Special Senses: Vision, Taste, Smell, Hearing, and Equilibrium
1/58
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
59 Terms
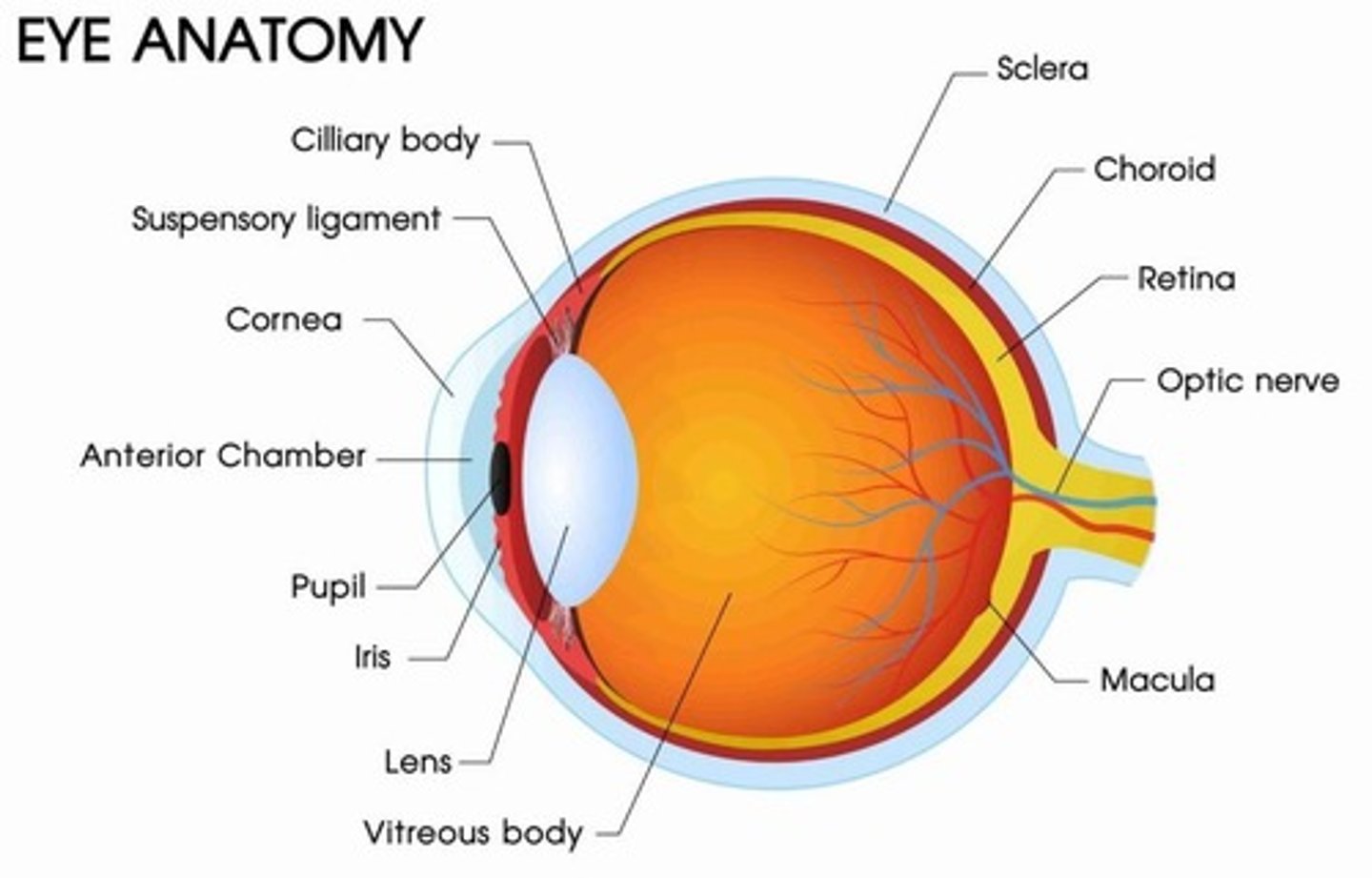
Fibrous tunic
Composed of sclera and cornea.
