PDA Lecture 23: Adrenergic Agonists and Antagonists
1/57
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
58 Terms
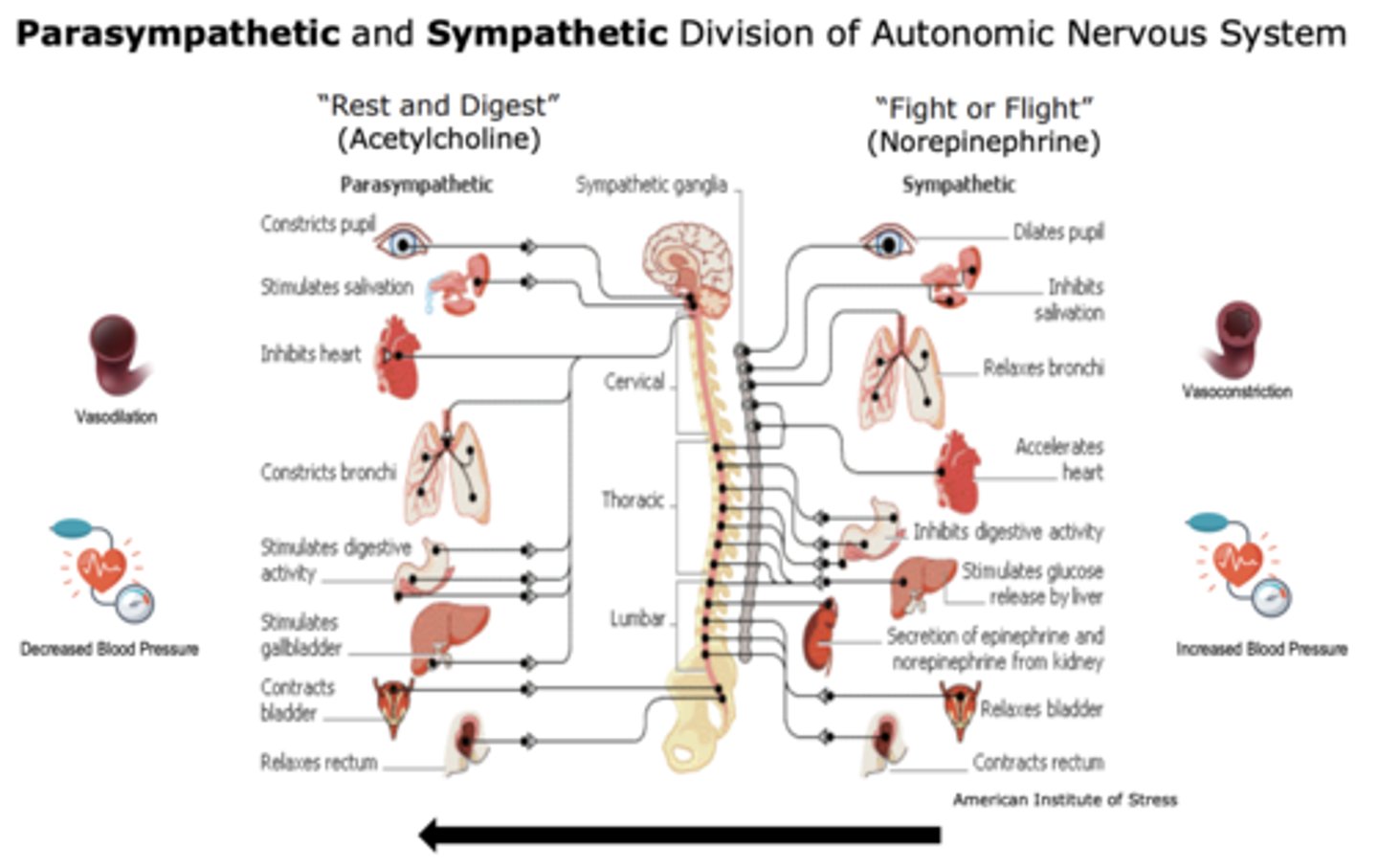
What receptors does norepinephrine activate?
Where does norepinephrine activate these receptors? Via what system?
