Sterile Compounding Final
1/180
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
181 Terms
What are the challenges of treating peds?
Unfamiliarity of diff w/ adults
Need custom doses for various weights
Need to consider volume to avoid fluid overload
Drug delivery method
Why is pediatric medication safety important?
Increased risk of harm b/c
Limited capacity to tolerate med errors
Possibly unsuitable commercial products
Complex calculations (BSA, etc.)
What is the best practice for pt weights?
Weigh on admission and each encounter
USE METRIC ONLY b/c conversion can cause errors and dosing references use metric only
What are the best practices based on the fact that pediatric drugs are high risk?
Perform independent verification to ensure proper volume prior to each addition esp there is no technology or automation for compounding CSPs
What are the possible methods of parenteral delivery?
IV push
IVPB bag
IVPB syringe
IV syringe continuous inf
Larve volume parenteral
What is IV push?
Rapid drug admin over 1 to 2min
Usually no dilution and dont at bedside
What is IVPB bag?
AKA small parenteral bags
Med delivery in standard volumes of 50, 100, 250ml
Can be commercially made w/ long shelf life and can customize pt-specific dose in standard bag volume
What are the benefits and uses IVPB syringe?
Enhanced ability to customize dose and volume
Controlled drug delivery of intermittent med over set amount of time
Accurately deliver <0.1ml/hr
Extremely common in ped doses that cannot be given using commercially available options
What is continuous infusion and when is it used?
Used for certain meds that you want to administer over time (REQUIRES UNIT OF TIME FOR THE RATE)
Sedation/analgesia for critically ill
CV agents
Meds w/ short HL
What are large volume parenterals?
Deliver continuous infusion to provide pt w/ maintenance fluids
Can be commercially available or customized
What is the process of using IVPB syringes?
Start with original drug product and reconstitute w/ NS or SWFI if needed (may be liquid already)
Dilute reconstitute/liquid even farther to standardized concentration to create stock soln
Transfer proper volume of stock soln into individual unit-dosed syringes
Label syringes w/:
Pt name and identifier
Dose
Diluent and volume
Date prep
BUD
pharmacy tech preparing/RPh check
Why are stock solutions mades at standardized concentrations?
Safety and efficiency
What is the rule of 6s?
Used to calculate infusion rate based on pt weight
6 * weight (kg) = mg drug added to 100ml of diluent
If you infuse at 1ml/hr, then 1mcg/kg/min
NOT USED ANYMORE
What is the downside of rule of 6s?
Risk of 10x error
Each pt on different mg dose since weights are different
Dose may not be w/in stability range
No standard concentration so no standard compounding
When are standard concentrations not used?
Settings where lots of ages treated such as NICU and PICU
What are the safety advantages of standard concentrations?
Less compounding variability
Validated stability references
Interoperability b/w IV room, EMR, syringe inf pump
What is standardize 4 safety and its goals?
Nationwide effort to standardize concentrations of drugs in order to improve transitions of care
Conc and dosing units for IV continuous meds for adults
Conc for compounded oral liquid meds
Conc and dosing units for IV continuous meds for peds
Doses for oral liquid meds
Conc for IV intermittent meds
Conc for PCA and epidural meds
What are smart pumps?
Deliver fluids, meds, blood products at low inf rates in small increments
Have standardized concentration and guardrails to alert practitioner when inf rate is outside of pre-determined limits
What is important about using smart pumps?
Ensuring syringe size and models are compatible w/ syringe pump
Using smallest syringe b/c larger syringe can lower rate
Tubing: for example microbore requires small priming volume
What are the special considerations in neonates in compounding?
Consider fluid status in order to ensure meds are at optimal conc to avoid fluid overload while still ensuring stability
Safety of excipients is important as well as the drug so preservative-free forms are preferred
What are the excipients that can be problematic in neonates?
Benzyl alcohol (bacteriostatic)
Propylene glycol
Ethanol
What are the effects of benzyl alcohol in neonates?
Gasping baby syndrome:
Metabolic acidosis
Resp distress
Seizures
HoTN & CV collapse
Death
What are the effects of propylene glycol in neonates?
CNS tox
Hyperosmolarity
Arrhythmia
Lactic acidosis
What are the effects of ethanol in neonates?
