BIOL 300 Discussion 9: Transcription
1/28
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
29 Terms
What is the different between Replication and Transcription?
Replication is DNA to DNA
Transcription is from DNA to RNA
What is the Major Enzyme for Replication?
DNA Polymerase
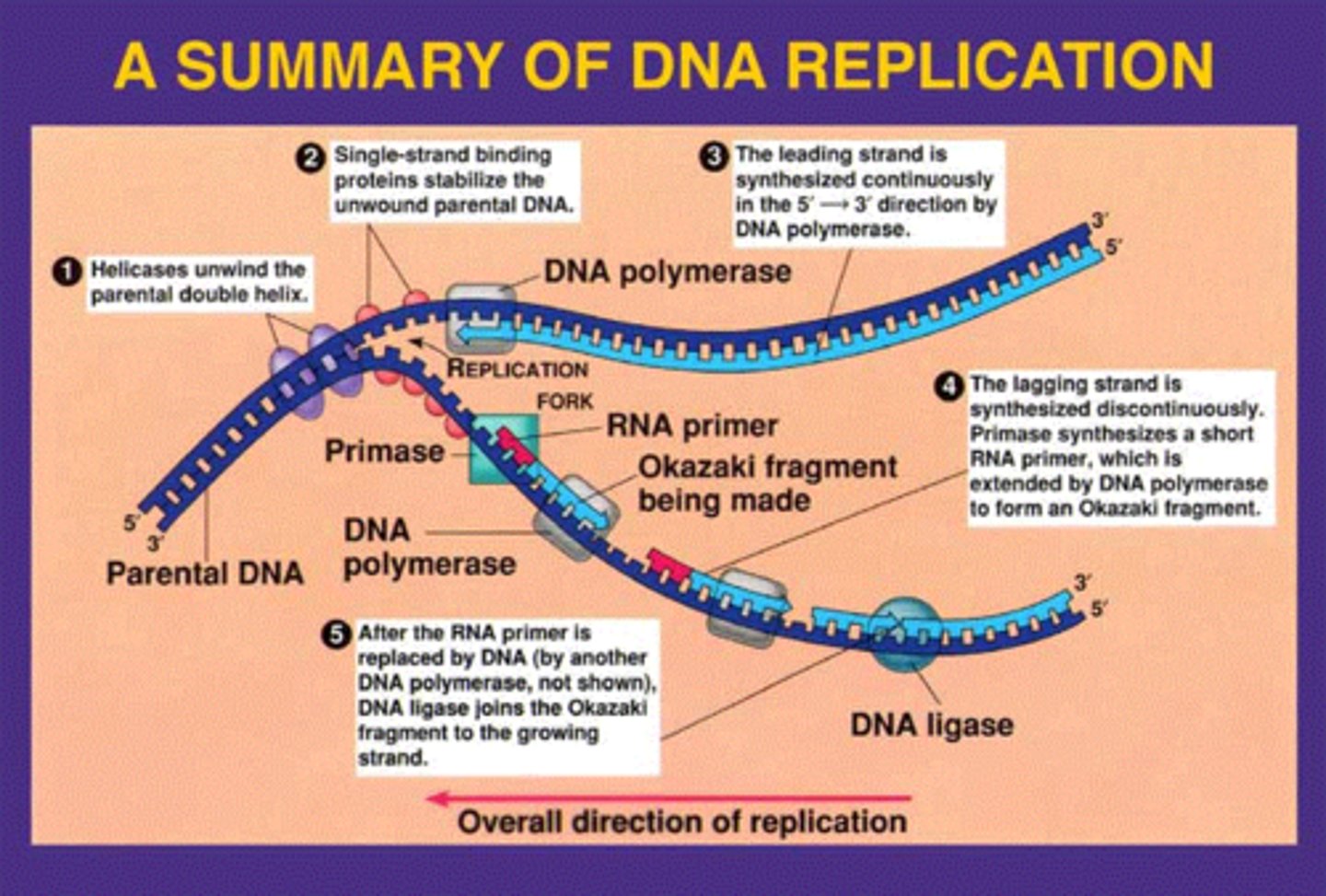
What is the Major Enzyme for Transcription?
