vet tech prep quezzies
1/460
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
461 Terms
what is “seg” short for?
segmented neutrophil
what are the phagocytic cells?
neutrophils and monocytes (macrophages and dendritic cells)
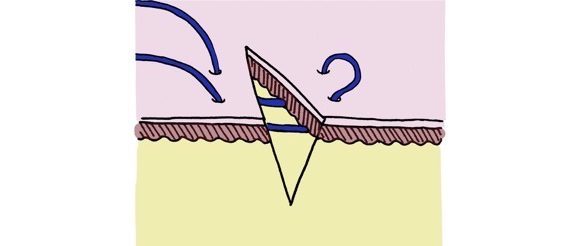
what are the common suture needle types?
taper point, taper cut, regular cutting, reverse cutting, blunt point
when should multifilament suture be avoided?
in contaminated wounds where wicking of bacteria would be a problem.
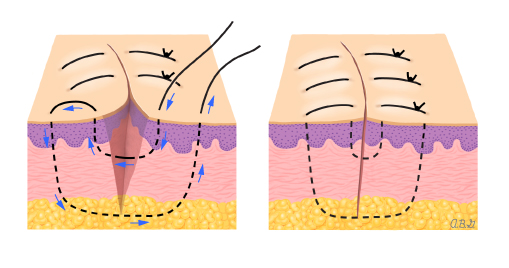
monofilament suture vs. multifilament suture
monofilament suture is a single strand that is less pliable and more susceptible to damage. multifilament suture is multiple braided or twisted strands with a greater strength and pliability than monofilament, but has an increased tendency for bacterial colonization.
what are the types of absorbable suture?
catgut, dexon, monocryl, vicryl, caprosyn, PDS II, maxon, biosyn
what are the types of non-absorbable suture?
nylon, polypropylene (prolene), silk, polybutester (novafil), polymerized caprolactam (vetafil)

what suture pattern is this?
simple interrupted
what suture pattern is this?
simple continuous
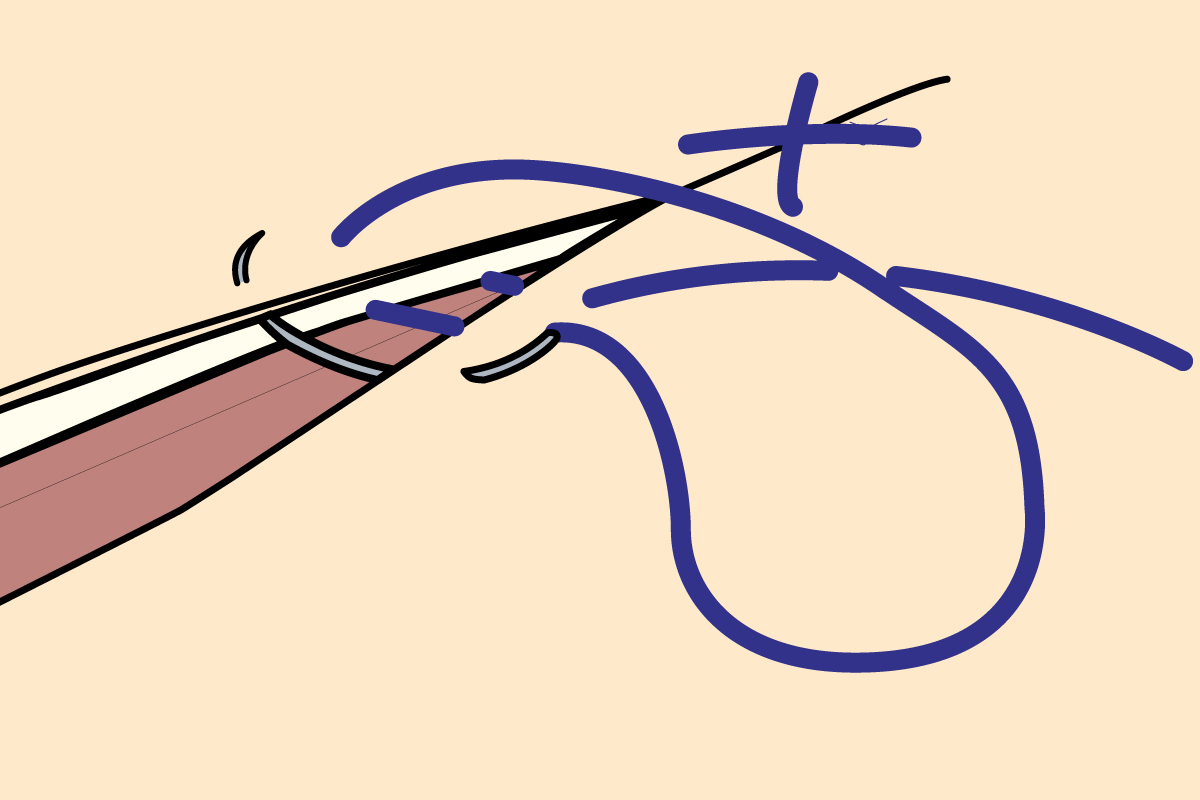
what suture pattern is this?