Neurotox
Impaired brain devo
How are pediatric medications usually dosed?
Weight or BSA
What are the BSA equations?
sqrt(in*lb/3131)
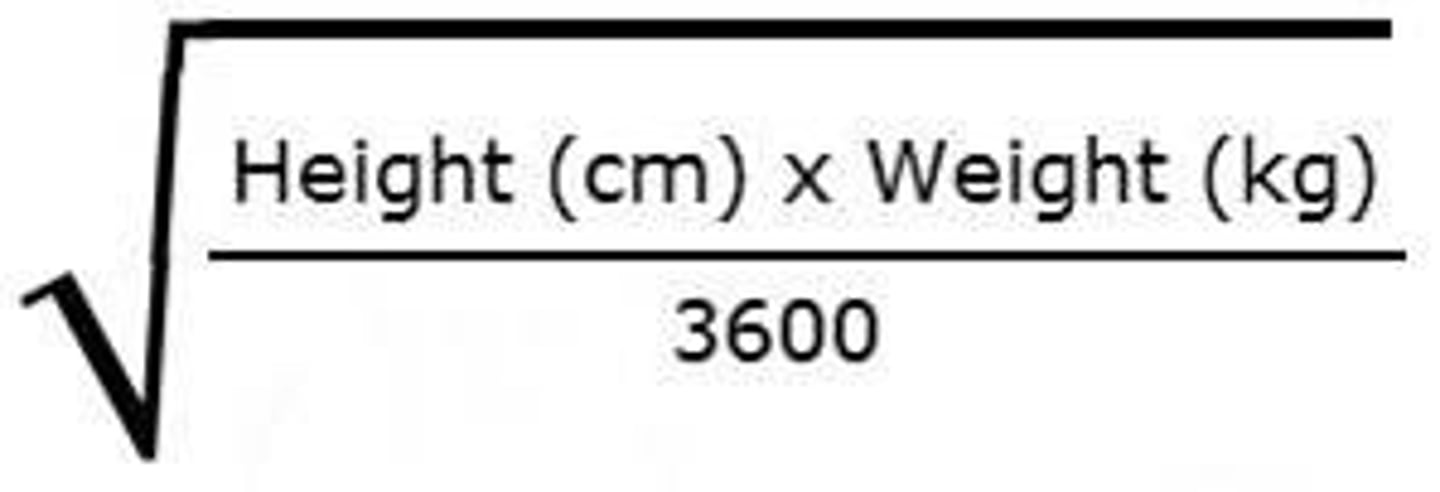
What are the meds that are dosed based on BSA?
Chemo
Steroids
What do we have to consider when thinking of med concentrations?
Fluid status and conditions that may decrease fluid reqs like RDS, decreased renal function
Stability
What are the common products that require pediatric stock solutions?
Antibiotics
Analgesia
Anti-convulsants
Electrolytes
Diuretics
What is CAPS?
Central Admixture Pharmacy Services
Worlds largest parenteral makers
What is the purpose of CAPS?
Outsourcing compounding for health systems
What are the things that CAPS offers?
Parenteral nutrition
Cardioplegia
Chemo
CRRT
Standardized drug delivery
Controlled substances
Prefilled anesthesia syringes
Prefilled pain pumps
What do 503b do?
Made for no specific patient in mind
What do 503a do?
Local customers w/ more customized CSPs for specific pt
When does cleaning occur at CAPS?
B/w every drug every day
What are the quality assurance measures by CAPS?
Rapid sterility testing
Barcode automation
Extended BUD validation
QA reports
How fast is the turn around for CAPS?
4hrs
What is the reception and administration building at nephron?
HR
Executives
Marketing
Inside sales
Regulatory
What is home infusion therapy?
Pharmacy-based decentralized pt care org w/ UP797 expertise
Provides care to pt w/ acute or chronic conditions related to parenteral admin of drugs, biologics, nutrition through canths and/or needles
Extensive professional pharmacy services, care coordination, infusion nursing services, supplies and equipment
What is the Hx of home infusion?
Started in 1970s
$12.8B but will be $87B
1500 infusion pharmacies in US
What are the types of home infusion companies?
