Audiology term 1 test
1/124
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
125 Terms
Cross hearing can cause a shadow curve that follows the shape of the other ear’s …
Bone conduction thresholds
Sound is a … wave
Longitudinal
In terms of sound, condensation is ?
When the molecules are closer together (higher pressure)
The frequency of a wave is measured by
Hertz (Hz)
If 10² is 100, what is log10 of 100?
2
How to convert factors of x10 to decibels
Count zeros and multiply by 20
What is x100 in decibel terms
40dB
What is x1/1000 in decibel terms
-60dB
When doubling by decibel scale
+6dB
When halving by decibel scale
-6dB
The period of a 1kHz wave is
1 millisecond
The period of a 500 hz wave is
2 milliseconds
Period =
1 / frequency
What is the speed of sound in air
340 metres per second
Frequency is the
Number of wave cycles per second
What is the wavelength of a 340 Hz sound
1 metre
What is the wavelength of 3400Hz wave
10cm
dB A =
The A-weighted scale
What is the dB A scale best used for
Measuring quiet sounds
dB SPL measures
The physical amplitude of any sound
dB C is best used for
Human loud sounds
dB SPL =
Decibel sound pressure level
What is the reference sound pressure level for dB SPL …μPa RMS
20
dB HL =
Decibel hearing level
The dB HL scale allows the average human threshold to be what on the audiogram?
0dB
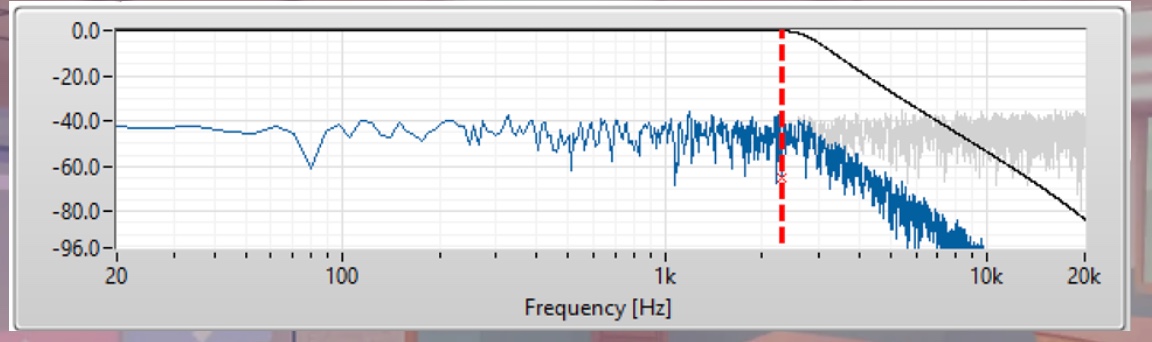
What is this?
A Low-pass filter
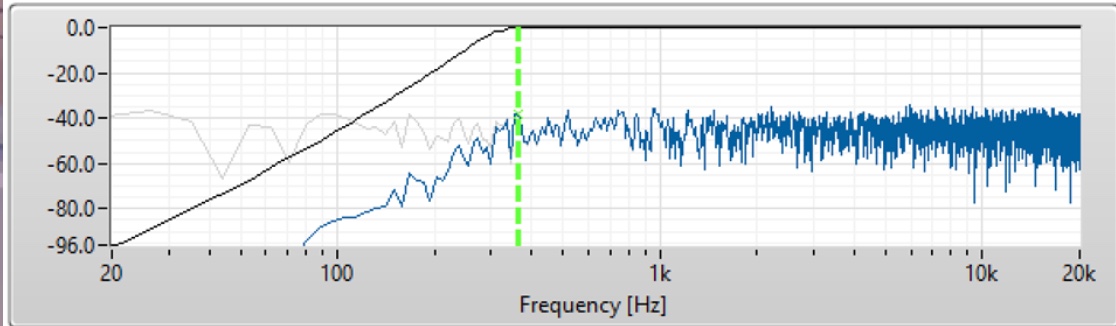
What is this?