RNA Polymerase
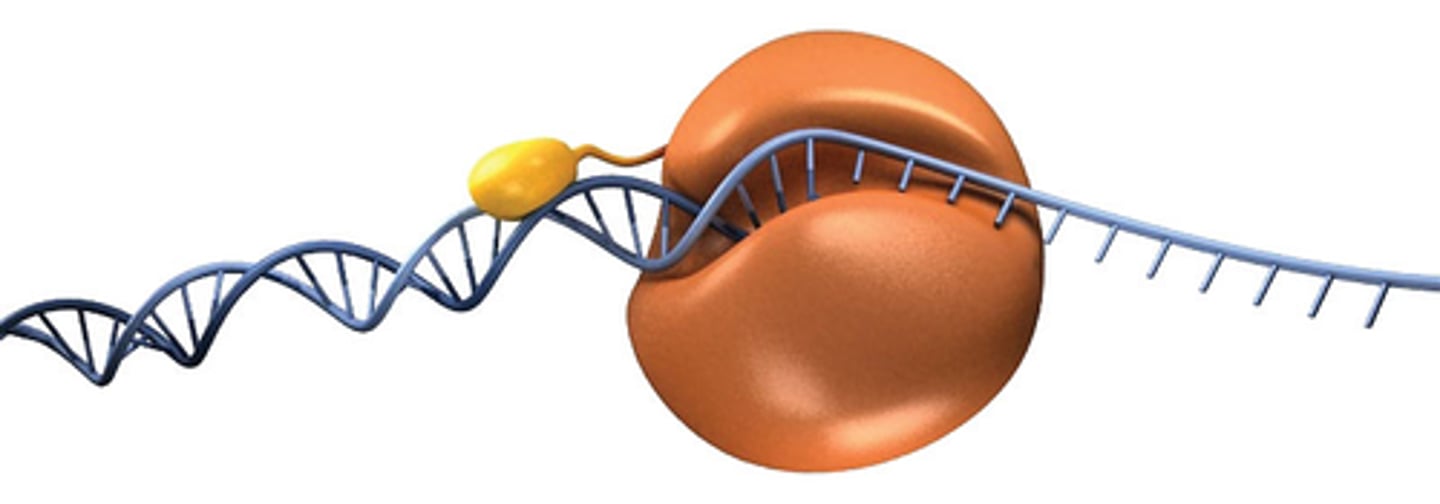
What region does Replication occur?
In the Replicon
What region does Transcription occur? In either
Pro: Cytoplasm
Euk: Nucleolus
Nucleoplasm
What are the three steps for Prokaryotic Transcription?
1. Initiation
2. Elongation
3. Termination
What is RNA Polymerase?
It is the enzyme responsible for transcription initiation; synthesizes RNA from DNA
What is Prokaryotic RNA Polymerase composed of?
