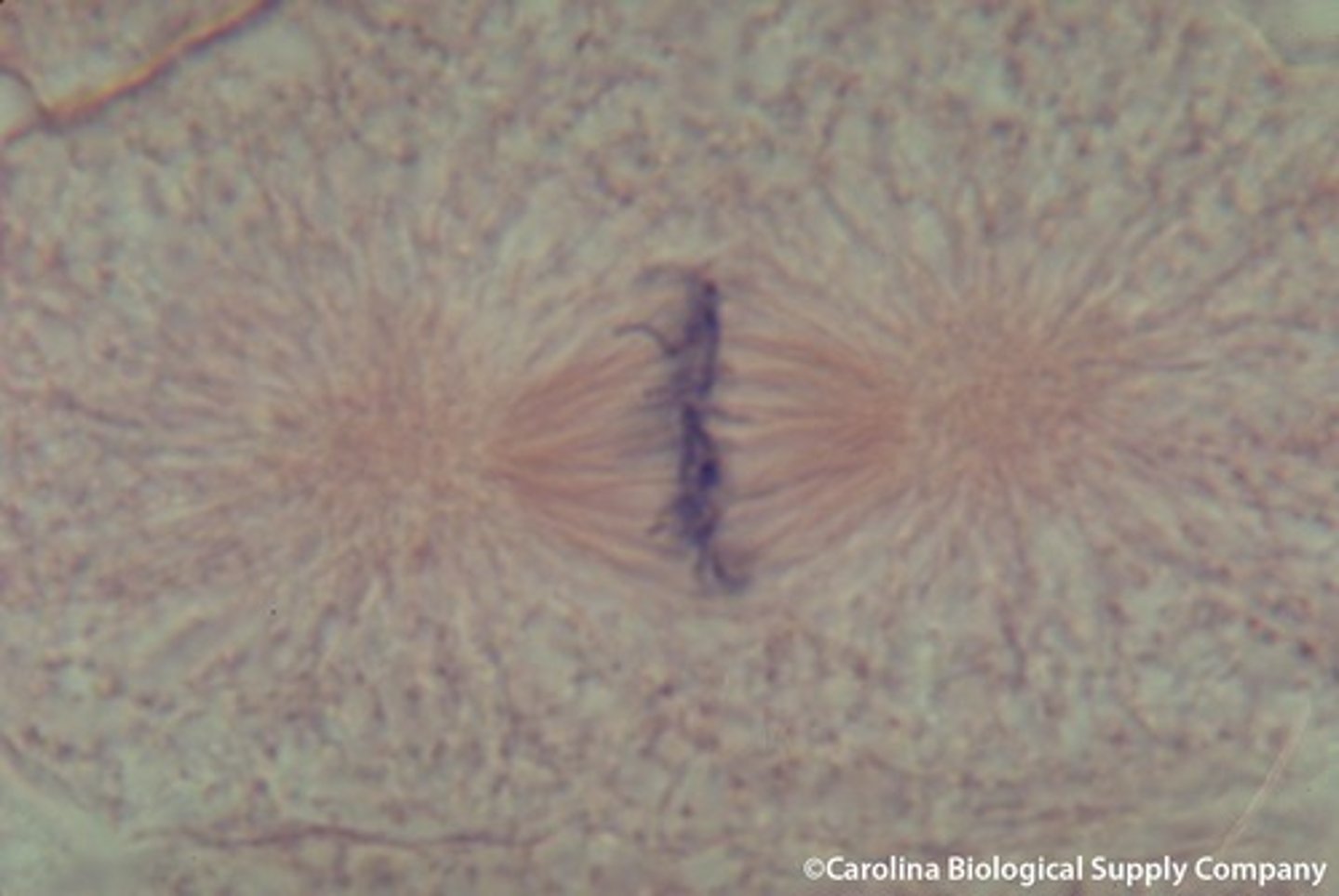
anaphase
- centromeres divide
- sister chromatids separate to opposite sides of the cell
- spindle fibers begin to shorten

telophase
- nuclear membrane starts to form
- chromosomes begin to uncoil
- the spindle fibers fall apart
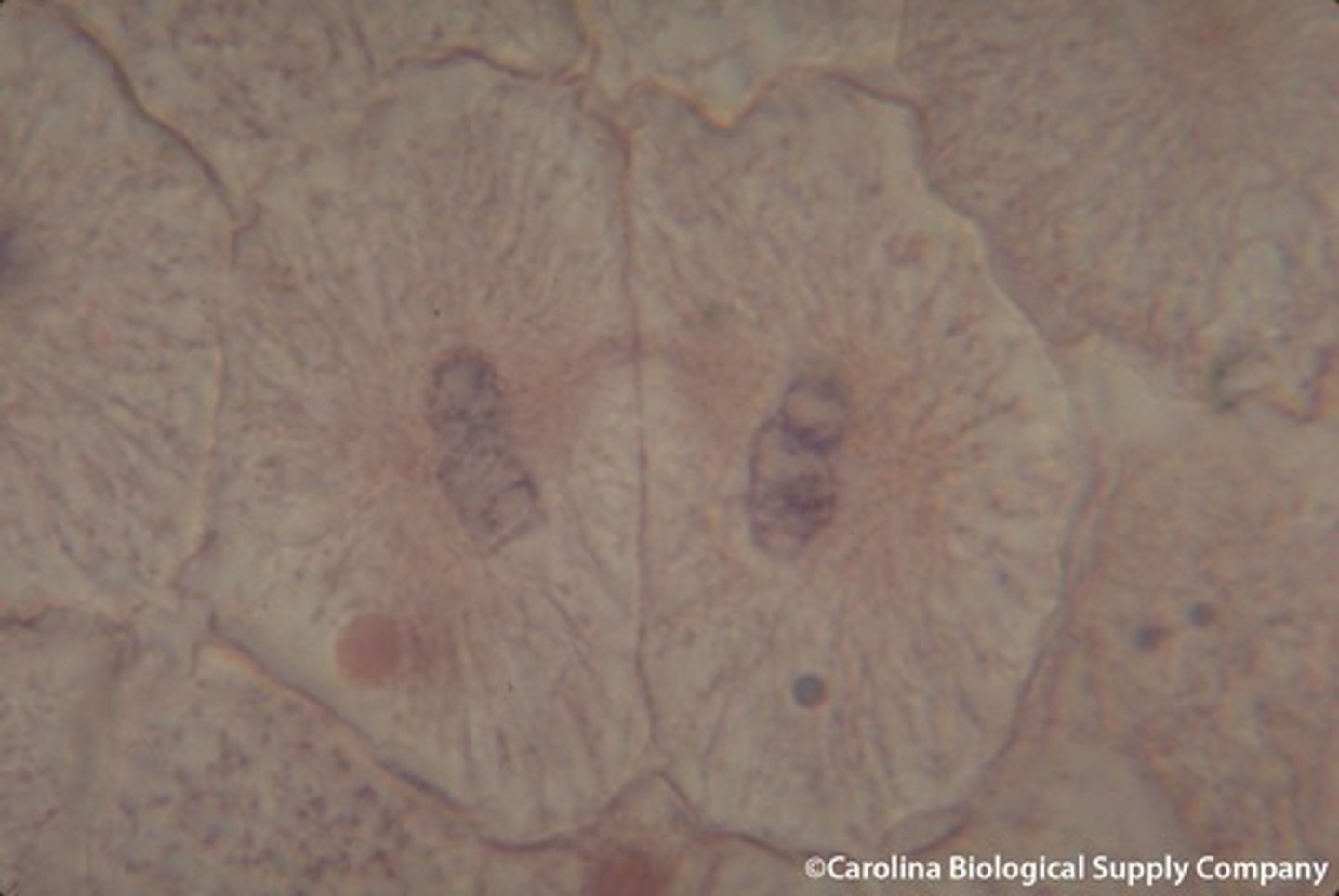
4 processes involving division by mitosis
- growth
- asexual reproduction