NE activares adrenergic receptors on smooth muscle via sympathetic system
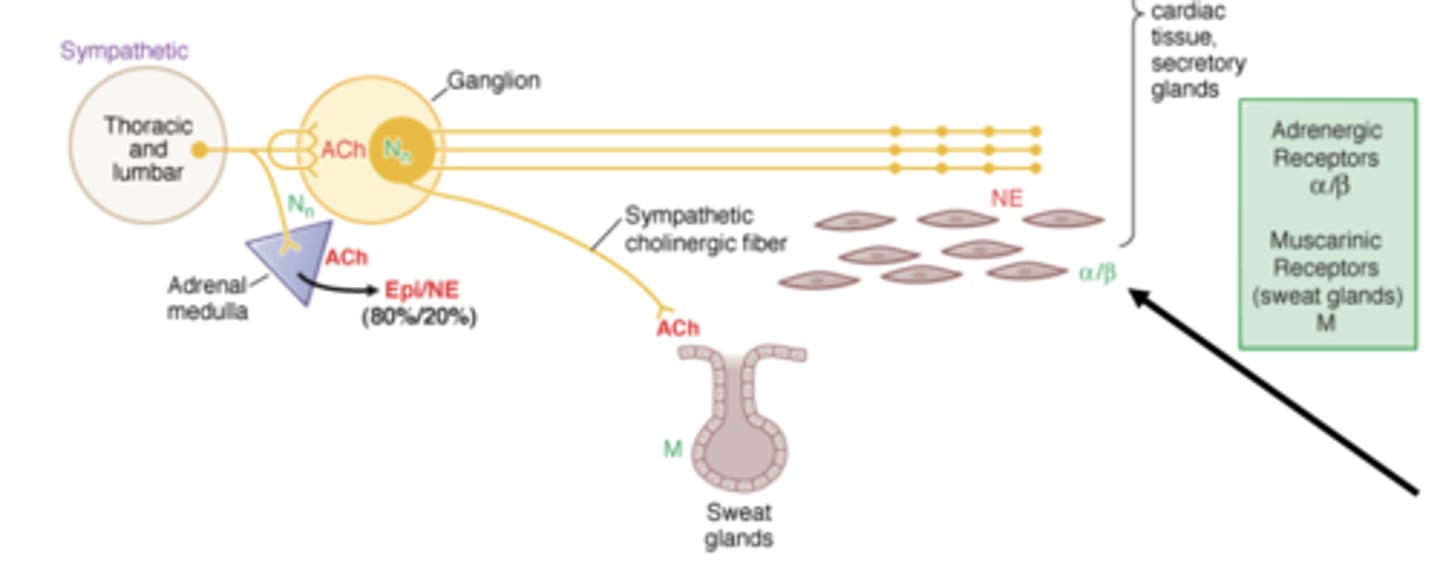
Adrenergic receptors can be found on ___________________ or on ______________________ as autoreceptors
- postsynaptic receptors (sending fight or flight message)
- presynaptic receptors as autoreceptors (providing feedback to presynaptic neuron
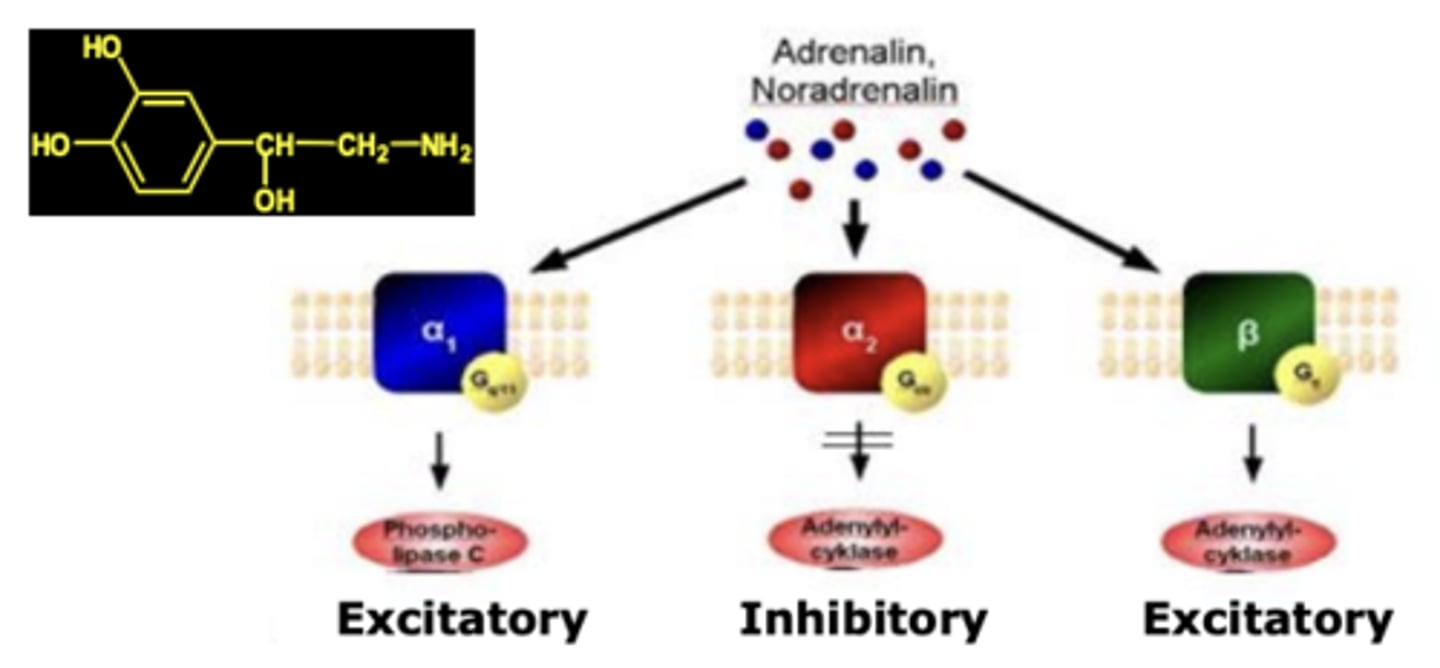
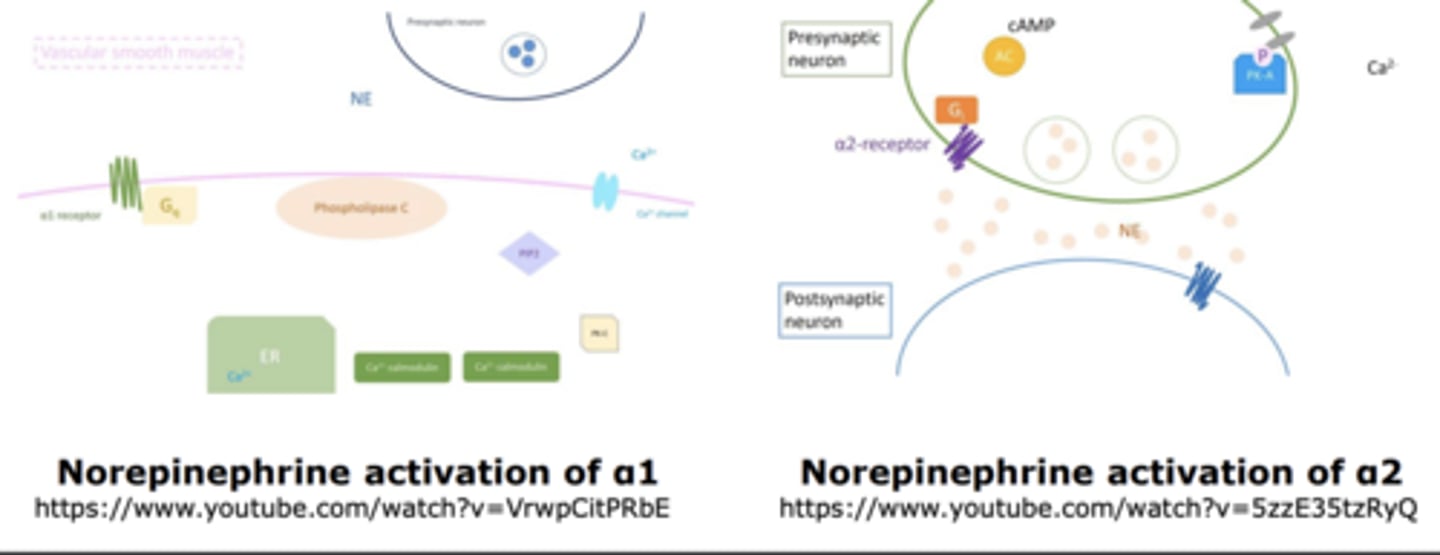
