Architecture Appreciation Test 3 - Briar Jones MSU
1/268
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
269 Terms
What mathematical concepts were emphasized during the Renaissance?
Rationality and proportions
What was the Renaissance's view on universal order?
It was grounded to earth
What aspect of human thought was highlighted in the Renaissance?
Human reason
What was the Renaissance's attitude towards aspirations?
Not aspired to heavens
What geometric shapes were considered pure forms in the Renaissance?
Circle and square
What characteristic of Renaissance art and design is often noted?
Symmetry
Gothic
A-historical, asymmetrical, believes architecture is service to God
Where did the 15th century Renaissance begin?
Florence
What artistic movement is characterized by the re-use of classicism?
15th century Renaissance
What is a key understanding in 15th century Renaissance art?
Perspective
What aspect of architecture was changed during the 15th century Renaissance?
Size and proportion of columns and pediments
What does the 15th-century Renaissance represent about human intellect?
It is equal to the power of God
What is Humanism?
A philosophical system based on the capacity of humankind for rational and objective thought and action.
What does Humanism stress about human reason?
Human reason is centered in human nature, interests, and ideals.
How does Humanism differ from religious philosophies?
It is distinct from religious philosophies based in a higher God.
What is the Renaissance?
The activity, spirit, or time of the humanistic revival of classical art, literature, and learning.
When did the Renaissance originate?
In the 14th century.
Where did the Renaissance begin?
In Italy.
What time period does the Renaissance cover?
From the 14th century to the 17th century.
What transition did the Renaissance mark?
The transition from the medieval to the modern world.
What is Renaissance Architecture?
The various adaptations of Italian Renaissance Architecture that occurred throughout Europe.
What characterized Renaissance Architecture?
The use of Italian Renaissance forms and motifs in more or less traditional buildings.
When did Renaissance Architecture continue until?
The advent of Mannerism and the Baroque in the 16th and 17th centuries.
"Renaissance Man"
Brunelleschi
Brunelleschi
architect, painter, sculptor, goldsmith
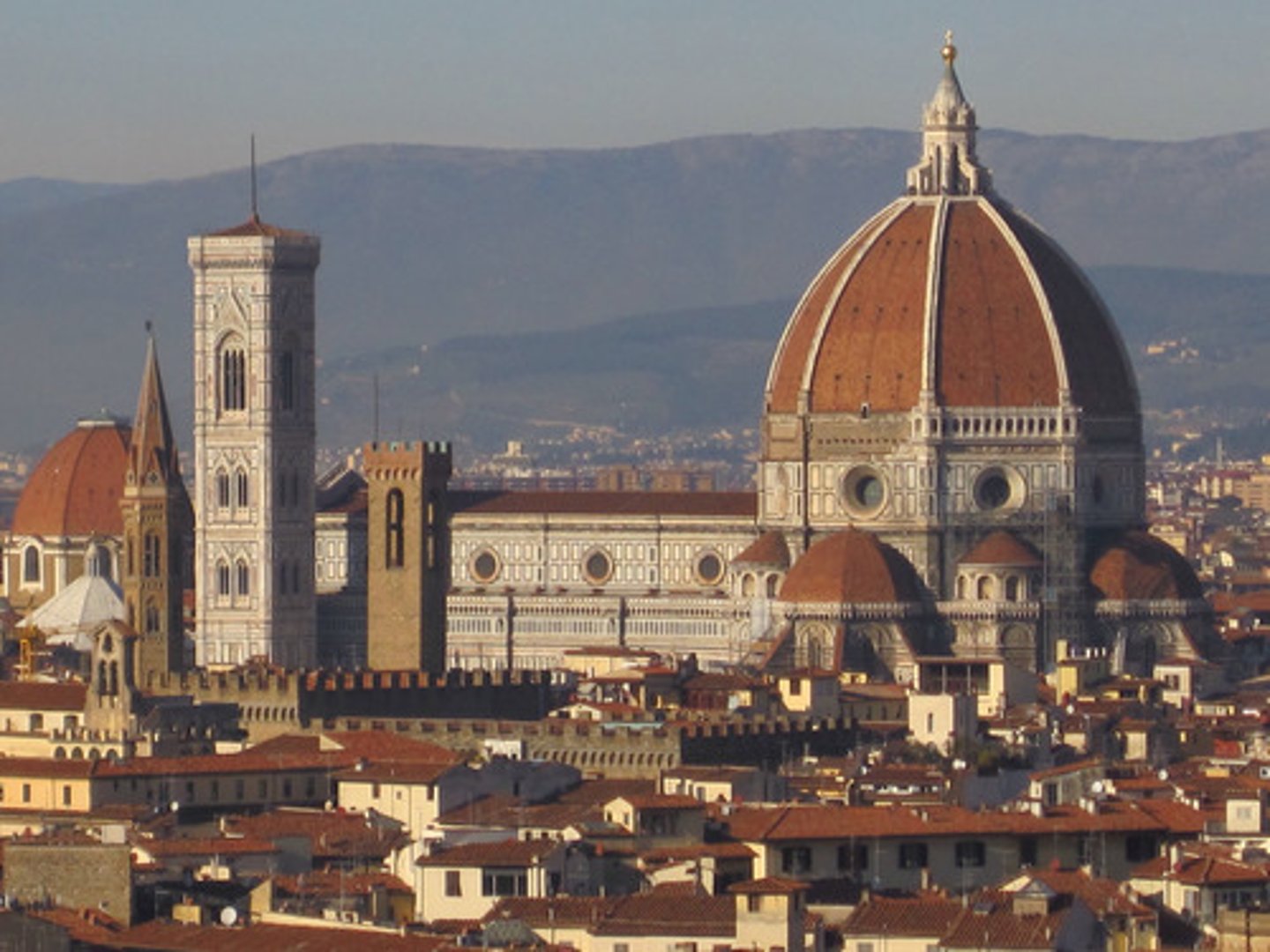
Duomo
Cathedral in Florence

What is Humanism?
believes human achievement is separate from religious dogma
How does Humanism relate to religious dogma?