- tissue repair
- embryonic development
cytokinesis
division of cytoplasm
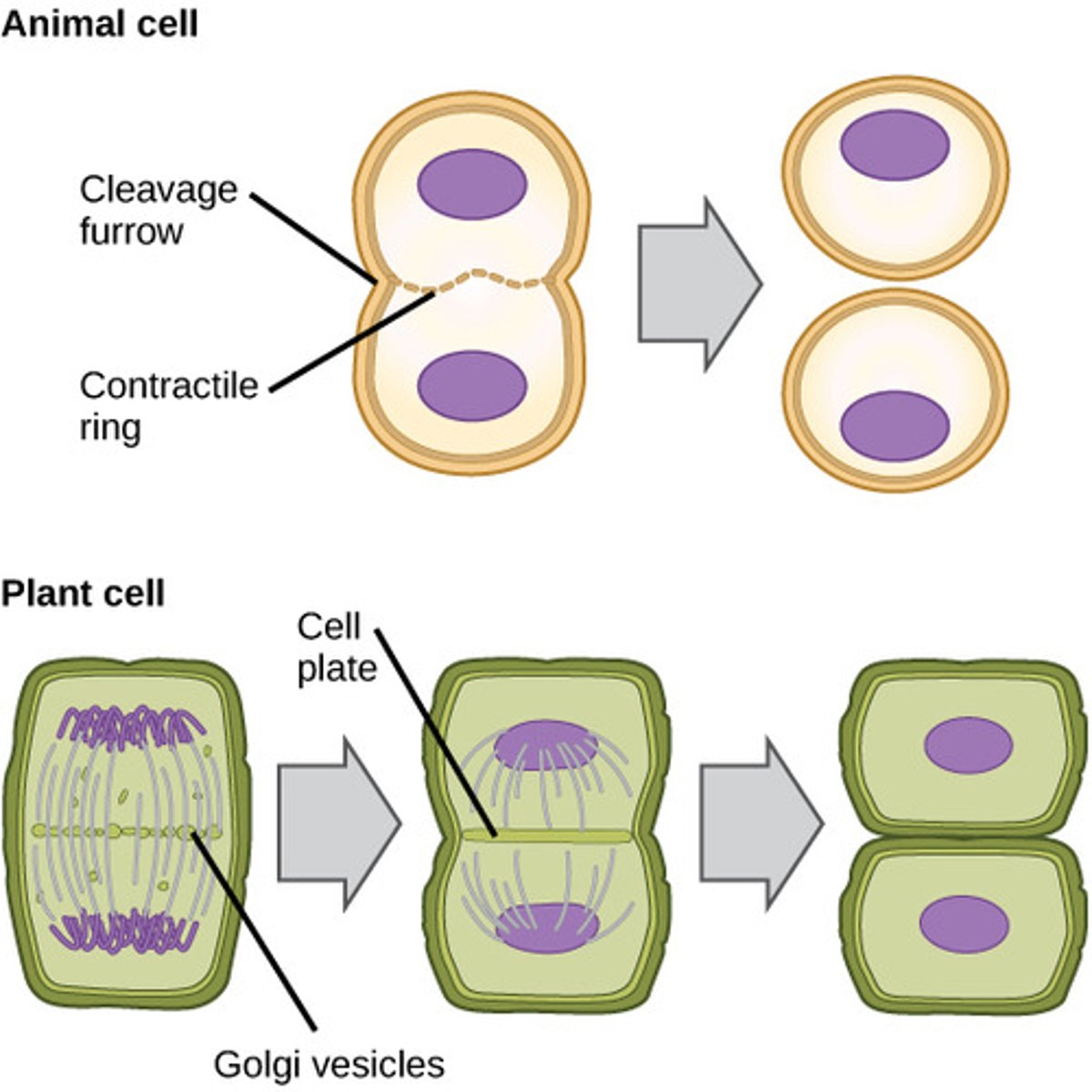
cytokinesis in plant & animal cells
plant: vesicles containing cell wall material line up between two nuclei. they form a cell plate, which then forms a new cell wall & create daughter cells
animal: animal cells form a cleavage furrow
apoptosis
