AP Biology Unit 7 Terms
1/97
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
98 Terms
Charles Darwin
He was a British nationalist that proposed the theory of biological evolution by natural selection.

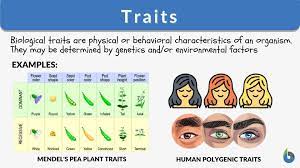
Traits
(Characteristics) are heritable = inherited/passed down from parents to offspring.
Genes
DNA code(s) that make up an organism's traits, characteristics, innate behaviors, etc
Individual Organism
One organism.
Population
Many organisms of the same species living together in a given space.
Community
Different species living together in a given space.
Ecosystem
Communities + nonliving factors such as rain, sun, etc.
Biome
Many similar ecosystems.
Biosphere
The whole system including the atmosphere.
Natural Selection
Ability of an organism to survive and reproduce based on their adaptation to an environment.
Fitness
Ability to survive and reproduce (including attracting a mate), NOT how big/strong.
Overpopulation
Populations produce more offspring than an environment can support.
Carrying Capacity
Maximum amount of organisms an ecosystem can support.
Genetic Variation
Individuals in a population have different traits.
Mutations
Any change in DNA.
Meiosis
A special type of cell division that creates gametes (sex cells).
Sexual Reproduction
The production of new organisms by the combination of genetic information of two individuals of different sexes.
Gene Flow
Movement of traits between populations.
Selective Pressure
Any cause that makes an organisms better or worse at surviving.
Density-Dependent Pressures
Amount of individuals in the population matters. (PANDA)
Density-Independent Pressures
Amount of individuals in the population does NOT matter. (PAW)
Adaptation
Good variations are passed down and increase fitness.
Batesian Mimicry
Specie looks like a harmful species to avoid being eaten.
Mullerian Mimicry
Venomous species looks like another venomous species.
Aggressive Mimicry
Predator looks like prey to capture the actual prey.
Cryptic Coloration
Camouflage = organism blends in with its environment.
Aposematic coloration
Organisms “signal” that they are poisonous through bright coloration.
Uniform Dispersion
Organisms are equally spaced out.
Random Dispersion
Organisms are randomly spaced out.
Clumped Dispersion
Organisms are grouped together.
Microbiology
Biology on a small scale. (i.e. cells)
Macrobiology
Larger biology (i.e. natural selection and ecology)
Nucleus
“Brain” of the cell; has all of the genes of an organism. (contains chromosomes = genes)
Cell
Has lots of different organelles.
Allele
ONE gene(or trait) represented by a letter.
Genotype
Genetic makeup of an organism. (which 2 alleles the organism has)
Phenotype
The physical trait of the organism from the genotype and behavioral traits.
Dominant Allele/Gene
Dominant always wins and shows in phenotype (capitalized letter).
Recessive Allele/Gene
Only shows in phenotype when there is no dominant allele (lowercase letter).
Homozygous
BOTH letters in a genotype are the SAME.
Heterozygous
BOTH letters are DIFFERENT.
Stabilizing Selection
Intermediate (middle) phenotypes are more fit than extremes.
Directional Selection
One extreme phenotype is more fit than the others.
Disruptive Selection
Both extremes are more fit.
Predation Selection
Environment acts on prey and predator.
Physiological Selection
Acts on body functions and structures.
Coevolution
2+ species evolve together.
Evolution
A gradual change in genes of a population over time because favored traits survive and reproduce (natural selection).
Emigration
Exit to a new location.
Immigration
Into a new location.
Sexual Dimorphism
Two different forms of the same species (usually between male and females).
Genetic Drift
Change in allele frequency from generation to generation due to chance events. (occurs by chance)
Artificial Selection
Humans select for desirable traits in agricultural products or animals, rather than leaving the species to evolve and change gradually without human interference, like in natural selection.
Frequency
% or decimal of how often something occurs (# / TOTAL #)
Allele Frequency
# of dominant or recessive alleles / total alleles.
p
Frequency of dominant allele.
p2
Frequency of homozygous dominant.
q
Frequency of recessive allele.
q2
Frequency of homozygous recessive.
2pq
Frequency of heterozygous.
Gene Pool
Total gene copies in a population.
Locus
Physical site of where a gene is held on a chromosome.
Biogeography
Geographical distribution of organisms.
Pangea
All land masses were once all together.
Fossil
Remains or traces of past organisms
Fossil Record
Gives a visual of evolutionary change over time.
Sedimentary Rock
Contain fossils = strata = gives a “timeline”
Transitional Fossils
Show evolutionary links between groups of organisms.
Comparative Morphology
Analysis of the structures of living and extinct organisms.
Homology
Characteristics in related species that have similarities even if the functions differ.
Embryonic Homology
Many species have similar embryonic development.
Vestigial Structures
Structures that are conserved even though they no longer have a use. (ex./ tailbone and appendix in humans)
Molecular homology
Many species share similar DNA and amino acid sequences.
Analogous Structures
Similar features due to adapting to the environment NOT because of ancestors.
Convergent Evolution
Come together.
Homologous Structures
Similar features due to a common ancestor.
Divergent Evolution
Separate into two.
Comparative Embryology
Similar embryological development in closely related species.
Phylogenetic Trees/Cladograms
Diagrams that show evolutionary relationship of different species w/ a common ancestor.
Outgroup
The lineage that is least closely related to the remainder of the organisms in the phylogenetic tree or cladogram.
Shared Derived Traits
Traits that indicate common ancestry.
Biological Species Concept
Organisms that can interbreed (mate) with one another to produce viable, fertile offspring are the same species.
Speciation
Creation of a new species due to inability to interbreed.
Allopatric Speciation
Physical separation by a geographical barrier causes divergent evolution.
Sympatric Speciation
Divergent evolution NOT due to physical separation.
Prezygotic Barriers
Barriers that stop organisms from interbreeding BEFORE fertilization (sperm meets egg).
Postzygotic Barriers
Barriers that stop organisms from creating viable offspring AFTER fertiliation.
Habitat Isolation
Two+ species live in different habitats.
Mechanical Isolation
Two+ species reproductive structures cannot fit together.
Behavioral Isolation
Two+ species have different courtship behaviors or mate preferences.
Temporal Isolation
Two+ species reproduce at different times.
Gametic Isolation
Two+ species produce eggs/sperms that cannot combine.
Hybrid Breakdown
Offspring generations breakdown/progressively become unhealthy.
Reduced Hybrid Viability
Hybrid cannot survive or is unhealthy.
Reduced Hybrid Fertility
Hybrid cannot produce offspring.
Extinction
Disappearance of a species.
Deletarious
Traits reduce fitness.
Adaptive
Traits increase fitness.