Smedes Flashcards
1/201
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Smedes Flashcards
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
202 Terms
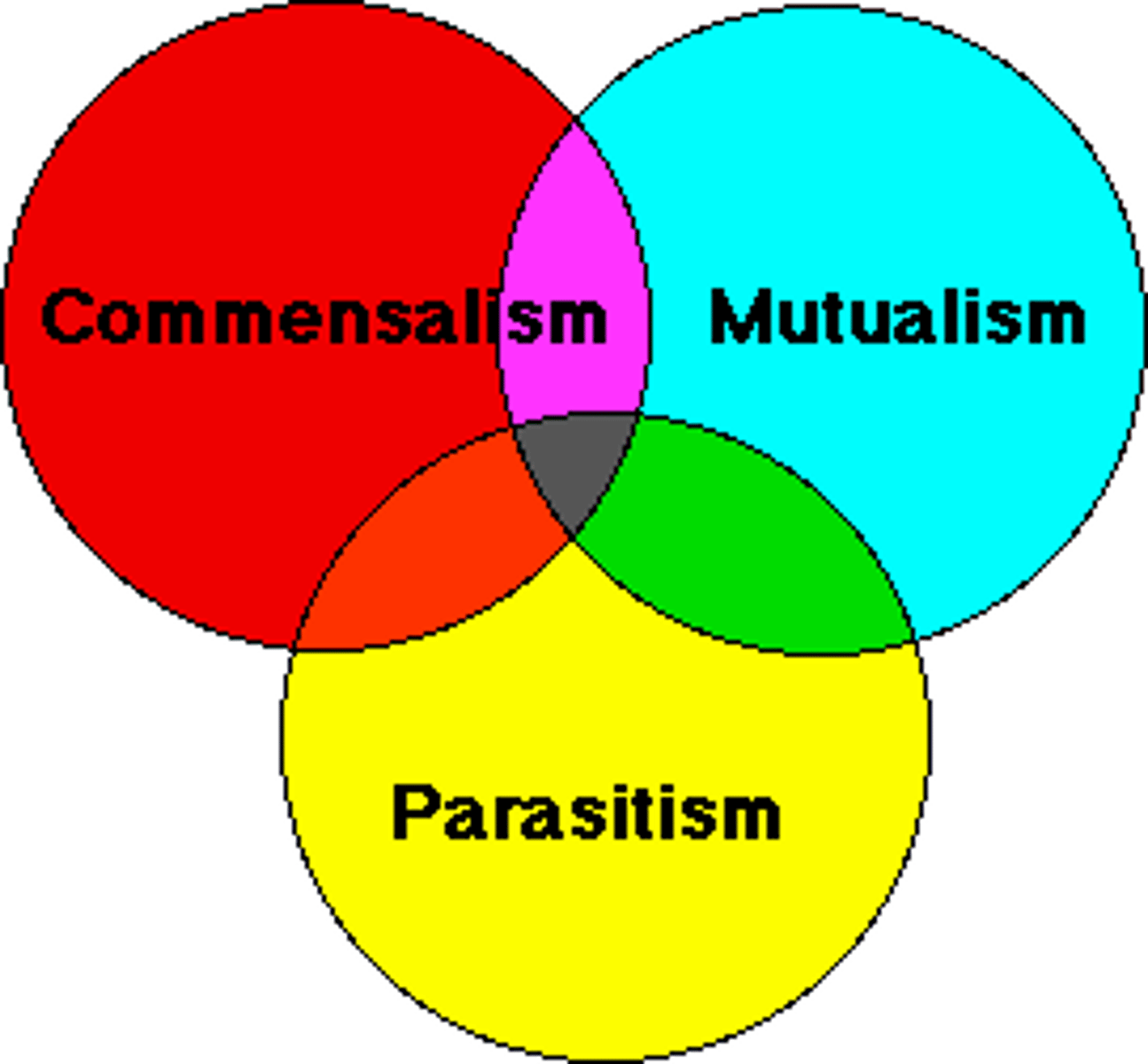
Symbiosis
A relationship in which two different species live in close association with each other in a long-term relationship
Ecosystem
All of the abiotic (non-living) and biotic (living) components of a given area

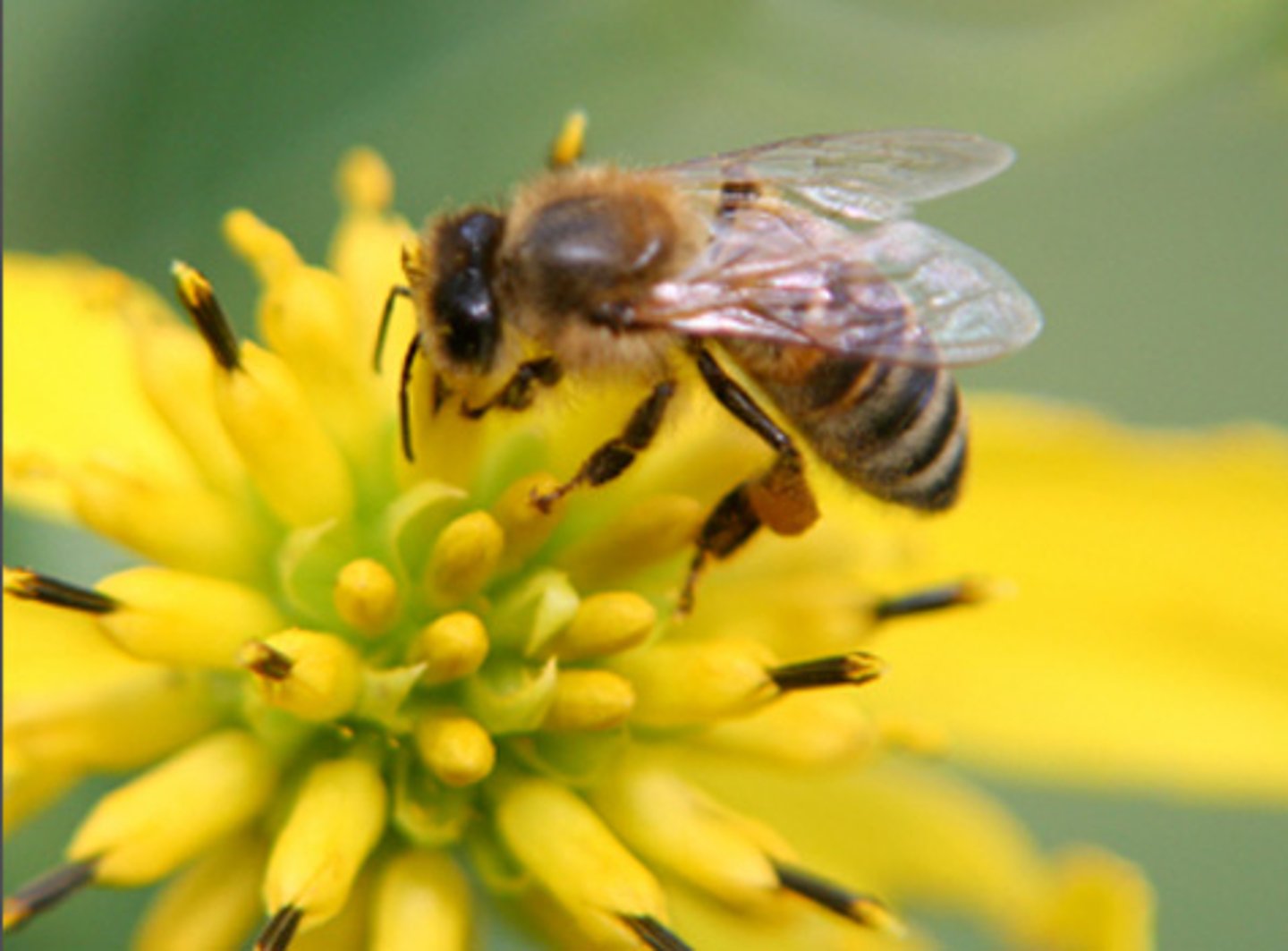
Mutualism
A relationship between two species in which both species benefit

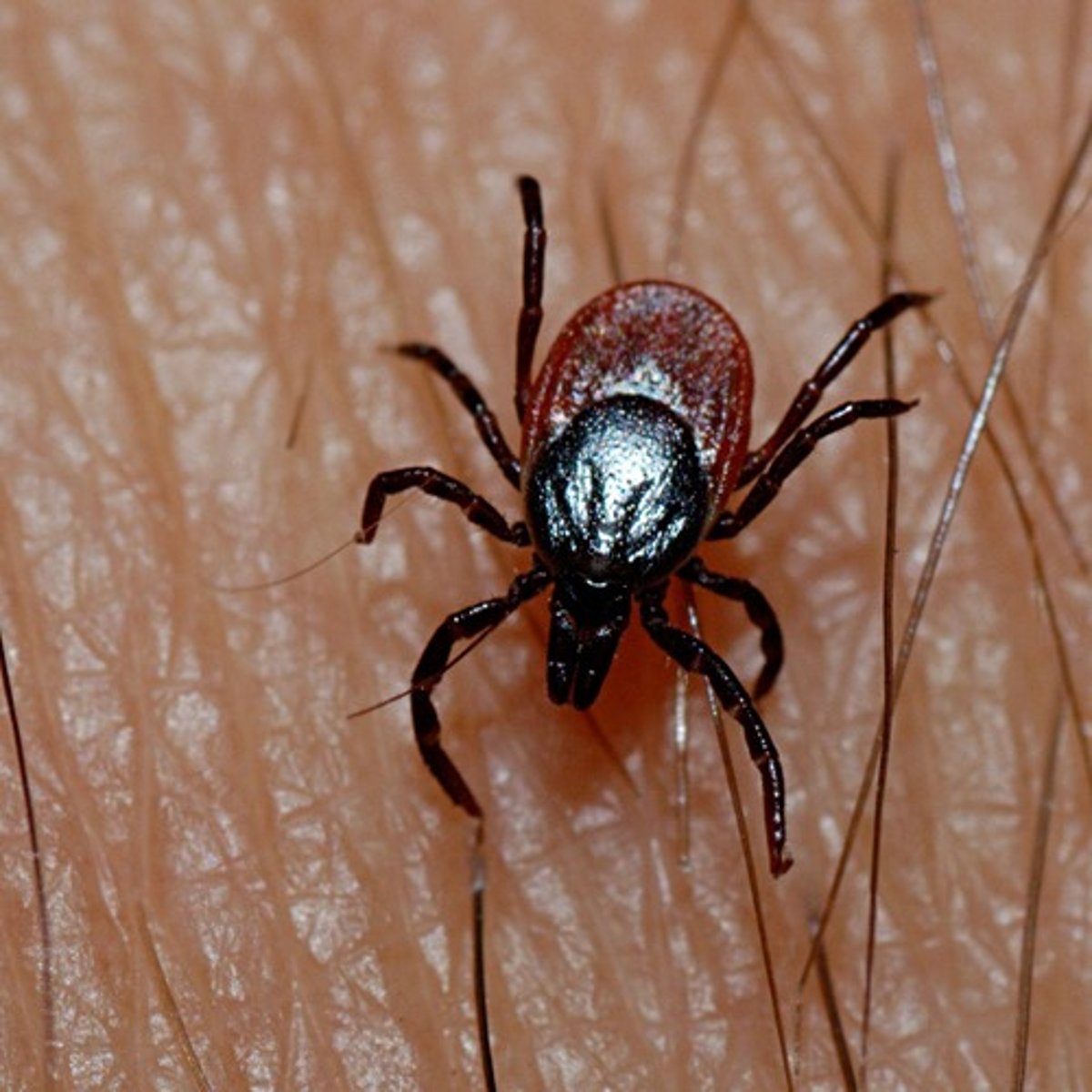
Parasitism
A relationship between two organisms of different species where one benefits and the other is harmed. The parasite often lives inside of and using the host as an energy source, although not always.

