Phase Equilibrium
1/12
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
13 Terms
What is the phase rule?
Expand and explain
F = C - P + 2
Where
F = degrees of freedom
- Least number of intensive variables (eg. temperature, pressure, concentration etc)
- components that must be fixed in order to describe the system
C = no. components
- smallest number of constituents by which composition of each phase in system at equilibrium can be expressed in a formula
P = no. phases present
- homogeneously distinct portions of a system that is separated from other portions
Using the phase rule, if F =1, what does this mean?
If F = 1, the system is UNIVARIANT
- Must fix 1 variant in the system (eg. if temperature is known, pressure is known)
- In order to maintain equilibrium, there must be corresponding change between variables
- exist along line between 2 phase regions
Using the phase rule, if F = 2, what does this mean?
System is BIVARIANT
- Must describe 2 intensive properties such as pressure and temperature to describe sample
- Able to change independently without affecting the state of the system
- exists within the areas marked
Using the phase rule, if F = 0, what does this mean?
System is INVARIANT
- 0 degrees of freedom
exists at the intersection of lines bounding the 3 phase regions
What is a "consulate temperature"?
The temperature where 2 phases disappear, forming only 1 phase
How to work out mole fraction?
no. moles of A / moles A + B
- Should range between 0-1
- Used to normalise axis
What is the Eutectic composition?
Lowest melting point of both materials
- Both components are solid (crystalline material- microfine dispersion of crystals)
When will eutectics not occur?
When melting point is very different
What happens if a mixture, containing more A than the eutectic mixture, is cooled?
Crystals of pure A will appear
- when it reaches eutectic temperature = both crystallise out
What is a pharmaceutical advantage of this phenomenon of eutectic mixtures?
- eutectic mixture of the drug and substance readily soluble in water
- soluble "carrier" dissolves
- leaves behind the drug in vivo
Phase diagram of water?
Triple point of water: all 3 phases are present
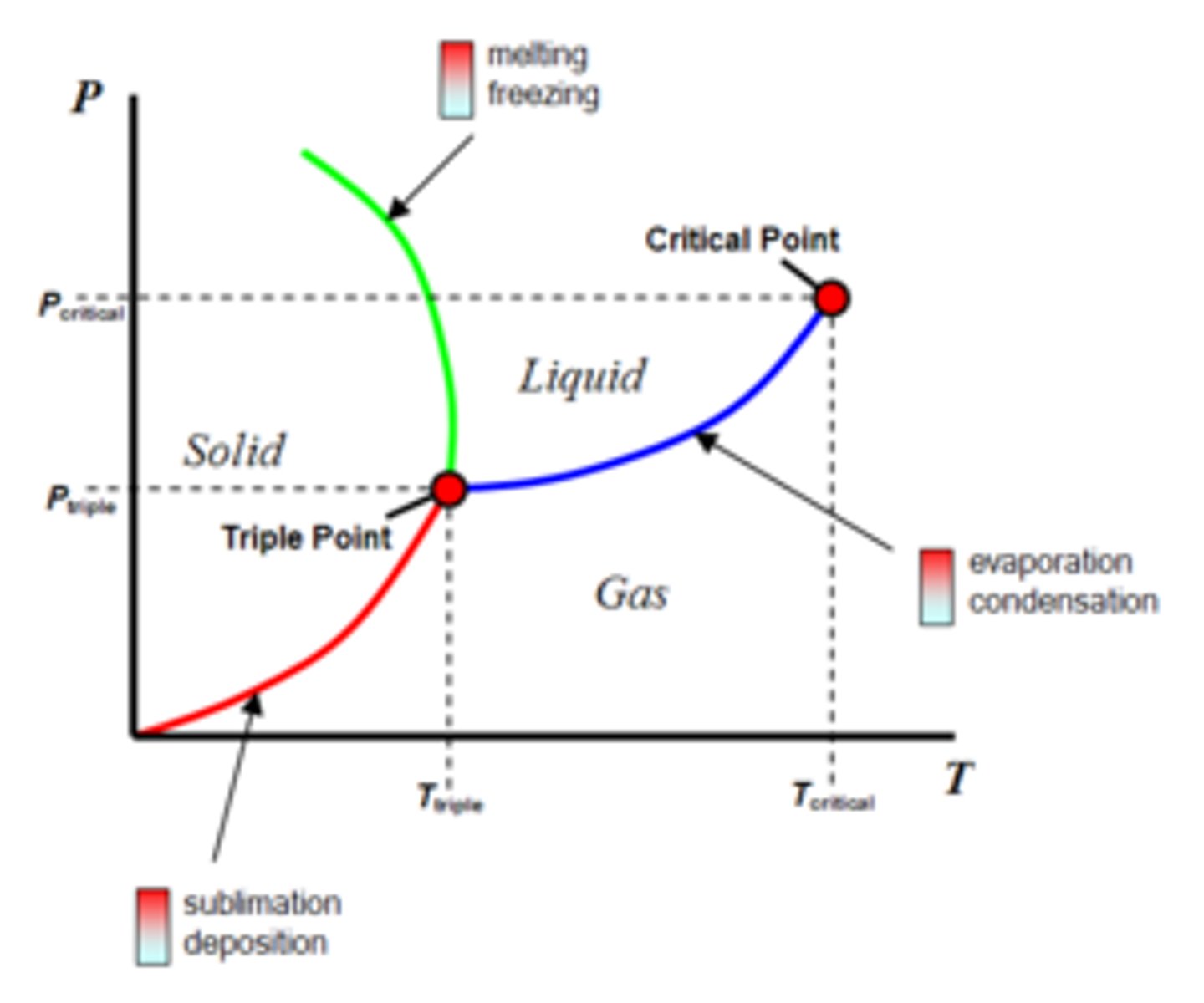
What is sublimation and how does it occur?