Independent companies
National companies
Part of health system
Entities providing 1 or 2 therapies
Entities providing multiple therapies
What are the advantages of home infusion?
Treatment at home
Nurse vitis home to maintain vascular access and ensure pt safety
Pt can resume work and lifestyle
Cost savings b/c decreased LoS
Safe and effective
Pumps are small, portable, and easy to use
Avoid nosocomial infections
Qualified RPh/nurse available 24/7
WHat are the limitations of home infusion?
Not all drugs appropriate
Pt/caregiver must be willing and able to be educated
Home environment requires electricity, running water, safe, clean
Refrigerator may be required
Pt/caregiver must have phone and willing to be in contact abouts meds, progress, deliveries
What is the workflow of home infusion?
Intake
Nursing
Pharmacy department
Distribution
Reimbursement
What does intake in home infusion do?
Case manager at hospital, MD office, HUB receive referral through portal, fax, HCP call
Set up EMR w/ demographics, insurance info
Coordinate benefits for inf materials, nurse visits, lab facilities, supplies
Communicate w/ pt about financial responsibilities
Receive Rx and other clinical info needed for authorizations
What does nursing in home infusion do?
Call referral source back after benefits approved and discuss venous access if 1st dose and what dose to start at home
Set up nursing vitis to change dressing, take blood for labs, change bags, and/or admin meds
Monitor ADRs, anaphylaxis, line care, disease progression
Initiate IV access if hep-lock or midline and may remove PICC once therapy completed
What are the parts of pharmacy department in home infusion?
Pt service associate
Pharmacist
IV techs
What does pt service associate in pharmacy department of home infusion do?
Set up pt chart while verifying pt demographics, address, allergies
Discuss med storage w/ pt/caregiver
Create delivery tickets listing meds and supplies to be sent
What does pharmacist in pharmacy department of home infusion do?
Confirm orders, review pt profile, create care plan, monitor labs
Call pt weekly to review compliance, ADRs, supplies
Conduct MTM if needed
Stage drug checks prior to mixing, QA final orders, check final supplies and drugs for delivery
What do IV techs in pharmacy department of home infusion do?
Stage and label preps
Compound all meds based off compounding order sheet using aseptic tech
Pull all supplies needed to admin med based on delivery ticket
Maintain clean room: document temps, humidity, pressure, cleaning
Inventory
What does distrubtion of home infusion do?
Oversee ordering and inventory
Oversee delivery drivers and 3rd party couriers
What does reimbursement of home infusion do?
Bill insurance (primary and 2ndary) and pts
Collect payments
Post payments
What are the common disease state that are treated by home infusion?
Cancer
CHF
Crohns
Dehydration
GI diseases
Immune disorders: immune thrombocytopenia, lupus
Infection: OM, endocarditis
MS
Pain: hospice, cancer-related pain
RA
What are the drugs given by home infusion?
IV Abx: ceftriaxone, ertapenem, vanc, etc.
IVIG
TPN
IV opioids: opioids, hydromorphone
Chemo: 5FU, cytarabine
Inotropic therapy: milrinone, dobutamine
Specialty infusions: remicade, stelara, etc.
ANYTHING THAT CAN BE SAFELY ADMINISTERED AT HOME
What are the important factors to consider when thinking of home infusion?
IV access type
Evaluate therapy prescribed
Monitoring requirements
What are the types of IV access and what are the factors that need to be considered when thinking of home infusion?
PICC, port, hep-lock, midline, SC access
Verify access suitability for med being administered
Large volume?
Vesicant?
What needs to be considered when evaluating therapy prescribed for home infusion?
CSP stability
Duration and freq of treatment
Mode of admin
Storage and admin requirements: reconstituting, priming, flushing, etc.
Requirement of ANAKIT if 1st dose of therapy at home
What are the monitoring requirements that need to be considered for home infusion?
Labs if ordered
Weight if therapy is weight-based
ADRs
Signs of disease progress/improvement
Signs of infection
Pt specific factors: allergies, height, weight, age, sex, lifestyle
What are the characteristics of hep-lock IV including insertion steps?