- Which metabotropic G-protein-coupled receptors do these adrenergic receptors activate? What does it increase/decrease?
• α1 ->____ ->Increases _______________
• α2 ->____->Decreases _________________
• β->_____ ->Increases ___________________
• α1 ->Gq ->Increases phospholipase C
• α2 ->Gi/o->Decreases adenylate cyclase
• β->Gs ->Increases adenylate cyclase
What does decreasing or increasing these enzymes (phospholipase C, adenylate cyclase) result in?
results in respective decreases or increases in fight or flight response in autonomic system organs
Adrenergic receptor agonists will increase _________________ and decrease _______________
- "fight or flight"
- "rest and digest"
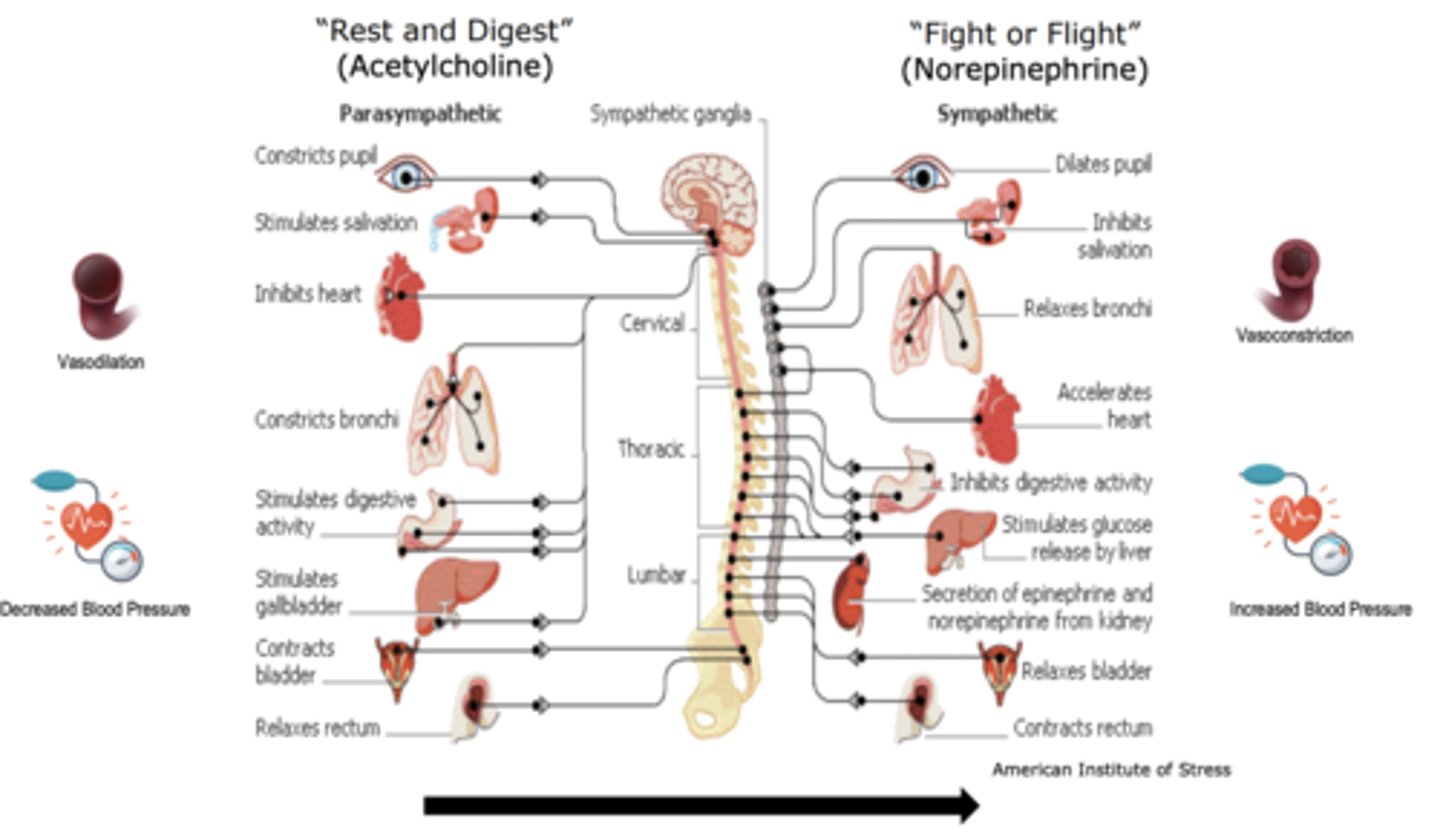
Beta receptor agonists ______________ "fight or flight" response
increase
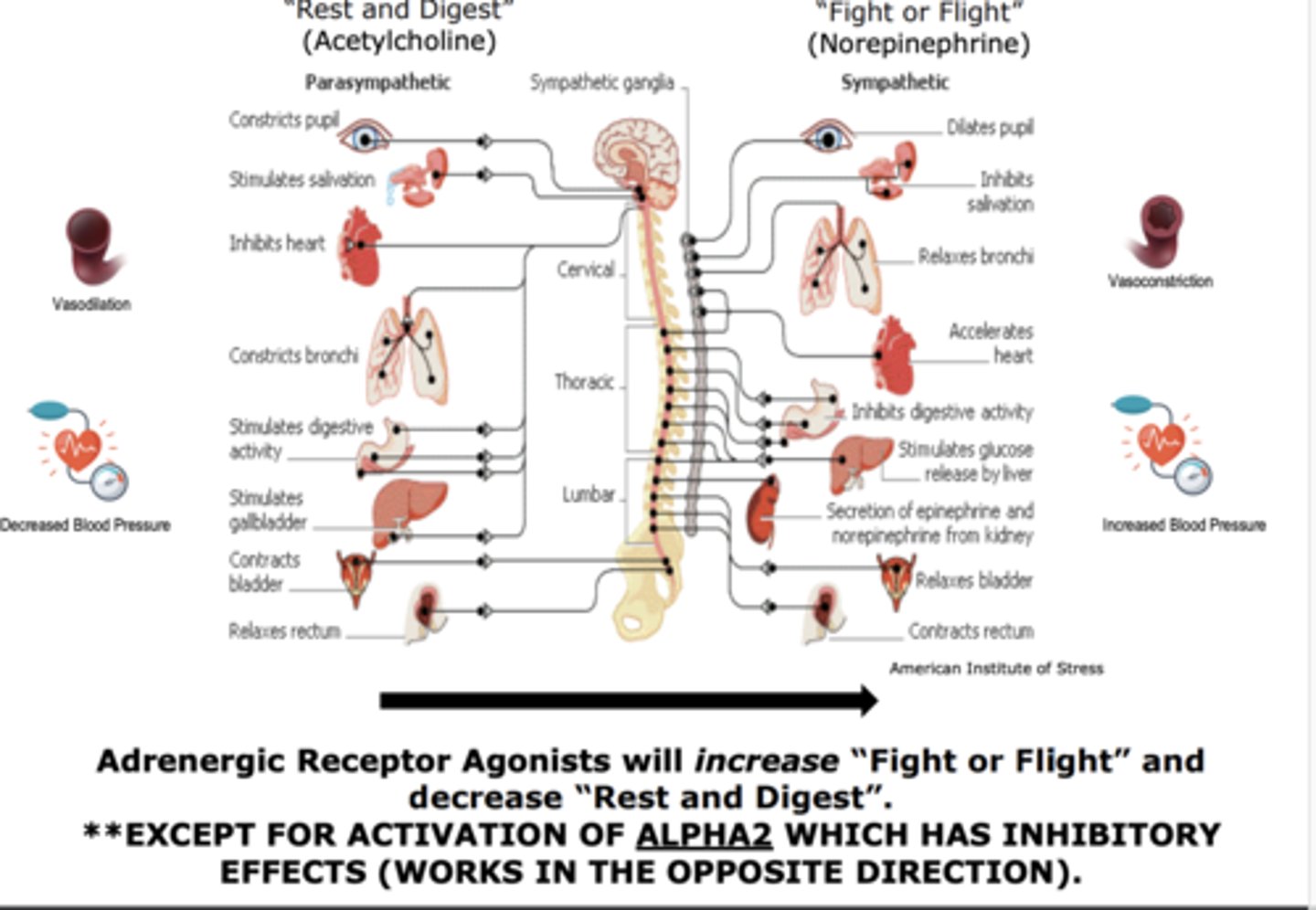
Adrenergic Receptor Agonists will increase “Fight or Flight” and decrease “Rest and Digest”. **EXCEPT FOR ACTIVATION OF.......