It focuses on human achievement separate from religious dogma.
What classical view does Humanism reconcile with Christian belief?
The classical view of human potential.
What did Humanism advocate for in terms of human achievement?
It wanted excellence in human achievement, believing that all was possible.
Early renaissance
A style of Italian Renaissance art and architecture developed during the 15th century
What are the characteristics of the Early Renaissance?
the development of linear perspective, chiaroscuro, and in buildings, by the free and inventive use of classical details
Who is the father of the Renaissance?
Brunelleschi
What was the first Renaissance Building?
The Foundling Hospital
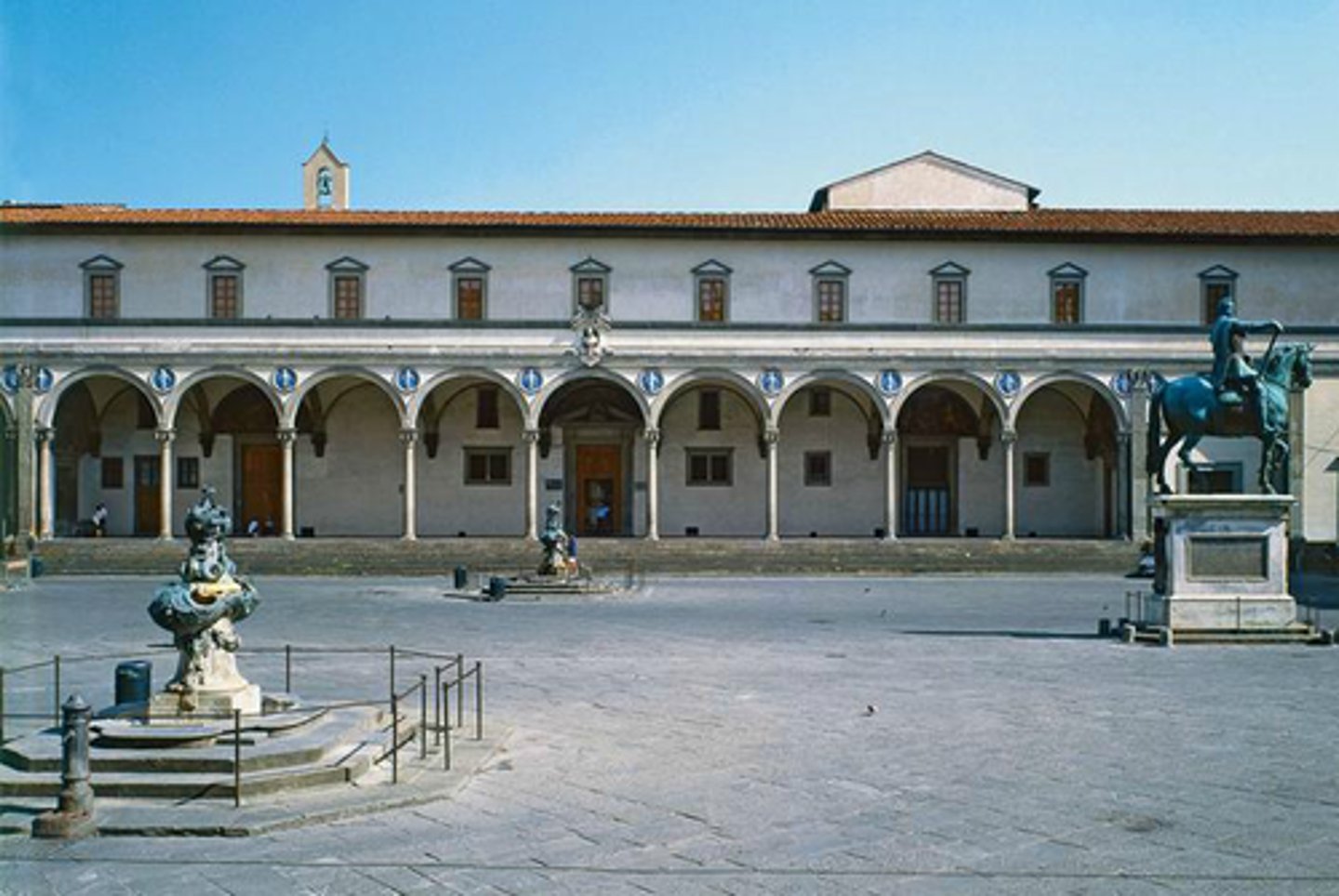

Foundling Hospital
Brunelleschi, Italy 1422
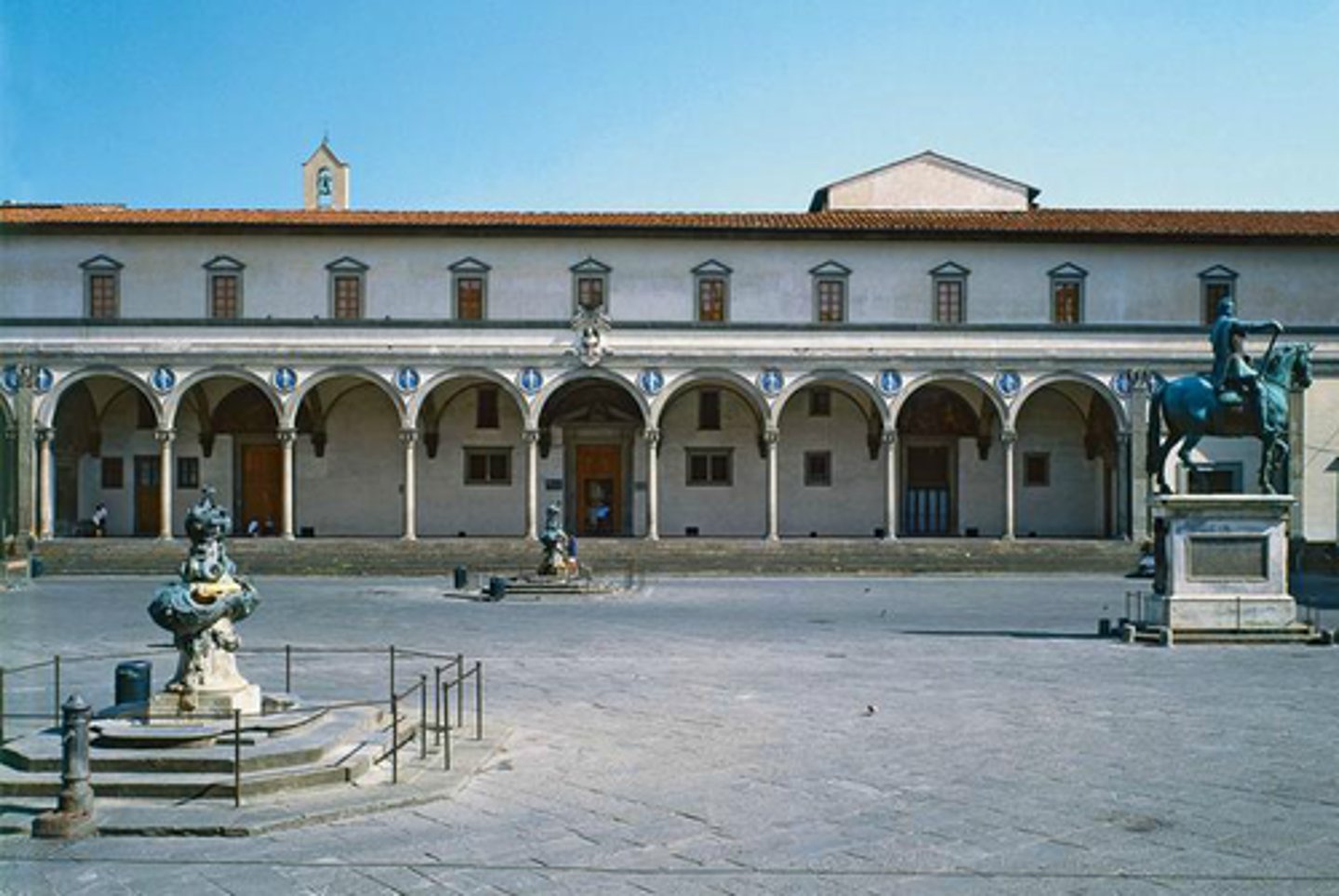

Characteristics of Brunelleschi's work in the foundling Hospital
symmetrical forms, proportions relate to one another, application of scientific perspective
The Duomo
Dome of the Cathedral of Florence, 1418-1436
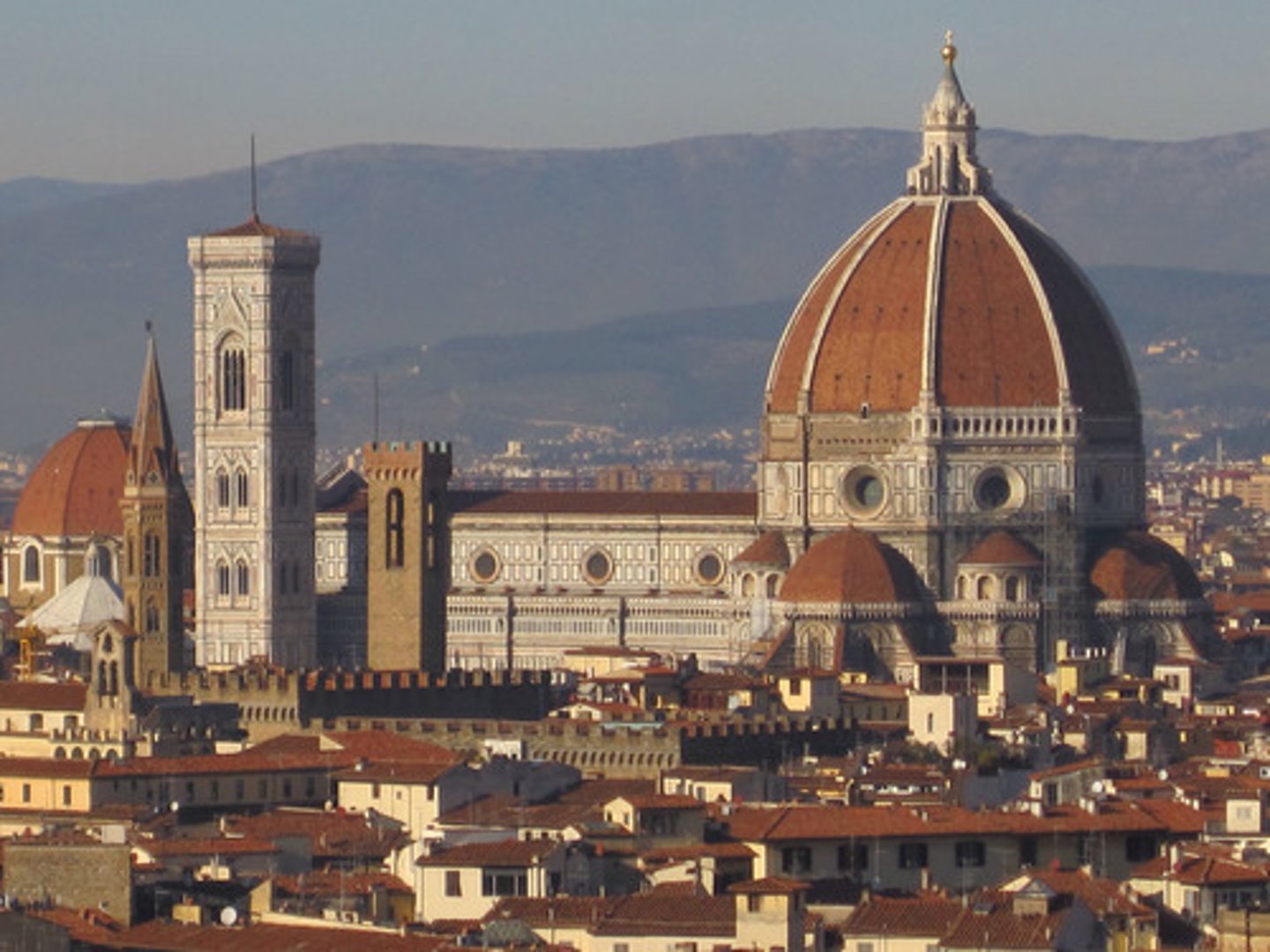

What is the Duomo known for?