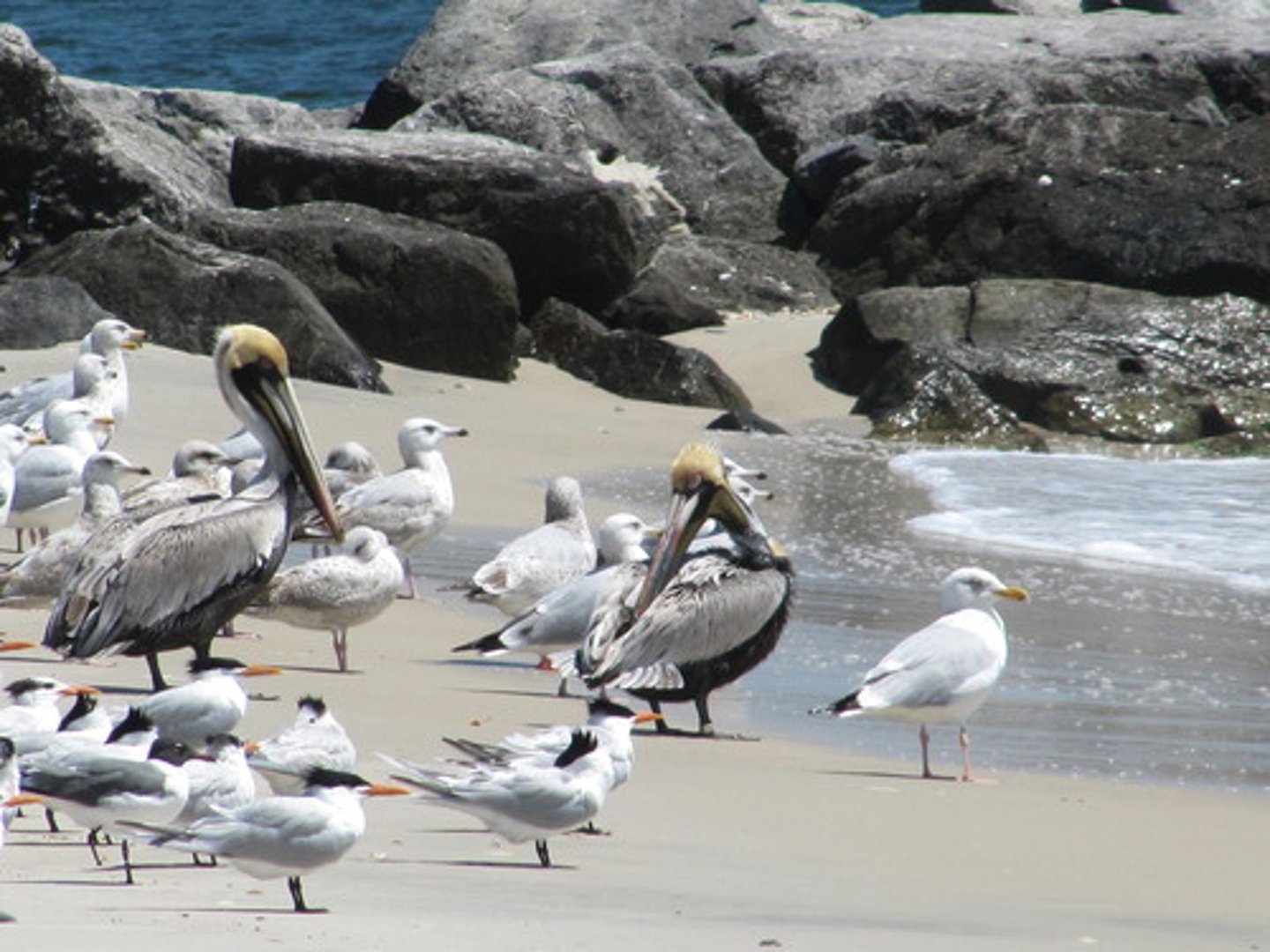
Interspecific competition
competition between members of different species, such as lions and hyenas competing for food

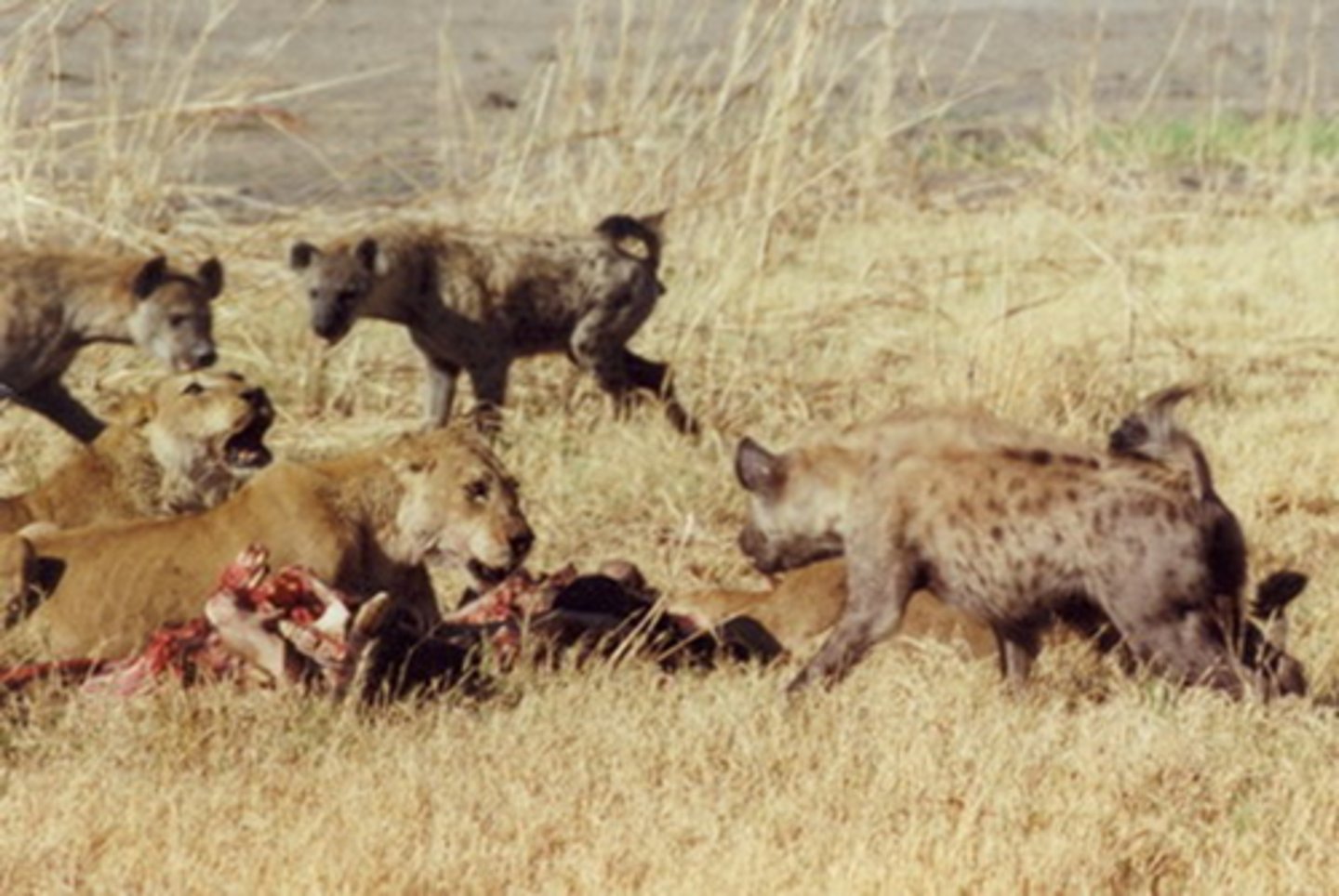
Competition
A common demand by two or more organisms upon a limited supply of a resource; for example, food, water, light, space, mates, nesting sites. It may be intraspecific or interspecific.

Resource partitioning
The evolution of behavioral and physical adaptations that allow two species to reduce their competition for a shared resource
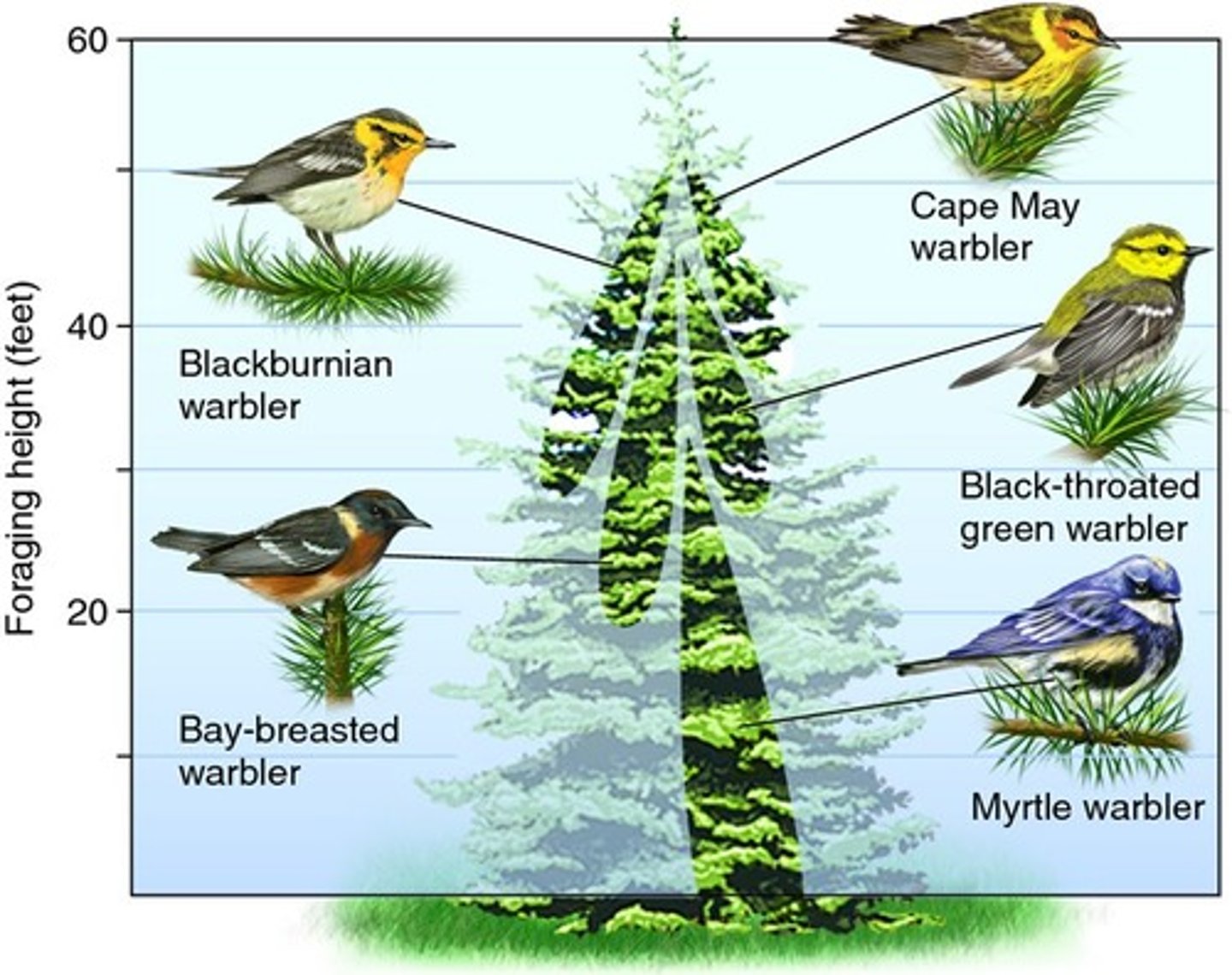
Coevolution
Process by which two species evolve in response to changes in each other. Can often result in resource partitioning or mutualistic relationships

population
A group of individuals that belong to the same species and live in the same area

community
All the different populations that live together in an area

Salt Marsh
An estuary marsh, found along the coast in temperate climates. Mix of fresh and salt water. Highly productive breeding grounds for many fish and shellfish species.

