The Heart Review
1/62
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
63 Terms
Brachiocephalic
head and upper limb
jugular
neck from the brain
cubital
atery in the elbow
Carotid
neck pulse
Great Saphenous
Longest vein not in arteries
Femoral
upper leg
Phrenic
Supplies the diaphragm
Brachial
Formed by the union of the radial and ulnar veins; upper arm
Basilic and Cephalic
Two superficial veins of arm
Renal
Artery serving kidney
Gonadal
Testicular or ovarian veins
Common Iliac
Drains the pelvic organs and lower limbs
Subclavian
Major artery serving the arm
Popliteal
What the femoral artery becomes at the knee
Celiac Trunk
An arterial trunk that has three major branches, which run to the liver, spleen, and stomach
Vertebral
Major artery serving the skin and scalp of the head
Radial
Artery generally used to take the pulse at the wrist
axillary
armpit
facial
face
the vena cava
vein entering the heart
function of the heart
pumps blood through the heart and supplies the body with oxygen
oxygenated blood
moves out of the heart to supply cells with oxygen
deoxygenated blood
moves into the heart for oxygen
away from
arteries carry blood ____the heart
to
veins carry blood ____ the heart
arteries
in pulmonary circulation…
____ carry deoxygenated blood to the lungs
veins
In pulmonary circulation…
____ carry oxygenated blood from the lungs
oxygenated
in normal circulation…
arteries carry ____ blood
deoxygenated blood
in normal circulation…
veins carry _____ blood
Superior vena cava
right atrium
tricuspid valve
right ventricle
pulmonary valve
pulmonary trunk
pulmonary artery
path of deoxygenated blood
vena cava
deoxygenated blood enters
right atrium
after the vena cava…
tricuspid valve
valve after the right atrium
right ventricle
tricuspid valve dumps blood here
pulmonary valve
valve, deoxygenated blood is pumped through after the right ventricle
pulmonary truck
trunk splits into right and left after the pulmonary valve to go to the lungs
left and right pulmonary artery
artery splits in 2 that delivers deoxygenated blood to both lungs for oxygen
pulmonary veins
left atrium
bicuspid valve
left ventricle
aortic valve
aorta
path of oxygenated blood
pulmonary veins
oxygenated blood enters here from the lungs
left atrium
pulmonary veins dump blood here
bicuspid (mintral) valve
valve that pumps blood to the left ventricle
left ventricle
bicuspid valve dumps blood here
aortic valve
blood from the left ventricle passes through this valve
aorta
blood is pumped to the rest of the body from this
valves closing
the sounds of the heart are the….
lub
1st Sound
bicuspid and tricuspid valves
valves closing during the 1st sound
atriums and ventricles
where the 1st sound valves closing located
dub
2nd sound
aortic and pulmonary valves
valves closing during the 2nd sound
aorta pulmonary trunk
where the 2nd sound valves are located
quickly
aorta closes…
p wave
SA node fires
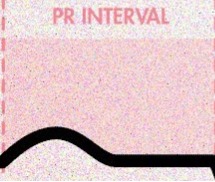
QRS wave
AV node fires
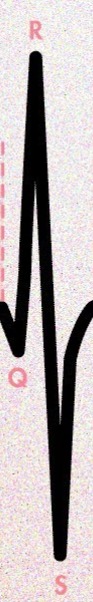
T wave
ventricles fill with blood

Sinoatrial node (SA)
nervous tissue signals atria to contract
Atrialventicular node (AV)
nervous tissue that signals the ventricles to contract
Right atrium
the nodes are located in the…
blue
veins closer to the skin appear….
they have more pressure on their walls
why are artery walls thicker
systolic number
pressure excreted on the arteries when the left ventricle contracts
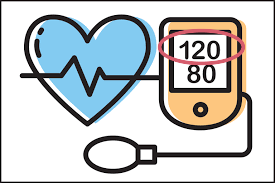
diastolic
pressure excreted on arteries in between contractions (resting)
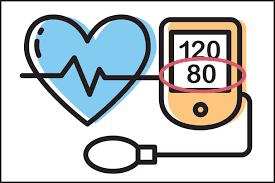
the pressure excreted on the arteries
blood pressure measures…