LP2 HW/Study Guide #1 - Prokaryotes & Antibiotic Resistance
1/60
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
61 Terms
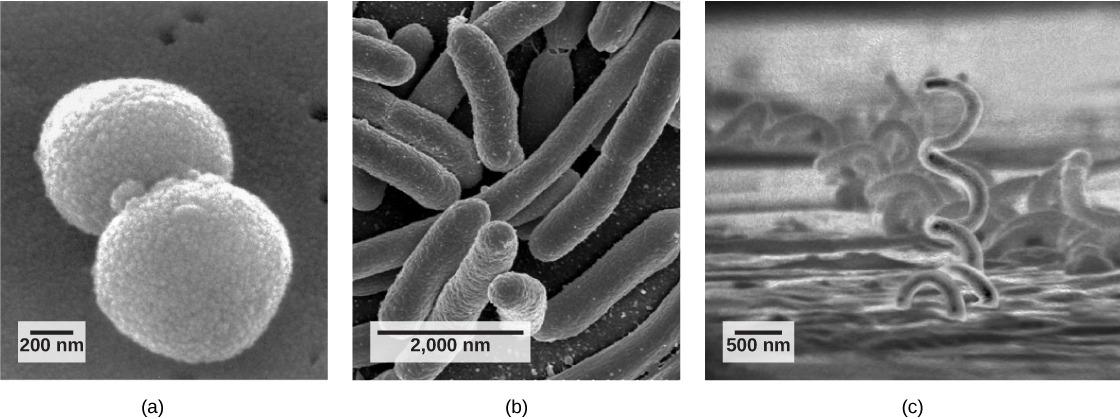
Fill in the Blanks Below with the Correct Identifications:
Identify Prokaryotic Shape "a"
Identify Prokaryotic Shape "b"
Identify Prokaryotic Shape "c"
(a) Cocci
(b) Bacilli
(c) Spirilli
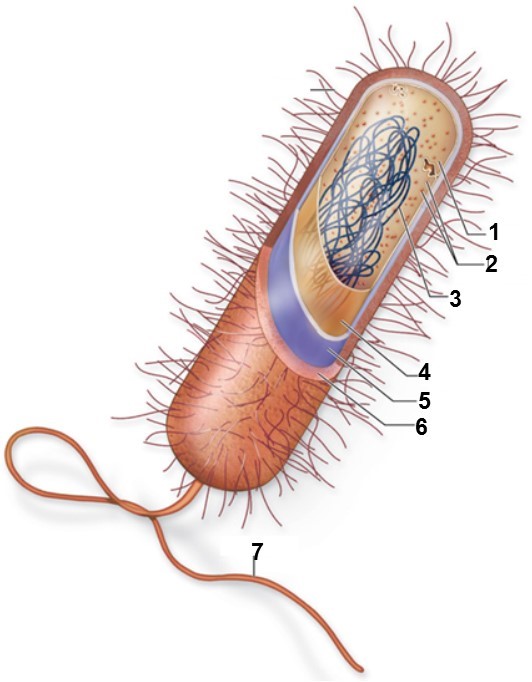
Label .. Word Bank to Answer this Question:
Flagellum, Cell Wall, Cytoplasm, Plasma Membrane, Capsule, Ribosome, Nucleoid
What is #1
What is #2
What is #3
What is #4
What is #5
What is #6
What is #7
1) Cytoplasm
2) Ribosome
3) Nucleoid
4) Membrane
5) Cell Wall
6) Capsule
7) Flagellum
A dormant, tough, and resistant structure formed by some bacteria under unfavorable conditions.
Endospore
A lipid bilayer that separates the cell's interior from the external environment and controls the passage of substances in and out of the cell.
Plasma Membrane
A protective and adhesive layer that some prokaryotic cells have outside the cell wall.
Capsule
A region in the cytoplasm where the prokaryotic cell's DNA is located, but it is not enclosed within a membrane-bound nucleus.
Nucleiod Region
A whip-like structure used for cell movement.
Flagellum
Folding’s of the plasma membrane that may be involved in various cellular processes, including cell division and respiration.
Mesosomes
Hair-like projections that help with attachment to surfaces and can be involved in DNA transfer between cells (conjugation).
Pili
Small, circular pieces of DNA that can be found in some prokaryotes, often carrying extra genetic information.
Plasmids
Storage structures that can contain reserve nutrients or other molecules.
Inclusions
The gel-like substance filling the cell's interior, where various cellular processes take place.
Cytoplasm
This outermost layer provides structural support and protection to the cell, and in some cases, it may be surrounded by a capsule.
Cell Wall
Tiny structures involved in protein synthesis.
Ribosomes
Eubacterial Cell Walls are made of this.
Peptidoglycan
What is the composition of archaea cell walls?
Proteins or Glycoproteins
In what types of environments do bacteria live?
A) Extremely hot/cold.
B) Digestive system of humans/animals.
C) Deep underground.
D) All of the above
E) B & C
D) All of the above
In bioluminescent bacteria, the light-emitting compound is called ________.