A high-pass filter filter
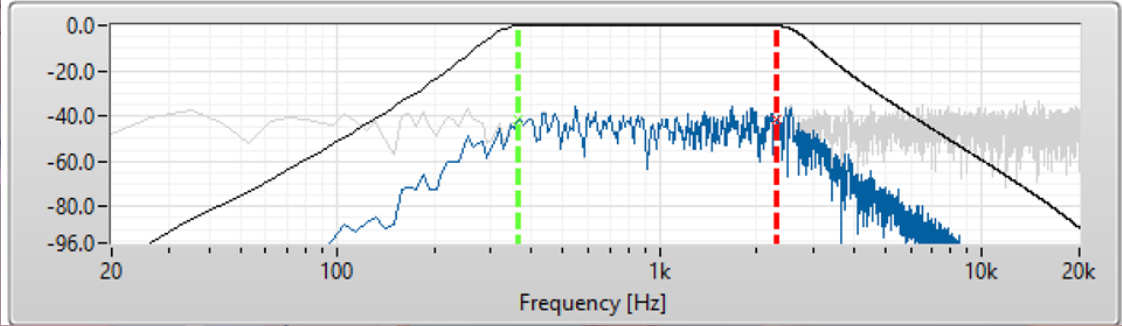
What is this?
A band-pass filter
Doubling your distance from a 50dB SPL sound source
Reduces its level by 6 dB
Transmission loss is the
Difference in SPL on either side of the barrier
Reverberation time is given by the
RT60
Head shadows are larger at
High frequencies
Sound waves are
Minute fluctuations in atmospheric pressure
What is the range of human hearing
20Hz to 20kHz
What do sound level meters do?
Give an overall measure of frequency
Why do you use spectral analysis
To see every frequency of every part of the wave
What does filter mean
To take the energy of a signal and remove some of it
An audiogram has … at the top and … at the bottom
Quiet sounds, loud sounds
On an audiogram different …
Frequencies of speech lie on different parts
What type of frequencies can wrap around objects?