It is the largest dome built since the Romans.
What was a significant mechanical achievement in the construction of the Duomo?
It was built without centering.
How was the Duomo designed in terms of its structural support?
It was built to be self-supporting as it was constructed.
What was the Cathedral in Florence, or Duomo, designed with
It employed ribs and double shells
The Church of San Lorenzo
Designed In Florence, Italy, Brunelleschi was hired by Medici
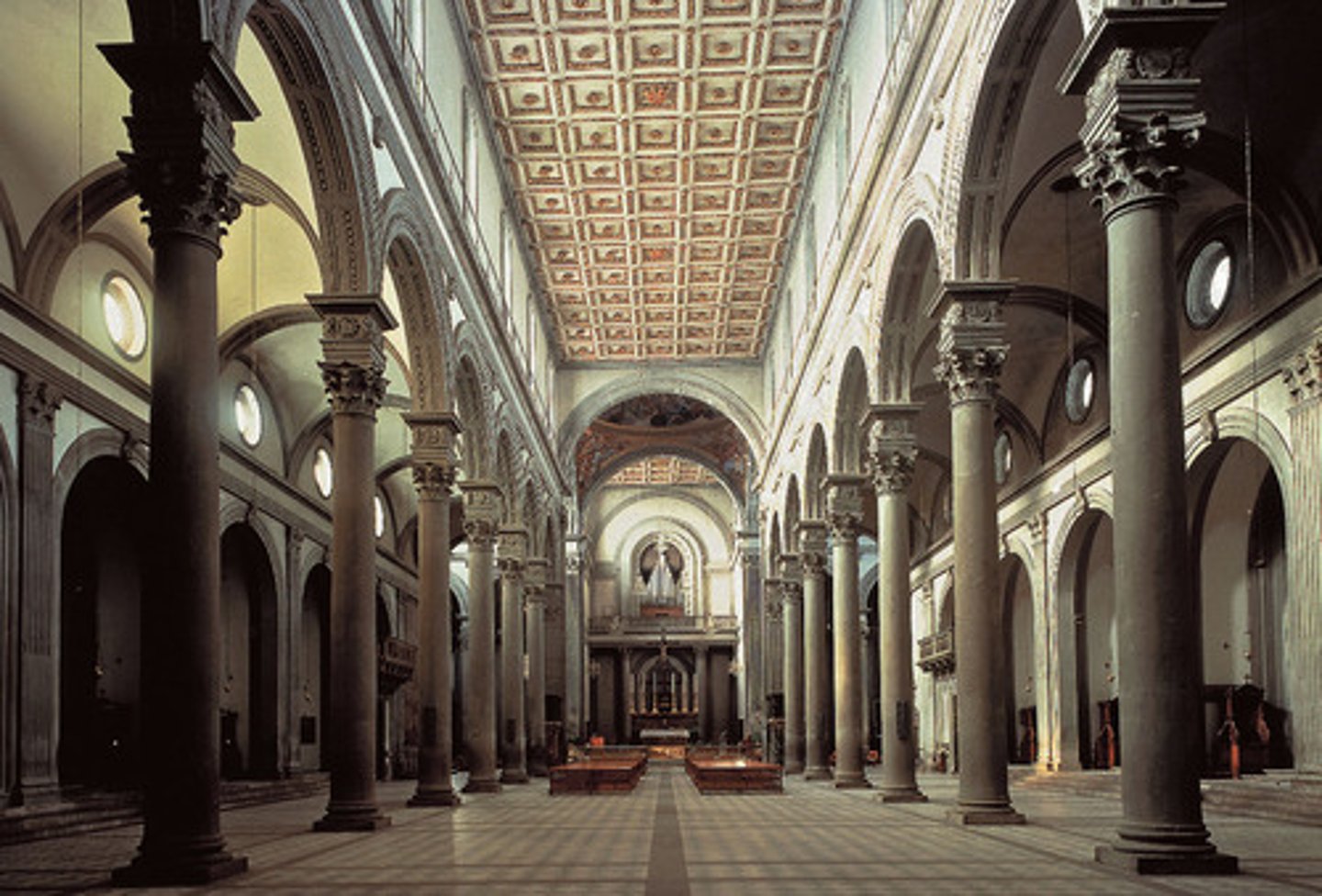

The Church of S. Spirito
Designed by Brunelleschi, through proportions and volumes made of CUBES
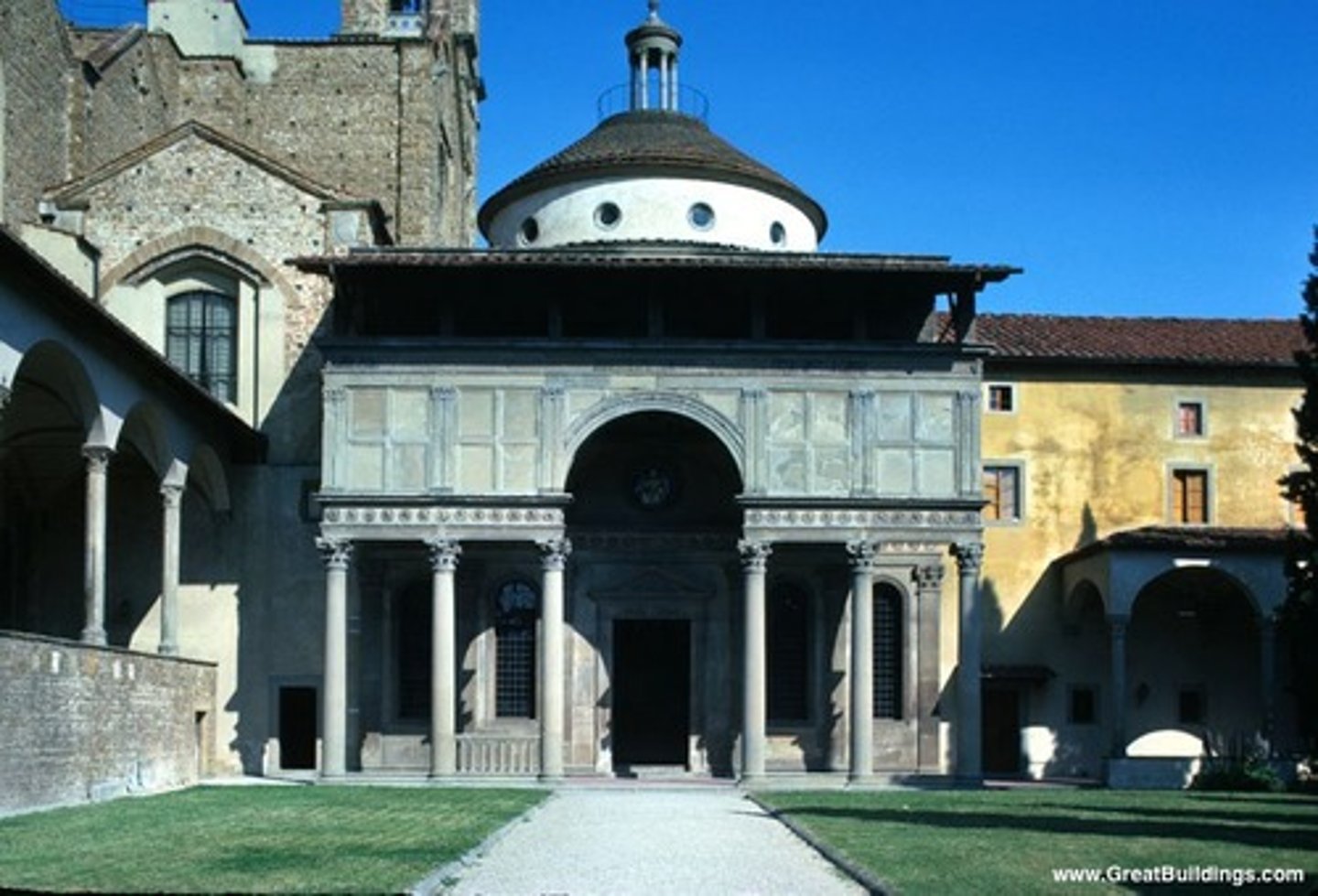
Pazzi Chapel
Brunelleschi

Who wrote the bible for Renaissance architects?
Vitruvius- The ten books of architecture
Who was Vitruvius?
A Roman architect and theorist.
When was Vitruvius active?
From -46 to -25.
What is the title of Vitruvius' notable work?
THE TEN BOOKS ON ARCHITECTURE.
What is significant about THE TEN BOOKS ON ARCHITECTURE?
It is the only complete book on architectural design and theory to survive from the ancient world.
What influence did Vitruvius have?
He had enormous influence on Renaissance architecture.
What were the two thoughts from Vitruvius
1. Firmness, Commodity, and Delight 2. Vitruvian Figure
What did Vitruvius think about platonic forms?