Inserted by nurse Q3-5d
After blood return, remove needle and keep access
Tegaderm used to stabilize access
Add extension set so pt can give own meds
Add clamp and cap to prevent blood spilling
Acceptable for short-term home care
SASH flushing
Only certain meds given
Easily removed
What are the characteristics of midline IV including insertion steps?
Inserted and removed by RN w/o x-ray
Cath placed into large veins in arm and extends into peripheral vasculature up to shoulder
Add extension set
Use tegaderm to stabilize access
NOT CENTRAL LINE: cannot give TPN, vesicants, irritants
SASH flushing
What are the characteristics of PICC including insertion steps?
Line threaded through major vein in arm/chest into SVC w/ xray confirmation of line placement
Dressing changed QW
Removed by certified nurses
Good for pt who require freq/cont access
Lasts ~6 months
2-way valve: blood backs up, requires clamping, SASH flush, (if not being used, heparin BID)
1-way valve: no blood, no clamping, SAS
What are the characteristics of port cath including insertion steps?
Inserted underneath skin and goes into vena cava
Needs to be accessed
1-way valve: no heparin needed (SAS)
Needle inserted after palpating and can easily take shower
Used for chemo mostly
What are the characteristics of tunneled caths including insertion steps?
Single, double, or triple lumen
End hangs out chest
2-way valve: needs clamp and SASH
Dressing changed 3/week after 1st inserted
What are the characteristics of SC access including insertion steps?
Small needle goes into leg w/ long line
Remove needle and keep cath in
Can last 1 week
Used for hospice (morphine), hyperemesis, high Fe pt
What are the modes of delivery for home infusion?
IV push
Gravity flow
Home pump
Pole-mounted pump
Ambulatory pump
How do you take care of IV lines?
Sock-like to prevent pulling
Disposable cuffs to take showers
What are the characteristics of IV push?
Easiest for pt
Small volume (10 to 20ml) given over 2 to 10min
Pt/caregiver must be competent
What are the characteristics of gravity flow and types?
30min to 1hr
Requires bole, tubing, +/- rate control device
Cost effective
Straight tubing: count drops
Dial-a-flow: use wheel to calculate flow
Rate-limiting: IV cath access (kinks, size, etc.)
What are the characteristics of elastomeric device (home pump)?
100ml or 250ml balls
Filled w/ saline then medication
Rate determined by size of ball and tubing
Attach, unclamp, then go on w/ day
What are the characteristics of ambulatory pump?
Most accurate (follows programmed dosing schedule)
Spike bag, attach to pump
Put pump and bag in fanny pack (can be cumbersome)
Great for Q4H meds (Abx)
Can be used for TPN (backpack)
PCA mode for pain control
What are the 4 settings of ambulatory pumps and examples of drugs?
Continuous: milrinone, 5FU
Intermittent: Abx
TPN (run 12 to 18hrs) w/ adj for tapering up or down during 1st and last hors
PCA (locked out): morphine, hydromorphone
What is the clinical monitoring done for home infusion?
RPh must have ongoing clinical monitoring including:
Documentation
Collaboration w/ HCPs about monitoring results
Interpreting clinical monitoring to make dose adj, continuation or D/C of therapy recommendations
Pt counseling and MTM
What are the types of lab monitoring done for home infusion?
CBC: infection resolution
WBC count, ANC, CRP, ESR
Vanc: trough and kidney function
Daptomycin: CPK QW at least
Milrinone/dobutamine: BMP, CMP, CBC, Mg, K
Warfarin: INR, PT
What is the type of pt counseling done for home infusion?
Med info: drug, dose, route, freq, duration
Goals and how to monitor goals
Hand hygiene and how to care for vascular access
How to admin meds and precautions
How to inspect meds, containers, supplies
How to use equipment appropriately and troubleshooting
Potential ADRs, DDIs, CIs
How to prepare, store, handle, dispose of meds, supplies, biomedical waste
When to contact MD/RPh and what to do in emergencies
What is tonicity?
Concentration of nonpermeable solutes inside cell vs conc outside cell
MOVEMENT OF WATER
What is osmolarity?
Measure of PERMEABLE and nonpermeable solute concs
Number of osmotically active particles in 1L of soln
What is hypotonic, isotonic, hypertonic in terms of osmolarity?