Low frequencies
What type of frequencies will be blocked?
High frequencies
Reverberation refers to the fact that
Sound takes time to die away
How can you measure reverberation?
RT60
Transmission loss is the
Difference in SPL on either side of a barrier
If you double the density of a wall
The transmission loss increases by 6dB (you loose 6dB)
If you double the thickness of a wall
Transmission loss increases by 6dB
To get a large transmission loss we want
High mass, low stiffness, high damping, and a large impedance mismatch
To improve the acoustics of a classroom we
Reduce reverberation time, and increase sound absorption
The opposite of medial
Lateral
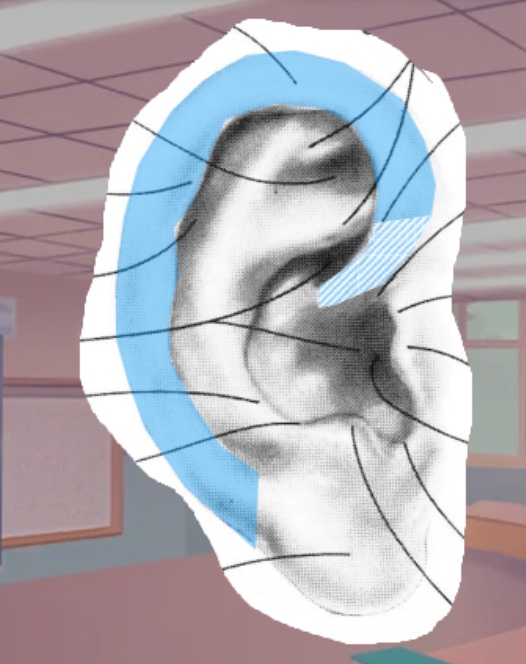
What is this part of the pinnacle called
Helix
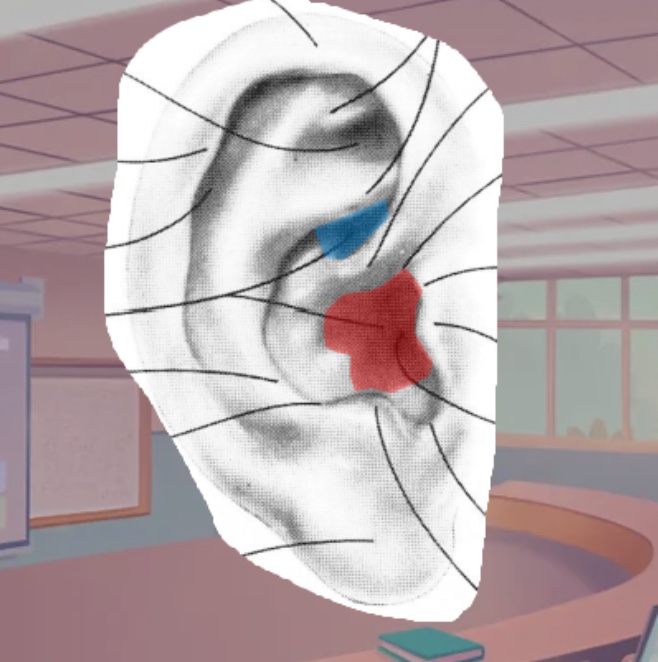
What is the red shaded part of the pinna called
Cavum concha