Direct conversion from solid to vapour
eg. dry ice, freeze-drying for preservation
Lower pressure to form ice, and heat slightly
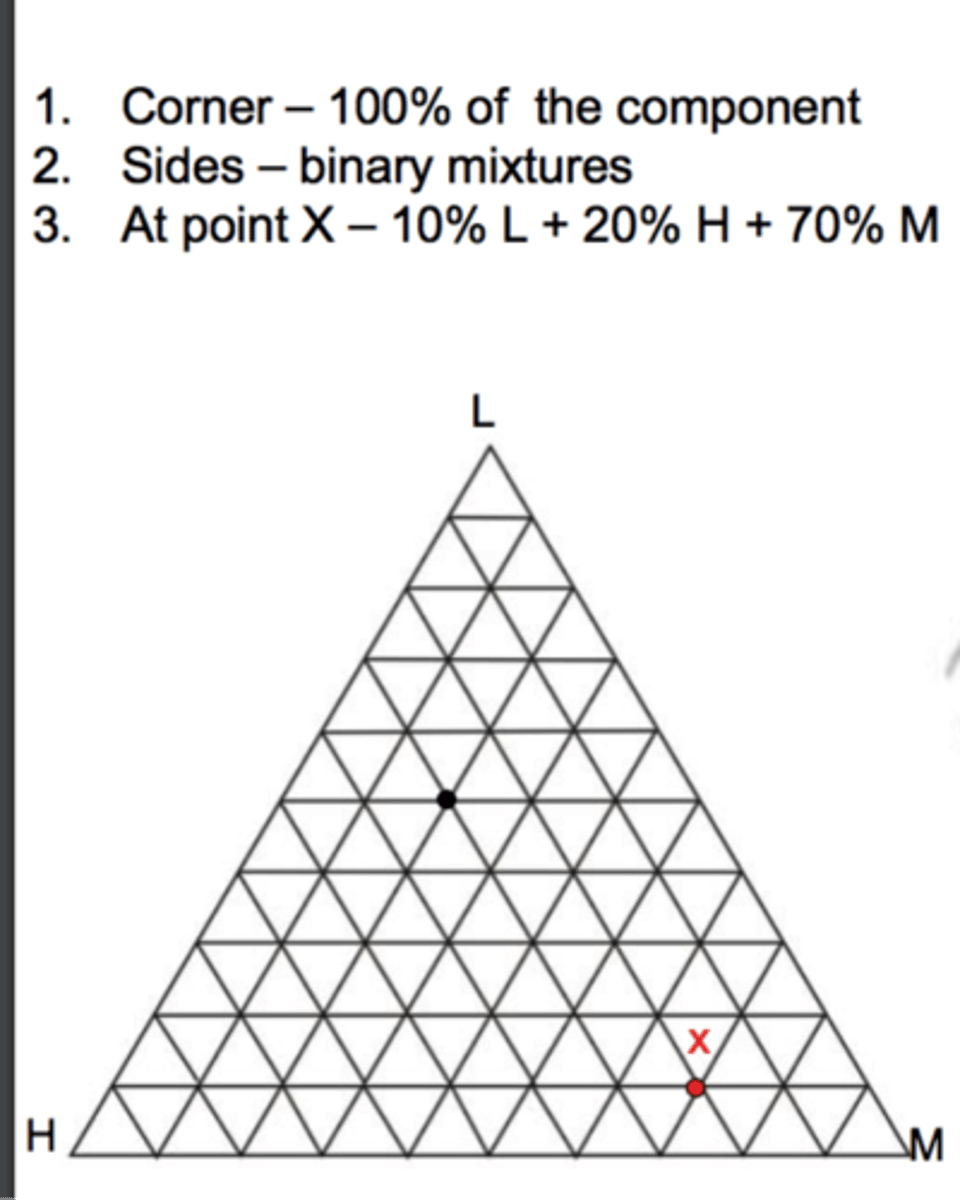
3 phase diagram (Ternary)?