Hypotonic: <280mOsm/l
Isotonic: 280 to 300mOsm/l
Hypertonic: >300mOsm/l
How is osmoles calculated from moles?
Number of moles * number of particles
What is the equation of osmolarity (mOsm/L)?
Osmoles * 1000/volume (L)
What is the use of osmolarity?
Determine if central or peripheral line can be used by adding Osm of each component
See effect of soln
How is mOsm calculated from mEq?
Calculate mOsm for each measurable ion in soln
Univalent: mEq = mOsm
Divalent: mEq/valence = mOsm
Add mOsm for all ions to obtain total
How can you calculate osmolarity (mOsm) of base solution?
Weight (g/L) x number of species x 1000/MW
Add mOsm for each additive
(Osmolarity of A x volume of A) + (osmolarity of B x volume of B)/total volume
What is the basic brain anatomy in terms of miedications?
CSF protects tissues from mechanical and metabolic insults and is made from choroid plexus
Blood-CSF barrier
BBB restricts chemical access
When is intracerebroventricular administration used?
Certain indications
Infections: severe meningitis, encephalitis
Cancer
Refractory pain
IC hemorrhage
What are the drug delivery routes to CNS?
Lumbar cistern (thecal sac): intrathecal
Lateral ventricle: intraventricular
What are the pros and cons of intrathecal drug delivery?
Bedside
Low risk
Local anesthetic
Separate puncture for each inj leading to cumulative risk
IC hemorrhage risk
What are the pros and cons of intraventricular drug delivery?
Dangerous to repeatedly tap so can but Ommaya reservoir SC w/ cath to ventricle
Infection, IC hemorrhage risk
What are the properties of drugs to be considered before ICV or intrathecal admin and why?
pH
Osmolarity: 281mOsm/L
Volume: rigid skull and non-compressible fluid can lead to increasing CL of drug and/or damage equal to volume injected
CL: hydrophilic drugs trapped
Concomitant systemic admin
Excipients: dont want any preservatives
What is the importance of excipients in intrathecal or IVC admin and what is an example?
Dont want preservatives b/c benzyl alcohol can cause metabolic acidosis, cerebral palsy, IV hemorrhage
Abx like pen G can cause seizures in systemically
Only certain products have preservative-free forms
What are the indications of parenteral nutrition (PN)?
Gut dysfunction
Malabsorption
Critically ill/trauma/catabolic
Severe pancreatitis
No enteral access
Enteral nutrition not possible to be resumed in 7 to 10d
What is the classification of PN by ISMP?
High alert b/c complex and many aseptic manipulations
What are the typical components of PN?
Base: AAs, dextrose, ILE, sterile water
Electrolytes
Vits and trace elements
Others (not recommended): famotidine, insulin, heparin
What are the 2 delivery methods of PN?
Traditional dextrose-AA (2-in-1) w/ ILE separate
Total nutrition admixture (TNA AKA 3-in-1 or all-in-1) w/ ILE included
24hrs of nutrition at constant rate or cyclic
What is the hang time of ILE?
12hrs b/c infection risk
What are the filters for PN?
ILE: 1.2 microns b/c fat globulins require larger filters
2-in-1: 0.22 microns which can filter micro-precipitates and bacteria
Y-site: 1.2 and 0.22 micron filters (0.22 near 2-in-1 and 1.2 micron downstream of ILE)
What are the advantages and disadvantages of 2-in-1 PN?
More stable
0.22 micron used: bacterial and micro-precipitate
Clear
Decreased cation interactions
Some premixes available
Might need multiple inf
More complex admin
What are the advantages and disadvantages of 3-in-1 PN?
Increased convenience
Reduced entries into central venous cath
More efficient prep
Convenient for home-care pharmacies
Possibly improved fat CL
Requires 1.2 micron filter (doesnt elim bacteria)
Admix w/ ILE is less stable over time b/c more incompatibilities
Difficult to visualize precipitates
Home admin may increase catheter occlusion risk
What is the process of ILE destabilization?
Addition of low pH (like dextrose) or electrolytes leading to deflocculation, coalescent, then creaming/breaking
What does the choice in delivery method of PN depend on?
Pt served
Convenience
Compatibility/stability issues
Logistics: ordering process, labeling format