ALPHA2 WHICH HAS INHIBITORY EFFECTS (WORKS IN THE OPPOSITE DIRECTION)
α1 ________________ "fight or flight", α2 _________________ "fight or flight"
- increases
- decreases
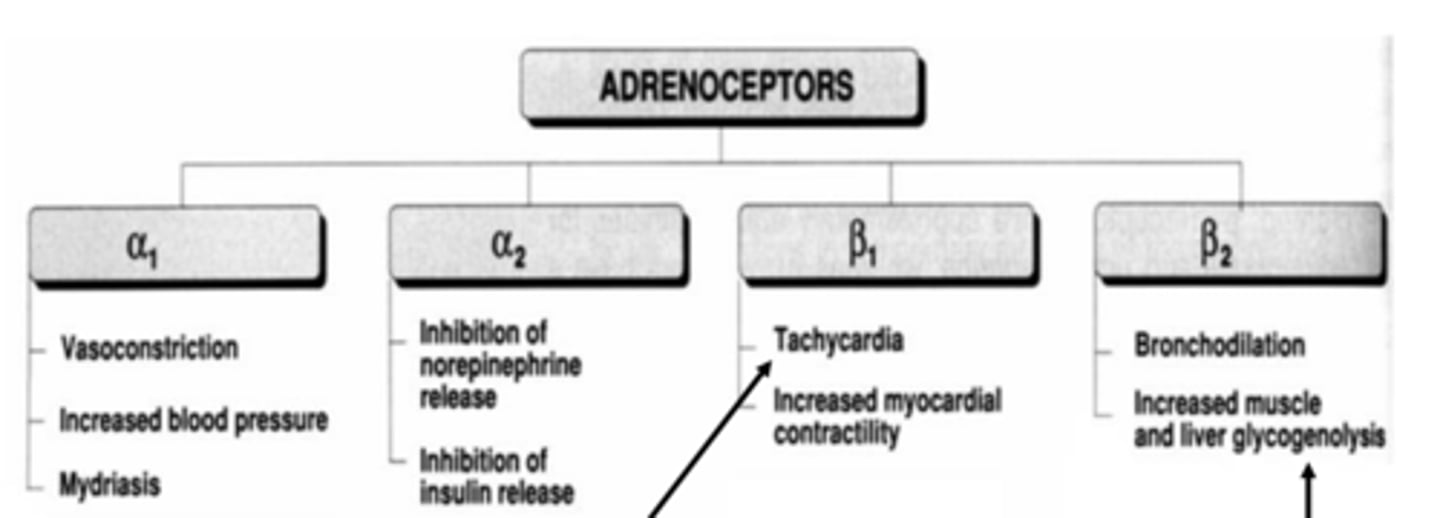
Common ANS effects mediated by adrenergic receptor subtypes when activated: α1 (3)
- vasoconstriction
- increased BP
- mydriasis (dilates pupil)
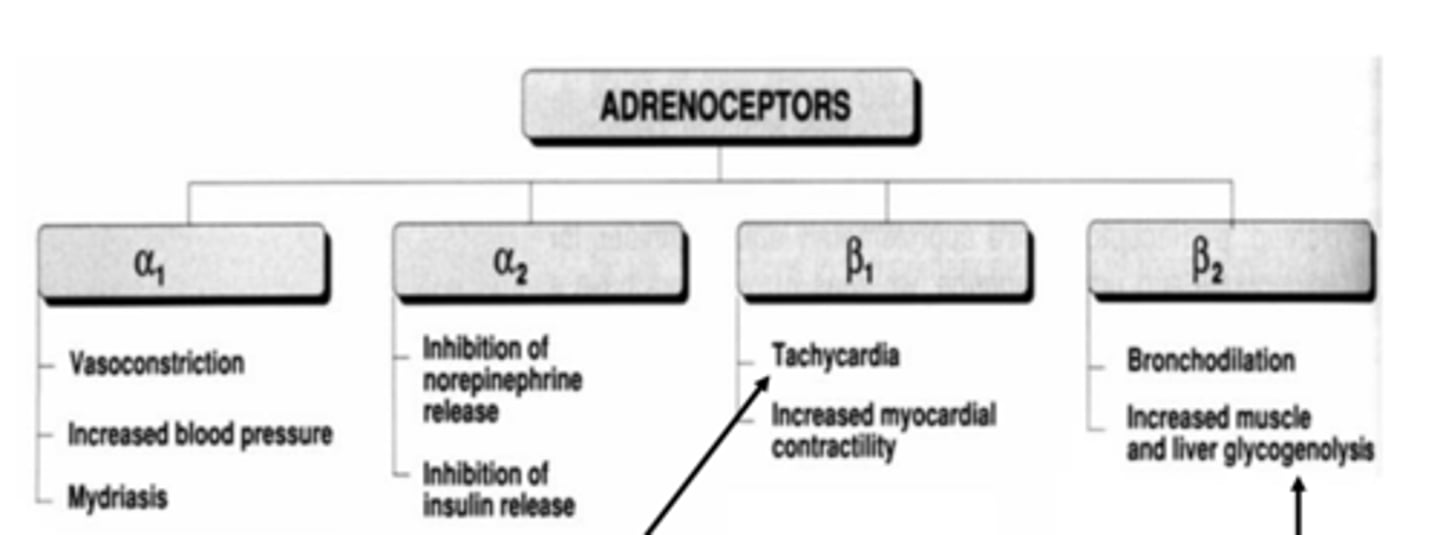
Common ANS effects mediated by adrenergic receptor subtypes when activated: α2 (2)