A) fluorescein
B) luciferin
C) safranin
D) fuchsin
B) luciferin
Many bacteria cause devastating diseases in plants and animals; however, some bacteria are used to produce ________.
A) antidiabetic agents
B) antibiotics
C) antivirals
D) antifungals
B) antibiotics
Gram stain is a laboratory technique used to distinguish between various kinds of bacteria based on the characteristics of the ________.
A) plasma membrane
B) cell wall
C) ribosomes
D) DNA
B) cell wall
Which of the following bacteria exist as diplococci?
A) Neisseria meningitidis.
B) Staphylococcus aureus.
C) Streptococcus pyogenes.
D) Chlamydia trachomatis.
A) Neisseria meningitidis.
Which of the following are gram-positive bacteria?
A) Staphylococcus spp.
B) Streptococcus spp.
C) Bacillus anthracis.
D) All of the above.
D) All of the above.
Bacteria that require oxygen for survival are known as ________.
A) obligate aerobes
B) obligate anaerobes
C) facultative anaerobes
D) aerobes
A) obligate aerobes
Gram-positive bacteria stain ________.
A) red
B) purple
C) orange
D) green
B) purple
Rod-shaped bacteria are known as ________.
A) rotini
B) spirilli
C) cocci
D) bacilli
D) bacilli
Which of the following statements about bacteria is NOT true?
A) Most bacteria are pathogenic (disease-causing).
B) Bacteria live in diverse environments.
C) Bacteria constitute an overwhelming percentage of the earth's total biomass.
D) Bacteria are used in industry to produce many products.
A) Most bacteria are pathogenic (disease-causing).
Which of the following bacteria is pathogenic in humans?
A) Mycoplasma pneumoniae.
B) Borrelia burgdorferi.
C) Clostridium botulinum.
D) All of the above.
D) All of the above.
Which of the following is a characteristic of the bacterium Escherichia coli?
A) Normally inhabits the digestive tract of many animals.
B) Is gram-negative.
C) Is a facultative anaerobe.
D) All of the above.
D) All of the above.
Clostridium botulinum is a bacteria that cannot live in oxygen. It is described as a/an ______.
A) obligate aerobe
B) obligate anaerobe
C) facultative anaerobe
D) facultative aerobe
B) obligate anaerobe
Which of the following bacteria are important in the production of oxygen?
A) Chlamydias.
B) Cyanobacteria.
C) Proteobacteria.
D) Spirochaetes.
B) Cyanobacteria.
Some bacteria produce an endospore that enables them to ________.
A) synthesize proteins
B) survive under intolerable conditions
C) fix nitrogen
D) avoid destruction by the host's immune system
B) survive under intolerable conditions
Which of the following bacteria causes the sexually transmitted disease syphilis?
A) Haemophilus influenzae.
B) Mycoplasma pneumoniae.
C) Treponema pallidum.
D) Clostridium botulinum.
C) Treponema pallidum.
Which of the following statements about the proteobacteria is NOT true?
A) Mitochondria may have evolved from them.
B) They are important oxygen producers.
C) They include the nitrogen-fixing bacteria Rhizobium spp.
D) They are highly diverse, but share many molecular traits.
B) They are important oxygen producers.
While visiting Yellowstone Park, you see the famous geyser "Old Faithful." What type(s) of Archaea would you most likely find in this water?
A) Acidophiles.
B) Thermophiles.
C) Psychrophiles.
D) Halophiles.
B) Thermophiles.
Bacteria that produce light are referred to as ______.
A) bioluminescent
B) fluorescent
C) opalescent
D) translucent
A) bioluminescent
Archaea and Eukarya share which of the following features?
A) Cell wall of similar composition.
B) Cell membrane of similar composition.
C) Histone proteins in the DNA.
D) Thermophilic species.
C) Histone proteins in the DNA.
How do antibiotics primarily function in inhibiting bacterial growth?
A) They inhibit cell wall formation.
B) They damage the cell membrane.
C) They interfere with protein synthesis.
D) All of the above.
D) All of the above.
Which method is commonly used to test antibiotic sensitivity in medical laboratories?
A) Kirby-Bauer method
B) PCR (Polymerase Chain Reaction)
C) ELISA (Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay)
D) Western blotting
A) Kirby-Bauer method
How do scientists interpret a large zone of inhibition in a sensitivity test?
A) The antibiotic is ineffective.
B) The antibiotic is highly effective.
C) The bacteria are resistant to the antibiotic.
D) The bacteria are immobile
B) The antibiotic is highly effective.
How do scientists determine the sensitivity of bacteria to different antibiotics in a sensitivity test?
A) By measuring the diameter of the zone of inhibition
B) By counting bacterial colonies
C) By observing bacterial motility
D) By analyzing bacterial color changes
A) By measuring the diameter of the zone of inhibition
In antibiotic sensitivity testing, what does it mean if the organism grows up to the disk?
A) The organism is resistant to the antibiotic.
B) The organism is highly sensitive to the antibiotic.
C) The organism is not affected by the antibiotic.
D) The test is inconclusive.