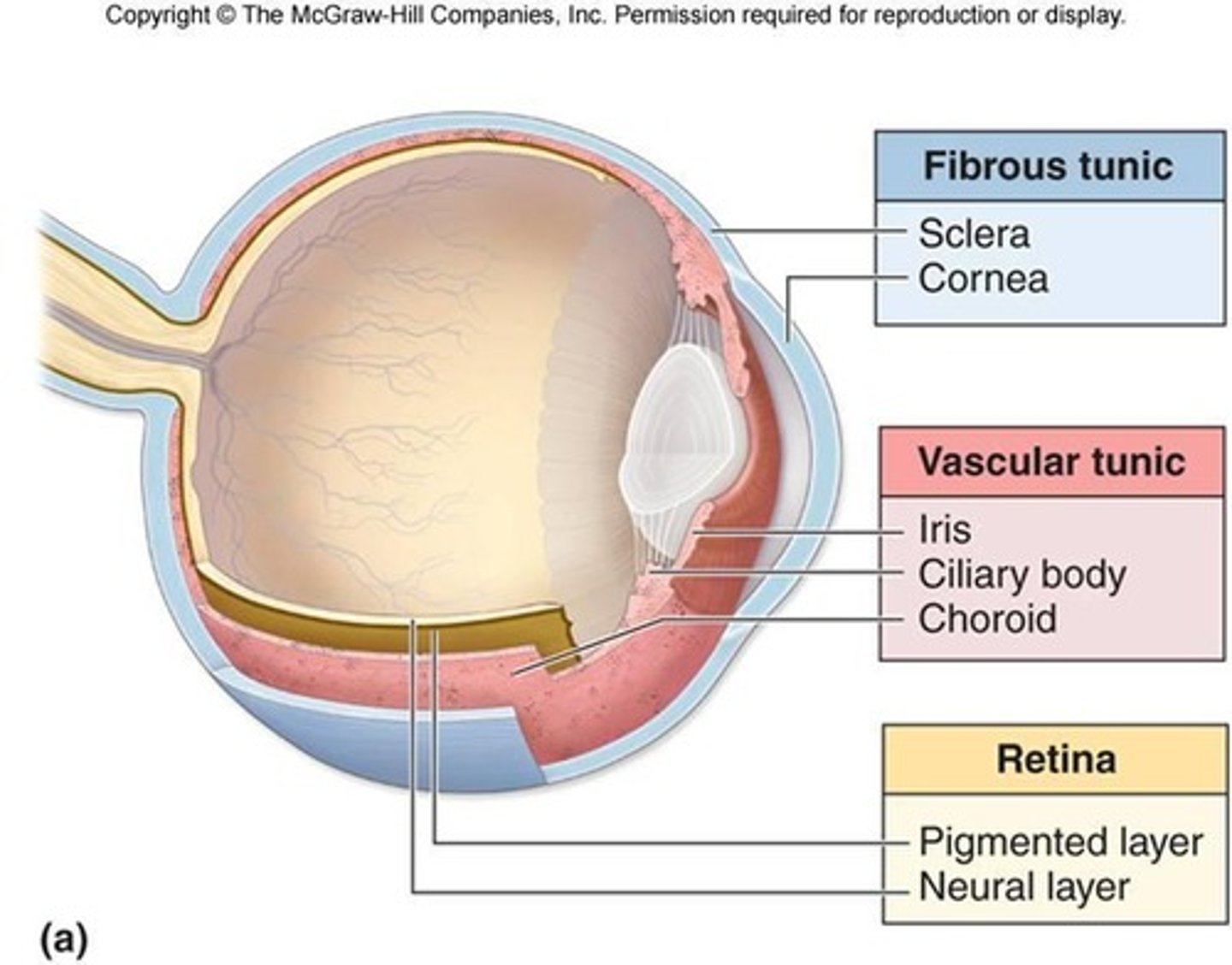
Vascular tunic (Uvea)
Composed of choroid, ciliary body, and iris.
