Atoms, Isotopes, and Ions
1/20
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
21 Terms
negative ion
When an atom gains an electron, it becomes a _______________ ion.
atom
Smallest particle of an element that retains the element's properties
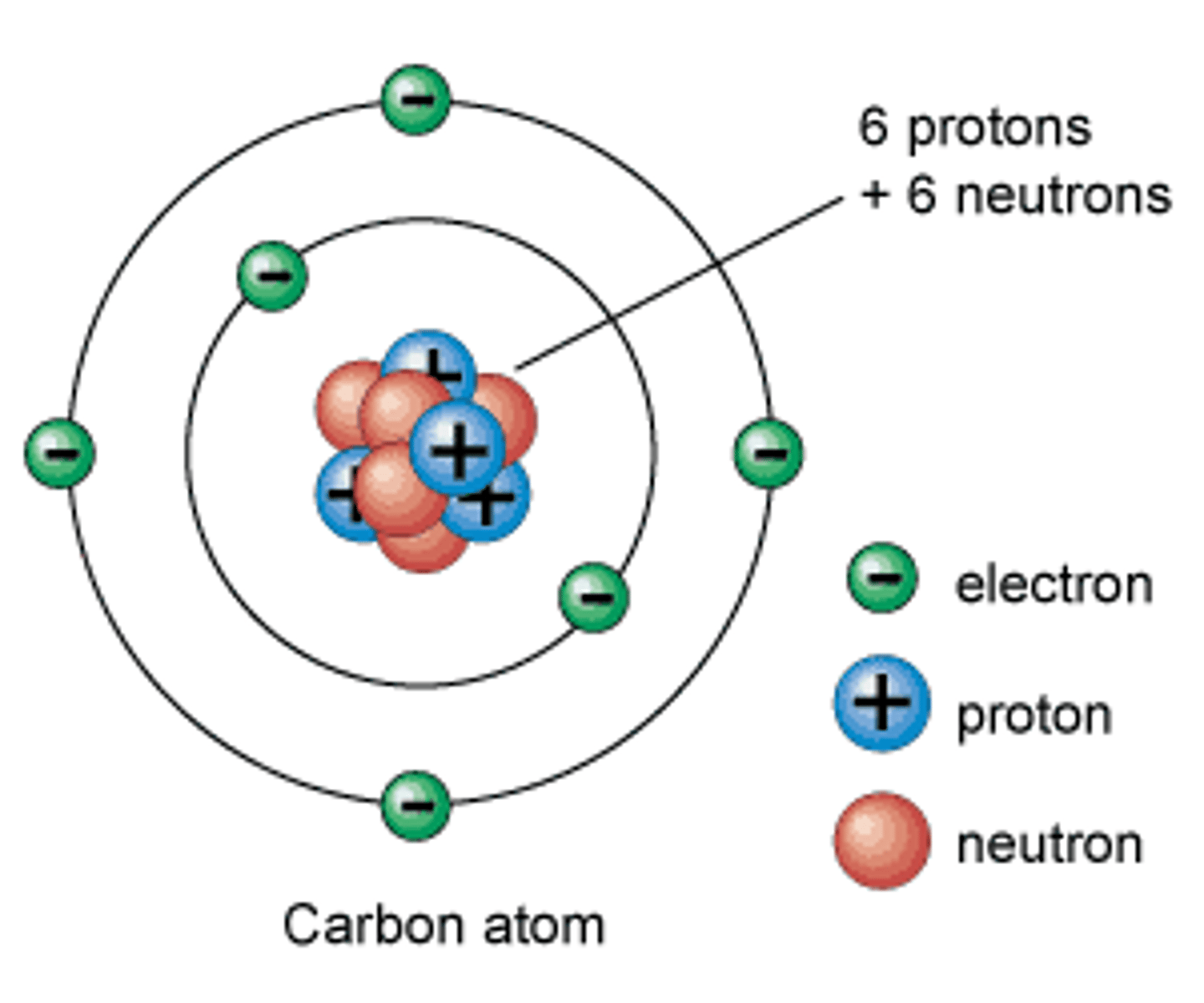
proton
A positively charged particle located in the nucleus of an atom

neutron
A small particle in the nucleus of the atom, with no electrical charge
electron
A tiny, negatively charged particle that moves around the nucleus of an atom.