vertical mattress
what suture pattern is this?
horizontal mattress
what suture pattern is this?
cruciate
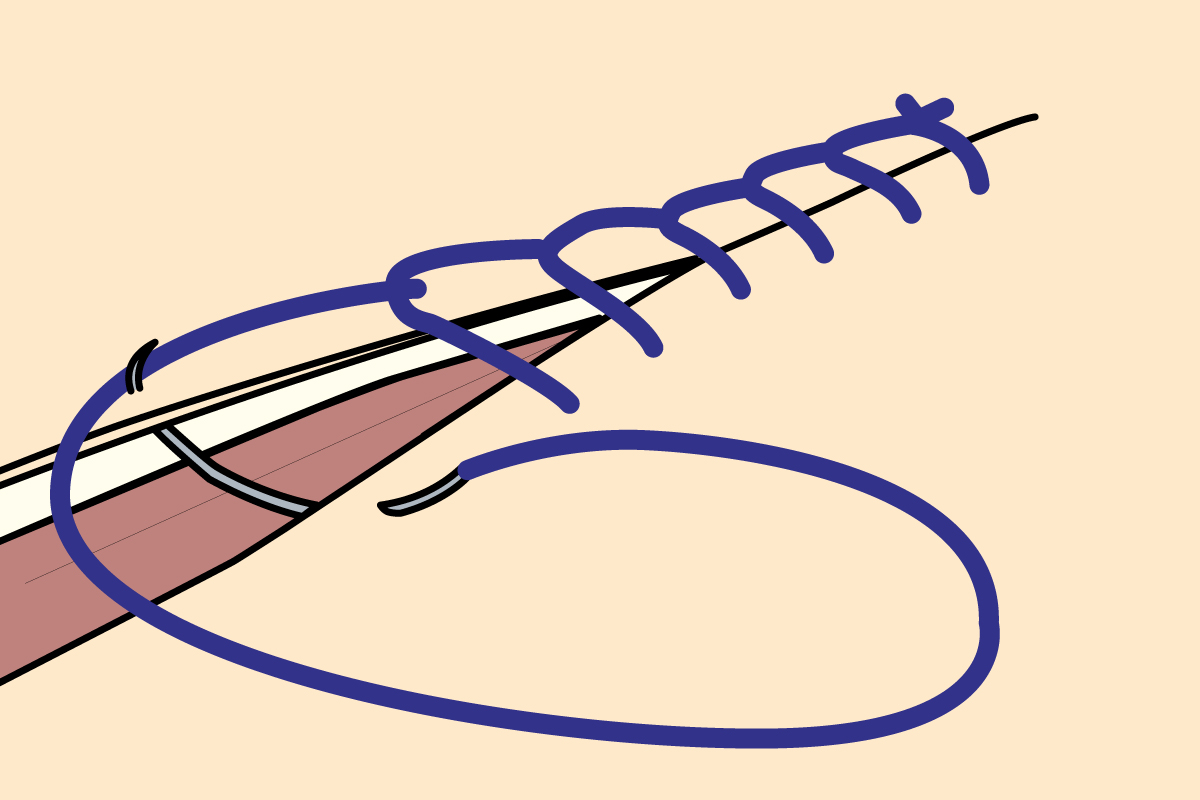
what suture pattern is this?
ford interlocking
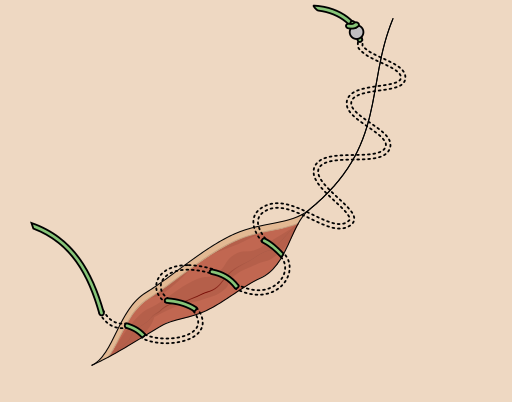
what suture pattern is this?
continuous subcuticular
what causes cutaneous larval migration in humans?
ancylostoma - hookworms
culture or draining lesions of which bacteria gives a characteristic sweet smell?
pseudomonas
pyrethrin is derived or extracted from which plant?
chrysanthemum
what is the maximum times tourniquets can be left in place on the equine patient?