Sensory tunic (Retina)
Composed of photoreceptors; optic nerve (CN II) is made up of the axons of the retinal ganglion cells.
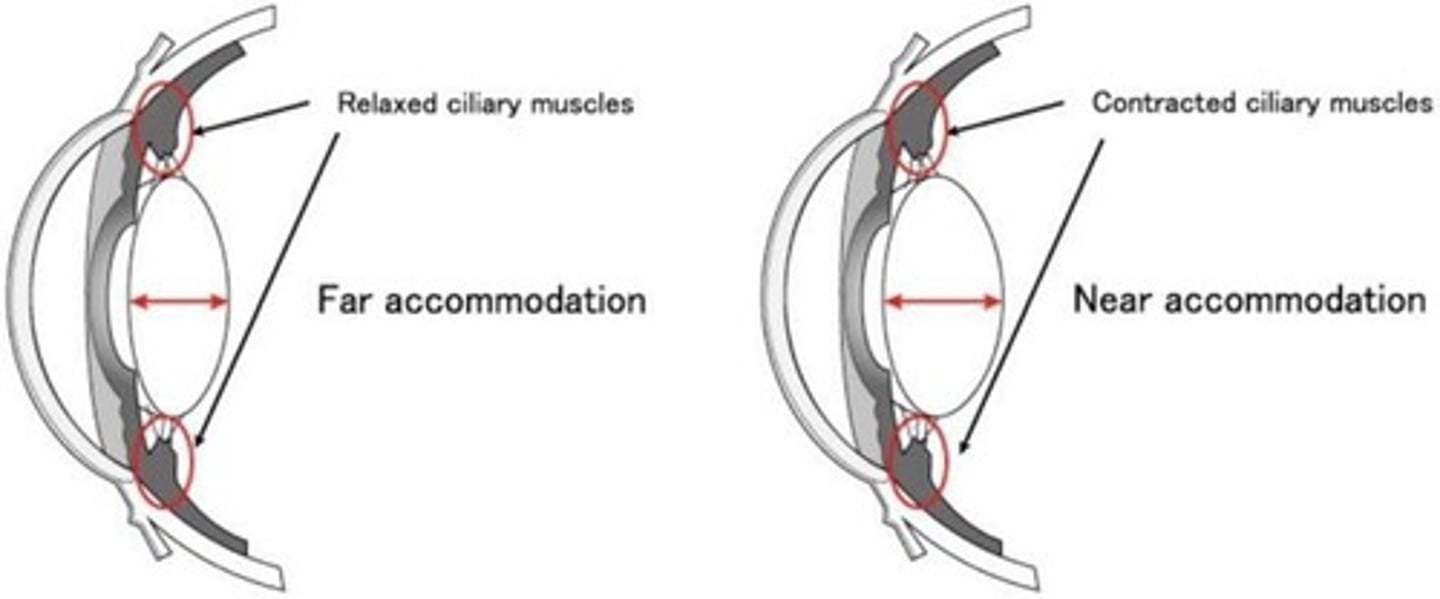
Lens
Used to focus light on the retina by changing shape.
Anterior segment
Anterior to the lens and filled with aqueous humor.
Posterior segment
Posterior to the lens and filled with vitreous humor.
Superior rectus muscle
Action: Elevation of eyeball; Innervation: Oculomotor nerve (CN III).

Inferior rectus muscle
Action: Depression of eyeball; Innervation: Oculomotor nerve (CN III).
Medial rectus muscle
Action: Adduction of eyeball; Innervation: Oculomotor nerve (CN III).
