BIO Lec. 14 - animal diversity
1/72
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
73 Terms
The Kingdom Animalia shares a common ancestor with ___.
a flagellated protozoan (Choanoflagellate)
Choanoflagellate
similar to a type of sponge cell
3 Main Traits of Animals:
1) Multicellular body plan
2) Chemoheterotrophic
3) Diploid form dominant
1) Multicellular Body Plan
via specialization of cells
nervous and muscle tissue (only in animals)
no cell walls
2) Chemoheterotrophic
ingest food
3) Diploid form dominant…
gametes the only haploid stage
6 Major Innovations
1) Embryonic germ tissue
2) Body Symmetry
3) Gut
4) Body Cavity (coelom)
5) Segmentation
6) Cephalization
Embryonic germ tissues
(0, 2, 3)
(ecto-, meso-, endoderm)
Body Symmetry
none, radial, bilateral
Gut
none, incomplete, complete
Body Cavity (coelom)
fluid filled space
none, pseudocoelom, coelom
Segmentation
none, present, present with fusion
Cephalization
increased development of head
Sponges (Porifera)
very simple animals
no germ cell layers.
no body symmetry (usually).
no true tissues or organs - just a few cell types.
Porifera
Sponges:
choanocytes cells -create water flow & filter food
spicules - internal spines for protection
Choanocytes cells
create water flow & filter food
Spicules
internal spines for protection
Nearly all animals have ___ or ___ symmetry
radial or bilateral
Radial Symmetry
animals move slowly, if at all.
Bilateral Symmetry
more rapid movement
sensory organs concentrated at head
Cnidarians
jellyfish, corals, anemones
(slightly more complex animals)
Cnidarians Traits
radial symmetry
two germ cell layers
true tissues
gut with one opening
Cnidocytes/ nematocysts
stingers on tentacles - used for food capture and defense
Cnidarian life cycles
sessile polyp stage (e.g. anenome, corals)
+
free-swimming medusa stage (e.g. jellyfish)
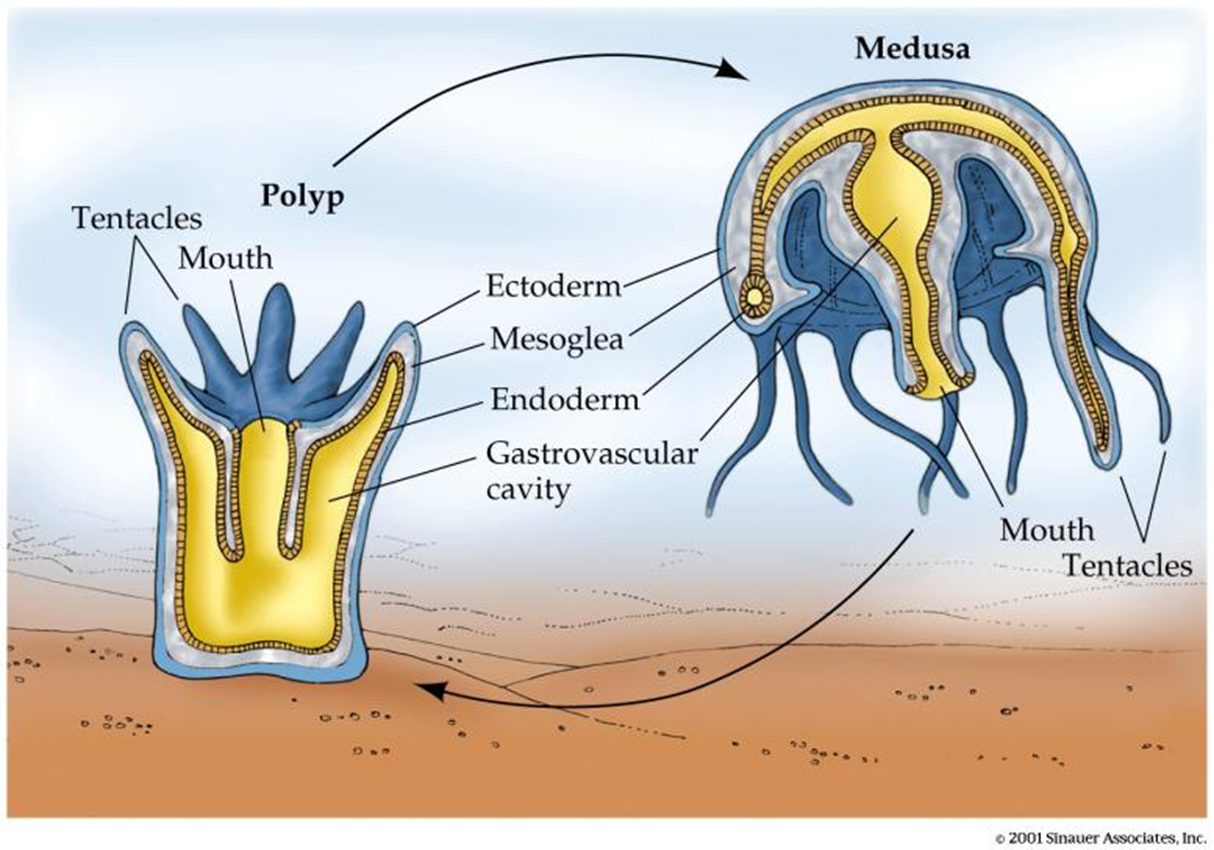
Cnidarian life cycle: polyp & medusa stage
Traits of Animals with 3 Germ Cell Layers:
usually bilaterally symmetrical and 1 of the following:
No body cavity: acoelomates
Body cavity: pseudocoelomates, coelomates - most animals
Acoelomates
no body cavity
flatworms
Pseudocoelomates
body cavity
roundworms
Coelomates
body cavity
most animals
Coelom (Body Cavity) Advantages:
Movement -
more flexible.
hydrostatic skeleton.