they were eternally and absolutely beautiful
Became basic design modules
circles and squares
Circles and squares
based on whole number proportion relationships
Church of Sant Andrea
Leon Battista ALBERTI
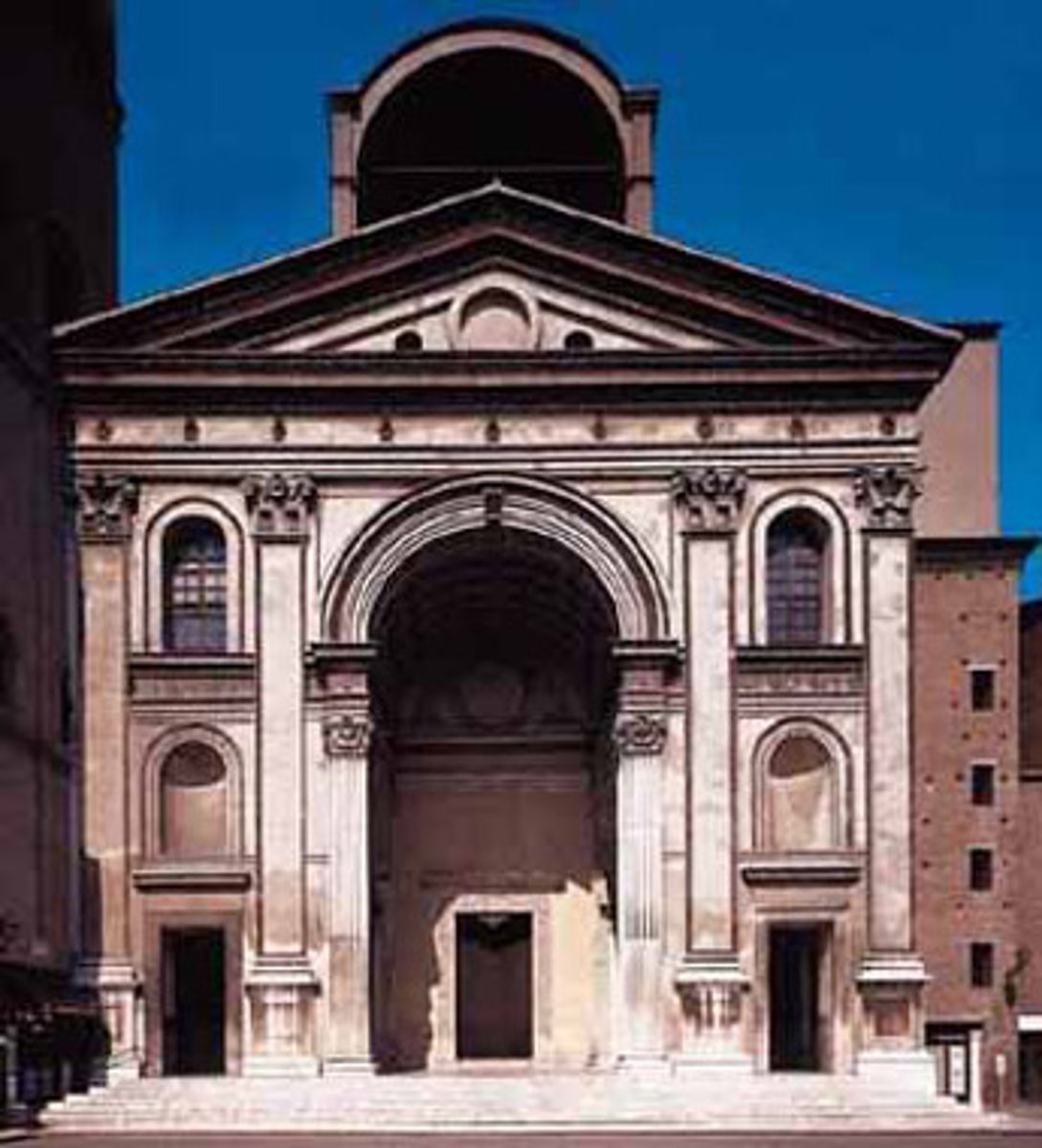

Who was Leon Battista ALBERTI
theorist, historian, scientist, and architect
Who wrote a second ten books based on the books of Vitruvius?
Leon Battista ALBERTI
What did Leon Battista ALBERTI promote?
architecture as an intellectual activity
Ideal city of Sforzinda as a circle plan
Man is the center!
Villa Rotunda, 1500, Vicenza Italy
Andrea PALLADIO
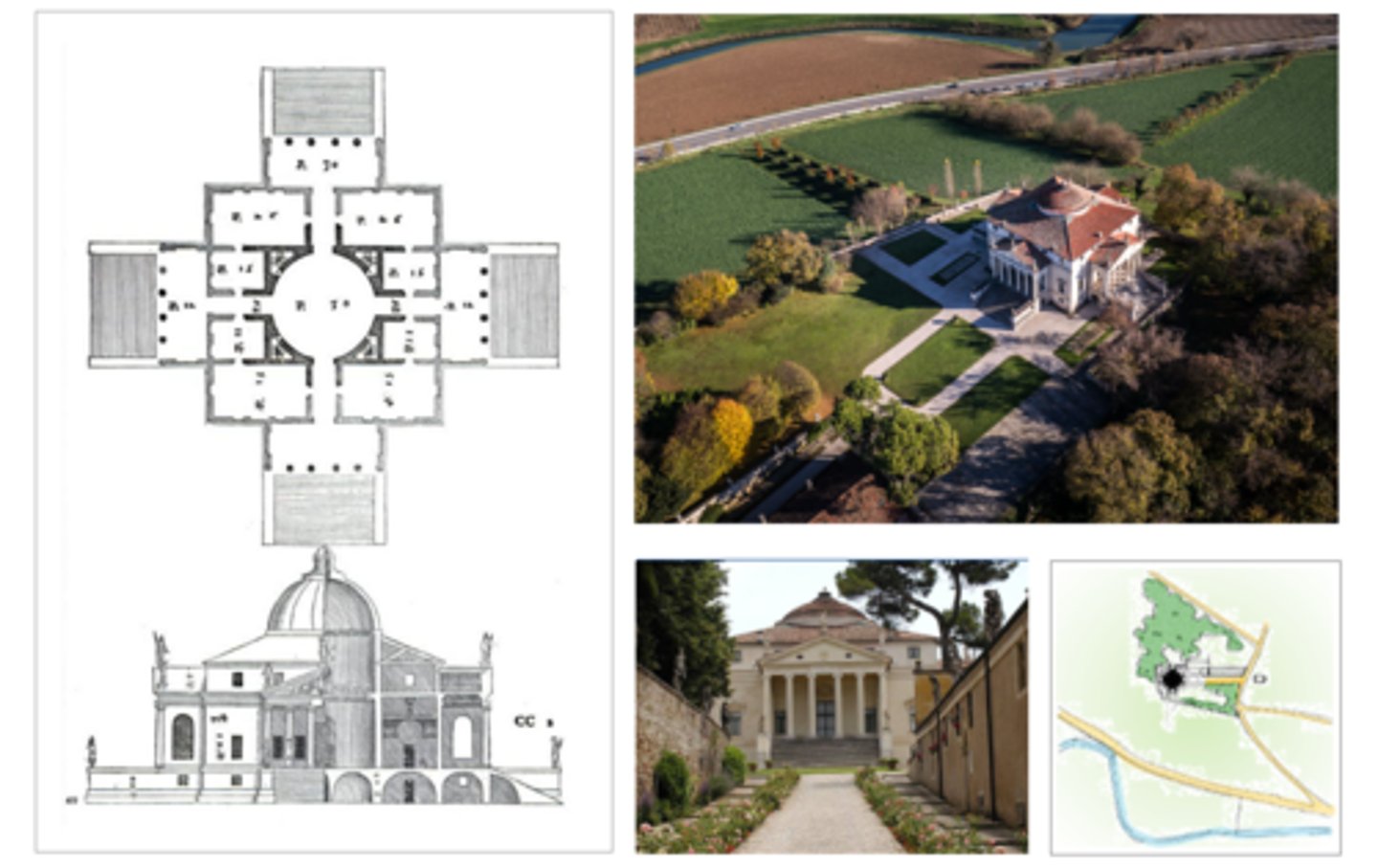
What is Villa Rotunda known for?