- inhibition of norepinephrine release
- inhibition of insulin release
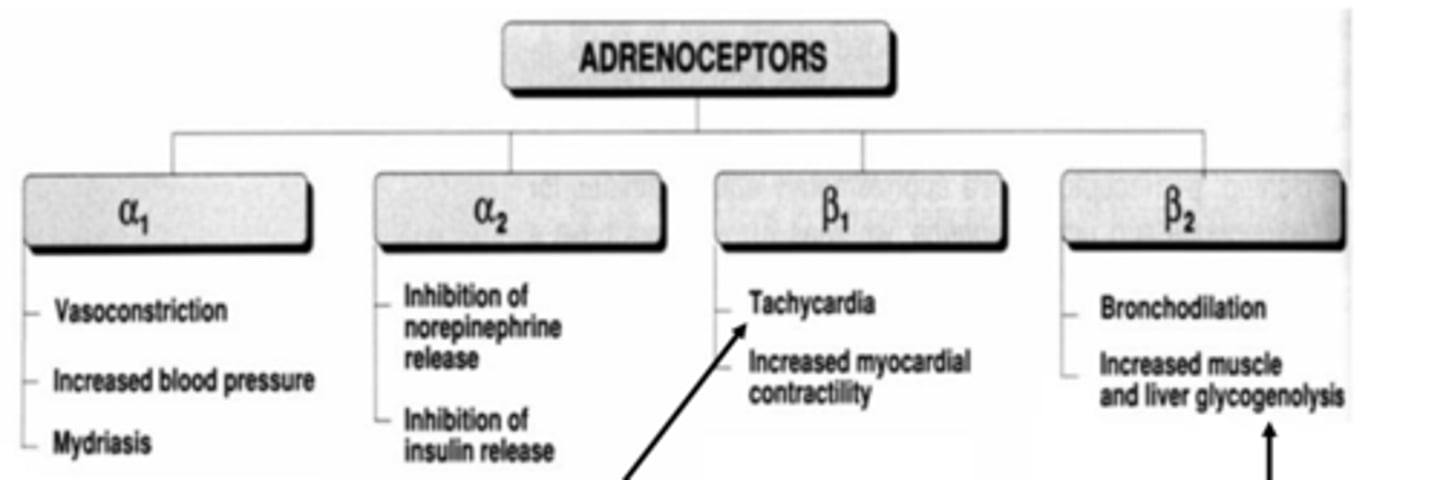
Common ANS effects mediated by adrenergic receptor subtypes when activated: β1 (2)
- tachycardia
- increased myocardial contractility
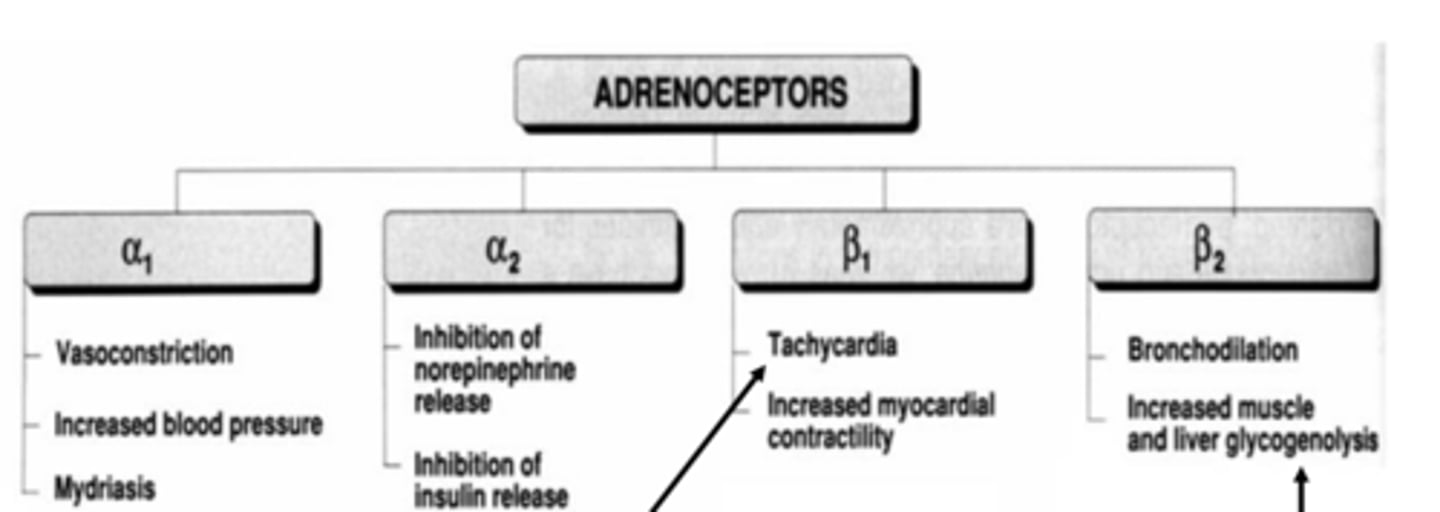
Common ANS effects mediated by adrenergic receptor subtypes when activated: β2 (2)
- bronchodilation
- increased muscle and liver glycogenolysis (breakdown of glycogen to glucose)