the death of cells which occurs as a normal & controlled part of an organism's growth/development
cyclin
= a family of proteins that control the cell cycle
- bind & activate cyclin dependent kinase enzymes (CDKs)
- cyclin proteins appear at different stages & help regulate cell cycle
roles of the four cyclins involved in control of the cell cycle
cyclin A, D, & E: induce DNA replication, centrosome duplication & spindle fiber apparatus formation
cyclin B: controls mitotic spindle formation & alignment of sister chromatids
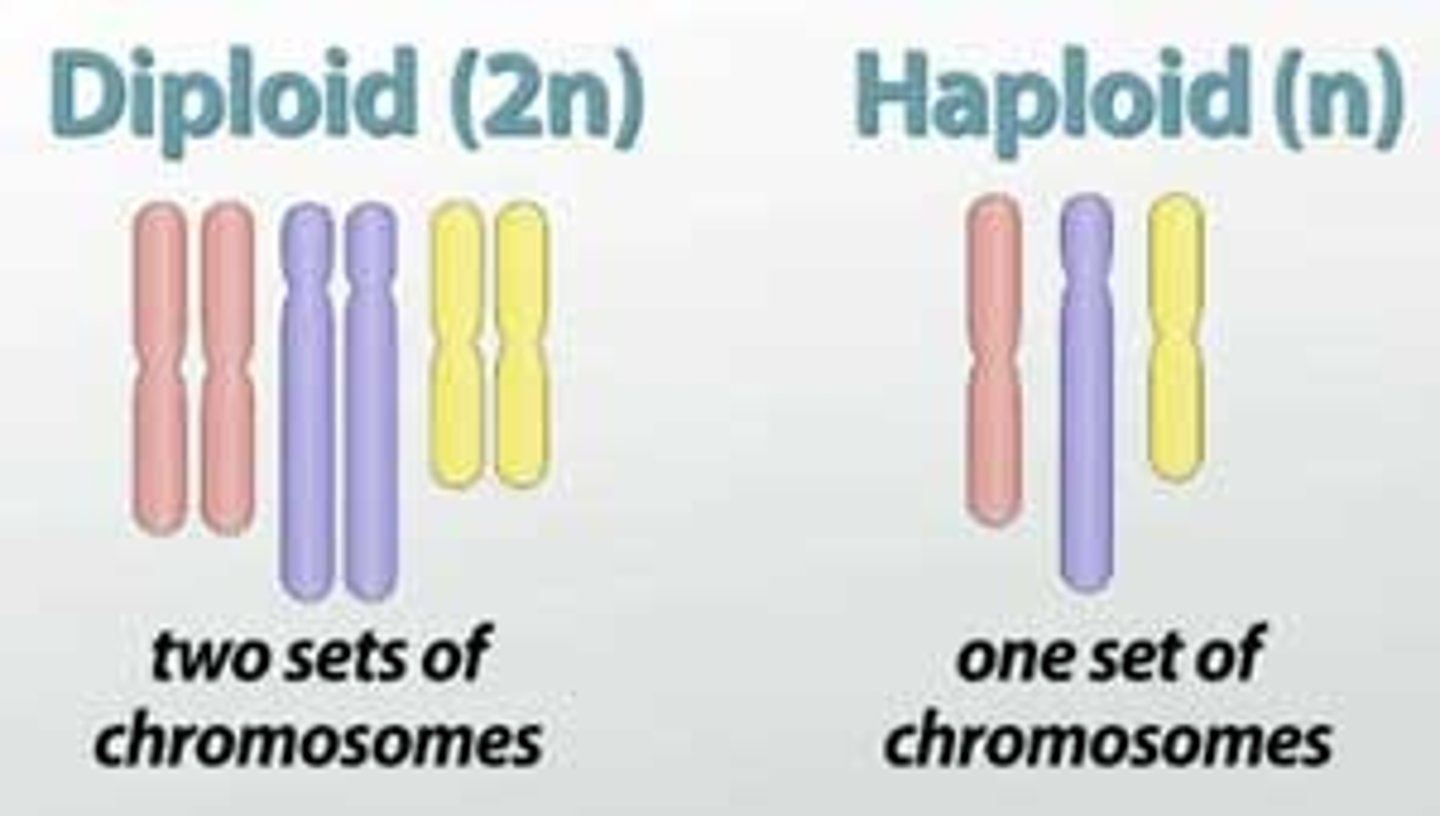
diploid
(of a cell/nucleus) containing 2 complete sets of chromosomes, 1 from each parent
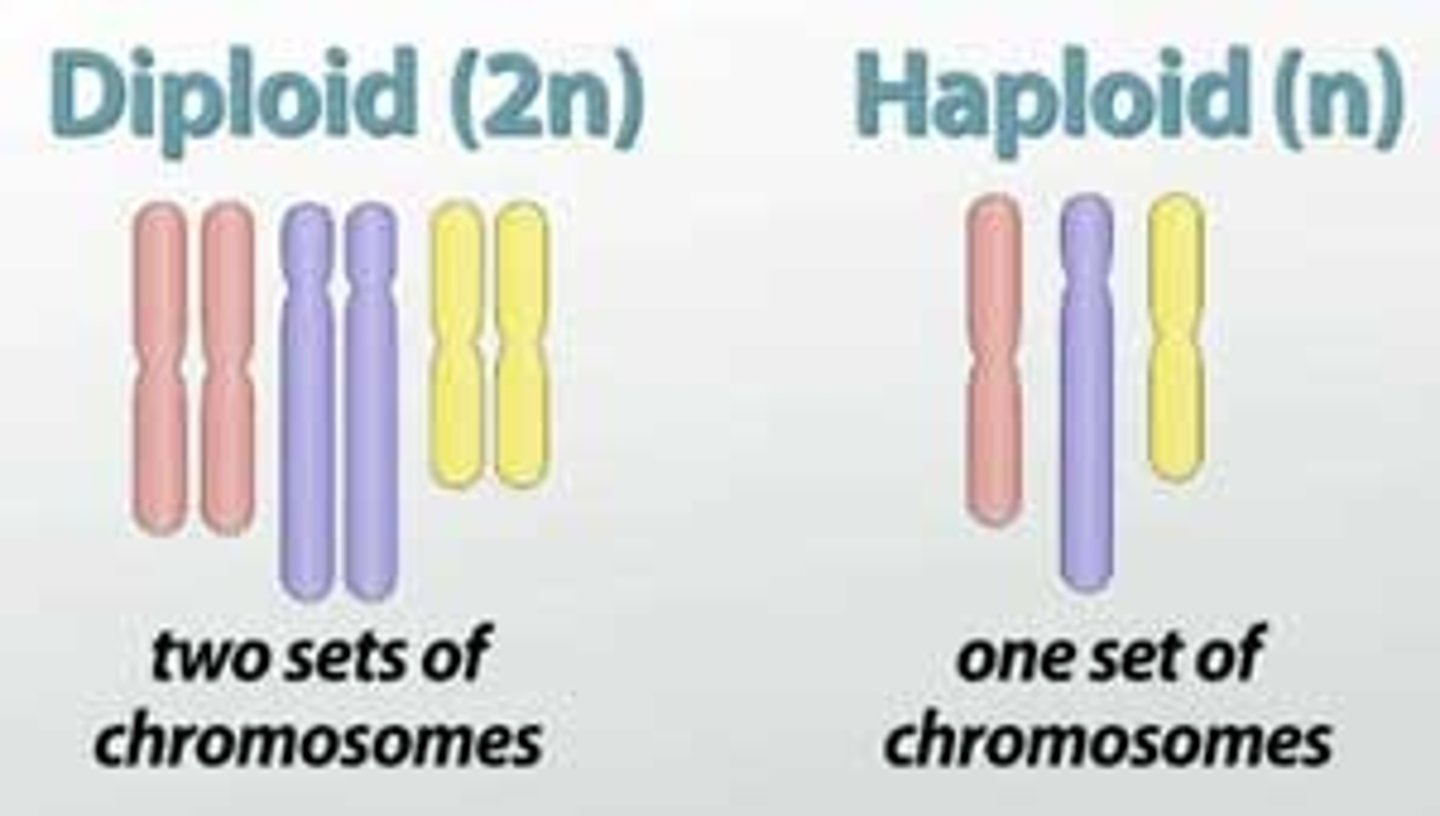
haploid
(of cell/nucleus) having a single set of unpaired chromosomes