Aquatic
relating to water
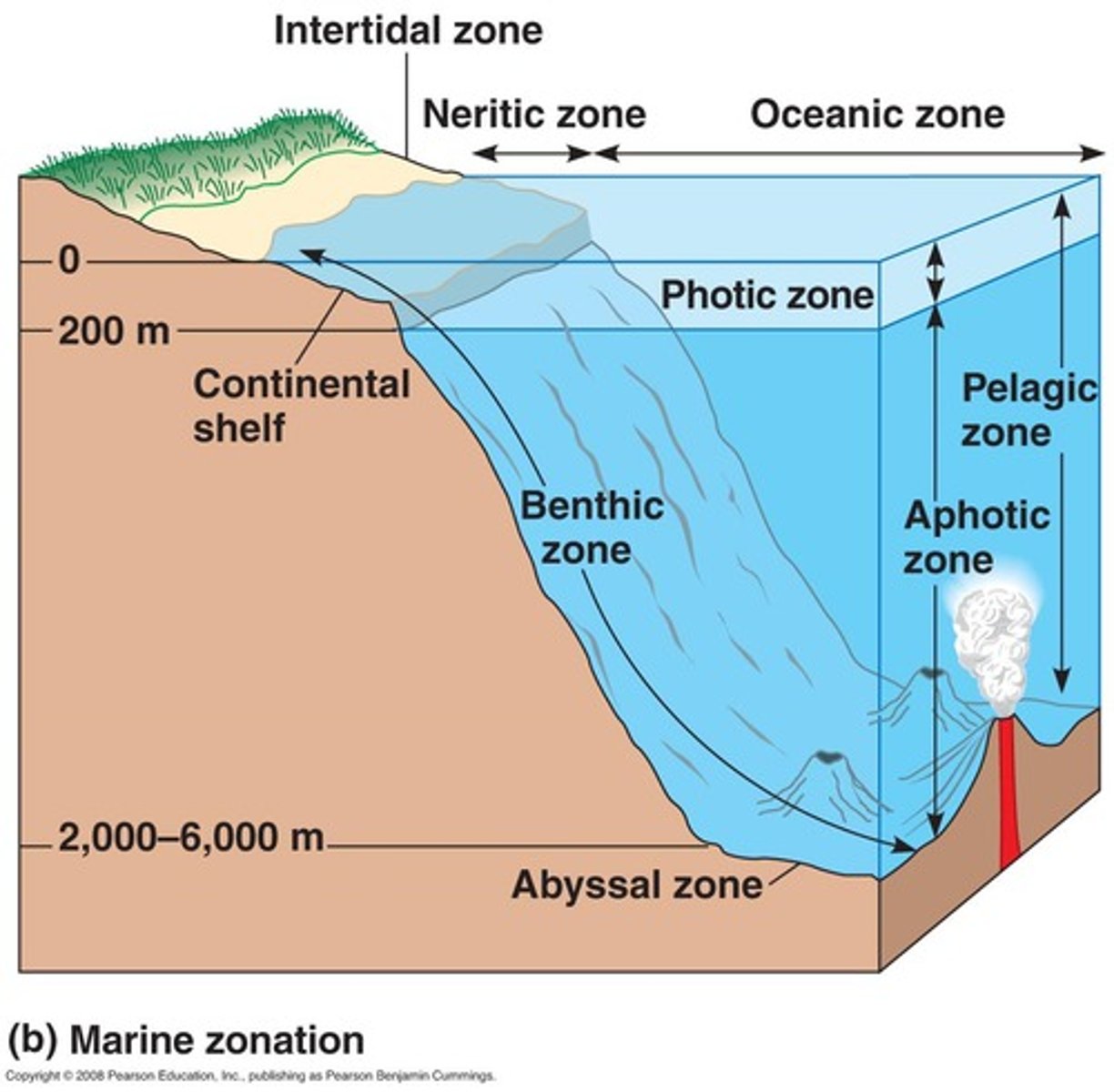
benthic zone
bottom of an aquatic ecosystem; consists of sand and sediment and supports its own community of organisms
Open Ocean
Deep, salty aquatic biome. Largest boime on earth. Algae in this biome produce a significant portion of earth's oxygen via photosynthesis
Coral reef
Shallow, warm, ocean biome featuring the symbiotic relationship between coral and algae. Coral supply the calcium-carbonate reef for algae to live in, as well as nutrients and CO2. The algae use nutrients and CO2 for photosynthesis and release sugar for the coral to use as energy.

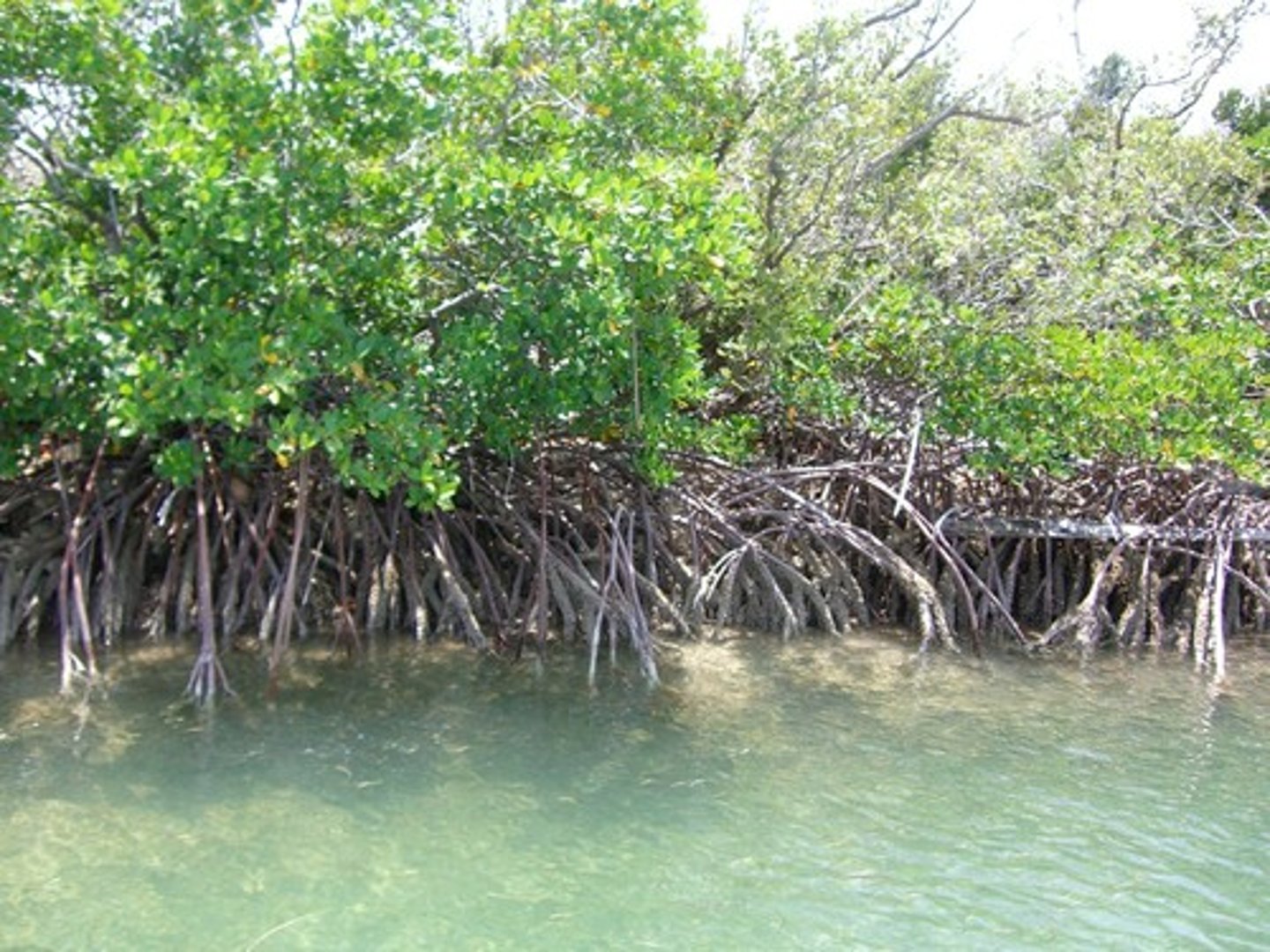
Mangrove swamps
A swamp biome that occurs along tropical and subtropical coasts, and contains salt-tolerant trees with roots submerged in water. Roots provide organic matter and habitat for many fish & shellfish species as well as stabilizing the shoreline from erosion.

Estuary
A habitat in which the fresh water of a river meets the salt water of the ocean. High levels of organic matter term-50are deposited by the river, making them high nutrient, highly productive ecosystems.
Algae
a very simple plant without stems or leaves that grows in or near water.
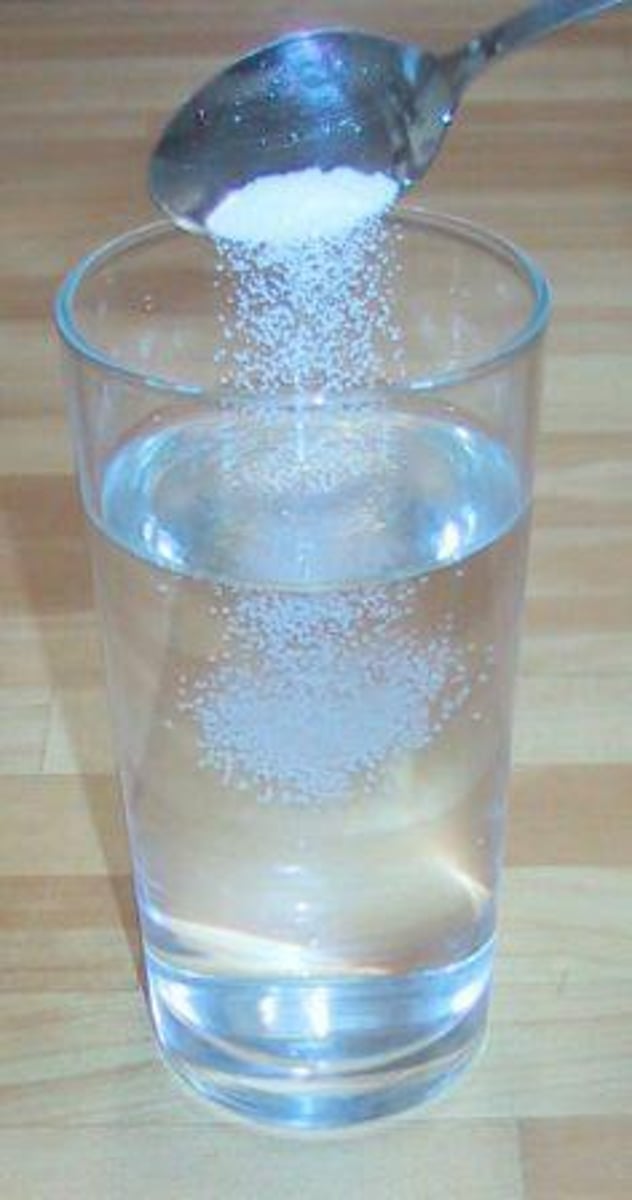
Salinity
A measure of the amount of dissolved salts in a given amount of liquid.