A core enzyme, a2BB'w(sig)
What is the Holoenzyme of RNA Polymerase composed of?
5 different subunits consisting of 2 alpha, 1 beta, 1 beta prime, and 1 sigma
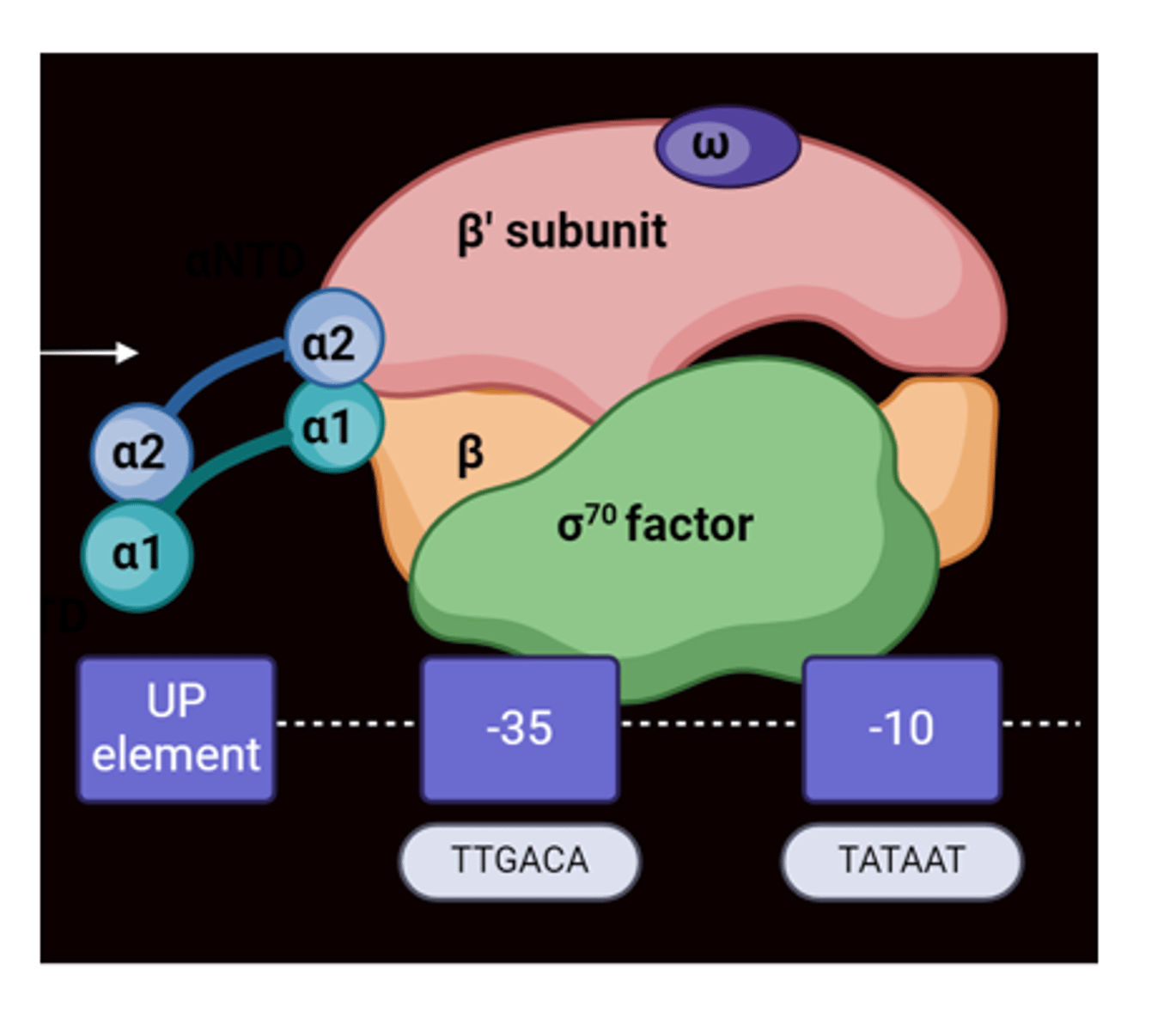
What is the Prokaryotic Promoter? what binds to it?
A specific DNA sequence where RNA pol binds to begin transcription.
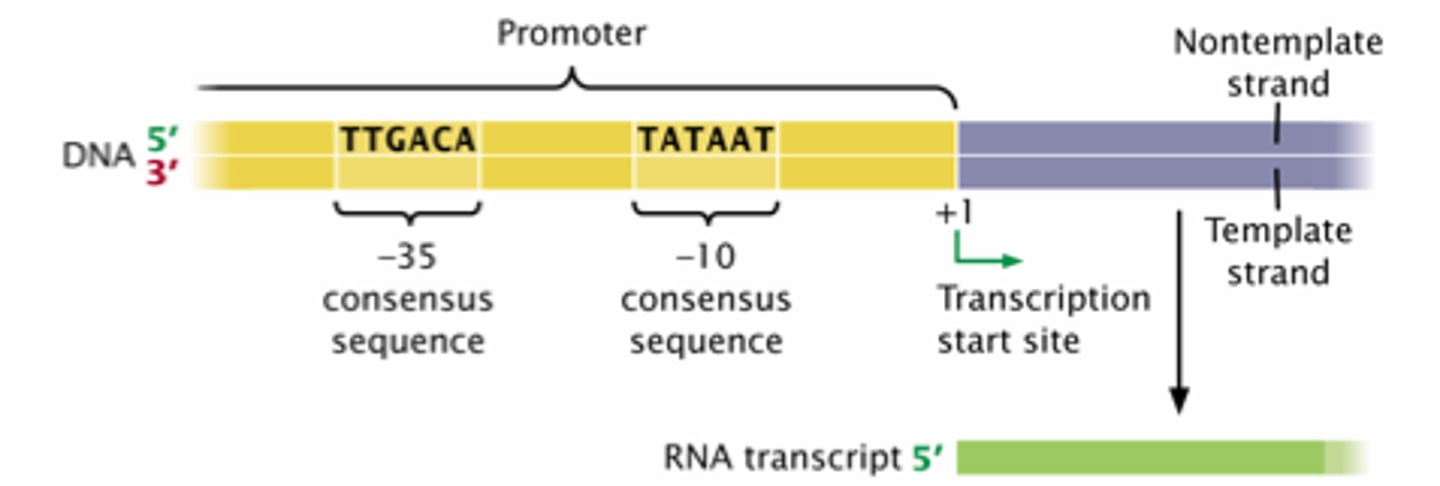
Where are Consensus Sequences located? Why are they important?