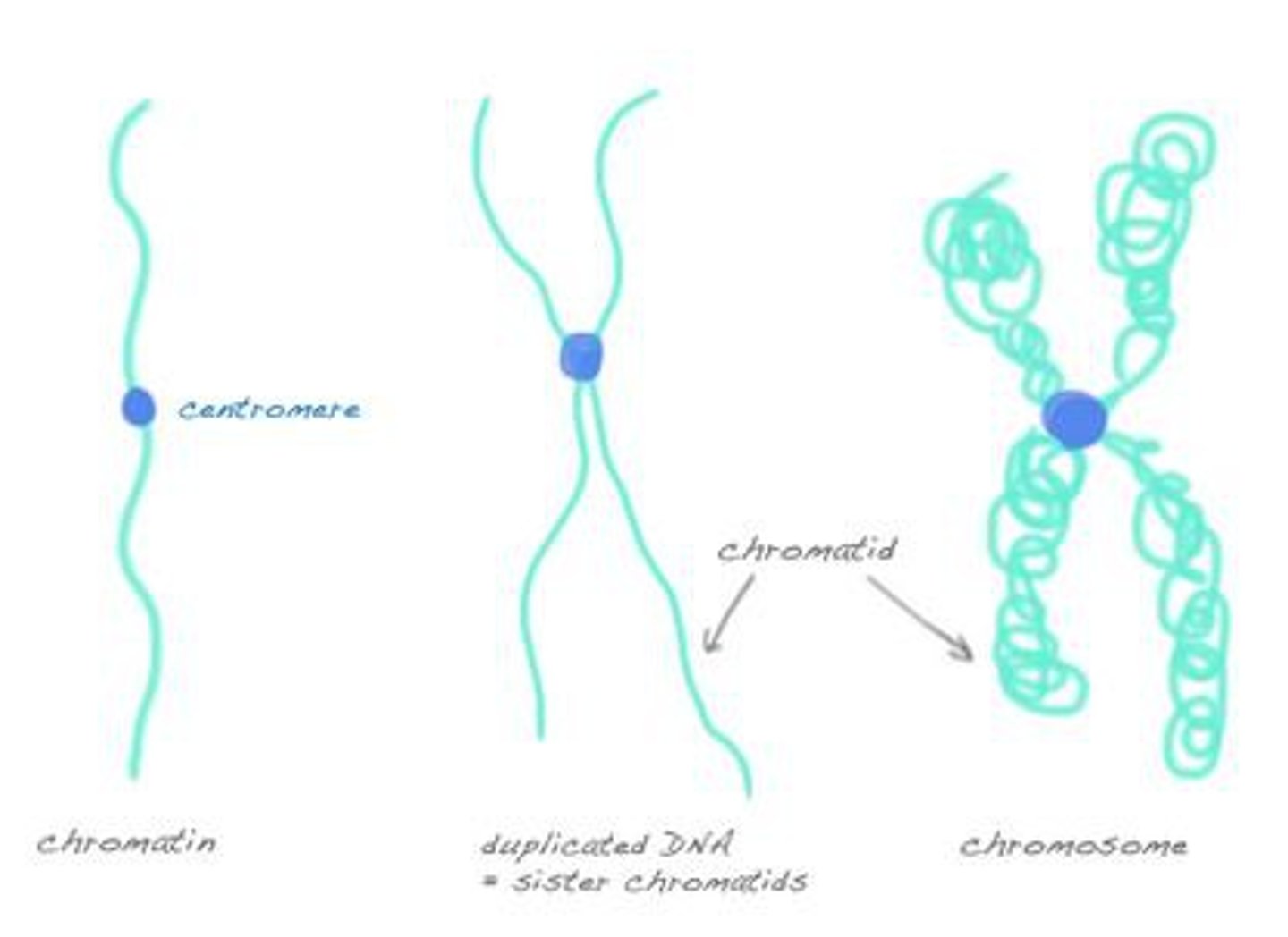
chromatin v. chromosomes v. chromatids
chromatin: the loose combination of DNA & proteins
chromosomes: are made up of a pair of chromatids
chromatids: each of the two thread-like strands into which a chromosome divides during cell division. each contains a double helix of DNA
explain why cells need to supercoil their DNA molecules.
