Lecture 2
1/26
Earn XP
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
27 Terms
Retrospective: questionnaires
Pros: easy to get
Cons: often unreliable, subject to bias
Prospective: sleep diaries
Pros: can be modified to target a specific sleep problem
Cons: labour-intensive, require motivation, captures limited subjective information
What are examples of retrospective and prospective subjective estimation and their pros and cons?
Measures gross levels of motor activity
Estimates sleep-wake patterns → sleep fragmentation
What is actigraphy?
Pros: non-invasive, can be used at home
Cons: records activity-rest patterns so limited sleep data
What are the pros and cons of actigraphy?
Observing motor activity at night
Pros: cheap
What function does video recording serves for studying sleep and what is its pros?
People who are sleep deprived so they fall asleep easily
Brain imaging is often done with which type of people?
Uncomfortable
Invasive
Expensive
What are 3 cons of using brain imaging to study sleep?
Measures hemoglobin concentration
Pros: non-invasive, portable
What does functional near-infrared spectroscopy measures and what are its pros?
It measures heart rate variability and body temperature
An example of a portable EEG is “Oura”, but what does it measure?
Record sleep patterns and are implanted for many day
What function do depth electrodes serve for studying sleep?
In the context of pre-operative or diagnostic epilepsy non-responsive to medication
In what context depth electrodes are used?
Pros: very precise
Cons: very invasive → only for animals
What are the pros and cons of single cell recordings?
Type | Measurement | Function |
|---|---|---|
EOG | Eye movements | Categorize REM sleep or SWS |
EMG | Muscle tonus | Detect REM sleep + diagnosis of sleep disorders |
EKG | Heart rate | Diagnosis of cardiac anomalities in sleep |
EEG | Brain’s electrical activity | Detect sleep onset, sleep stages and detection of anomalies |
What are the 4 different types of polysomnography, their measurements and functions?
Type | Measurement | Function |
|---|---|---|
EOG | ||
EMG | ||
EKG | ||
EEG |
Amplitude: deviation from the baseline
