Exam Questions on Core Practical - things to note!
1/18
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
19 Terms
Devise an experiment to compare the rates of hydrolysis of 2-chlorobutane, 2-bromobutane and 2-iodobutane. State the trend in the rates of reaction. Justify your answer.
Remember - you must establish conditions to make it a fair test!

What anhydrous compounds may be used as a drying agent in drying an organic product?
anhydrous sodium sulphate
anhydrous magnesium sulphate
anhydrous calcium chloride
Describe how the student should prepare the 250.0cm³ of ethanedioic acid solution.

The student thought that the enthanedioic crystals used may have been slightly damp. Explain the effect this would have on the value of n calculated.
lower mass/ moles/ concentration of H2C2O4
so titre will be lower and value of n (moles of water of crystallisation) will be higher
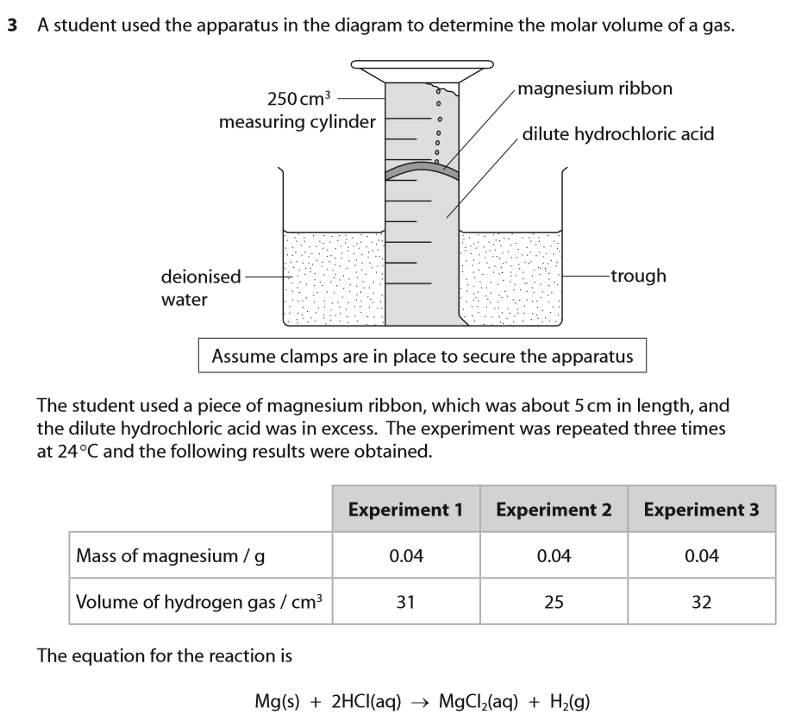
Give three reasons for the differences between your calculated value (in experiment to measure the molar volume of gas using magnesium and hydrochloric acid) and the actual volumes of hydrogen gas obtained by the student. For each reason, identify a change to either the apparatus or the chemicals that could be made by the student to improve the result.

How do you convert to gdm^-3 from moldm^-3
Multiply moldm^-3 by the molar mass (mass of 1mol of a compound in grams)