A) The organism is resistant to the antibiotic.
Which bacteria is normally considered nonpathogenic but can cause various infections, including food poisoning?
A) Escherichia coli
B) Staphylococcus aureus
C) Bacillus cereus
D) Streptococcus pyogenes
C) Bacillus cereus
Why has the use of antibiotics in agriculture become a topic of concern?
A) It leads to the overpopulation of bacteria.
B) It accelerates the evolution of antibiotic-resistant bacteria.
C) It increases the lifespan of bacteria.
D) It promotes the growth of beneficial bacteria
B) It accelerates the evolution of antibiotic-resistant bacteria.
What is the primary reason doctors prescribe antibiotics when a patient has a fever?
A) To alleviate pain
B) To boost the immune system
C) To combat bacterial or viral infections
D) To reduce inflammation
C) To combat bacterial or viral infections
What is the main difference between gram-positive and gram-negative bacteria?
A) Gram-positive bacteria have a thicker cell wall than gram-negative bacteria.
B) Gram-negative bacteria have a thicker cell wall than gram-positive bacteria.
C) Gram-positive bacteria have an outer lipid layer.
D) Gram-negative bacteria lack a cell wall.
A) Gram-positive bacteria have a thicker cell wall than gram-negative bacteria.
What is the significance of beta-lactamase enzymes in bacterial resistance?
A) They break down bacterial cell walls.
B) They destroy antibiotics.
C) They enhance bacterial metabolism.
D) They inhibit protein synthesis in bacteria.
B) They destroy antibiotics.
What does a control disk in antibiotic sensitivity testing indicate?
A) The absence of antibiotics
B) The presence of a placebo
C) The standard against which the other results are compared
D) The presence of a highly concentrated antibiotic
C) The standard against which the other results are compared
How do bacteria obtain genes that confer antibiotic resistance?
A) Through mutations in their existing genes
B) Through bacterial conjugation, transduction, and transformation
C) By producing enzymes that destroy antibiotics
D) By increasing their metabolic rate
B) Through bacterial conjugation, transduction, and transformation
Which statement about antibiotic-resistant bacteria is true?
A) They are less likely to survive and multiply in the presence of antibiotics.
B) They have genes that confer resistance to certain antibiotics.
C) They are more susceptible to antibiotics than non-resistant bacteria.
D) They cannot evolve in the presence of antibiotics
B) They have genes that confer resistance to certain antibiotics.
Which type of bacteria is more likely to be resistant to antibiotics due to its cell membrane structure?
A) Gram-positive bacteria
B) Gram-negative bacteria
C) Anaerobic bacteria
D) Aerobic bacteria
B) Gram-negative bacteria
Antibiotics that kill bacteria directly are classified as ________.
A) fungicidal
B) bacteriostatic
C) bactericidal
D) antibacterial
C) bactericidal
Archaea classified as ________ can live in extremely cold conditions, such as in the Antarctic region.
A) psychrophiles
B) acidophiles
C) thermophiles
D) alkaliphiles
A) psychrophiles
Which of the following are classified as cyanobacteria?
A) Oscillatoria sp.
B) Serratia marcescens.
C) Treponema sp.
D) Nostoc sp.
E) A and D.
E) A and D.
Plasmids, ringlike structures composed of DNA, are integral in bacterial ________.
A) metabolism
B) motility
C) conjugation
D) asexual reproduction
C) conjugation
Which of the following is a gram-positive bacterium that also forms spores?
A) Bacillus anthracis.
B) Staphylococcus aureus.
C) Streptococcus pyogenes.
D) Escherichia coli.
A) Bacillus anthracis.
Archaea classified as ________ can exist in soil, sediment, and other less extreme environments.
A) methanogens
B) mesophiles
C) extremophiles
D) halophiles
B) mesophiles
Bacteria collected from a sick patient by a throat swab stains purple on a slide. What is the likely pathogen in this case?
A) Vibrio cholerae.
B) Streptococcus pyogenes.
C) Staphylococcus aureus.
D) Neisseria meningitidis.
B) Streptococcus pyogenes.
What is the purpose of incubating petri dishes during antibiotic sensitivity testing?
A) To promote bacterial growth
B) To prevent bacterial growth
C) To observe bacterial motility
D) To measure bacterial density
A) To promote bacterial growth
What is MRSA?
A) A strain of bacteria resistant to methicillin
B) A type of virus
C) A fungal infection
D) A type of antibiotic
A) A strain of bacteria resistant to methicillin
What can scientists infer about bacteria if they show resistance to multiple antibiotics in a sensitivity test?
A) The bacteria are highly sensitive to those antibiotics.
B) The bacteria possess a wide range of antibiotic resistance genes.
C) The bacteria are not affected by any antibiotics.
D) The bacteria have low resistance levels.
B) The bacteria possess a wide range of antibiotic resistance genes.
Who is credited with the discovery of penicillin, the first antibiotic used to treat bacterial infections?
A) Marie Curie
B) Alexander Fleming
C) Louis Pasteur
D) Robert Koch
B) Alexander Fleming