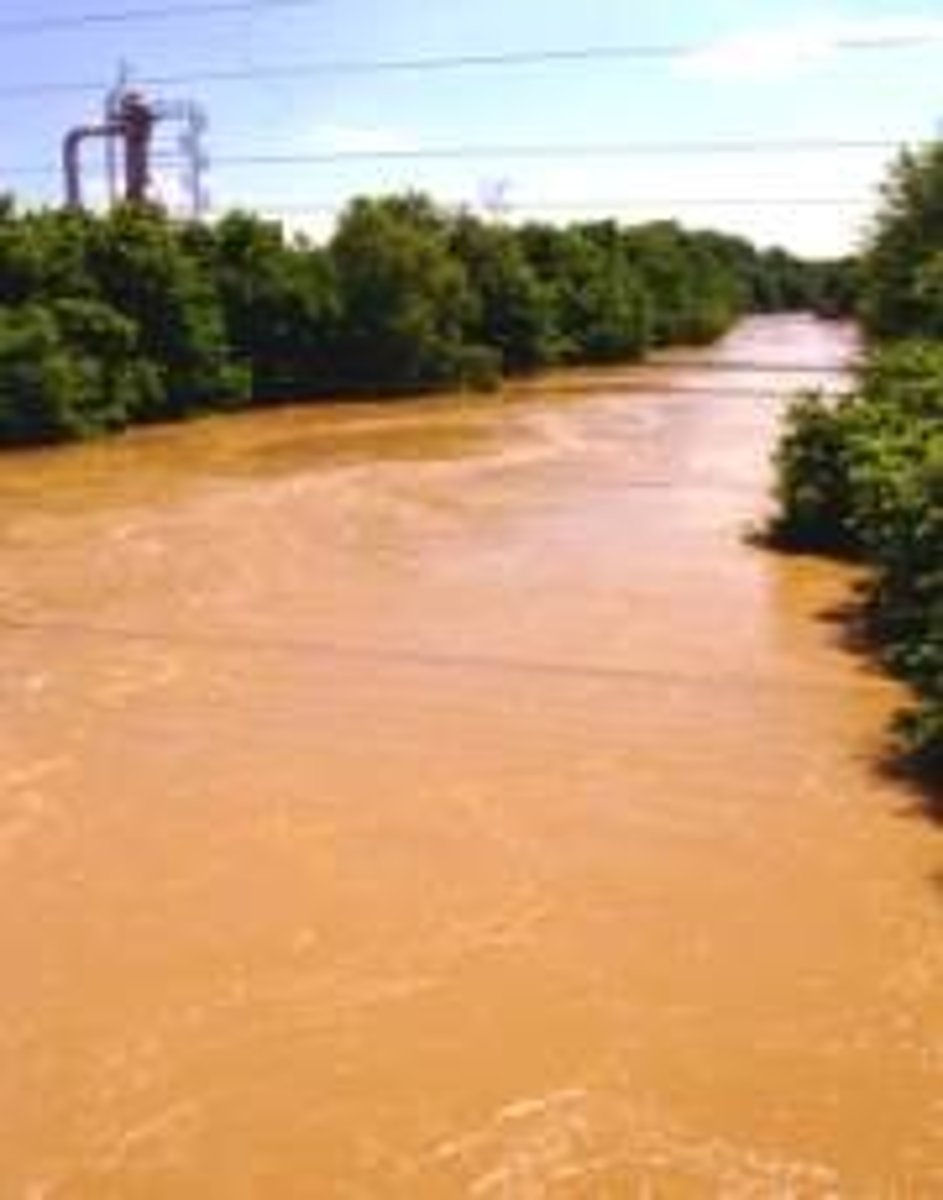
Turbidity
A measure of how cloudy water is (higher turbidity = more cloudy). Sediments like sand and leaf litter increase turbidity.

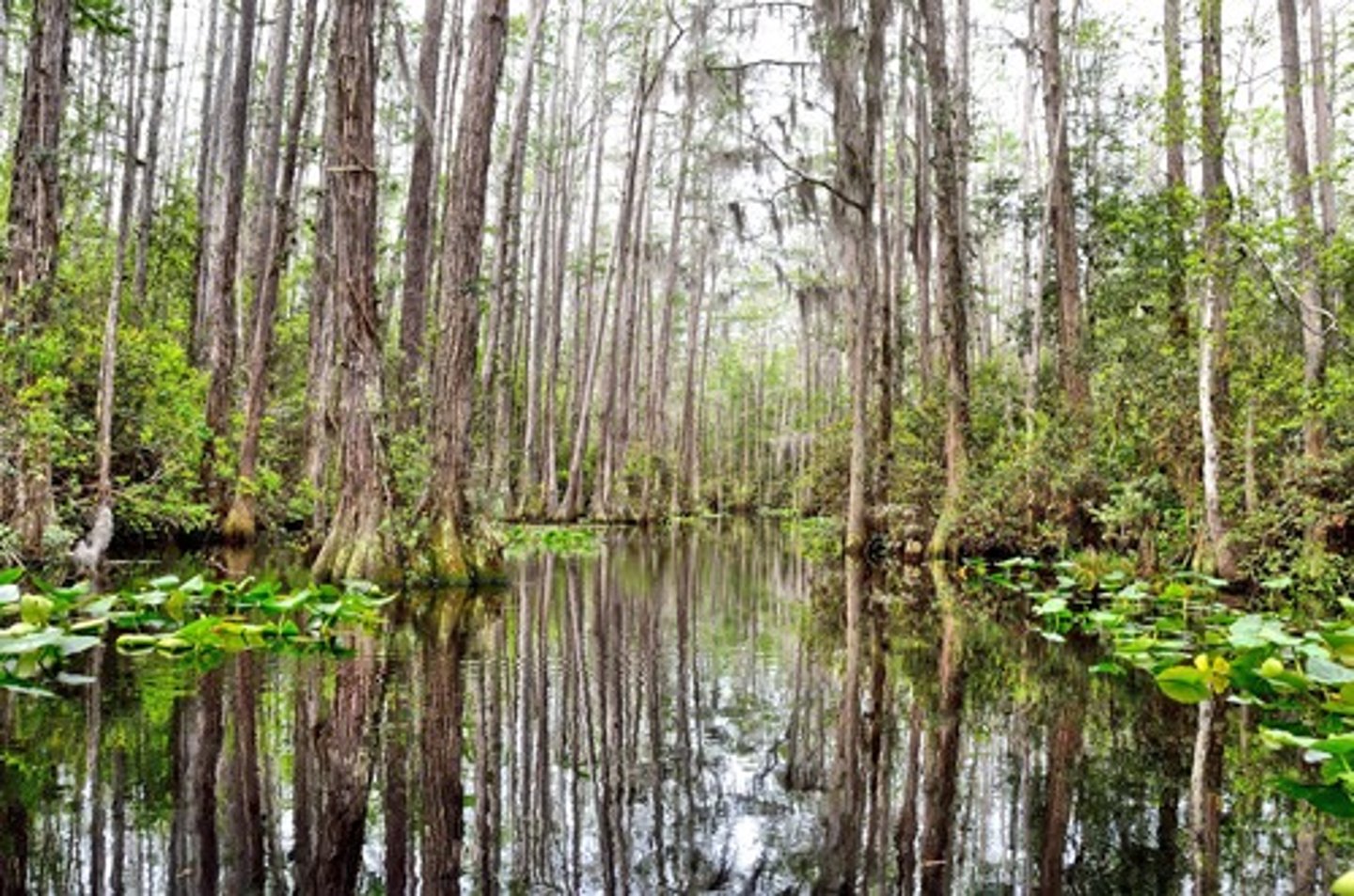
Freshwater Wetlands
An aquatic biome that is submerged or saturated by water for at least part of each year, but shallow enough to support emergent vegetation such as trees and cattails. Plants must have adaptations to allow them to survive water-logged soil.

biome
An area with a particular average temperature and precipitation (climate)
Terrestrial
relating to the land (not aquaitc, or water-based)
Climate
The average weather conditions in an area over a long period of time
Taiga (boreal forest, northern coniferous forest)
Forests with mostly coniferous (cone-bearing) trees that can tolerate cold winters and short growing seasons. Needles of coniferous trees are adapted to tolerate freezing temperatures, so they stay on all year (evergreen).
Cold temperature, waxy, tough needles that don't break down easily both contribute to slow decomposition and low soil nutrient levels.
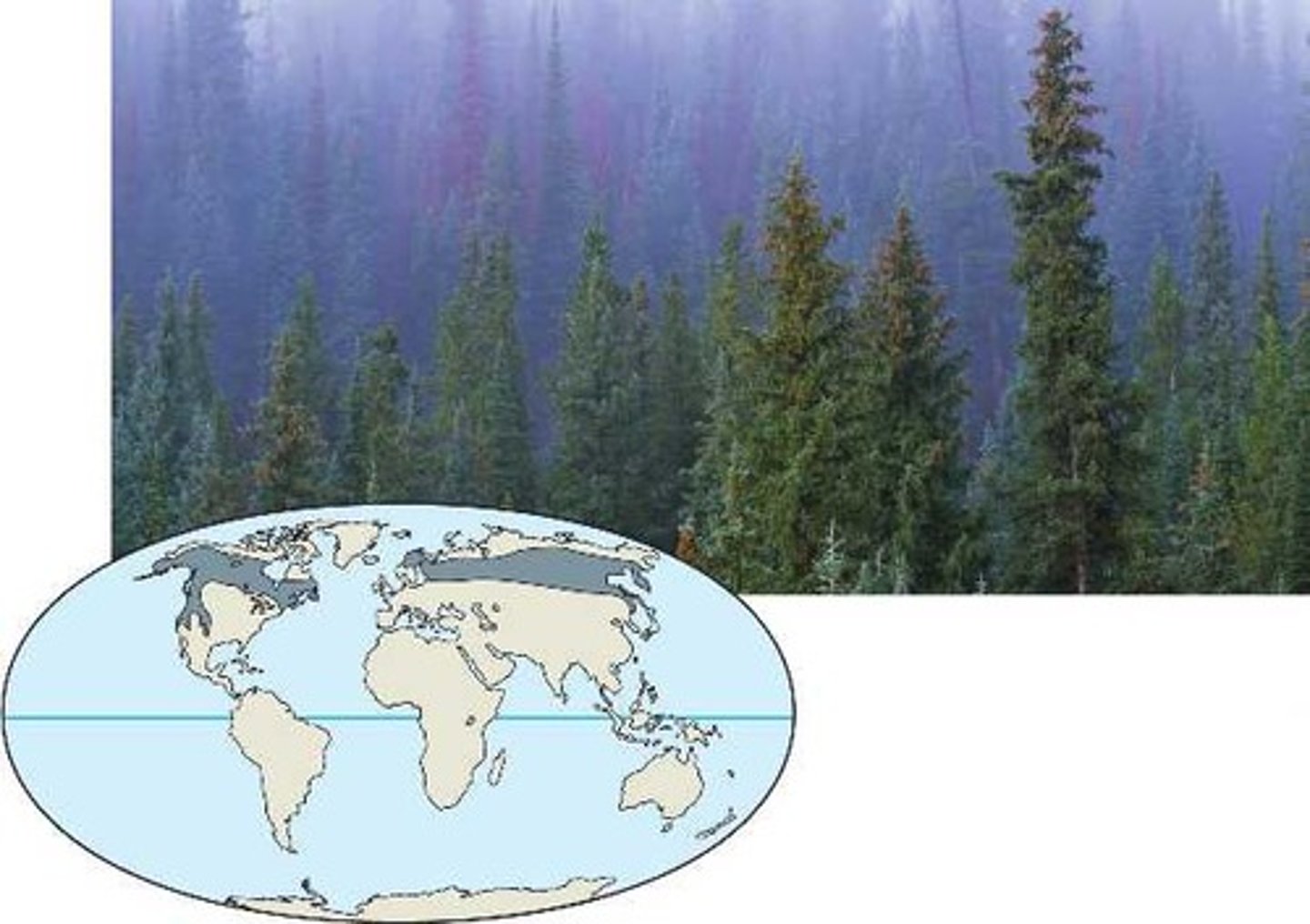
Tundra
Flat, cold, treeless biome with permanently frozen soils in winter, and a short, 4 month growing season in the summer. Even in summer, deeper soil remains totally frozen (permafrost) preventing taller trees from establishing roots. Mostly shrubs, grasses, mosses, and lichens that can withstand shallow, waterlogged soil & cold temperatures.
Cold temp. = low decomp. = low soil nutrients
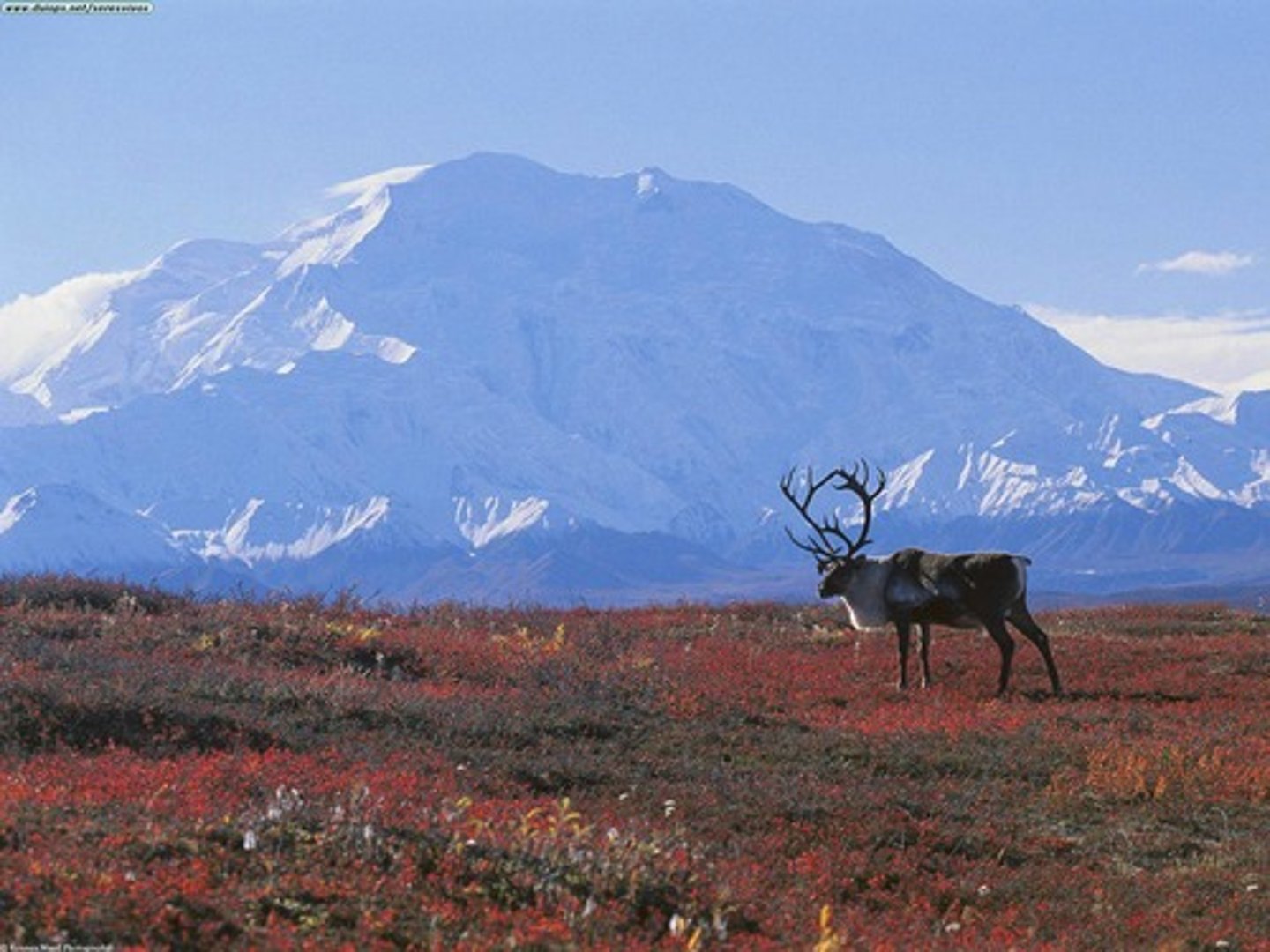