cells need to super coil because it results in condensed structures called sister chromatids.
- to become more organized
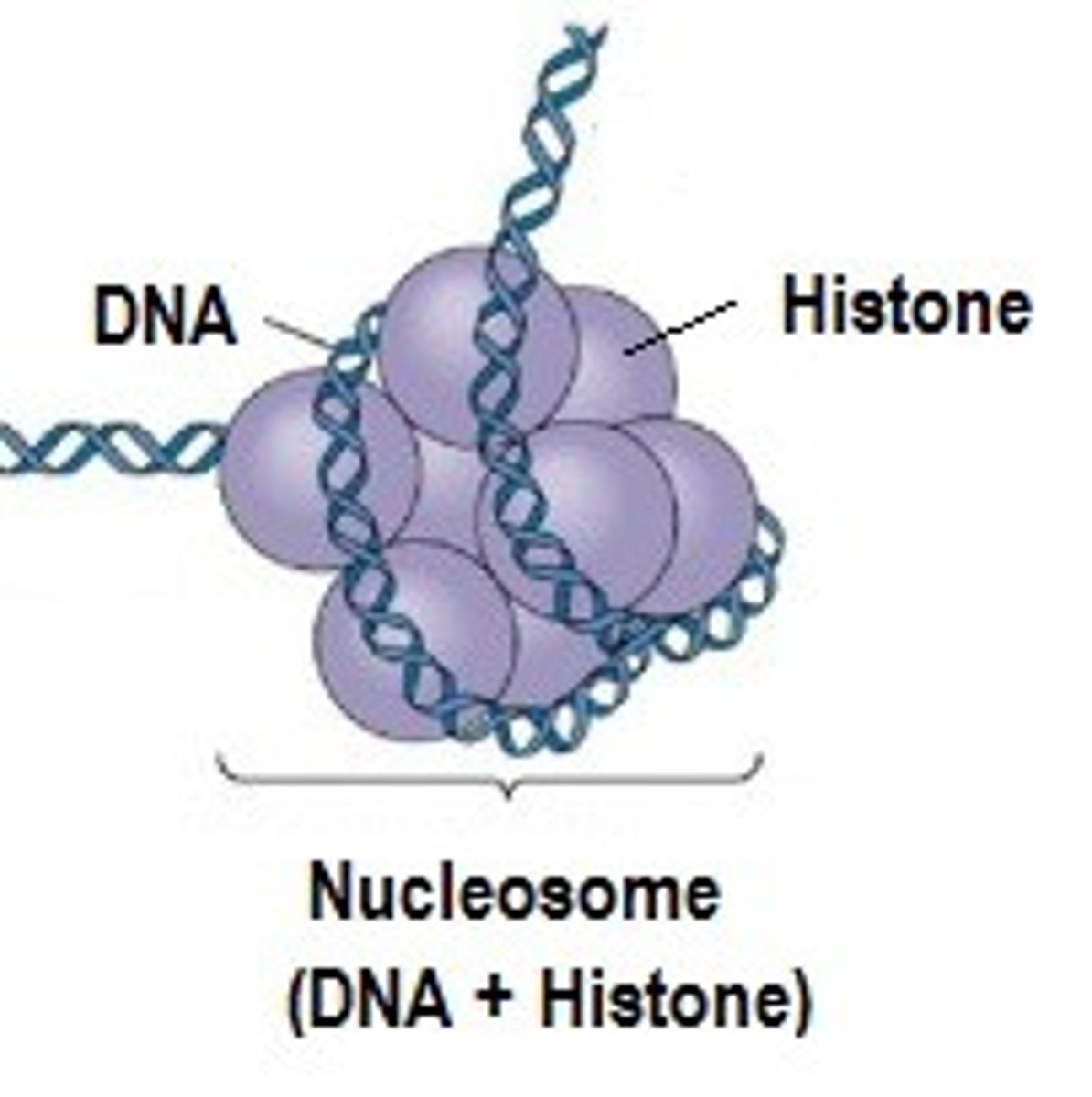
outline how DNA molecules are supercoiled
1. DNA is wrapped around special protein molecules called histones combined loop of DNA and protein is called nuclear zone
2. nucleosones are packaged into a thread. end results is a fiber knows as chromatin.