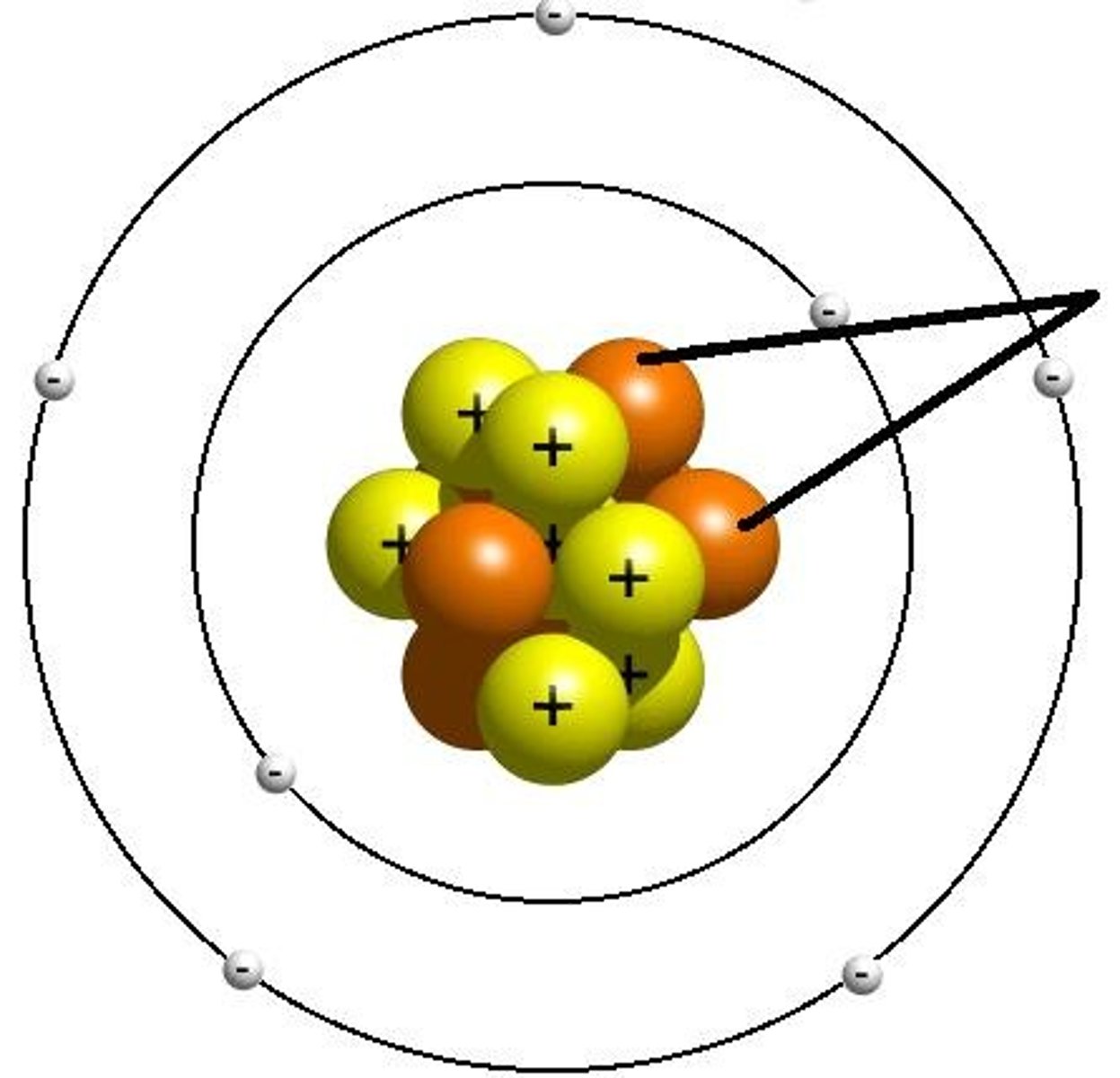
ion
Charged particles that are formed when an atom loses or gains (an) electron(s).

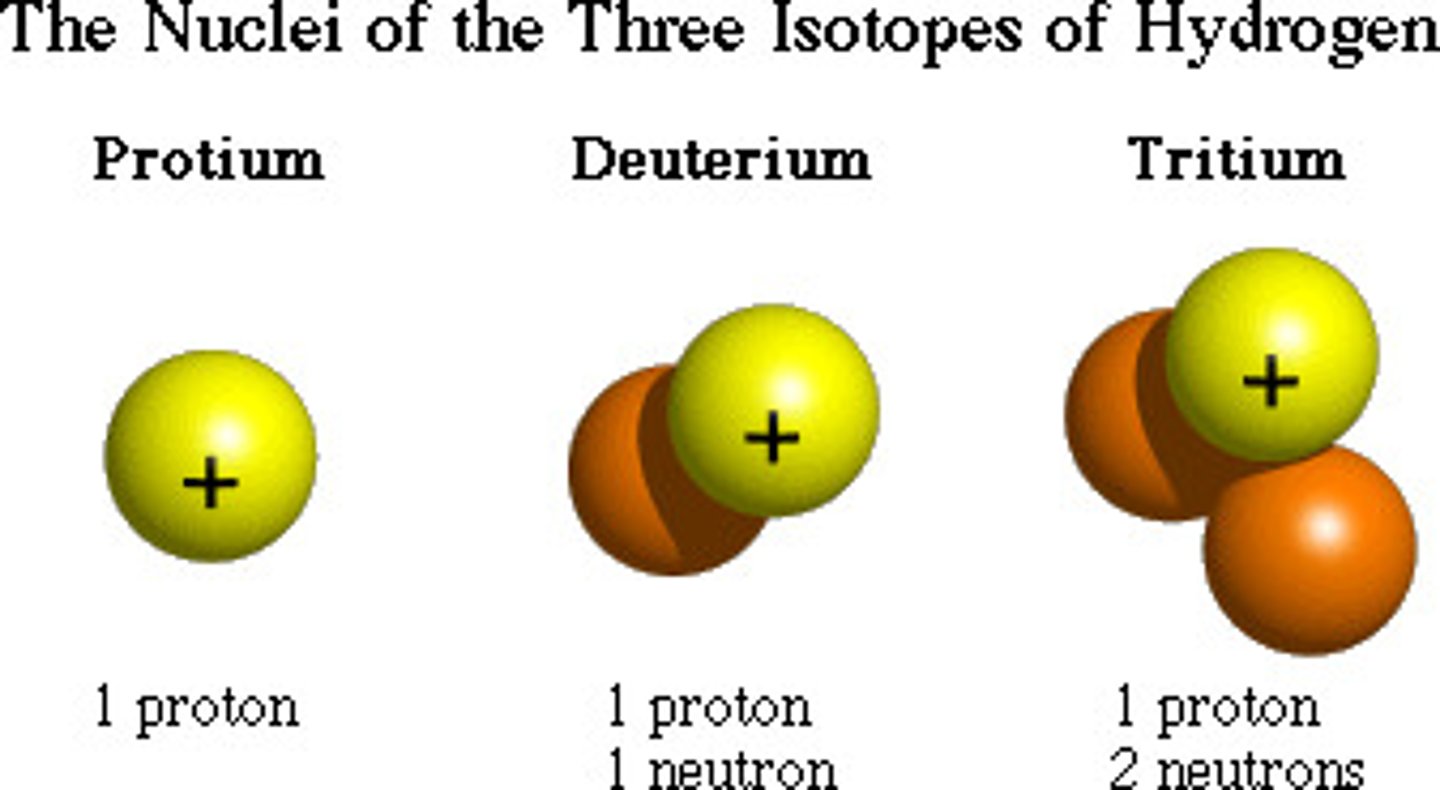
isotope
Atoms of the same element with the