Lateral rectus muscle
Action: Abduction of eyeball; Innervation: Abducens nerve (CN VI).
Superior oblique muscle
Action: Depression and abduction of eyeball; Innervation: Trochlear nerve (CN IV).
Inferior oblique muscle
Action: Elevation and abduction of eyeball; Innervation: Oculomotor nerve (CN III).
Oculomotor Nerve (CN III)
Parasympathetic nerve involved in eye function.
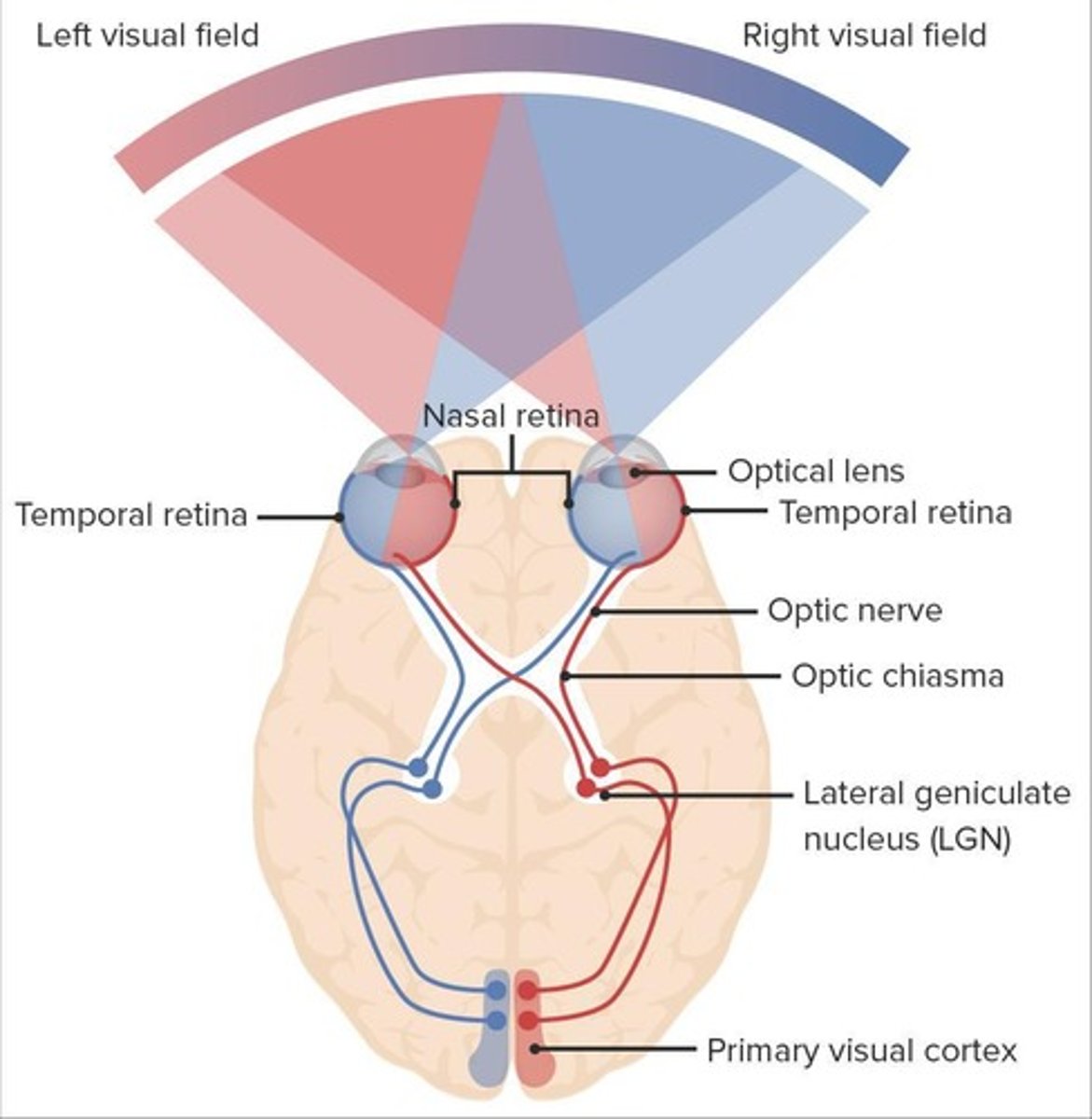
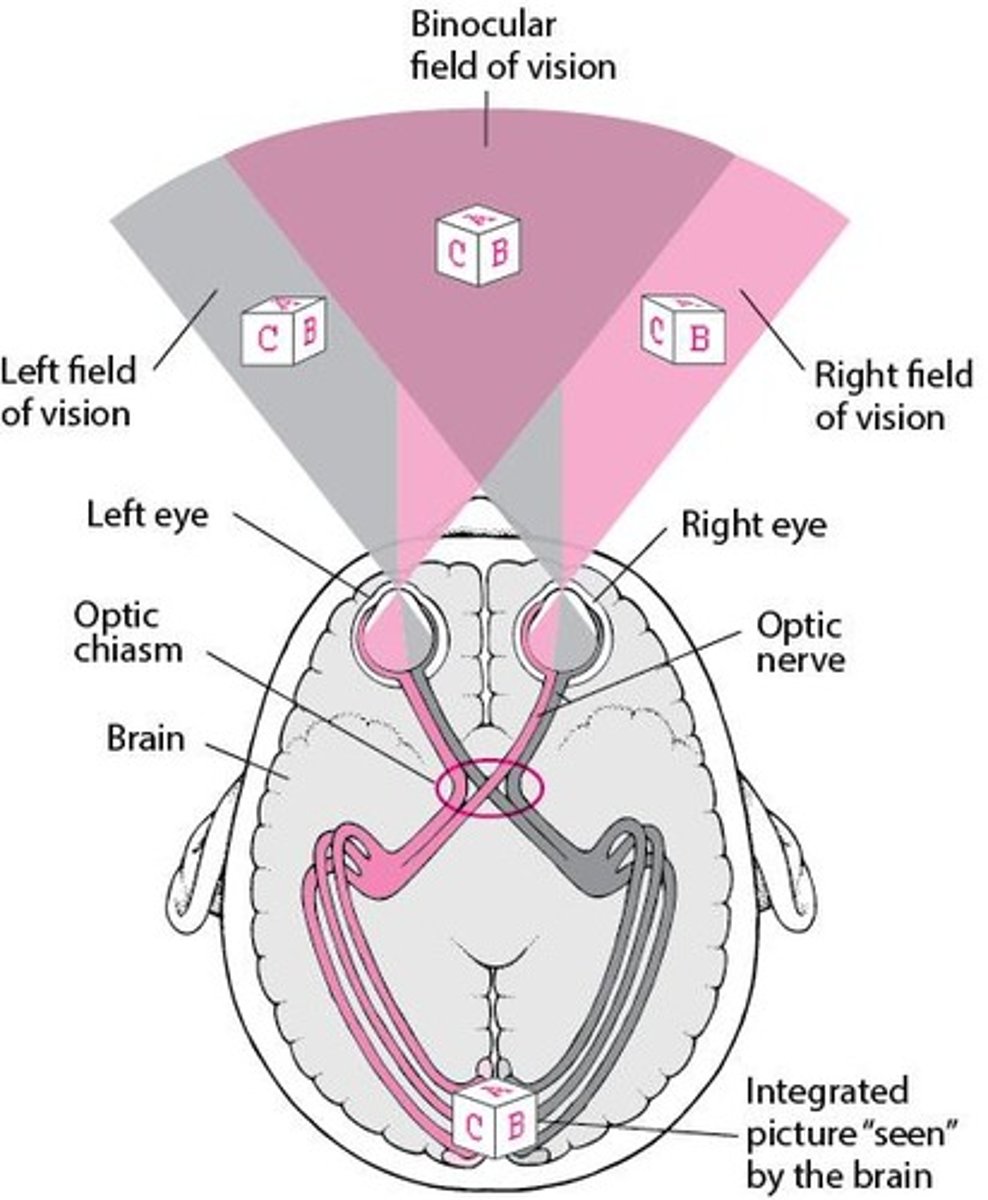
Visual Pathway
Order: 1. Photoreceptors 2. Ganglion cells 3. Optic chiasm 4. Optic tract 5. Thalamus 6. Primary visual cortex.