(Investigation into molar volume of a gas - refer to diagram for method/ apparatus) Give a reason why the student added a small pinch of calcium carbonate to the acid before starting the reaction.
Saturate solution with CO2/ to stop CO2 formed from dissolving
(Titration) Explain three actions the technicians might take in the procedure, just before the end-point of the titration, to ensure that the volume of acid added at the end-point is accurate.
add the acid from the burette drip by drip to avoid ‘overshooting’ the end point
continuously swirl the conical flask to ensure all the acid and alkali react together
place a white tile underneath the conical flask to ensure a clear colour change can be observed
rinse side of flask with distilled water between additions to rinse all reactants into the solution so all can react
compare colour of solution at the end point with previous titrations to ensure consistency of end point colour
rise end of jet of burette with distilled water to ensure all hydrochloric acid is in the conical flask (no drip left on burette)
Colours of methyl orange and phenolphthalein in different pHs:
Methyl Orange:
alkali - yellow
acid - red
Phenolphthalein:
alkali - pink
acid - colourless
(investigation into the molar volume of a gas) If the temperature had been less than 20 degrees Celsius and the pressure remained at one atmosphere, deduce the effect, if any, on the molar mass calculated in part (b)(ii).
the calculated molar mass would be greater
this is because at lower temperatures there would be more molecules in the same volume (the density would be greater)
(hydrolysis of haloalkanes) The precipitate forms as a result of reactions between aqueous silver ions and aqueous halide ions. Explain why halide ions are present in the mixture containing a halogenoalkane which has only covalent bonds.
water acts as a nucleophile (in the aqueous silver nitrate
water hydrolyses the haloalkane
causing the heterolytic fission of the H-Hal bond
(oxidation of primary alcohols to form carboxylic acids) Give one reason why the yield calculated is lower than expected.
incomplete oxidation
side reactions
transfer losses
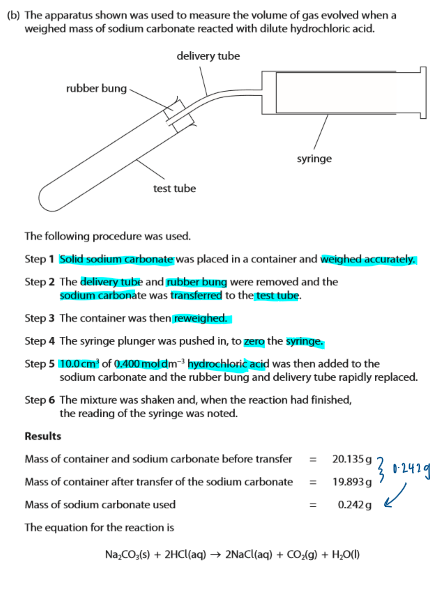
The actual volume of carbon dioxide collected was less than calculated. Give two reasons for this.
gas escaped before the bung was replaced
gas/ carbon dioxide is (slightly) soluble in water / acid / solution




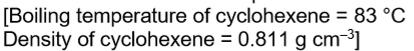
Cyclohexene can be prepared by reacting cyclohexanol with phosphoric (V) acid. The mixture is warmed in a water bath for 15 minutes before distilling off a mixture of cyclohexene and water. Devise a procedure to obtain a pure, dry, sample of cyclohexene from the distillate. Include a reason for each step.
separate cyclohexene from water using a separating funnel
remove the lower aqueous layer because it has a higher density
suitable drying agent
separate cyclohexene from the drying agent (i.e. decant)
redistil product
collect the distillate boiling between 80 and 86 to collect pure cyclohexene
Some alcohols can be oxidised by acidified potassium dichromate (VI), Na2Cr2O7. Reflux apparatus can be used to carry out the oxidation of alcohols. Using the apparatus for distillation instead of reflux is not an efficient way to produce ethanoic acid from ethanol. Explain why.
ethanol would be oxidised to ethanal
because ethanal has a lower bpt
OR
ethanal will distil before ethanoic acid
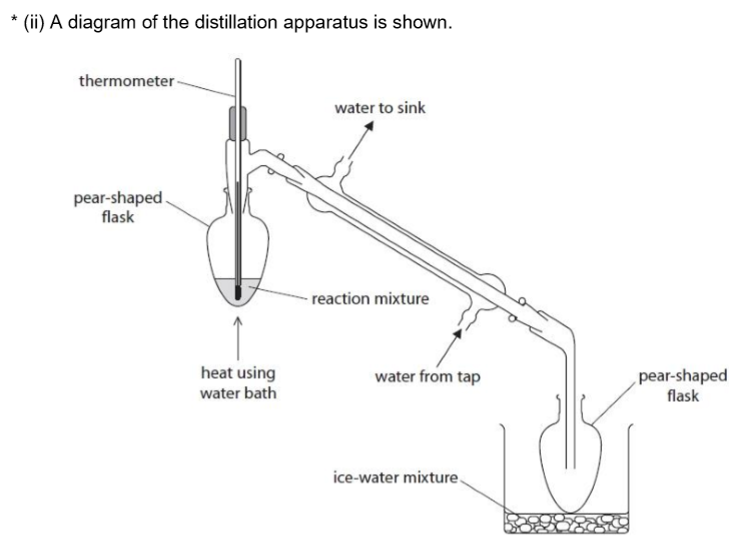
Discuss the improvements that should be made to the set-up of the apparatus. Include the likely effect of the errors identified on the yield or purity of the product. Assume the apparatus is suitably clamped.

Give reasons why :
Surround flask with ice bath to cool mixture
add anti-bumping granules to reaction mixture
set up apparatus for heating under reflux
reaction is very exothermic / releases a lot of heat
anti bumping granules promote smooth/ even bubbling
used to prevent loss of any volatile substances/ reactants/ products