same number of protons (atomic number) but a different atomic mass (number of neutrons).
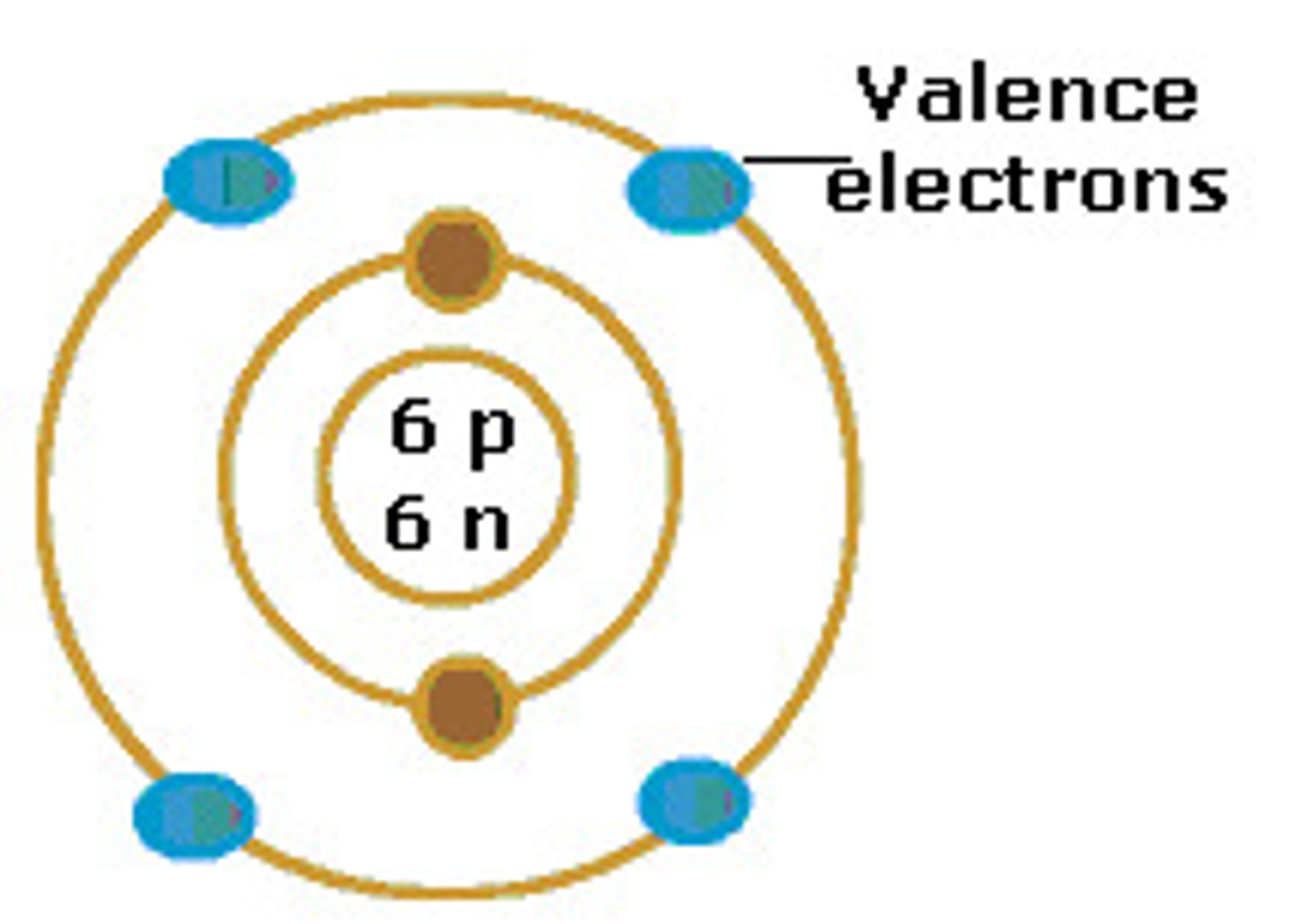
atomic number
Number of protons in an atom
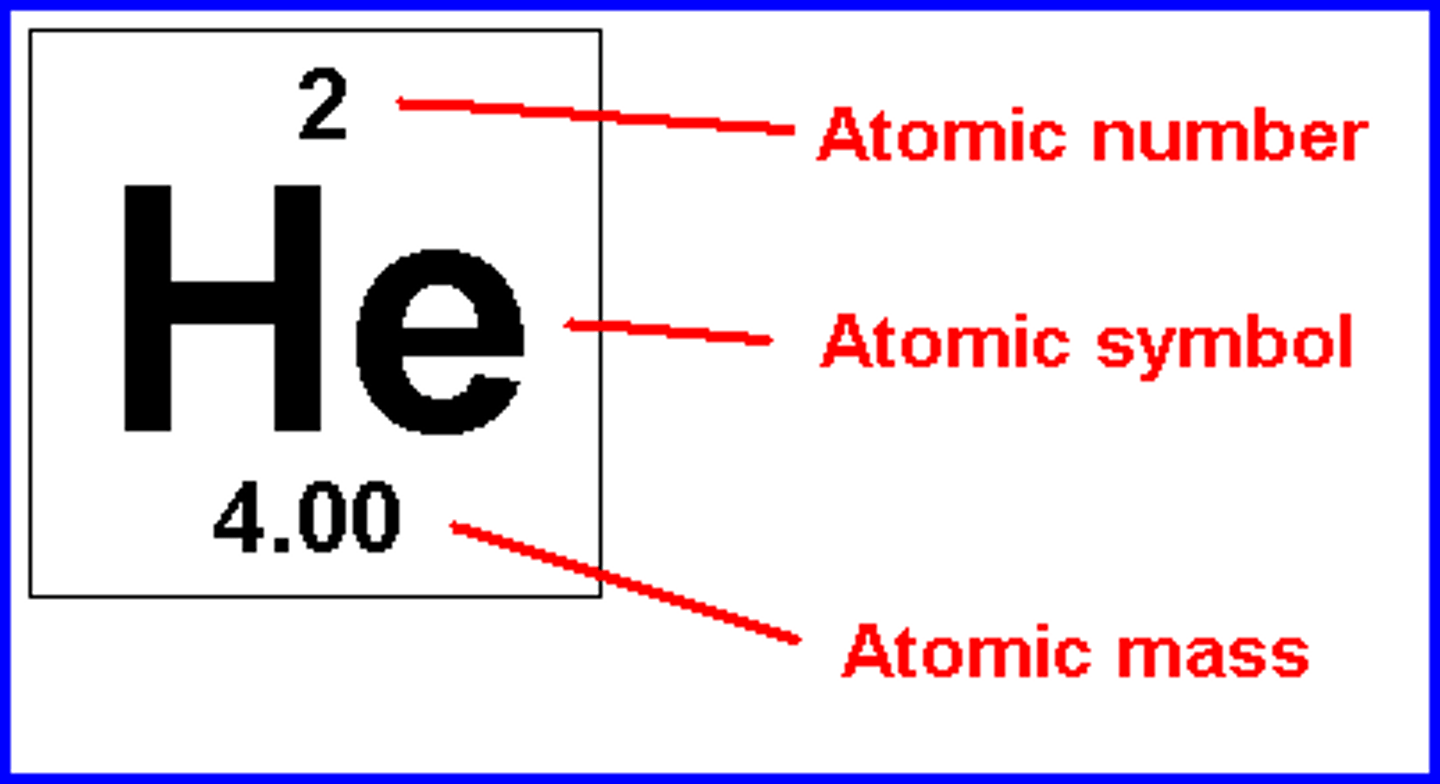
