Exercise 25: Survey of Protists - Algal Autotrophs
1/48
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
49 Terms
What are the two components that make up the scientific name?
Genus name
Species
Scientific name Italicized (T/F)
True
Why would we use a scientific name?
It might mean something different in a different language or even region - scientific names keep it clear
What is the genus name and what is the species name? Aloe vera
Genus: Aloe
Species: vera
The Genus names are ___________ and species names are ____________
Uppercase; lowercase
What does “auto” as a prefix mean?
Self
What is an autotroph?
Make their own food
We are only identifying ___________.
Eukaryotes
What is the order of the taxonomic group?
Domain
Kingdom
Phylum
Class
Order
Family
Genus
Species
The higher you go in taxonomy, the more/less inclusive you are.
More
The lower you go in taxonomy, the more/less population there is.
Less
If species are in the same family, they are similar/different in:
Principles
Characteristics
Similar
What are the 4 Kingdoms in Domain Eukarya?
Protista
Fungi
Plantae
Animalia
What is the big difference of Eukarya from Archea and Bacteria?
Organelles
Base of food chain
Animal- or plant- like
Polyphylic
Has supergroups
Based on these characteristics, what kingdom of Eukarya is this?
A) Plantae
B) Protista
C) Fungi
D) Animalia
B)
A taxonomic group that includes multiple species or lineages that do not share a common ancestor
In order words - a tricky group to categorize well
Polyphyletic
It takes the place of phylum level in the protists kingdom
Supergroups
What are the supergroups in protists?
Archarplastida
Chromalveolata
Excavate
Amoebozoa
Rhizaria
Opisthokoma
What supergroup is this?
Members:
green algae, red algae, charophytes
Distinguished Features:
Plastids, unicellular, colonial, and multicellular
Archaeplastida
What supergroup is this?
Members:
Stramenpiles: Brown algae, diatoms, golden brown algae, water molds
Alveolates: ciliates, apicomplexans, dinoflagellates
Distinguished Features:
Most with plastids; unicellular and multicellular
Alveoli support plasma membrane; unicellular
Chromalveolata
What type of member from the Chromalveolata supergroup has these protists?
Brown algae, diatoms, golden brown algae, water molds
Stramenopiles
What type of member from the Chromalveolata supergroup has these protists?
Ciliates, apicomplexans, dinoflagellates
Alveolates
What supergroup is this?
Members: Euglenoids, kinetoplastids, parabaslids, diplomonads
Distinguished Features: Feeding groove, unique flagella; unicellular
Excavate
What supergroup is this?
Members: Amoeboids, plasmodia’s and cellular slime molds
Distinguished Features: Pseudopods, unicellular
Amoebozoa
What supergroup is this?
Members: Foraminiferans, radiolarians
Distinguished Features: Thin pseudopods; some with tests; unicellular
Rhizaria
What supergroup is this?
Members: Choanoflagellates, animals, nucleariids, fungi
Distinguished Features: Some with flagella; unicellular and colonial
Opisthikonta
Algal autotrophs are plant- like so they have an organelle called ___________. They can be ____________, ____________, and _____________.
Chlorophyll; unicellular; filamentous; colonial
This characterization of cell looks like a string or a ribbon
Filamentous
This cellular characteristic can look like a family, multicellular
Colonial
Green algae Is the most ________ fresh water algae
Diverse
What member from Archeoplastida is this?
Could be Uni- or multicellular
Could be filamentous or colonial
Ancestors of land plants
Green Algae
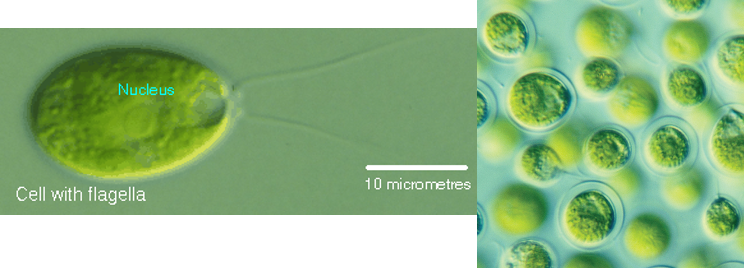
Genus of green algae that is motile and unicellular?