temperate seasonal forest
A biome with warmer summers and colder winters than temperate rainforests and dominated by deciduous (broadleaf - maples, oaks, etc.) trees.
High summer temp. = faster decomp.
Broadleaves easier to decomp. than needles = higher soil nutrients than boreal forests or temperate rainforests
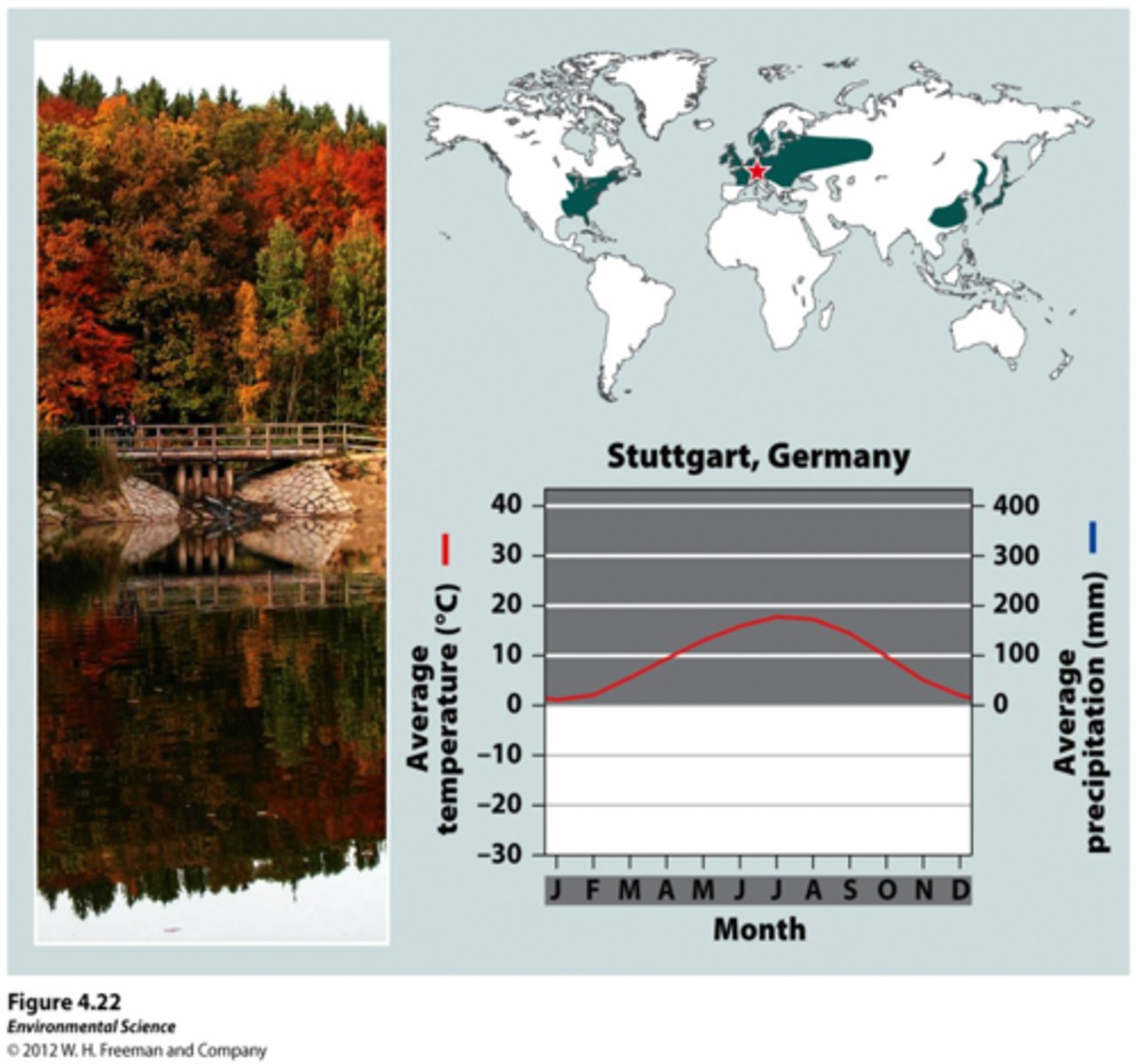
Temperate rainforest
Cool, rainy forests found along coasts, such as the northern Pacific. Water vapor from oceans keeps the temperature moderate and provides lots of moisture for high precipitation. Huge conifers like the red woods of California are found in these biomes.
Cooler temperature = slow decomp.
heavy rainfall & rapid absorption by large trees = low nutrient levels in soil
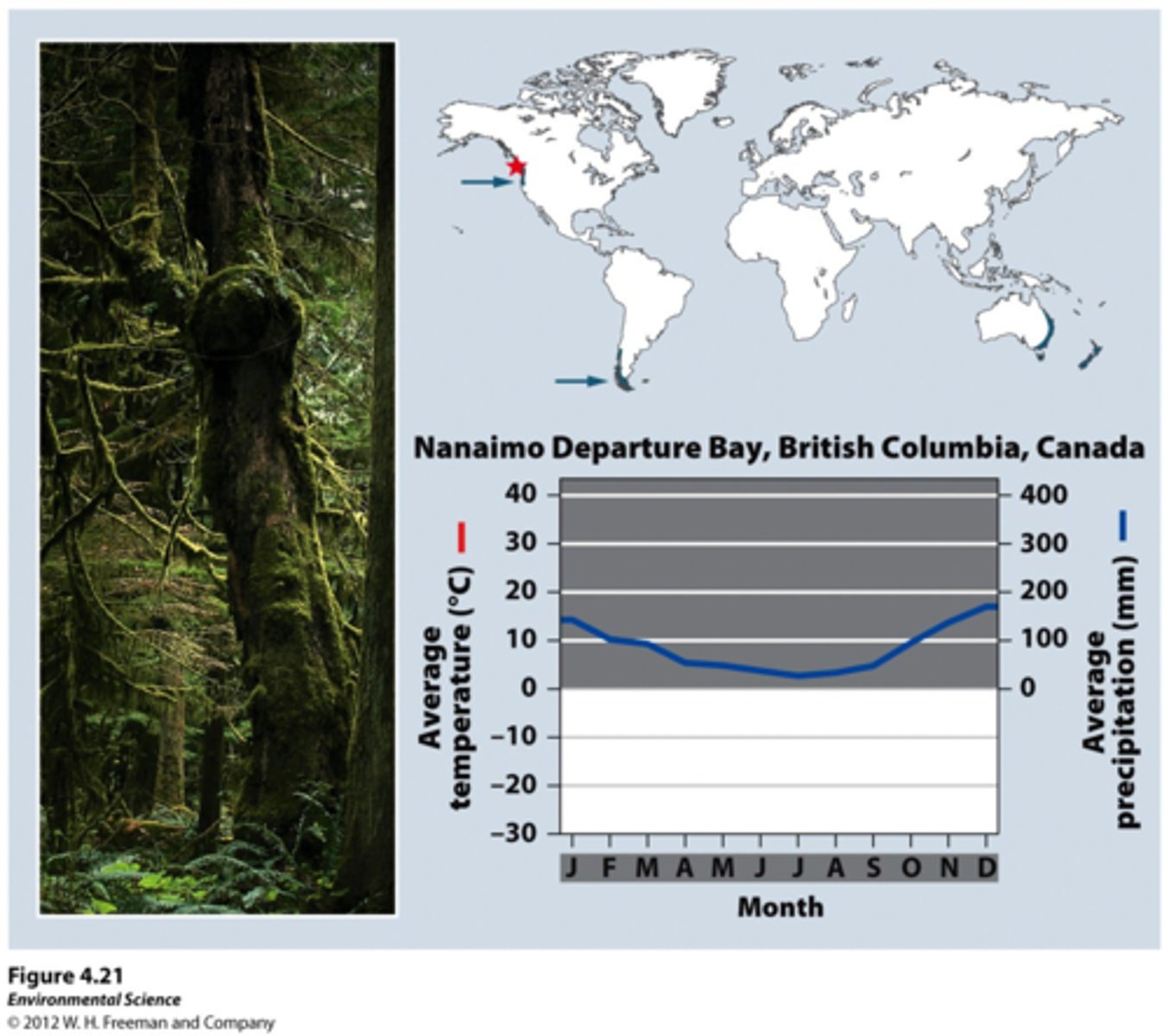
woodland/shrubland (chaparral)
Hot dry summers with mild, rainy winters. 12 month growing period, but relatively low precipitation in summer, and lower temperature in winter limit plant growth. Plants here must be adapted to both fires and drought (sagebrush, scrub oak, and shrubs).
High rain in winter = leaching of nutrients = low nutrient soil
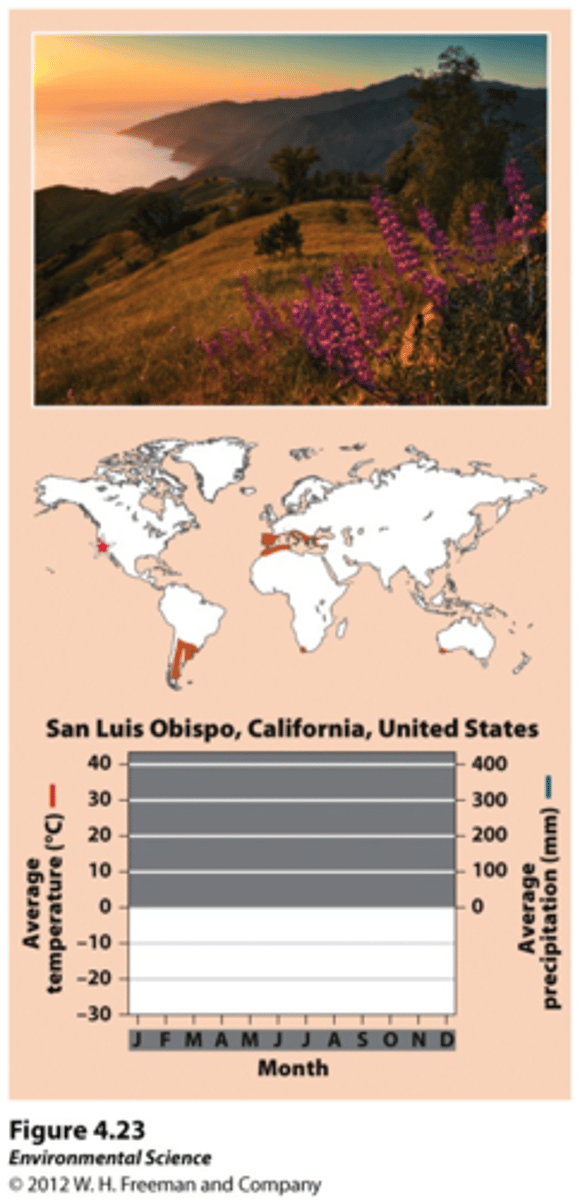
Tropical rainforests
Near the equator. Warm with lots of precipitation. Little seasonal temperature variation. Highly productive (high plant growth) terrestrial biome.
Hot temp. = rapid decomp. of organic matter
High plant growth = rapid absorption of nutrients
Low nutrient soils