atomic mass
The average number of protons and neutrons in the nucleus (usually an decimal)
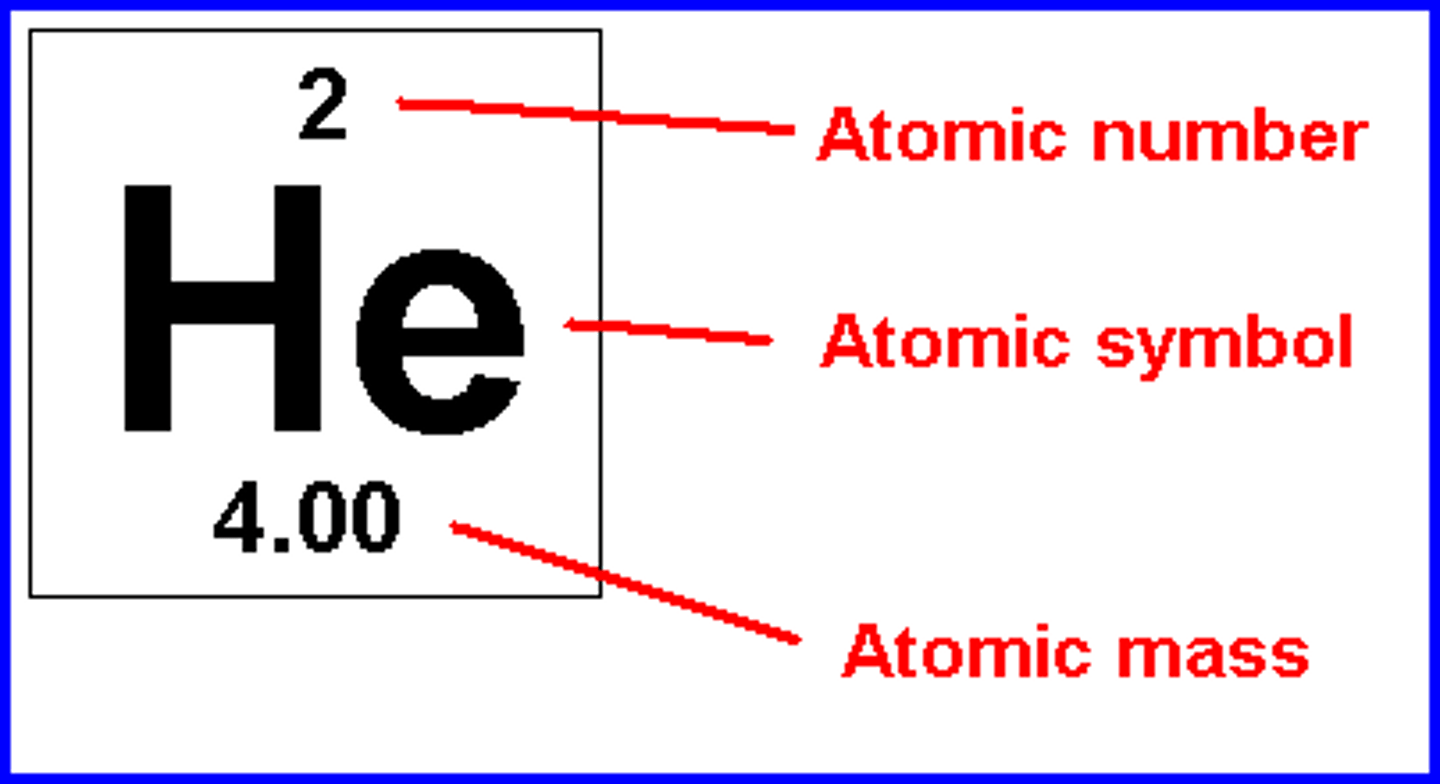
Cation
Positive Ion
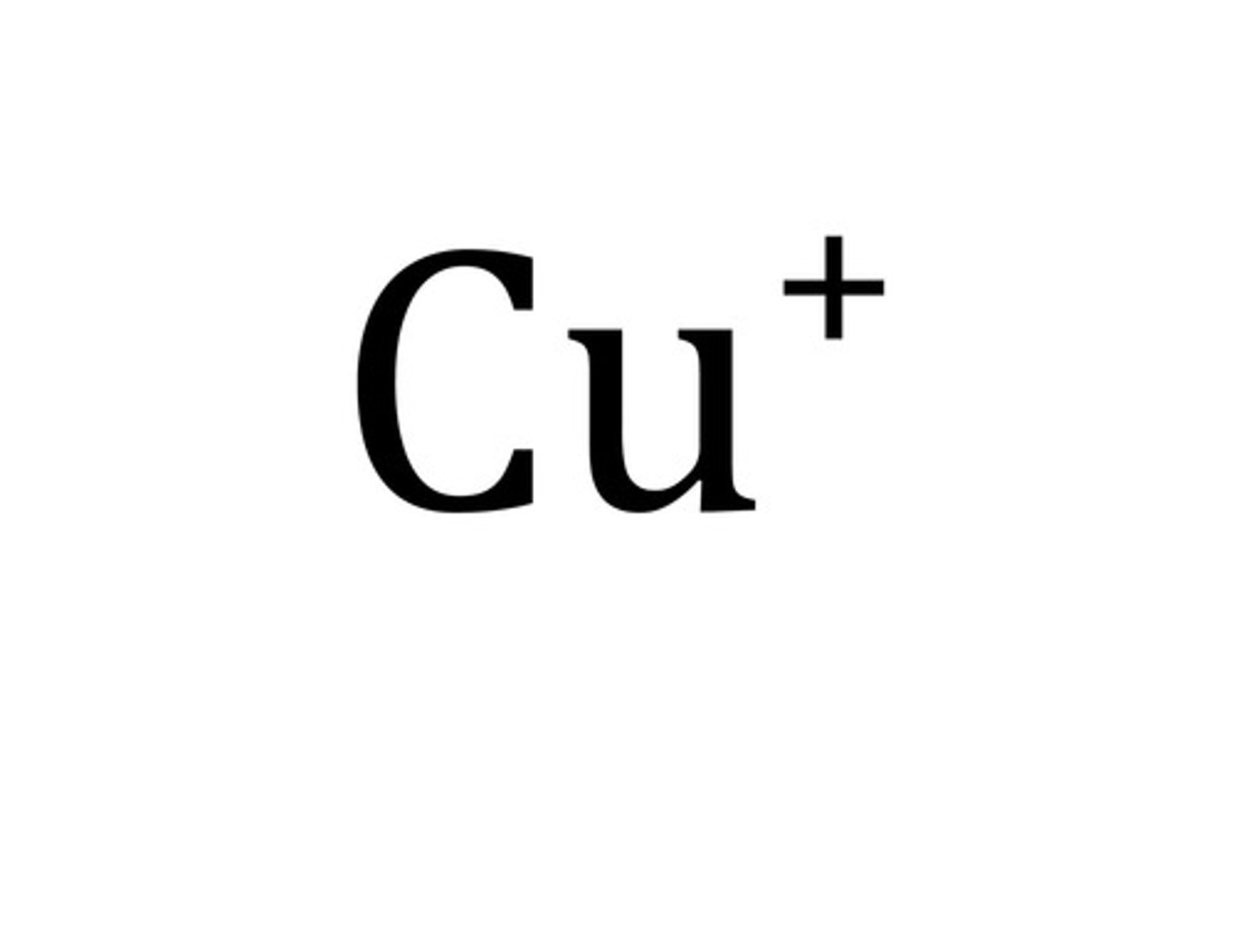
Anion
Negative Ion