Chlamydomonas
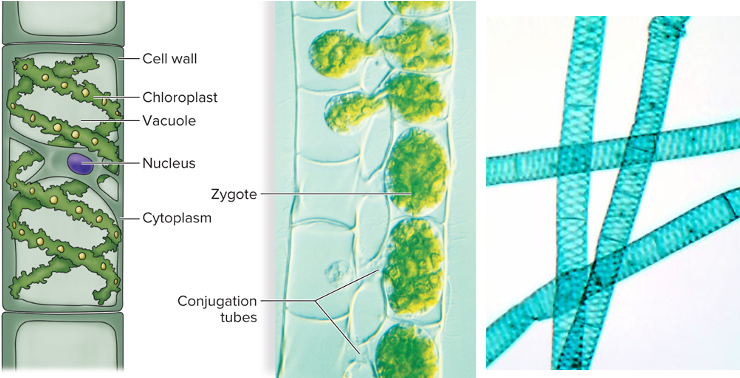
Genus do green algae that is filamentous. It is characterized as “pond scum.” It has a conjunction tube, nucleus, and zygote.
Spirogyra
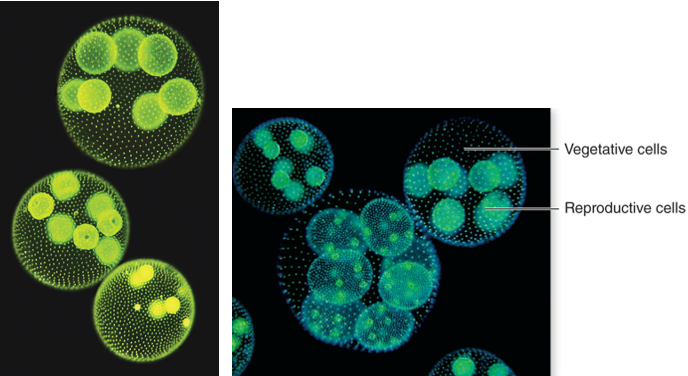
Genus of green algae that is colonial. It has reproductive cell and vegetation cells.
Volvox
Which supergroup is the Red algae in?
Archaeplastida
What member from Archeoplastida is this?
Multicellular
Filamentous or fleshy
Source of agar, ice cream thickener, sushi, cosmetics
Red Algae
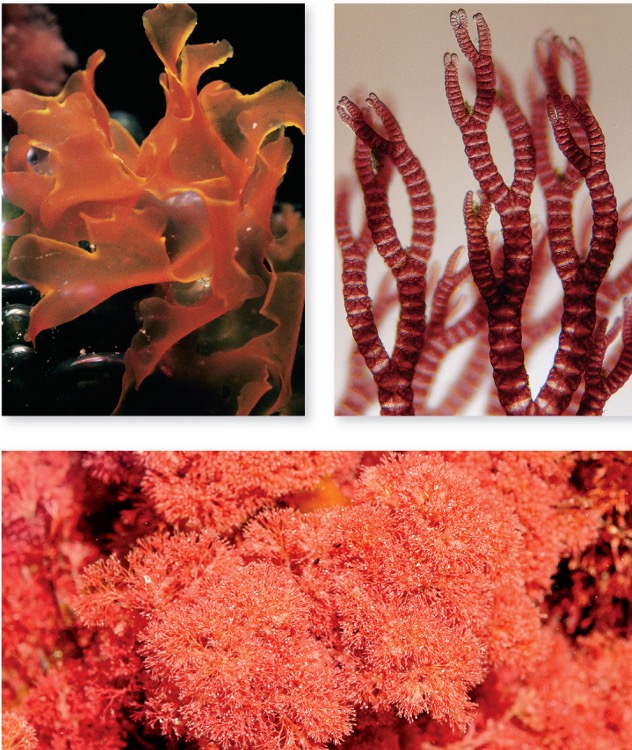
When something has a tissue-papery style we describe is as a ___________ characteristic
Fleshy
________ is a gelatinous substance derived from seaweed. It is commonly used in laboratories as a culture medium for growing microorganisms, as well as in the food industry as a thickening agent and vegetarian alternative to gelatin.