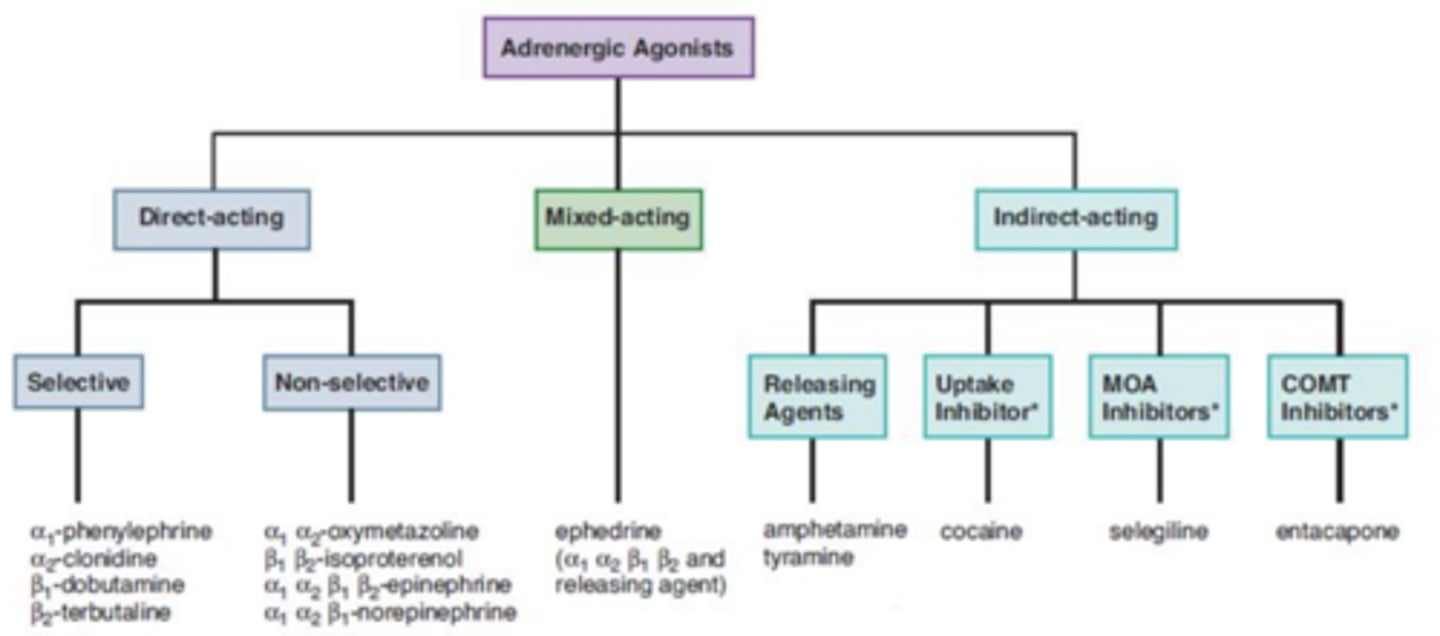
Adrenergic agonists can be....(3)
• Direct acting
• Mixed acting
• Indirect acting
Adrenergic agonists can have different ___________ for different _________
- affinities
- receptors

Direct-acting adrenergic agonists can be....
selective or non-selective
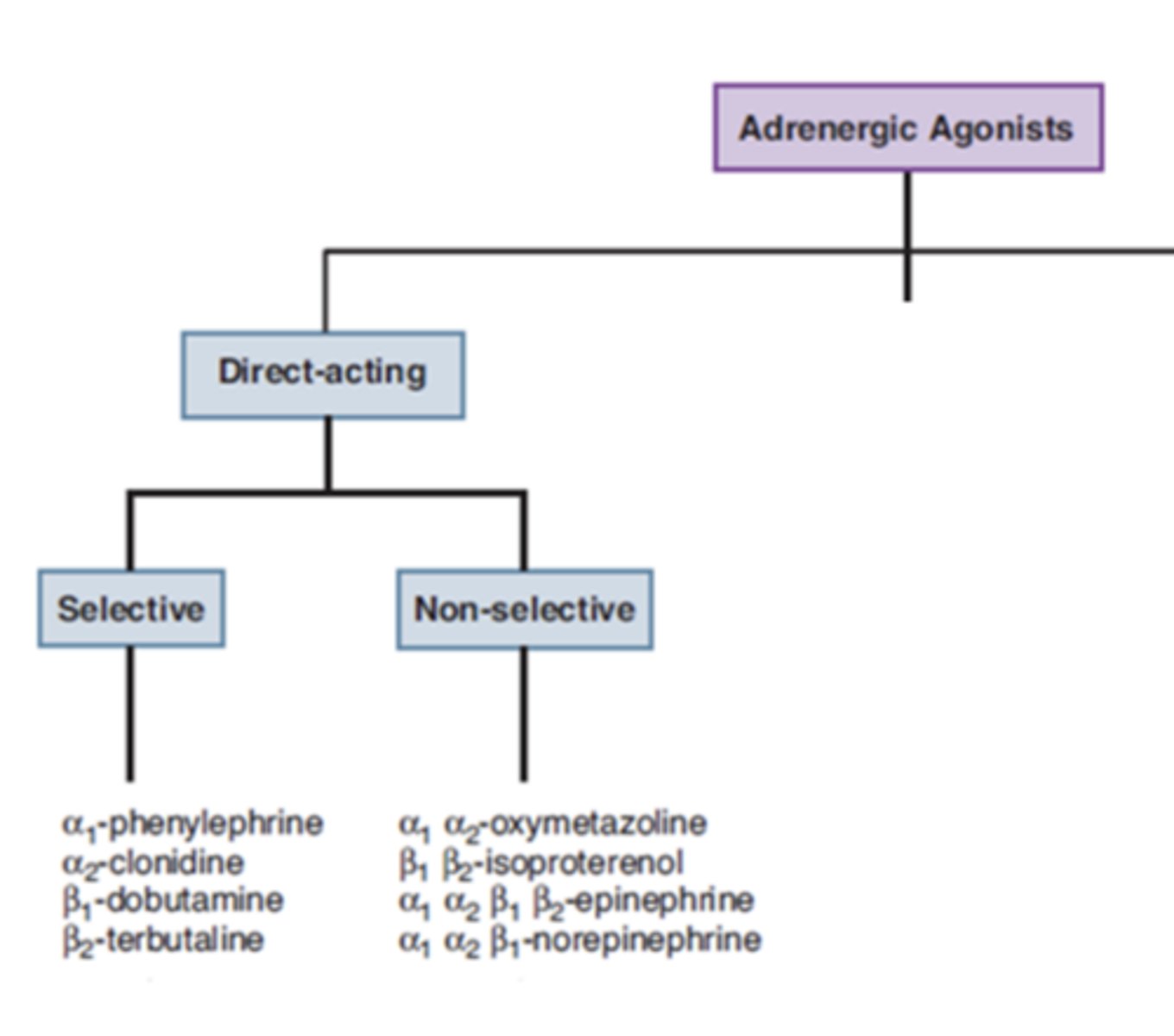
Directly acting non-selective adrenergic agonists: Epinephrine (increase “fight or flight” response)
- used in emergency treatment of what?