Mass number
the sum of the number of neutrons and protons in an atomic nucleus (whole number)
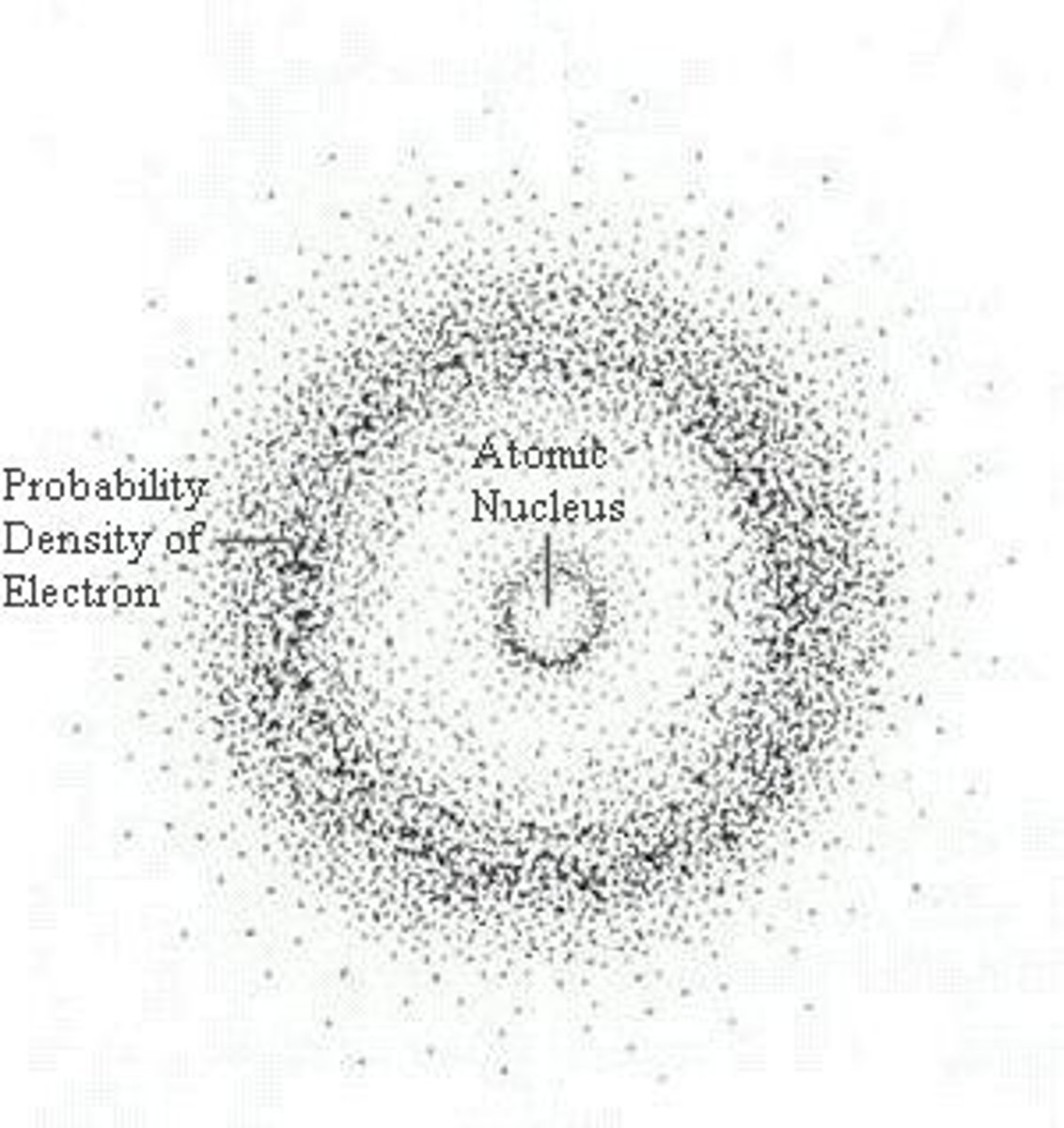
electron cloud
a region around the nucleus of an atom where electrons are likely to be found
Mass - atomic number (protons) = number of neutrons
How do you determine the number of neutrons in an atom?

Protons (1amu) + Neutrons (1amu)
What TWO parts of the atom contributes to the mass?