2 hours
a dog has recently obtained a fresh superficial linear wound after lacerating its flank on a fence. within what time period can this wound be optimally repaired by primary closure?
8 hours
what is the average cloacal temperature of a chicken?
107 degrees
how should a cuff be measured for selection for an indirect blood pressure reading?
the cuff diameter should be about 40% of the circumference of the leg
why are polyurethane catheters more appropriate for long-term (>7 days) usage in horses?
they are the least thrombogenic
how many 3-rooted permanent maxillary teeth are in the mouth of a dog?
6 - P4, M1, M2 on each side of the upper jaw (maxilla)
which hormone is the main cause of milk letdown?
oxytocin
what factors can lead to type II diabetes in pets?
chronic corticosteroid use, obesity, pancreatitis
what does NAVTA stand for?
the national association of veterinary technicians in america
what makes tungsten an ideal material for the filament and target of an x-ray machine?
it has a very high melting point (>3000 C) and has a high atomic number (74)
what is the appropriate medication for giardia infections?
metronidazole
oral ulceration may be seen in what chronic condition?
renal failure - severe azotemia causes generalized acidity in the body.
what medication is used to treat coccidia in dogs and cats?
sulfadimethoxine (albon)
clostridium haemolyticum (species affected, predisposing factors, key features)
cattle and sheep. damage to liver by the fluke Fasciola hepatica. hemoglobinuria, icterus, anemia.
clostridium chauvoei (species affected, predisposing factors, key features)
mainly sheep, cattle. damage or bruising to muscles from transport, injections, or rough handling. cracking of swollen lesions when touched, rancid butter odor on postmortem.
clostridium septicum (species affected, predisposing factors, key features).
mainly sheep, also cattle and goats. deep wounds such as bites, surgical sites, and parturition injuries. open wound without swelling and without gas accumulation.
clostridium perfringens type D (species affected, predisposing factors, key features)
sheep, cattle, and goats. increase in dietary intake. associated with overeating, “pulpy kidneys” due to rapid postmortem decomposition.
clostridium perfringens type C (species affected, predisposing factors, key features)
mainly cattle. increase in dietary intake. “purple gut” with sections of extremely reddened small bowel filled with hemorrhagic fluid.
clostridium novyi type B (species affected, predisposing factors, key features).
mainly sheep, also cattle. damage to liver by the fluke Fasciola hepatica. large necrotic black lesion in liver.
clostridium tetani (species affected, predisposing factors, key features).
mainly horses and pigs, all animals. puncture wound. general body stiffness, sensitivity to noise, sound, and movement.
clostridium botulinum (species affected, predisposing factors, key features)
uncommon in animals. ingestion of preformed toxin in feed. ascending paralysis.
clostridium sordellii (species affected, predisposing factors, key features)
mainly cattle. unknown. sudden death syndrome.
for which very contagious and rapidly fatal disease are ferrets vaccinated against?
canine distemper
eimeria, cystoisospora, cryptosporidium, sarcocystic, and toxoplasma are all what type of parasite?
coccidia
what is the gold standard diagnosis for nematodes?
fecal flotation with zinc centrifugation.
what types of parasites are nematodes?
roundworms, hookworms, and whipworms.
what is the most common roundworm in dogs and cats?
toxocara canis
what type of parasites cause the zoonotic ocular lava migrans?
roundworms
what medications are used to treat roundworms?
piperazine, pyrantel, fenbendazole
how are roundworms transmitted and what is most common?
fecal-oral and transplacental (most common)
where do roundworms live in the body?
small intestine
what are the most common hookworm species?
ancylostoma caninum and uncinaria stenocephala
what type of parasite causes zoonotic cutaneous larva migrans?
hookworms
how does percutaneous larva migrans occur?
larvae migrate through the skin into the lung where they molt and are swallowed and passed into the small intestine.
what medications are used to treat hookworms?
fenbendazole, pyrantel.