Within the Promoters, RNA Pol recognizes these sequences and binds.
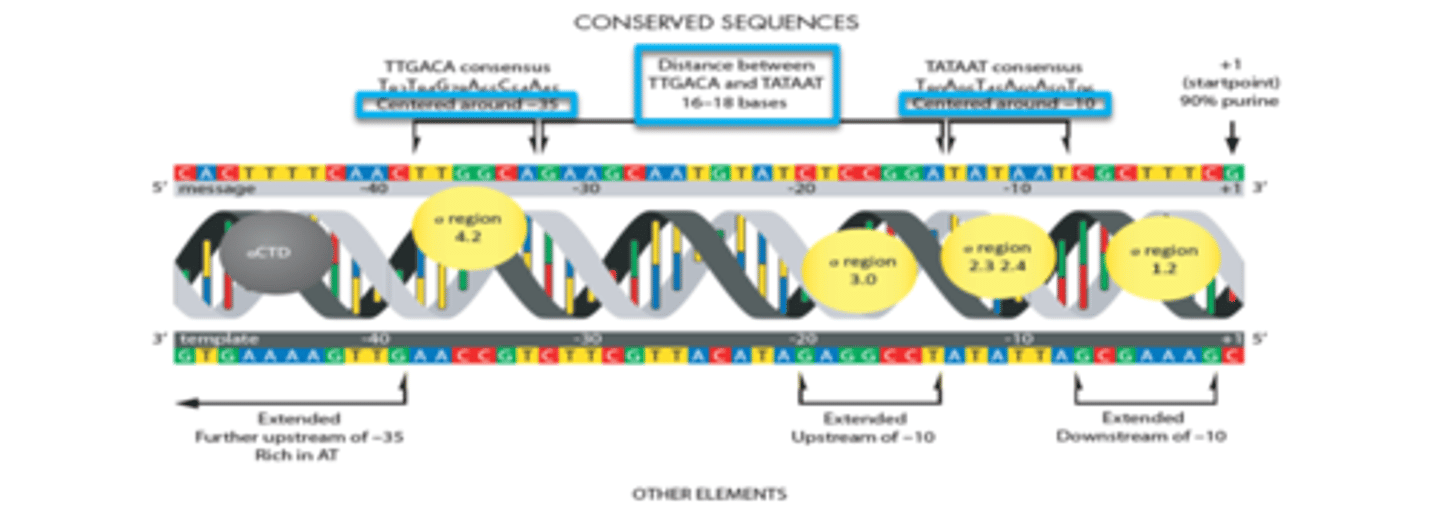
What are Consensus Sequences?
Calculated order of most frequent/common residues found at each position in the sequence alignment.
What are Conserved Sequences
Similar or identical sequences in DNA; occur across species
Increasing or Decreasing # of nucleotides between the 2 consensus sequences does what?
Affects transcription rate
Changing nucleotides (insertions/deletions) between the 2 consensus sequences does what?
Does not affect transcription rate.
How many classes of RNA Polymerases are present?
There are three, RNA Pol 1,2, and 3
What is the function of RNA Pol 1?
Synthesizes rRNA
What is the function of RNA Pol 2?
Synthesizes mRNA
What is the function of RNA Pol 3?
synthesizes multiple types of RNA
What are Cis-Acting elements?
Elements located within the DNA sequences
What are Trans-acting elements
Elements that will bind to the Cis-Acting elements (transcription factors)
Which RNA Polymerase has a C-Terminal Domain?
RNA Polymerase 2
What are Enhancers?
DNA sequences that can increase transcription rates by increasing the efficiency by which RNA polymerase binds to a promoter.
Where are promoters located in Eukaryotes? In Prokaryotes?
Around start point in Eukaryotes, Before the start point in Prokaryotes
What is the name of the TAATAT consensus sequence in Eukaryotes? In Prokaryotes?
TATA box in Eukaryotes, Pribnow box in Prokaryotes
What enzyme binds to the promoter in Eukaryotes? In Prokaryotes?
Transcription Factors in Euk.
RNA Polymerase in Prok.
Where is the Pribnow box found? TATA Box? (sequence number)
Pribnow box is -10
TATA box is -25
What proteins are needed for Prokaryotic Transcription initiation? Eukaryotic initiation?
Prokaryotes use Sigma factors,
Eukaryotes use General Transcription Factors
Does RNA polymerase bind directly to the promoter in Prokaryotes?
What about Eukaryotes?
Yes in Prokaryotes,
No in Eukaryotes