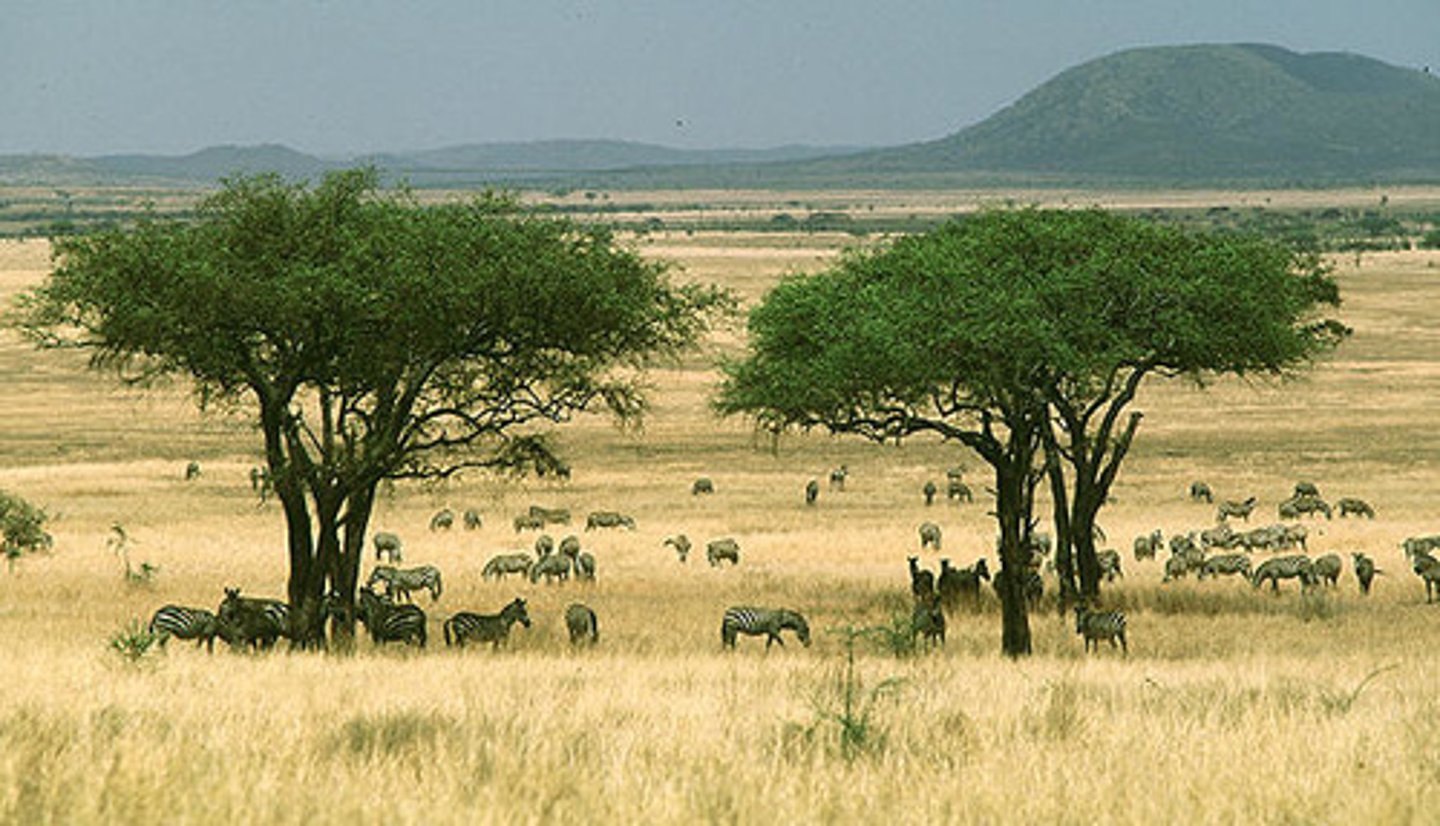
Savanna
Warm biome with distinct wet and dry seasons. Dominated by clustered trees and widespread grasses. Trees adapted to drought by dropping leaves in dry season.
Warm temperature = high decomp. = high soil nutrients

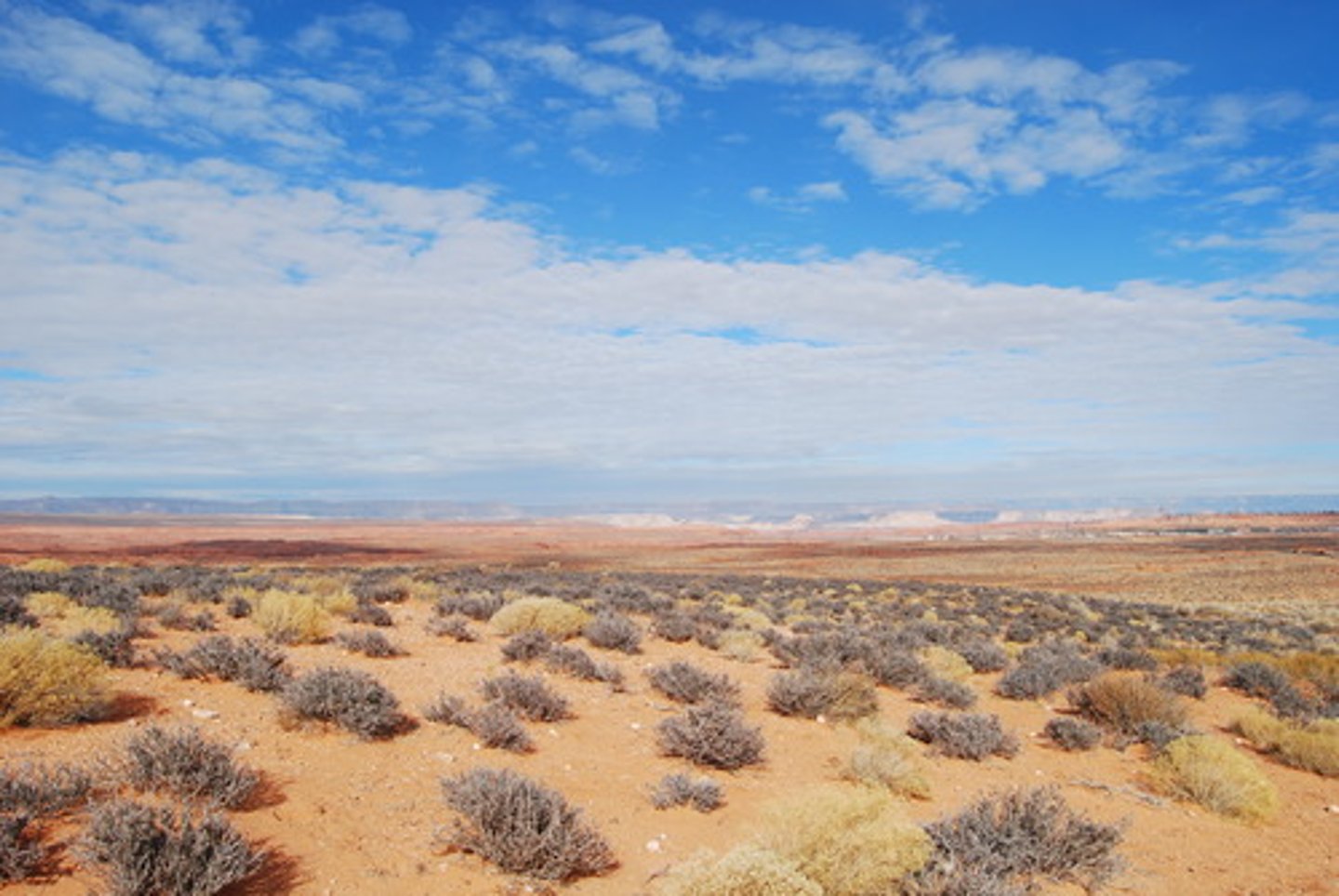
Desert
Occur around 30 degrees N & S latitude. Very high temperatures and low precipitation levels limit plants to drought-resistant species like cacti & succulents. Needles are modified leaves to prevent water loss and most photosynthesis happens in the stem, to limit water loss.