3. fiber is looped and coiled yet again
4. leading finally to familiar shape of chromosomes. chromosomes are not always present, only when the nucleus is about to divide.
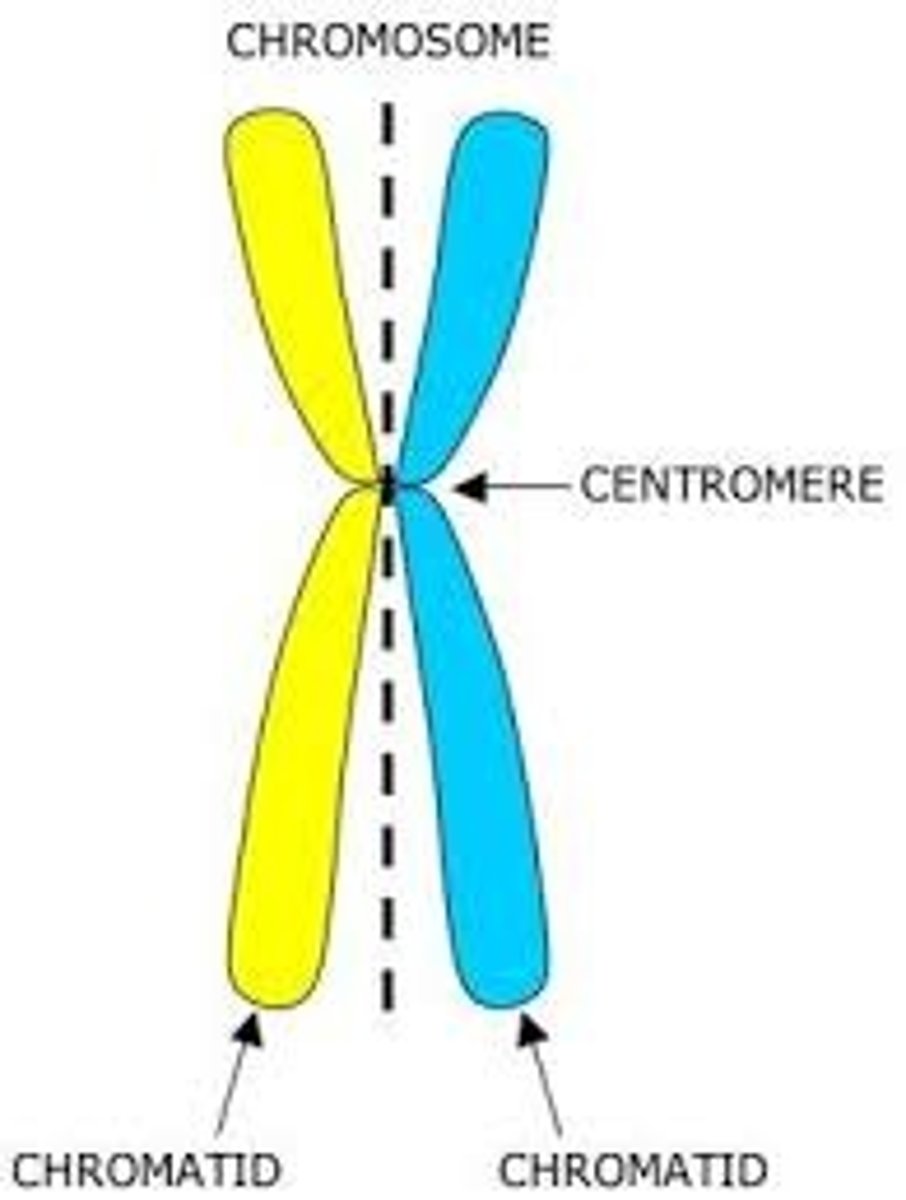
centromere
a region of condensed chromosome that looks pinched
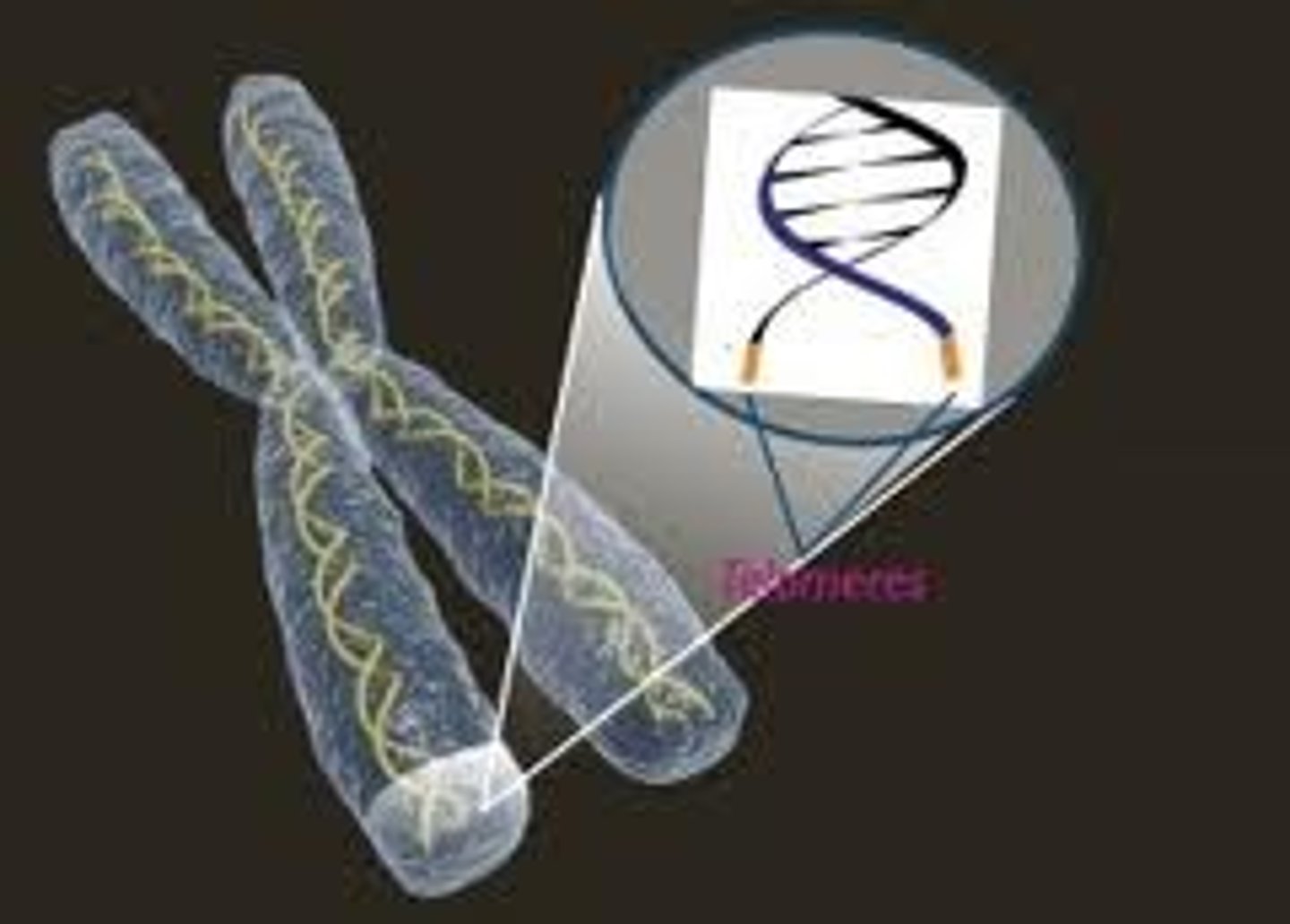
telomere
the end of DNA molecule
- prevents chromosomes from accidentally attaching to each other
histones
protein that organizes chromosomes and around which DNA wraps
tumor
a mass of unspecialized cells that pile up because of abnormal growth
cancer
malignant tumor; a group of diseases involving abnormal cell growth with the potential to invade or spread to other parts of the body
ancogenes
- signals for what the cells need to do (growth)
- can become cancerous after mutating ➟ if this occurs, apoptosis does not happen & the cells keep reproducing uncontrollably
proto-oncogenes & tumor-suppressor genes
proto-oncogenes: start cell division
tumor-suppressor genes: switch off cell division
oncogenes
genes that lead to controllable cell division
mutagens
agents that cause gene mutations
mutation
a change in an organisms genetic code. a mutation/change in the base sequence of a certain genes can result in cancer
carcinogens (& examples)
chemicals that cause mutations
ex: ultraviolet radiation, x-rays, & gamma rays
what factors (other than exposure to mutagens) increase the probability of tumor development in humans?
- late detection
- low immune system
- environmental influence
- life span
- size
- lifestyle choices
- heredity