Muscle Physiology Pt. 3
1/31
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
32 Terms
During muscle relaxation, what happens to the Ca that is bound to troponin?
It is removed via active transport and transported back to the terminal cistern
Why does muscle relax?
Action potential stops
What does tropomyosin do when muscle relaxes?
Blocks the actin site again
What does the recruitment of more muscle cells lead to?
Greater contraction
A higher amount of muscle contraction = ______ Muscle fibers engaged
Increase of-
What are graded contractions controlled by?
Nervous system
What happens when you stimulate increasing numbers of cells or motor units?
Increase the force of contraction
What is the muscle twitch?
A single response to a single stimulus
One stimuli = ___ twitch
One
What is it called when there are ~3 stimuli?
Wave summation
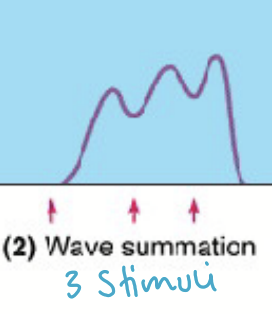
What is it called when there are multiple stimuli?
Incomplete tetanus
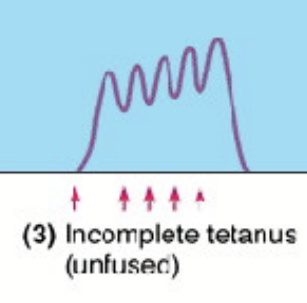
What is it called when there are a lot of stimuli back to back?
Complete tetanus
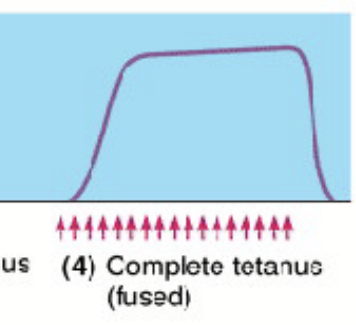
What does wave summation result from?
Stimulating a muscle before it had time to relax from a previous stimuli
What are you doing to the frequency of the stimuli when wave summation occurs?
Increasing it
What is tetany?
Comes after wave summation; it is a sustained muscle contraction
What can cause tetanus?
A bacterial toxin called clostridium tetnai
How often should people get vaccinated against tetany?
Every 10 years
What is Treppe?
The staircase effect
Explain Treppe
Its a step-like increase in the force of contraction until a uniform tension is reached. So muscles exhibit gradually increasing responses until they have warmed up
What is treppe caused by?
Increasing efficiency of the ion gates as they are repeatedly stimulated
T/F Treppe requires stimulation of the same intensity and frequency
True
What makes treppe differ from tetanus?
Tetanus has a stimulus and is followed by another stimuli before it can completely relax, which causes a more powerful contraction.
Treppe has a stimulation of the same intensity and frequency so it forms a staircase
What is Muscle Atrophy?
Decrease in muscle size
What happens to blood flow and fluid in the muscle when there is atrophy?
They decrease
What is hypertrophy?
Increase in muscle size
What is normal growth of muscle?
Hyperplasia of muscle cells
What is hyperplasia of muscle cells influenced by?
GH and IGF
What happens when you get a charlie horse?
Your muscle gets locked in a contracted state
What is exertional myopathy?
muscle damage due to intense physical exertion
What is myasthenia gravis?
It affects the neuromuscular junction. it is chronic muscle weakness disease
What is denervation?
The loss of nerves
What are examples of CNS disorder?
Disc disease and equine protozoa My.