Latitude
distance north or south of the Equator, measured in degrees
Altitude
Elevation (height) above sea level
Permafrost
permanently frozen layer of soil beneath the surface of the ground, particularly in tundra biomes. Thaws out in the winter to produce standing water and water-logged soils that further restrict plant growth in tundra biomes.
temperate grassland/cold desert
Great plaines (prairie) biome with cold, harsh winters and hot, dry summers restrict plant growth to mostly grasses and non-wood plants like wild flowers. Deep roots can reach water in droughts and store energy for quick regrowth after frequent fires due to such dry conditions.
High temperature & long growing season = rapid decomp. = high soil nutrients
Carbon reservoirs
Relatively stable, short-term stores of carbon on earth.
Ex: fossil fuels, soils and sediments, plant and animal biomass, and the atmosphere
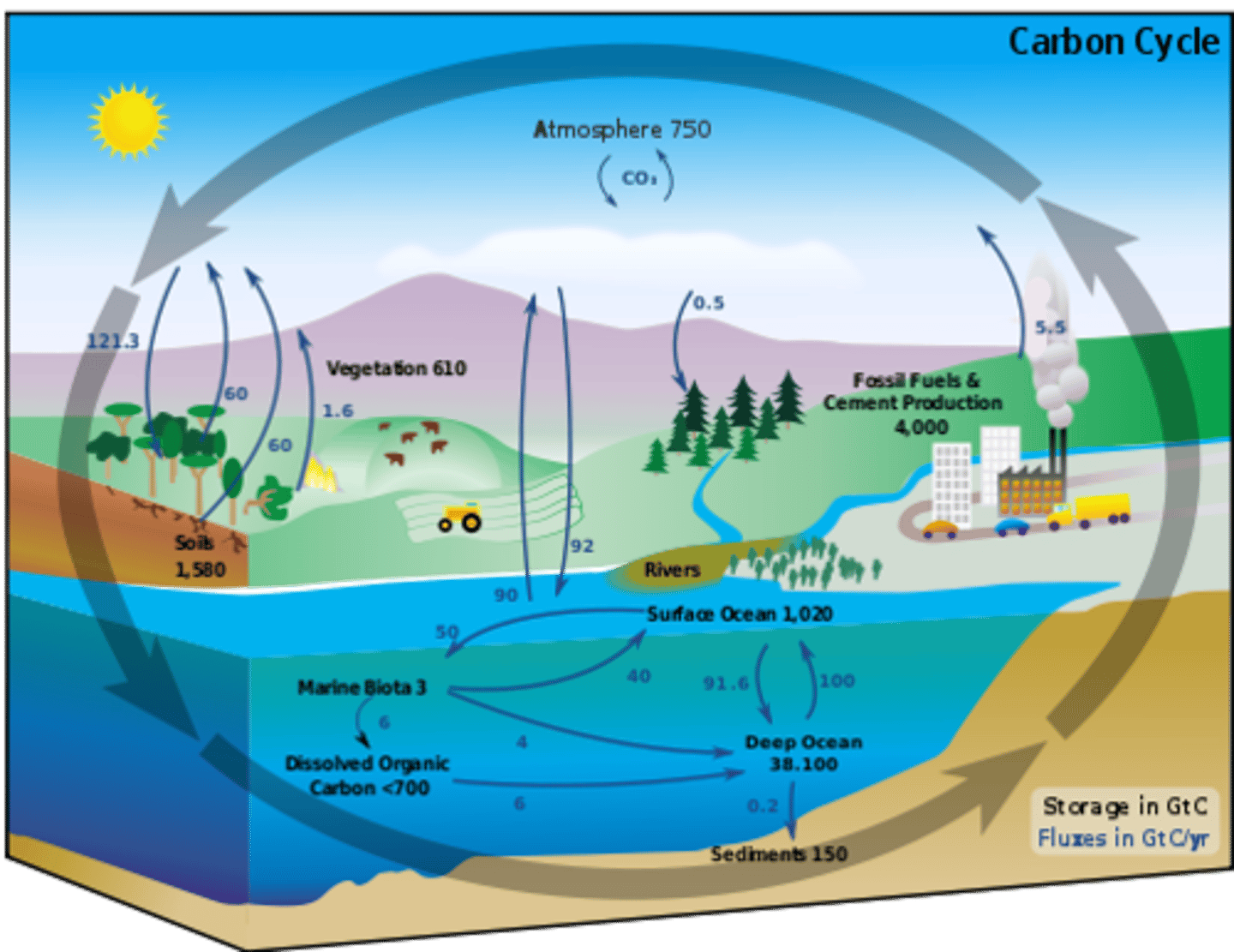
Carbon sinks
Relatively long-term stores that can take in more carbon dioxide than they produces
Ex: Plants, ocean, soils, sedimentary rock (can be either reservoirs or sinks, depending on their depth & time)

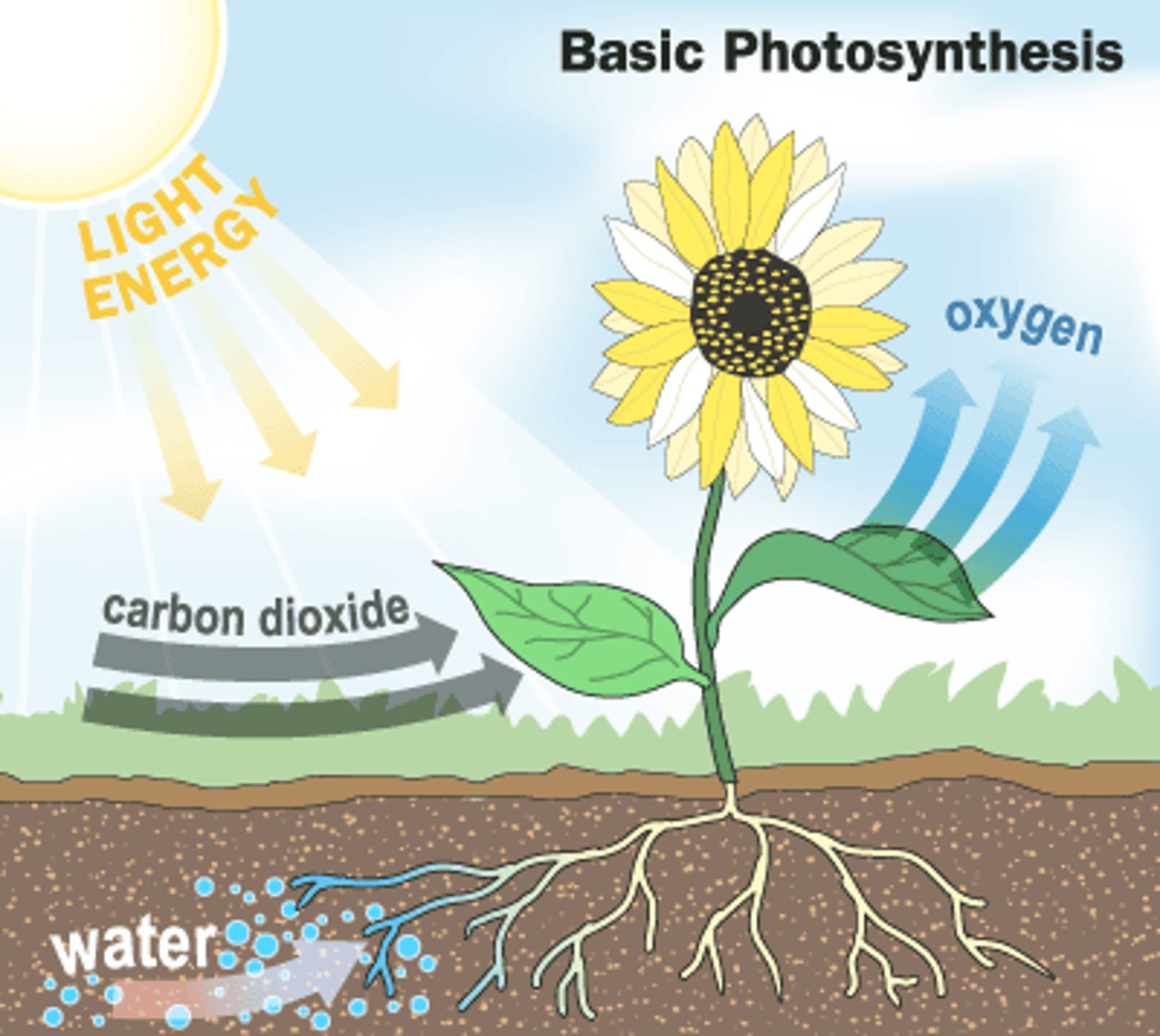
Photosynthesis
Plants use the sun's energy to convert water and carbon dioxide from the atmosphere into sugars and oxygen. Removes CO2 from atmosphere.
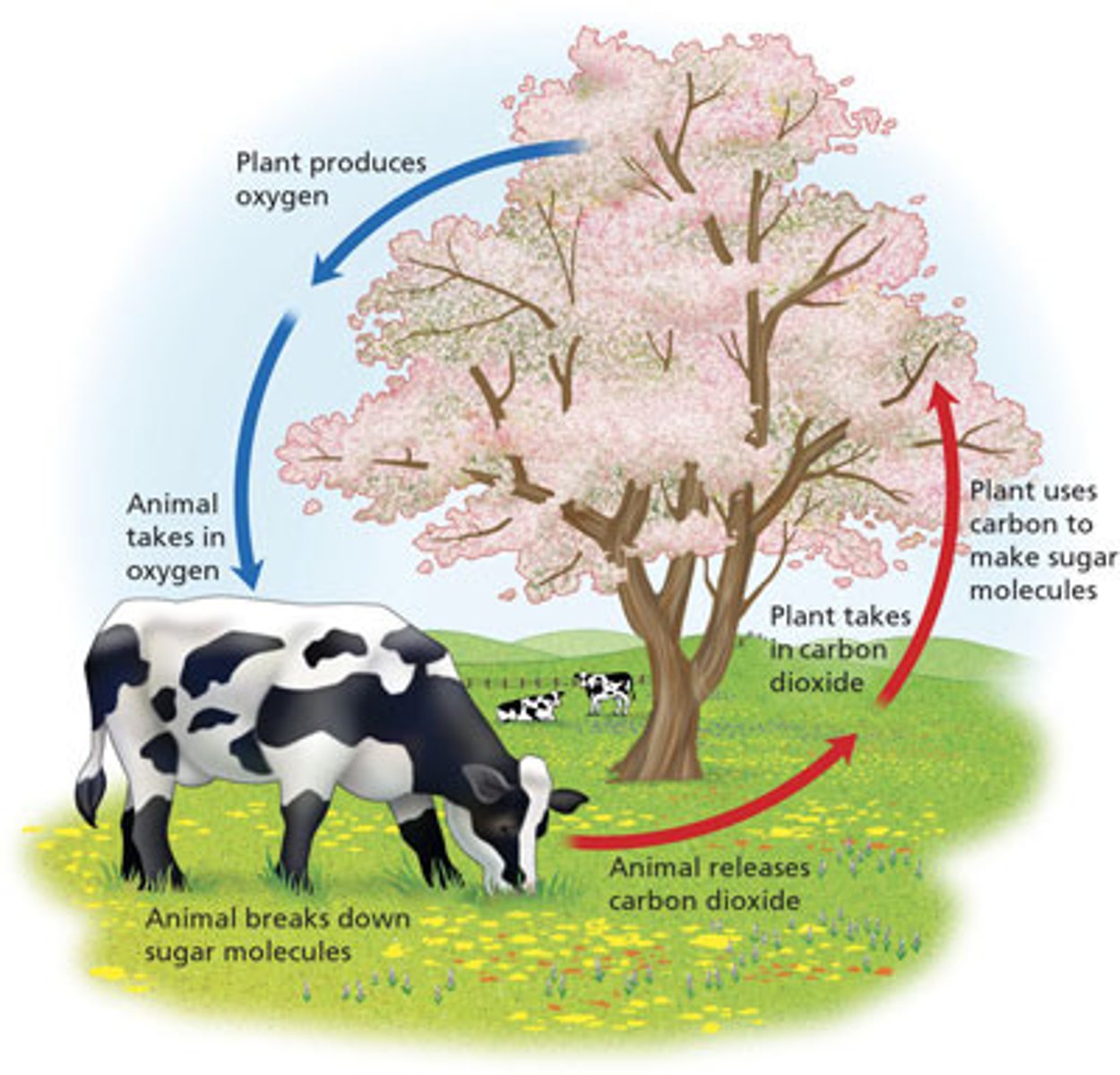
Cellular respiration
Process that releases energy by breaking down glucose and releasing CO2 into atmosphere
Decomposition
A chemical proc done by soil bacteria that breaks down organic matter and stores carbon in the soil and releases it into the atmosphere as CO2 and methane (CH4)