Solidifies when cooled
Agar
Red algae is used in cosmetics by adding _______
Color
Which supergroup is the Brown algae in?
Chromalveolata
What is another name for brown algae?
Kelp
What supergroup are Diatoms in?
Chromalveolata
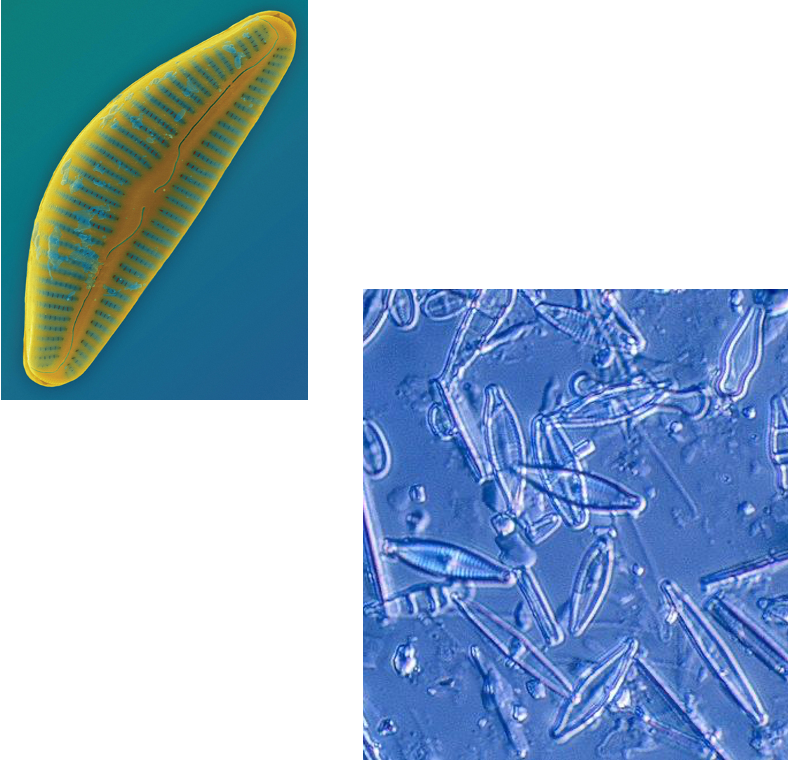
What member from the Chromalveolata group is this?
Unicellular
SIlicone dioxide (glass) cell wall
Diatoms
What group are Dinoflagellates in?
Chromalveolata
What member from the Chromalveolata group is this?
Unicellular, motile
Red tide toxin
Bioluminescence (they can glow)
Dinoflagellates
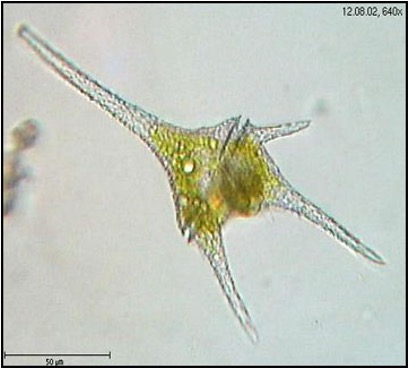
When together they produce a toxin that kill the sea animals called the _________
Red tide toxin
What supergroup are the Eulenoids in?
Excavate

What member from Excavata group is this?
Unicellular
Has a:
Flagellum
Nucleus
Chloroplasts
Contractile vacuole
Eyespot
Euglenoids
This characteristic in Euglenoids help detect shadows
Eyespot