what symptoms are associated with hookworm infection?
hemorrhagic diarrhea and severe anemia.
how are hookworms transmitted?
fecal-oral, transmammary, percutaneous infections.
what is the most common species of whipworm?
trichuris vulpis
how are whipworms transmitted?
fecal-oral
what are the symptoms of whipworm infection?
hyperkalemia and hyponatremia (pseudo-Addison’s)
where do whipworms live in the body?
large intestine
what type of parasite has eggs with bipolar plugs on the ends?
whipworm
what medications are used to treat whipworm infections?
treated with fenbendazole, prevented with milbemycin
what type of parasites are cestodes commonly referred to as?
tapeworms
what is the most common tapeworm in dogs and cats?
dipylidium caninum
what is the term commonly used to describe diarrhea in calves?
scours
which electrolyte abnormality is known to cause ventroflexion of the neck and extreme weakness?
hypokalemia (low potassium)
how do oral flea control products such as Program or Sentinel work?
stops egg hatching by interfering with chitin synthesis.
what is the correct term for dental decay, causing demineralization of the hard tissues of the tooth?
caries
what is the formula to calculate replacement fluids
body weight in kg x percent dehydration as a decimal = fluid deficit in liters
eg: 40kg dog, 5% dehydrated
40kgs x 0.05 = 2 liters or 2000 mL
what is the intermediate host of Dipylidium caninum?
ctenocephalides felis
anal pruritus and alopecia around the anal region and tail in the horse are associated with what parasite infestation?
oxyuris equi (equine pinworm)
what adverse side effect can occur in cats given metoclopramide and what is the antidote?
aggressive behavior, diphenhydramine
what percentage of mammary gland tumors in the cat are malignant?
90%
what is the best way to discover parasites passed in the feces in the L1 larval form?
Baermann technique
describe the “heel effect”
when a radiograph appears darker/more exposed on one side of the film due to a higher x-ray beam intensity on one side of the film
describe doyen forceps and their intended use
curved, non-crushing occluding clamp with longitudinal grooves. used to clamp intestine above and below a foreign body
what is the permanent dental formula for the dog?
2(I3/3 C1/1 P4/4 M2/3)
what is the number one way to prevent transmission of disease?
hand hygiene
what is the best course of action if only a small amount of an inhalant anesthetic is spilled?
the vaporizer should be closed, and the room should be closed off for 5-10 minutes while allowing the air to circulate by opening an external door or increasing air flow into the room with an external fan.
tularemia would most likely be carried by which animal?
rabbits
what organism causes tularemia?
Francisella tularensis
what is the common term for tularemia?
rabbit fever
how does the frequency of an ultrasound probe affect image resolution and penetrating ability?
higher frequency probes (7.5 or 10 MHz) have increased image resolution but sacrifice penetration. lower frequency probes (5 MHz) are better for imaging deeper structures or cavities but do not provide as much image resolution.
describe Poiseuille’s Law
catheters that are shorter in length and larger in diameter can deliver the largest amounts of fluids in the shortest amount of time.
what are examples of colloids?
hetastarch, blood products, Dextrans
what breeds are susceptible to ivermectin toxicity?
collie-type breeds, “white feet, don’t treat”
what are the five density shades seen on radiographs?
gas - very dark to black
fat - dark grey
soft tissue and fluid - mid-gray
bone - nearly white
metal - white
what purpose is the administration of the drug Guafinesin typically used for in horses?
muscle relaxation
it is estimated that blood urea nitrogen and creatinine levels become elevated when what percentage of kidney function is lost?
75%
urine becomes isosthenuric at what percentage loss of kidney function?
66%
what is cervical lymphadenitis?
swelling or abscess of the cervical lymph nodes in a guinea pigs neck
what organism most often causes cervical lymphadenitis?
Streptococcus zooepidemicus
what is the antibiotic of choice for cervical lymphandenitis?
enrofloxacin
what food is a good source of calcium for large animals?
legumes (clover and alfalfa) and beet pulp
what is not an acceptable site for intramuscular injection administration?
epaxial muscles
what is the neurotransmitter for skeletal muscles?
acetylcholinesterase
what is the transmitter for skeletal muscle?
acetylcholine
what are the CNS neurotransmitters?
GABA and dopamine
what is the inhibitory neurotransmitter in smooth muscle?
norepinephrine
what type of estrous cycle does a cow have?
non-seasonal polyestrous
what life stages of D. immitis does the definitive host harbor?
adult sexual stage