Carbon sequestration (storage)
The act of removing carbon from the atmosphere and storing it. Plants sequester, or store carbon from the atmosphere.
Direct exchange
Movement of carbon dioxide gas directly between the ocean and atmosphere.
Happens at a relatively stable rate, although excess atmospheric carbon will increase the level of CO2 in the ocean
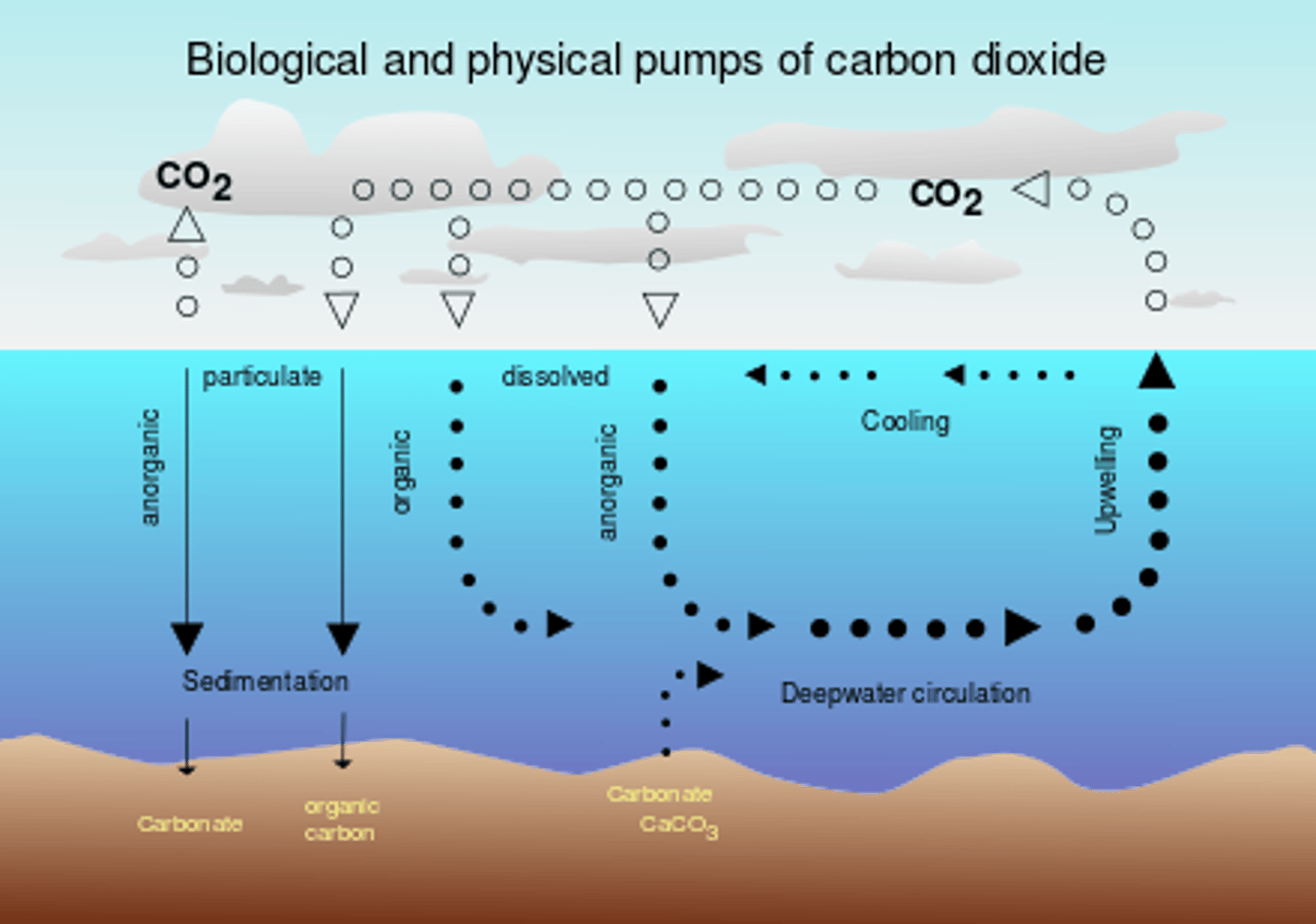
Sedimentation
The process of soil particles and decaying organic matter building up in layers on the ground or at the bottom of the ocean.
Over time, pressure from water or rock layers above compresses sediments into sedimentary rock (limestone) or FFs
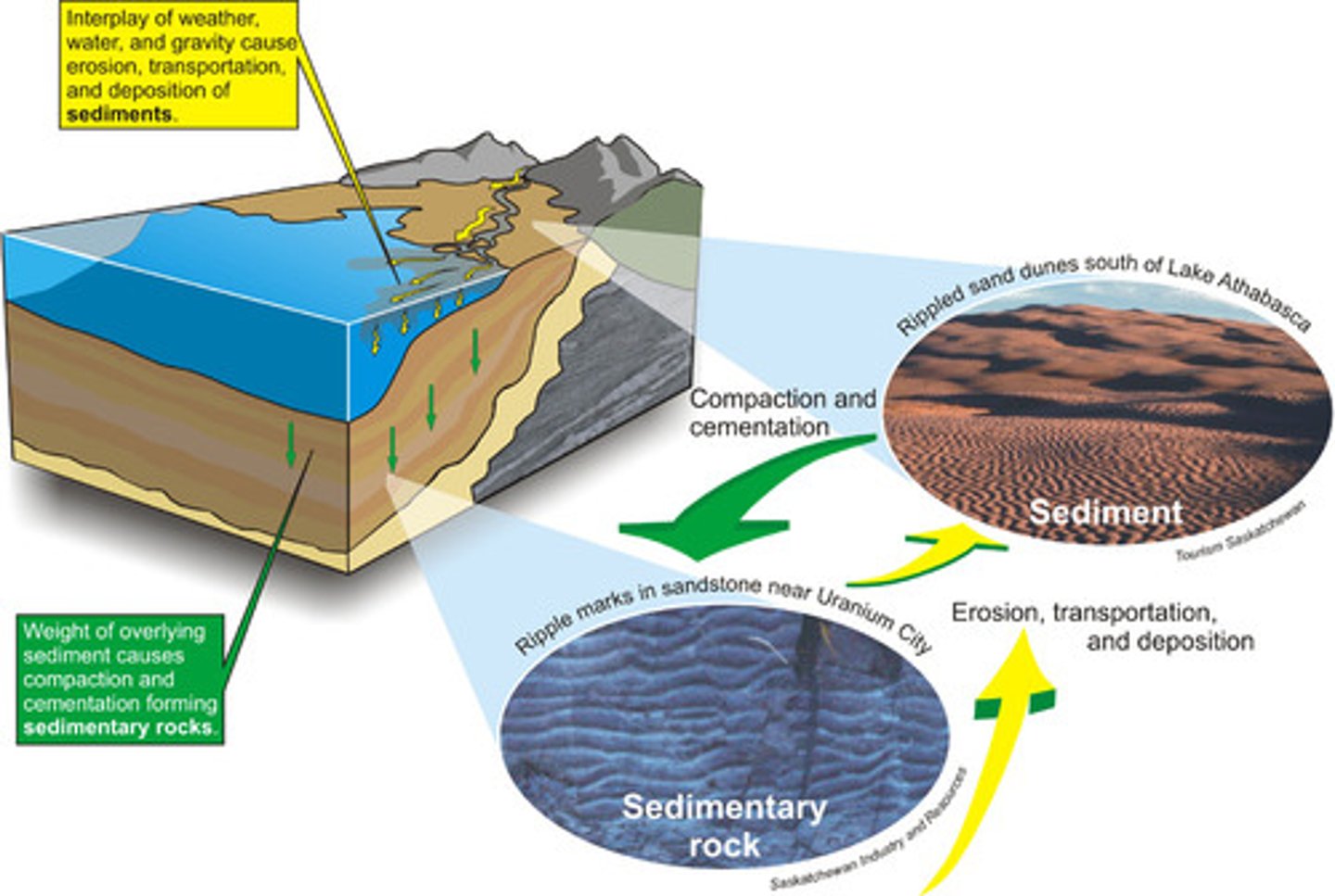
Burial
The formation of sedimentary rock like limestone, or fossil fuels, as layers of sediments are compressed under the ocean or overlying rock layers.
Extraction
Removal of fossil fuels (coal, oil, natural gas) from the ground, usually by mining or drilling.
A very rapid process compared to the sedimentation and burial required to form fossil fuel

Combustion of fossil fuels
Burning of fossil fuels (primarily in cars and power plants) to release energy
Releases carbon dioxide into the atmosphere very rapidly, acting as a carbon source

movement of nitrogen containing molecuels between sources & sinks/resorviors
What is the nitrogen cycle?
atmosphere
What is the main nitrogen reservoir?
for all biotic nutrients
What is nitrogen critical for?
Process of converting N2 into NH3
What is nitrogen fixation?
certain bacteria that live in the soil convert N2 into NH3
What is bacterial fixation?
humans combust FFs to convert N2 into NO3
What is synthetic fixaiton?
biotic organimsms absorb nitrogen into their bodies
What does assimilation mean?
decomposers converting dead biomass back into NH3 and returning it to soil
What is ammonification?
converison of NH4 into NO2 & then by bacteria
What is nitrification?
ammonium
What is NH4?
nitrogen gas
What is N2?
ammonia
What is NH3?
nitrate
What is NO3?
nitrous oxide
What is N2O?
convertimg NO3 into N2O & releasing into air
What is denitrification?
plants use photosynthesis to turn CO2 into organic compounds
What is carbon fixation?
carbon dioxide
What is CO2?
nitrogen dioxide
What is NO2?
movement of p atoms & molecules b/w sources & sinks
What is the phosphorus cycle?
it takes a long time to complete
What is special about phosphorus cycle?
yes
Are plant growth in ecosystems limited by phosphorus cycle?
weathering of P mineral rocks
What is the major natural source of P (phosphorus)?
No
Does phosphate dissolve well into water?
parts of the Earth's crust, like mountains, rise up over time
What is geological uplift?
rocks and deep ocean sediments
Which of the following features contains the largest amount of phosphorus in the phosphorus cycle?
atmosphere
Which of the following features is not included in the phosphorus cycle?
the sun
What is the hydrologic cycle powered by
the movement of water in its various solid, liquid, and gaseous phases between sources and sinks
what is the hydrologic cycle
the ocean
what is the primary resevoir of water on earth
ice caps and ground water
what are two smaller resevoirs of water
state of matter, where is it going- ex: precipitation is gaseous water in the atmosphere and coming to the land as surface water as a liquid
what do we like to focus on water cycle
evaoration and evapotransipiration
what are the two main sources that move liquid on earth to gas
transpiration
process plants use to draw groundwater from roots to their leaves
stomata on the plant open allowing water to evaporate into atm from leaf. Mvmt of h2o out of leaf creates low h2o potential, and more h2o is pulled up by roots
how to plants transpire
amount of h2o that enters atm from transpiration and evap combined
evapotranspirtion
either goes to surface water or becomes ground water
what are the two things that water can do
surface runoff
when water goes on land towards body of water
infiltration
when the water soaks into the ground and is in the ground water
inflitration is when the water can refill aquifers. and runoff replensishes above ground freshwater sources
why are inflitration and runoff important
the ground it falls on must be permeable
what is the condition that must be filled for precipitation to refill an aquifier
the runoff might get pollutants from the land into the water
why can runoff be bad
Primary productivity
rate at which organic matter is created by producers (via photosynthesis) in an ecosystem
GPP (gross primary productivity)
The total amount of solar energy that producers in an ecosystem capture via photosynthesis over a given amount of time
NPP (net primary productivity)
The energy captured by producers in an ecosystem minus the energy producers respire
Trophic levels
The hierarchical levels of the food chain through which energy flows from primary producers to primary consumers, secondary consumers and so on.
Conservation of matter
the principle stating that matter is not created or destroyed during a chemical reaction
Omnivore
A consumer that eats both plants and animals
Carnivore
A consumer that eats only animals.
Herbivore
A consumer that eats only plants.
First law of thermodynamics
Energy can be transferred and transformed, but it cannot be created or destroyed.
second law of thermodynamics
when energy is changed from one form to another, some useful energy is lost as heat
Energy pyramid
Shows the amount of energy that moves from one trophic level to another in a food web
10% rule
Only 10% of the total energy produced at each trophic level is available to the next level. The amount of energy passed up to the levels of the trophic pyramid decreases as you go up.