The ear canal consists of the … portion and the … portion
bony, cartilaginous
What are 3 functions of the cerumen (ear wax)
Cleaning, lubrication, antibacterial/antifungal
What are 3 layers of the tympanic membrane
Epidermal layer, mucosal layer, and lamina propria
Which part of the tympanic membrane has the lamina propria?
Pars tense (tense part)
A Marginal perforation is
One which lies close to the annulus and touches the edge. These do not heal as easily
The annulus is the
Thickened fibourous ring around the edge of the tympanic membrane
What are the 3 ossicles
Incus, malleus, stapes
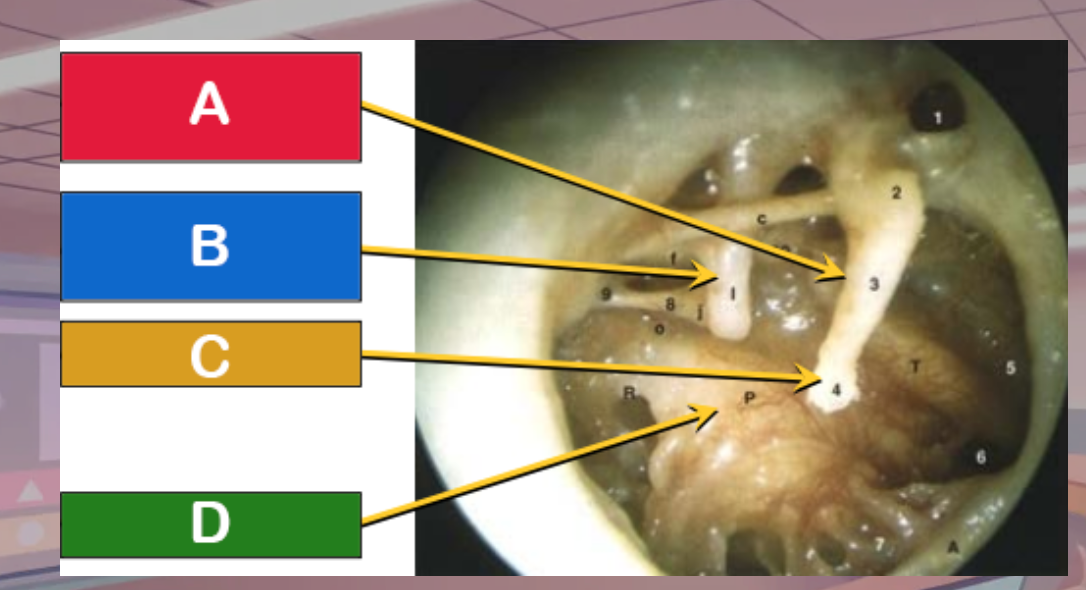
Which is the promontory
D
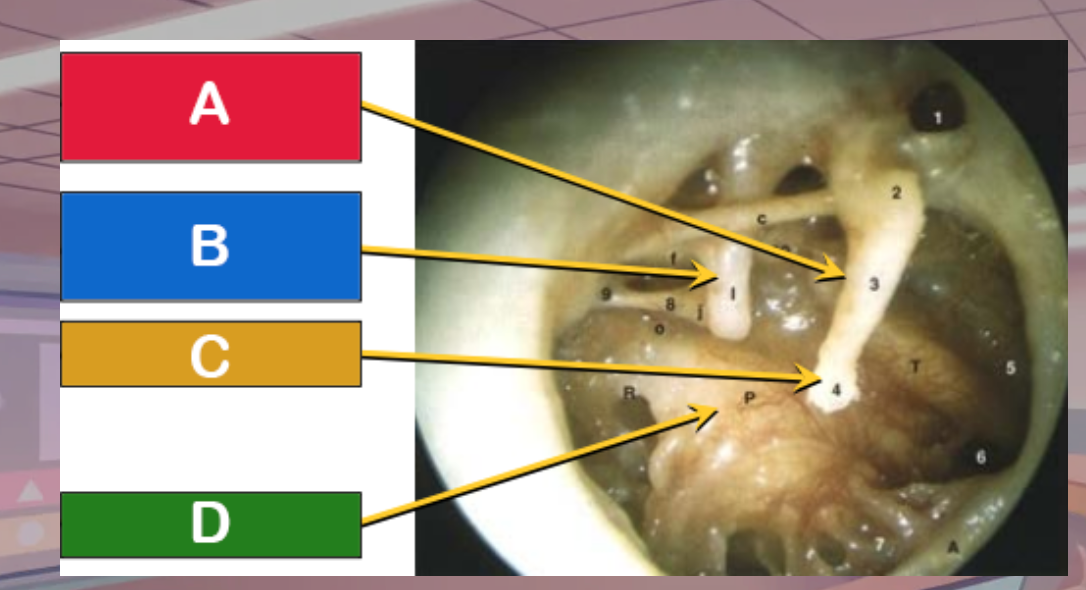
Which is the manubrium of the malleus
A
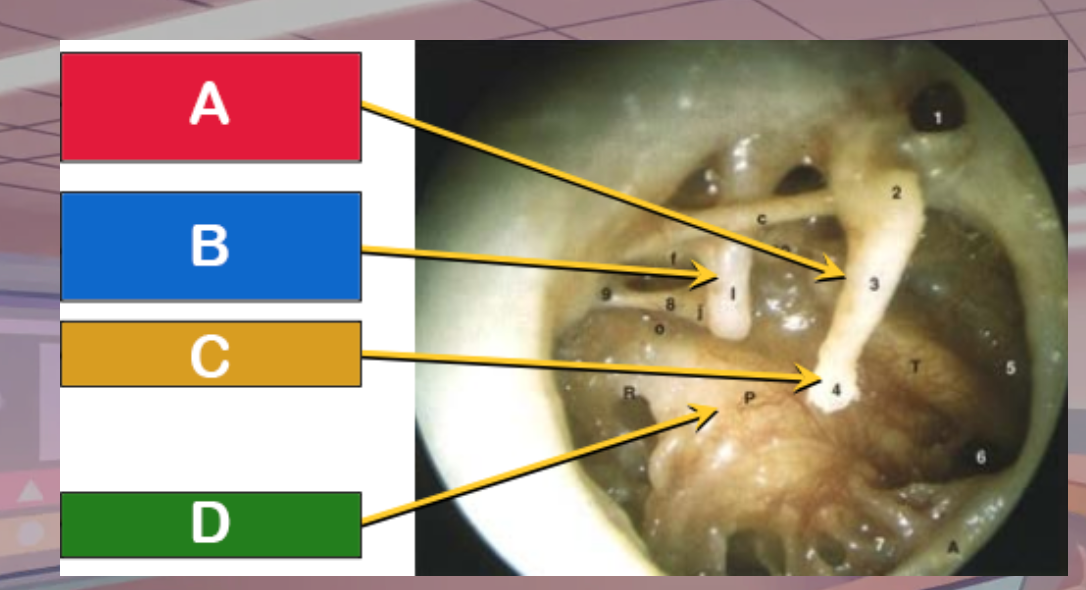
Which is the umbo
C
What middle-ear impedance matching process contributes the most?