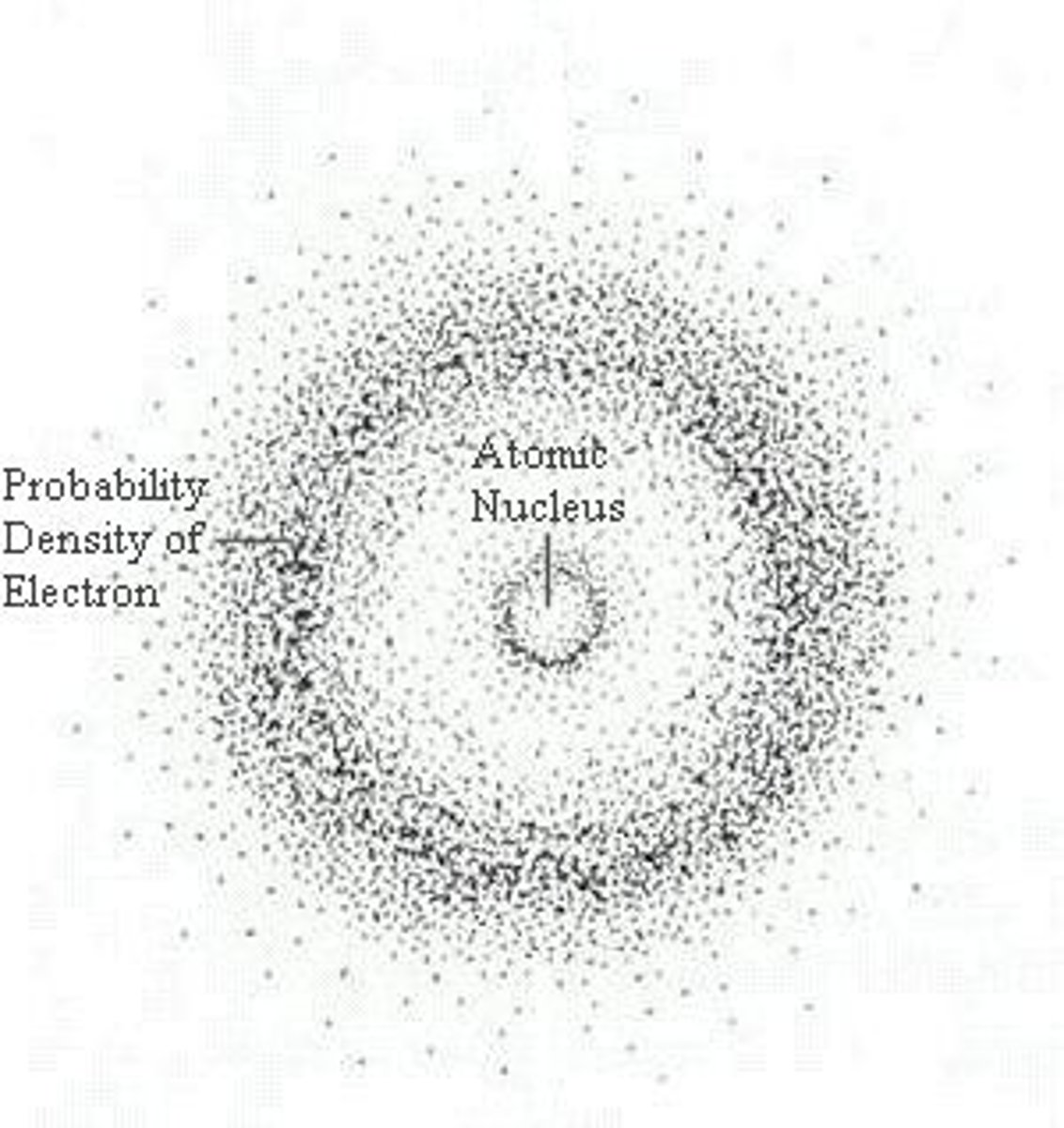
positive ion
When an atom loses a valence electron, it becomes a __________________ion.