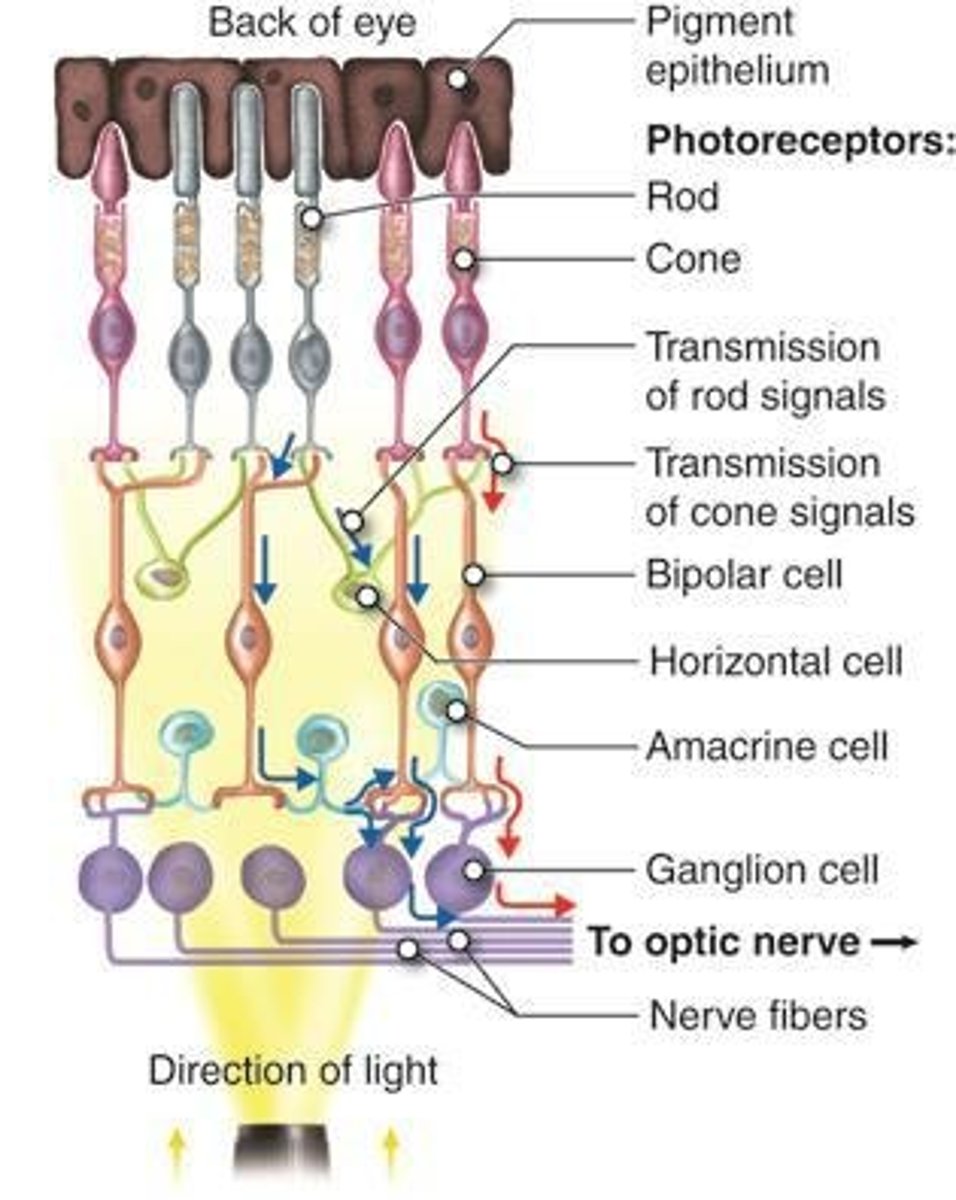
Photoreceptors
Convert light into an electrical signal.