Measures the synchrony of neurons
Frequency: number of cycles per second
Measures the speed of discharge of neurons
What is the difference between amplitude and frequency of EEG waves?
EEG signal
Aggregated activity of thousands of pyramidal neurons perpendicular to the scull
No, there are multiple frequencies combined
In EEG, is there only 1 frequency present at all times?
dominant
In EEG, there is usually a ___________ frequency
Beta | Alpha | Theta | Delta |
|---|---|---|---|
Wake | Resting wake, eyes closed | Sleep onset, NREM1, NREM2, REM | NREM3 |
13-30 Hz | 8-13 Hz | 4-8 Hz | 0.5-4 Hz |
Desynchronized: low amplitude | Synchronized: high amplitude |
Which frequency bands (beta, alpha, theta, delta) are associated with each stages of consciousness/sleep?
Beta | Alpha | Theta | Delta |
|---|---|---|---|
Spatial resolution: location in the brain
Temporal resolution: how quickly it can detect changes
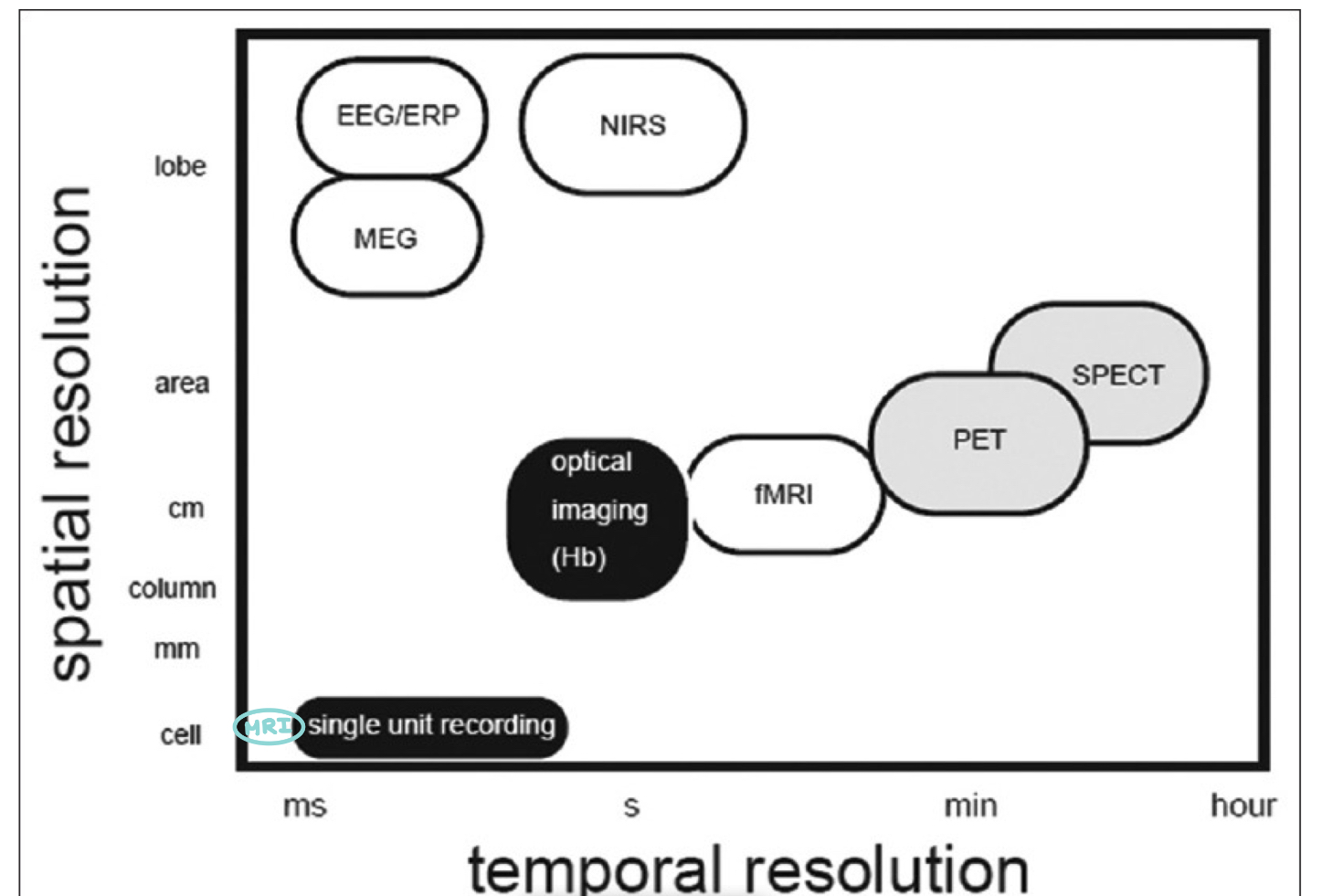
What is the difference between spatial and temporal resolution?
Stages | % | Infos |
|---|---|---|
Sleep onset | - | Gradual process |
NREM1 | 5 | General slowing of brain activity |
NREM2 | 50 | Mental activity range from simple to complex |
NREM3 | 15 | Brain activity is slow and synchronized |
REM | 25 | Mixed frequencies |
What are the 5 sleep stages and their characteristics?
Stages | % | Infos |
|---|---|---|
Sleep onset | ||
NREM1 | ||
NREM2 | ||
NREM3 | ||
REM |
Sigma
memory
neurodegeneration
Sleep spindles:
_________ activity
Plays a role in ___________ consolidation
Associated with protective processes against __________ and brain plasticity
Bipolar
cortical
preserving
K-complex:
________ wave of 0.5 seconds
Plays a role in thalamo-_______ gating
Involved in _________ sleep
REM sleep
In which sleep stage does the face get completely relaxed?
Theta
The vast majority of sleep is in which frequency?
increases
The duration of REM sleep ___________ as the night passes
NREM3 because it is the most important
Which sleep stage is predominant during the 1st half of the night and why?
NREM3
If we wake up in this sleep stage, we feel confused and cranky
Yes they develop it
Do babies develop muscle atonia or are they born with it?