The area ratio of the TM to the oval window
In humans how much bigger is the TM than the oval window?
17 times as large
The long crus/process of the incus is 1.3 times shorter than the
Manubrium of the malleus, thus causing a corresponding increase in force
The structure responsible for the aeration of the middle ear is the
Eustachian tube
Which wall of the tympanic cavity contains the entrance to the Eustachian tube
Anterior
Which middle ear muscled is innervated by the trigenimal nerve
Tensor tympani
What does the tensor tympani attach to
The malleus
Which middle ear muscle contracts in response to sound
Stapedius tendon
Which middle ear muscle contracts in anticipation to sound
Tensor tympani
Sound waves are
minute fluctuations in atmospheric pressure
Humans can detect frequencies between
20Hz and 20kHz
What does the cavum concha form
The vestibule at the entrance to the ear canal
Where is the cymba concha
In between the Crura of the anti-helix and helix
Rarefaction is when
Molecules are pulled further apart
What innervates the posterior, superior and anterior auricular muscles
The post auricular branch of the facial nerve
The main function of the pinna is to
Collect and direct the sound waves to the tympanic membrane
The pinna is important for directional hearing particularly when distinguishing between
Up/down and front/back
The medial 2/3s of the external auditory meatus (ear canal) is the …
Bony portion
The lateral 1/3 of the external auditory meatus (ear canal) is the …
Cartilaginous portion
What is responsible for the production of ear wax
The cartilaginous portion of the ear canal
How is cerumen (earwax) produced
A mixture of viscous secretions from sebaceous glands and less-viscous ones from modified apocrine sweat glands
Otoscopy means
Looking down the ear canal
What happens if you shine a light in a normal ear drum
The ear drum should be pearly, translucent and reflect light
The interaural inntenuation for air conduction with supra-aural is
40dB HL
What is the interaural attenuation for air conduction with inserts?
50-60dB HL
masking is the process whereby the …
Detection threshold for one sound (the probe) is increased by the presence of another sound (the masker)
What is the upwards spread of masking mean?
Low frequencies can mask higher frequencies, but higher frequencies can’t mask lower ones
How can you best mask a probe?
By presenting a masker centred at the same frequency
Narrow band noise is noise …
23-35% Around the frequency we’re interested in
Under masking occurs when …
Less than the minimum masking level is used, resulting in the non-test ear detecting the stimulus
Overmasking occurs when …
The level of masking is higher than the maximum point of plateau resulting in test ear hearing the masking noise
Masking plateau is
The range between the min and max levels, after 20dB of plateau we can accept the threshold as from the test ear
The lamina propria is a
Fibrous layer called the pars tensa
The epidermal layer is
Skin that lines the outside of the ear drum
The mucosal layer
Lines the middle ear cavity with mucosa
The malleus is the … the incus is the … the stapes is the …
Hammer bone, anvil, stirrup
Order of the ossicles is
Ear drum, malleus, incus, stapes, oval window
The ossicles pass …
Sound vibrations from the ear drum, through each bone, to the oval window of the cochlea