Space - enables organ growth (ovaries).
Size - can increase as more surface area for cellular exchange.
Types of Acoelemates
flatworms = Platyhelminthes
Many species are parasites:
Flukes
Tapeworms
Flatworms
no body cavity
bilateral symmetry
some organs
Pseudocoelomates
has a body cavity
Types of Pseudocoelomates
Roundworms = Nematoda
Many are parasites.
human roundworm
pinworm
hookworm
Two Forms of Coelomate Animals:
(grouped based on how body cavity forms)
“Protostomes” - blastopore = mouth
Deuterostomes - blastopore = anus
Benefit of segmented bodies
improved locomotion
Segmented worms
Segmented worms = Annelida
earthworms
leeches
bristle worms
Segmented Mollusca
clams, snails, octopus...
evolved from segmented ancestors.
body plan: foot, mantle, and visceral mass.
Mollusc body plan
Yields a diverse array of animals (superficially appear very different from one another)
Nematoda *
trichinella worm (pork)
1 dorsal nerve, 1 ventral nerve
Arthropods w/ Segmented External Skeletons
Insects, spiders, crabs, millipedes
Secreted body surface thickened & rigid (protein and chitin) = exoskeleton
Exoskeleton
Major innovation for animals.
growth by periodic molting (shedding) of exoskeleton.
muscle attachment site
strong
waterproof
5 Groups of Arthropods
Trilobites: all extinct
Arachnids and relatives: scorpions, spiders, ticks, horseshoe crabs...
Crustaceans: lobsters, crabs, barnacles, sowbugs
Insects – this group has the greatest number of species of any animal group!
Centipedes, millipedes
True or False: Barnacles are mollusks
False
How do you tell if your “bug” is really an insect?
three body regions (two)
single pair of antennae (two or none)
three pairs of legs (four or more)
Echinoderms examples *
sea stars, urchins, sand dollars, sea cucumbers etc.
Echinoderms Features
radially symmetrical body plan as adults (but immatures bilateral!)
water vascular system
calcified internal skeleton (most)
True or False: Protosomes are monophyletic
False
Chordate characteristics
Pharyngeal slits as feeding devices – modified as gills later
Notochord - supporting rod for better wiggle movement or swimming
Post-anal tail
Why do sea squirts or tunicates move?
(larval stage mobile - like lancelet).
adults are sessile filter feeders
Lancelets
has not changed much from early chordates— a filter feeder.
(early vertebrates filtered small animals from mud)
Origin of Vertebrates: Craniates charactieristics
Jointed internal skeletons around a vertebral column
Rigid skeleton more support for rapid swimming.
What craniates do NOT have a jointed internal skeleton around a vertebral column?
hag fish
Obtaining O2 from air: Fish examples
Jawless fish – lampreys (38 spp) + hagfish (20 spp)
Cartilaginous fish - sharks, rays, chimeras (850 spp)
Bony fish - bass, trout...(ray-finned and the lobe-finned fish and lungfish) (28,000 spp)
Where did fish jaws evolve from?
anterior gill arches
Fish Evolution to Amphibians
Fishes
Fins (first unjointed) - control swimming movement, provided stability in water.
Three fish lineages evolved jointed fins (~limbs?)
Amphibians (first terrestrial vertebrates) arose from one of these lineages.
Limbs – enabled the first amphibians to move quickly and precisely on land
Amphibians, the first terrestrial vertebrates, arose from ___.
a lineage of fish with jointed fins.
ex: Tiktaalik: many toes
Amphibian lungs evolve for ___.
land respiration
Amphibian species
caecilians — (caecilian - giving birth)
frogs and toads
salamanders
Chytrid fungus
eradicated more than 100 frog species across the globe; spread to an ecosystem in Panama
Amniotes
vertebrates completely independent of water for reproduction
Why do amniotes not need water to reproduce?
Amniotic egg: water-impermeable egg shells to keep embryo wet.
Internal fertilization
Water-proof skin
What animals are included in the 7000 reptile species on Earth?
turtles and tortoises
tuataras
snakes and lizards
crocodilians
There are 9,234 bird species. What characterizes them all?
feathers
Why are reptiles a poorly-defined group? *
They do not include birds, which would make them monophyletic.
There are 4,500 mammal species. What characterizes them all?
hair
suckle young with mammary glands
What are the 3 groups of mammals?
1. Monotremes – 5 spp.
2. Marsupials - 260 spp.
3. Eutherians/Placentals - 4,350 spp.
Monotremes
Egg laying mammals
Spiny Anteaters or Echidnas
Platypus
Marsupials
Give birth to tiny undeveloped young
Have pouch for young
Eutherians (Placentals)
Give birth to relatively well-developed young
Bats: ¼ of all mammal species
Rodents: ½ of all mammal species
All primates were ancestrally:
arboreal
insectivores
Hominids evolved in Africa from ___, ___ ancestors *
terrestrial, bipedal
True or False: Tuatara are lizards *
False