L6 sexual selection
1/27
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
28 Terms
What is the underlying cause of sexual selection?
Parker, Baker & Smith (1972) proposed
• Isogamy → Disruptive selection → Anisogamy: microgamete (male); macrogamete (female)
• Sexual conflict over investment in offspring → Sexual selection
What is Batemans principle?
asymmetry in factors that limit reproductive success of males and females
What are the asymmetric costs of reproductive success?
• Sex subject to strong selection (males) → competitive
• Sex subject to weak selection (females) → choosy
what is differential reproduction?
• 4th premise of Natural Selection: different due to survival ability → adaptive evolution
• Sexual selection: variation in ability of competitive sex to persuade choosy sex to mate → maladaptive evolution
What is sexual selection according to Darwin?
not a struggle for existence but on a struggle between males for possession of females
What are characteristics of males in sexual selection?
Males = competitive → male-male competition → intrasexual selection
What are characteristics of females in sexual selection?
Females = choosy → female choice → intersexual selection
What are examples of male-male competition?
• Contest e.g. giraffes (good having long necks)
• Deer - Red deer on Rum
- Asymmetries in reproductive success between males and females
- Dominant male with his harem (Monarch of the glen)
- Fights using antlers
- Roars
What are direct benefits of female mate choice?
- Obtain access to resources
- Obtain food or other nutrients captured or synthesised by males
- Obtain quality paternal care
- Obtain sufficient sperm to fertilise eggs
- Mate with the correct species
- Avoid harassment
- Reduce risk of predation
- Avoid direct transmission of parasites
What are indirect benefits of female mate choice?
- Obtain good genes for offspring
- Runaway selection: offspring inherit favoured trait and preference
What did fisher propose about female choice?
Fisher proposed a theoretical explanation (a model) in 1915"a sexual preference of a particular kind may confer a selective advantage, and therefore become established in the species"
Fisherian self-reinforcing mating preferences AKA runaway process
How can you see sexual selection from choosy females in peacocks tail?
1. Genetic variation in male trait (tail length), longer tail →survival advantage
2. Genetic variation in female tendency to mate with males of different trait values (tail length)
• Sons of males with long tails have better survival → spread of alleles for longer tails in males + spread of alleles that make females prefer long-tailed males
What is the fisher runaway process?
- All offspring inherit enhanced quality
- Females inherit choosiness
- Males inherit elaborate tail
What are the mechanisms of female choice?
1. Fisher runaway process
2. Zahavi handicap theory
What are the indirect genetic benefits of female choice?
• Indicator traits → tell female who is good quality
• AKA handicap or good genes models
Have empirical tests kept pace with theoretical developments? What do tests demonstrate?
no
• Tests demonstrate a relationship between male viability or fitness and expression of male trait
What is the Zahavi handicap theory?
- Costly trait = handicap
- Microgamete → Measure of genetic quality
- Cost to male → honest signal
has a feature which increases reproductive success but is also costly on the male
What is the evidence for the indirect benefits of female choice?
Peacocks
8 peacocks housed separately, 4 naive peahens randomly assigned to each pen, pens checked for eggs
weighed and measured on days
Significant effect of mean area of father's eye spot on mass of sons
Also a positive relationship between proportion of offspring surviving (due to being larger) and mean area of father's eye spot
What is the lek paradox?
If 'good genes' explain female choice, there should be little variation in fitness traits because the beneficial alleles become fixes → female choice cannot result in genetic (indirect) benefits → 'the lex paradox'
What resolutions have been proposed about the lek paradox?
- Traits are condition-dependent (GxE, not just G)
- Condition has high genetic variance (quantitative traits)
What is balancing sexual selection?