Optic nerve (CN II)
Retinal ganglion cell axons leave the eye as the optic nerve.
Optic chiasm
Partial crossover of fibers from the nasal aspect of each retina.
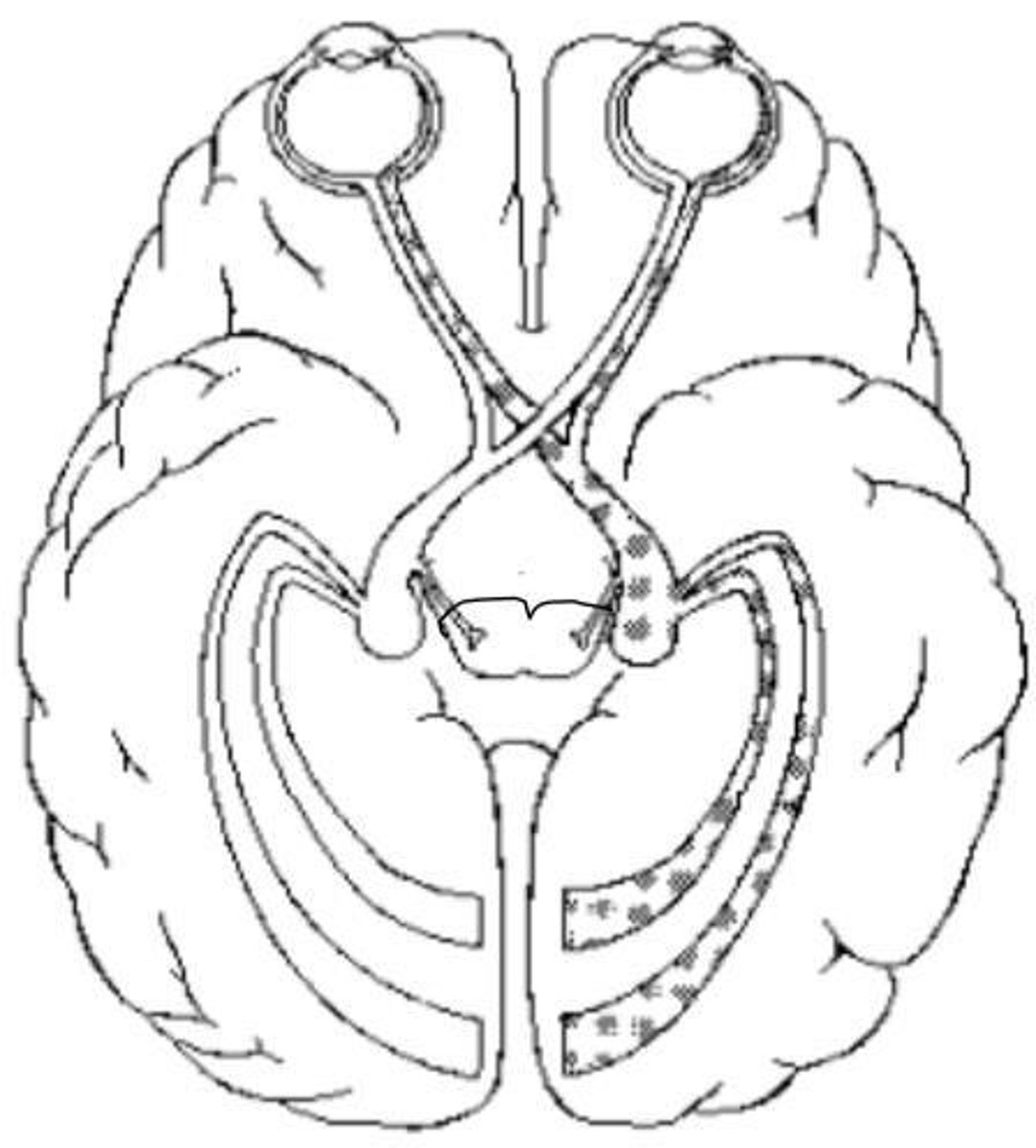
Optic tract
Carries information from the contralateral visual field.