It is a supreme example of theoretically inspired design.
How is Villa Rotunda architecturally characterized?
It is completely symmetrical.
What governs the elements of Villa Rotunda's design?
Proportional relationships.
What concept does Villa Rotunda embody in its design?
It turns the house into a temple.
Who wrote treatise on architecture THE FOUR BOOKS OF ARCHITECTURE
Palladio
What work is also attributed to Palladio?
Constructing villas between Venice and Vincenza 1550
Palazzo means
city house
What is the High Renaissance?
A style of Italian Renaissance art and architecture developed during the late 15th century.
San Giorgio Maggiore
scaled to present a public face to the town of Venice
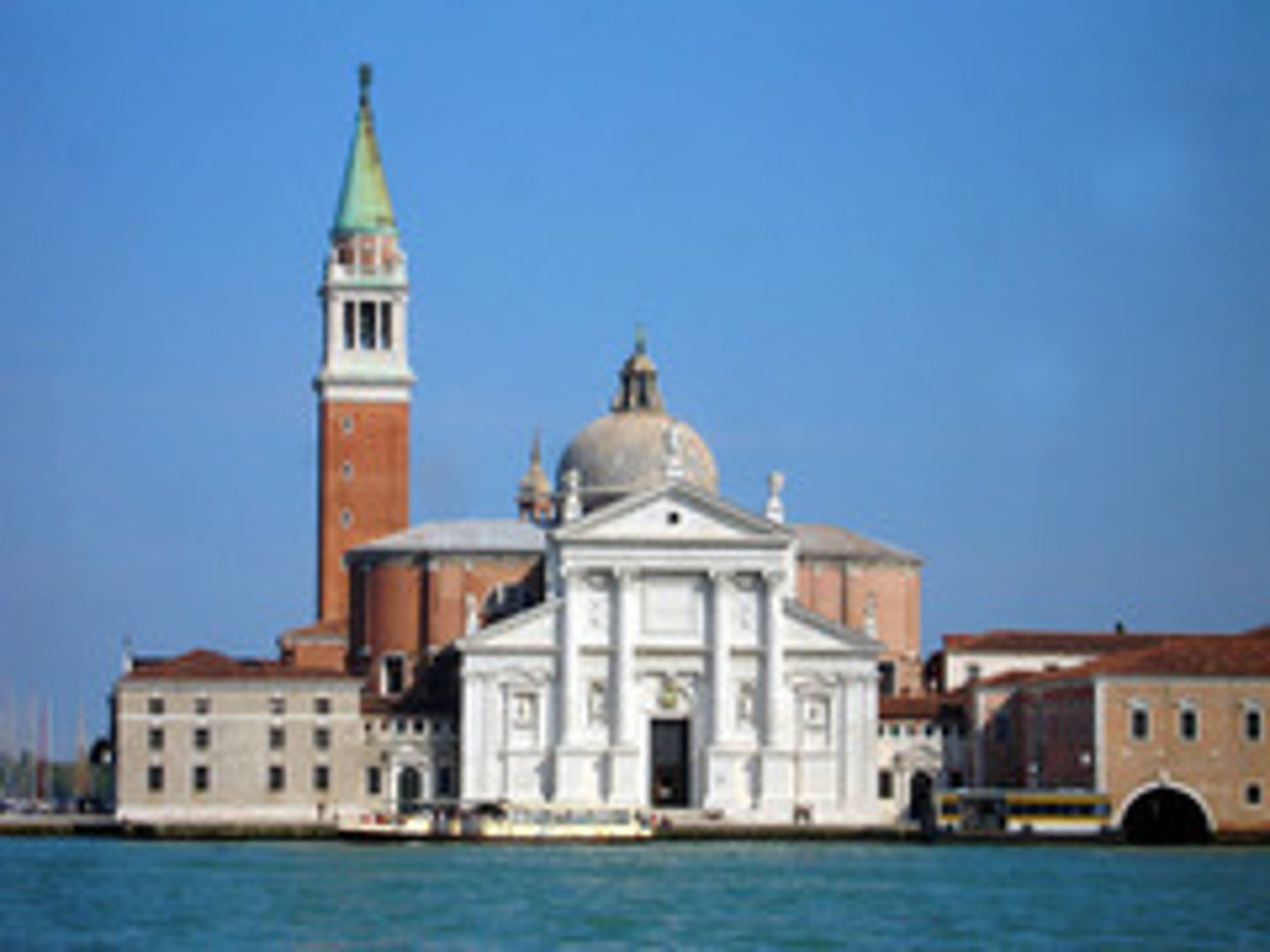

What characterizes High Renaissance art?