a form of natural selection that maintains genetic variation in a population by balancing the fitness advantages
Intra and intersexual selection may occur simultaneously or sequentially
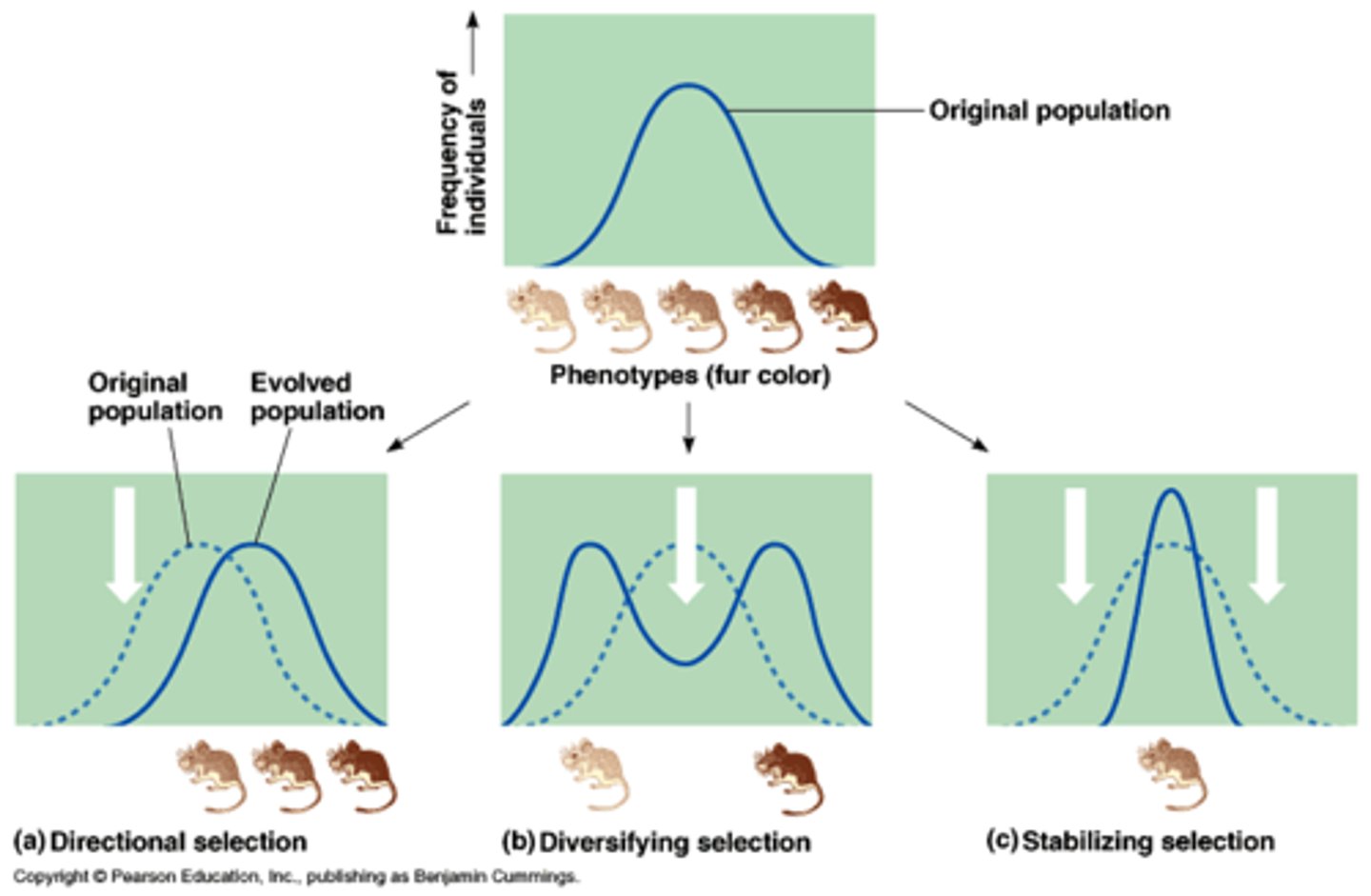
What is an example of balancing sexual selection?
Fiddler crab
- female choice (attractive signal trait) → short manus and long fingers → weaker claws
- male-male competition (contest trait) → large manus and short fingers → stronger claws
Why dont females signal sexual quality?
- Natural Selection is stronger in females
- Ornaments are too costly, better to invest in eggs
- May attract too many males → avoid harassment → sexual conflict
What is the dichotomy of competition in sexual selection?
- Contest competition = intrasexual selection
- Attractiveness competition = intersexual selection
What characters are favoured in mates?
- Scrambles to find
- Endurance rivalry (reproductiveness)
- Contests
- Behavioural and morphological choice
- Resources
- tactics
- Guarding
- Ability of sperm to outcompete others
What causes Differential allocation of resources/energy to offspring?
Postzygotic female choice → reproductive investment depends on mate attractiveness
Differential Allocation Hypothesis
What is the Differential Allocation Hypothesis?
Must trade off current and future reproductive investment
- DAH is therefore a parental effect (transgenerational indirect genetic effect, due to parental investment)
• May observe a skew in sex ratio of offspring
What is sexual conflict over investment in offspring?
As a result of sexual reproduction, usually there is conflict between males and females → interaction between two genetically different individuals
- Shared interests
- Disagreements: one sex imposes a cost on the other → sexually antagonistic selection
• Conflict over all aspects of reproduction, not just competition for mates → broader than sexual selection
- If remove sexual conflict, remove sexual selection
- But, removing sexual selection will not remove sexual conflict