Thalamus
Most fibers in the optic tracts synapse with neurons here.
Primary visual cortex
Final destination for visual information processing.
Fibers from the thalamus
Project to the primary visual cortex in the occipital lobes.
Right primary cortex
Integrates information from the left visual field.
Left primary cortex
Integrates information from the right visual field.
Visual information from the left eye
Travels in the Left Optic nerve.
Visual information from the left visual field
Travels in the Left Optic tract.
Peripheral vision crossing over
Occurs in the Optic Chiasm.
Five special senses
Include vision, hearing, taste, smell, and equilibrium.
Special sense of taste
Includes receptor type, location of sensory receptor organ, and how special and general sensation to the tongue is supplied.
Extrinsic muscles of the tongue
Include three muscles, their action, and innervation.
Special sense of smell
Includes receptor type, location of sensory receptor organ, and how impulses travel from the olfactory epithelium to the brain.
Special sense of hearing and equilibrium
Includes receptor type, parts of the ear, sensory receptor organs, and how impulses travel to the brain.
Primary cortical areas for smell, sight, and hearing
Located in specific lobes of the brain, supplied by anterior, middle, or posterior cerebral arteries.
Mechanoreceptors
Respond to mechanical force that deforms.
Thermoreceptors
Respond to change in temperature.
Chemoreceptors
Respond to chemicals.
Nociceptors
Respond to potentially damaging stimuli.
General Senses
Associated with touch, lack special sense organs.
Special sensory innervation to the anterior 2/3rds of the tongue
Comes from CN VII.
Sensory innervation to the posterior 1/3 of the tongue
Includes special sensory for taste and general sensory from Glossopharyngeal n. (CN IX) and Facial n. (CN VII).
General sensory innervation to the tongue
Supplied by the mandibular division of trigeminal n.
Styloglossus
Extrinsic muscle of the tongue.
Genioglossus
Extrinsic muscle of the tongue.
Hyoglossus
Extrinsic muscle of the tongue.
Primary Olfactory Cortex
Located mostly at the medial aspect of the temporal lobe; conscious awareness of odors.
Subcortical Route
Pathway to the Hypothalamus, Amygdala, and Other Regions of Limbic System to elicit emotional and memory-evoked responses to odors.
External Auditory Canal
Structure of the external ear.
Auditory Ossicles
Includes Malleus, Incus, and Stapes.
Malleus
Also known as the 'Hammer'.
Incus
Also known as the 'Anvil'.
Stapes
Also known as the 'Stirrup'.
Pharyngotympanic Tube
Structure of the middle ear.
Ossicles Amplification
Ossicles amplify sound waves received at the tympanic membrane 20X.
Semicircular Canals
Structure of the internal ear.
Cochlea
Structure of the internal ear.
Oval Window
Structure of the internal ear.
Round Window
Structure of the internal ear.
Tympanic Membrane
Sound waves enter ear and cause it to vibrate.
Cochlear Branch of CN VIII
Initiates a nerve signal when hair cells in the spiral organ are distorted.
Mechanoreceptor
Receptor type used for equilibrium.