An emphasis on draftsmanship and the illusion of sculptural volume in painting.
What architectural features are associated with High Renaissance?
Imitative use of orders and compositional arrangements in the classical style.
Which ancient architect's precepts influenced High Renaissance compositional rules?
Vitruvius
What was a key focus in the formulation of High Renaissance architecture?
Great attention to the precedents of existing ruins.
The Tempietto of San Pietro
Donato Bramante
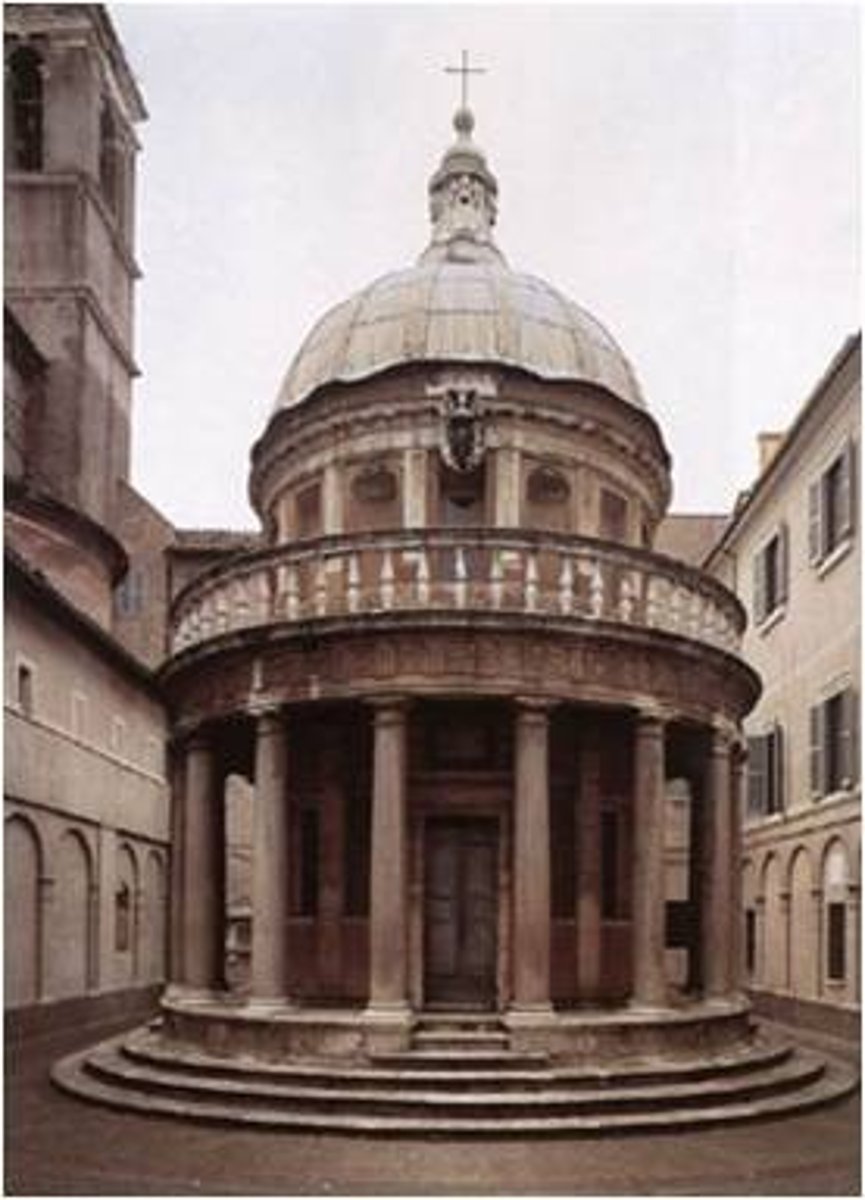

Who was Donato Bramante?
An Italian architect known for his work in the High Renaissance.
What are the years of Donato Bramante's life?
(1444-1514)
Where is Bramante from?
Tempietto, Rome
When was the Tempietto in Rome begun?
1502
With which famous artist was Donato Bramante a close associate?
Leonardo Da Vinci
Where did Donato Bramante begin his early work?
Milan
Why did Donato Bramante move to Rome?
After the French sack of Milan in 1499
Donato Bramante believed
Circle and Square represent the perfection of the divinity
What was believed to have happened in Tempietto, Rome?
Believed religious figure Saint Peter was killed/martyred here
Who was Pope Julius II?
Pope Julius II was the pope from 1503.
What did Pope Julius II introduce into the papal court?
He introduced humanist ideas.
What was one of Pope Julius II's goals for Rome?
To consolidate temporal power.
What did Pope Julius II aim to return to Rome?
The glory from Roman antiquity.
What years did Saint Peter's Basilica construction take place?
1505-1612
Who changed the design of Saint Peter's Basilica?
Michelangelo
What significant feature of Saint Peter's Basilica became an icon?
The dome
Why was a new church built over the crypt of Saint Peter?
The tomb of Pope Julius II would not fit in the old basilica.
What was Bramante's original scheme for Saint Peter's Basilica compared to?
It was on a scale grander than any Roman structure.
What was the size comparison of Bramante's original scheme?
About the size of the Baths of Diocletian.
How does the dome of Saint Peter's Basilica compare to the Pantheon?
It is comparable in size.
Saint Peter's 1505-1612

Mannerism (high Renaissance)
Inventive combinations of elements that purposefully play with classical rules and proportions are exaggerated
Michelangelo (1475-1564)
rebelled against Renaissance decorum, painter and sculptor
What were some of the works of Michelangelo?
He painted the ceiling of the Sistine Chael and sculpted David the Pieta
What is Mannerism?
A transitional style in European architecture in the late 16th century.
In which country did Mannerism particularly develop?
Italy