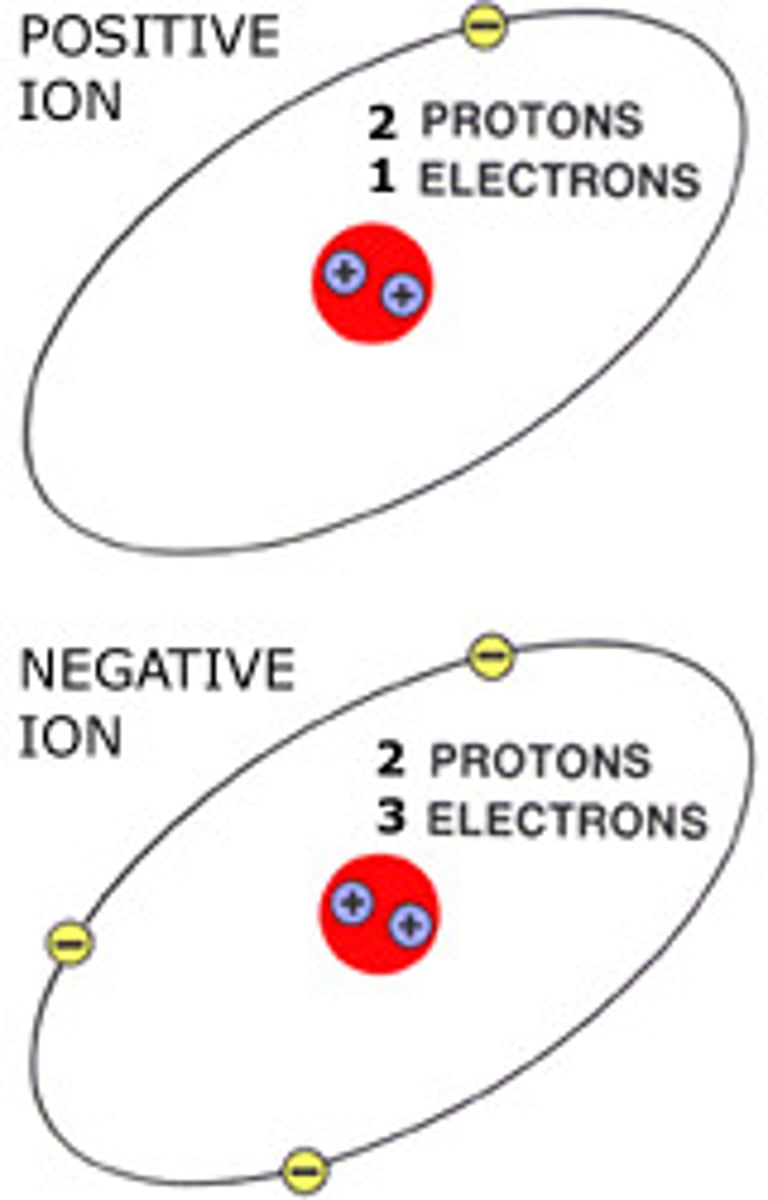
Because it lost an electron
Why does a potassium ion have a charge of +1
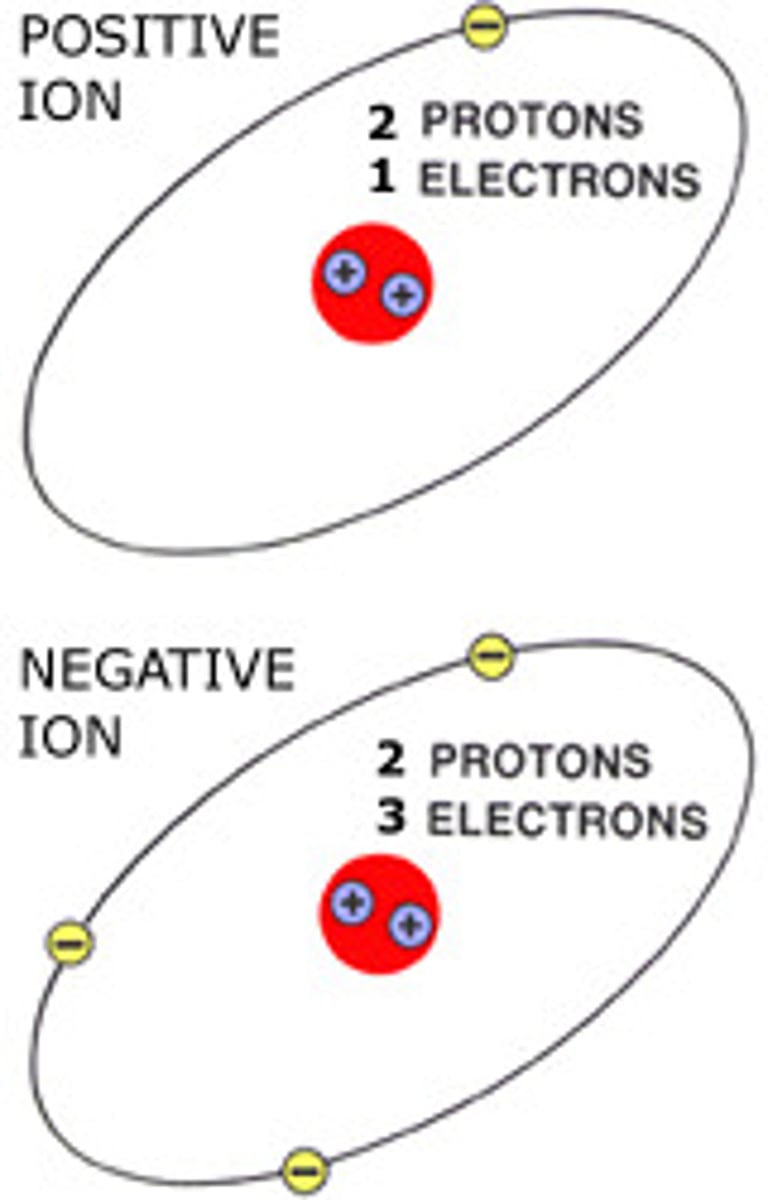
Because it gained an electron
Why does a bromine ion has a charge of -1?
Carbon-12 and Carbon-13 are isotopes of each other. Carbon-13 has one more neutron than carbon-12
Why does carbon-12 have a mass of 12 and carbon-13 have a mass of 13?
8 neutrons
If Oxygen has 8 protons and has a mass of 16, how many neutrons does oxygen contain?
9 neutrons
If Oxygen-17 has 8 protons and a mass of 17, how many neutrons does Oxygen-17 contain.