- In what ways is it administered? (3)
- What does the constriction of blood vessels lead to?
- _____________ in heart contraction and rate and helps prevent ________________
- relaxation of bronchi in lungs opens.........
- emergency treatment of anaphylactic shock (sudden drop in BP and airway closure)
- administered through inhalation, SC, IV
- constriction of blood vessels decreases swelling
- increases in heart contraction & rate helps prevent CV collapse
- relaxation of bronchi in lungs opens up airways
Why is epinephrine added to local anesthetics?
to prolong duration of anesthetic effect (vasoconstriction slows down absorption)
Directly acting non-selective adrenergic agonists: Norepinephrine (increase “fight or flight” response)
- is it commonly used?
- what can it be used in the treatment of?
- not commonly used
- can be used for the treatment of life threatening hypotension
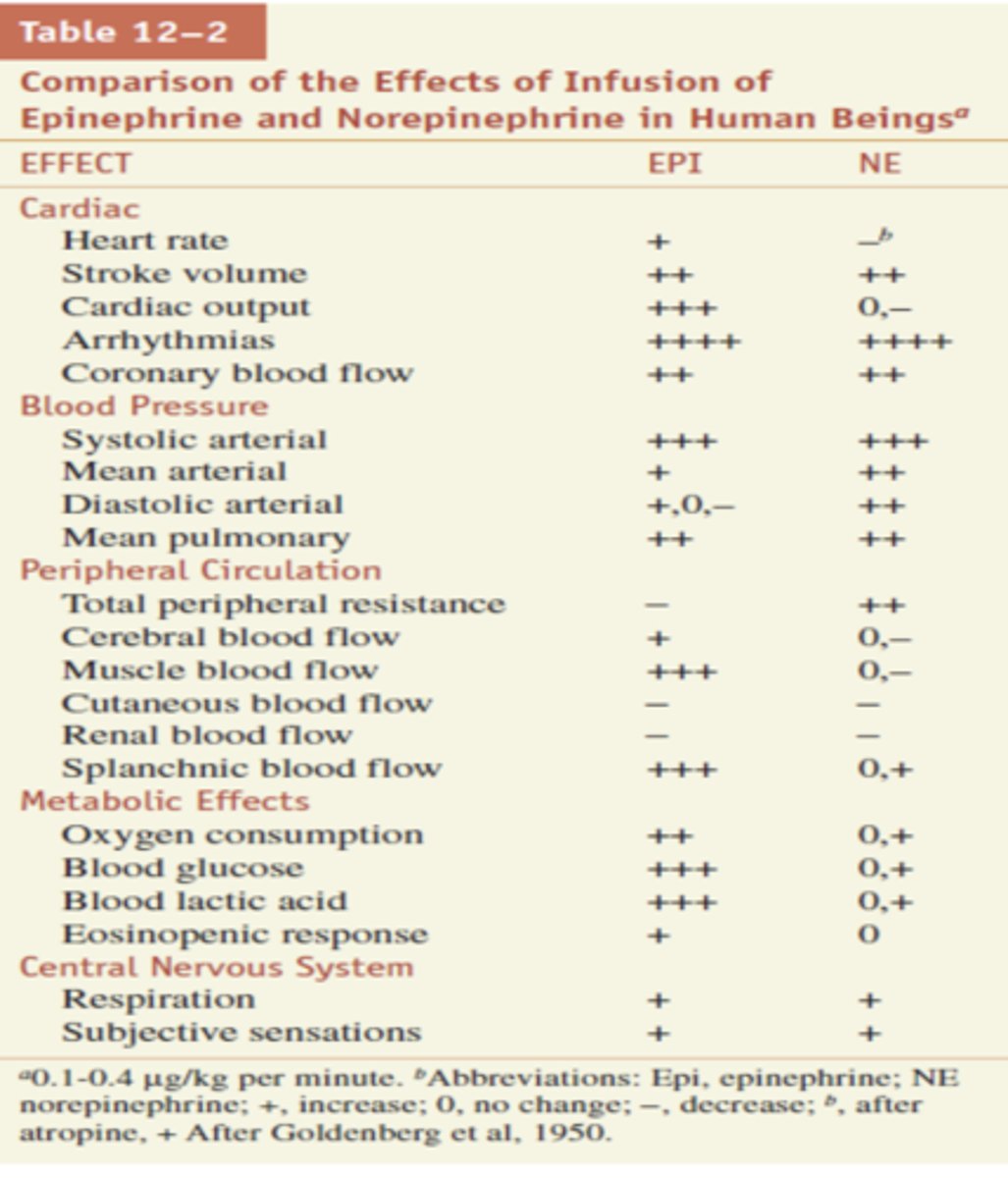
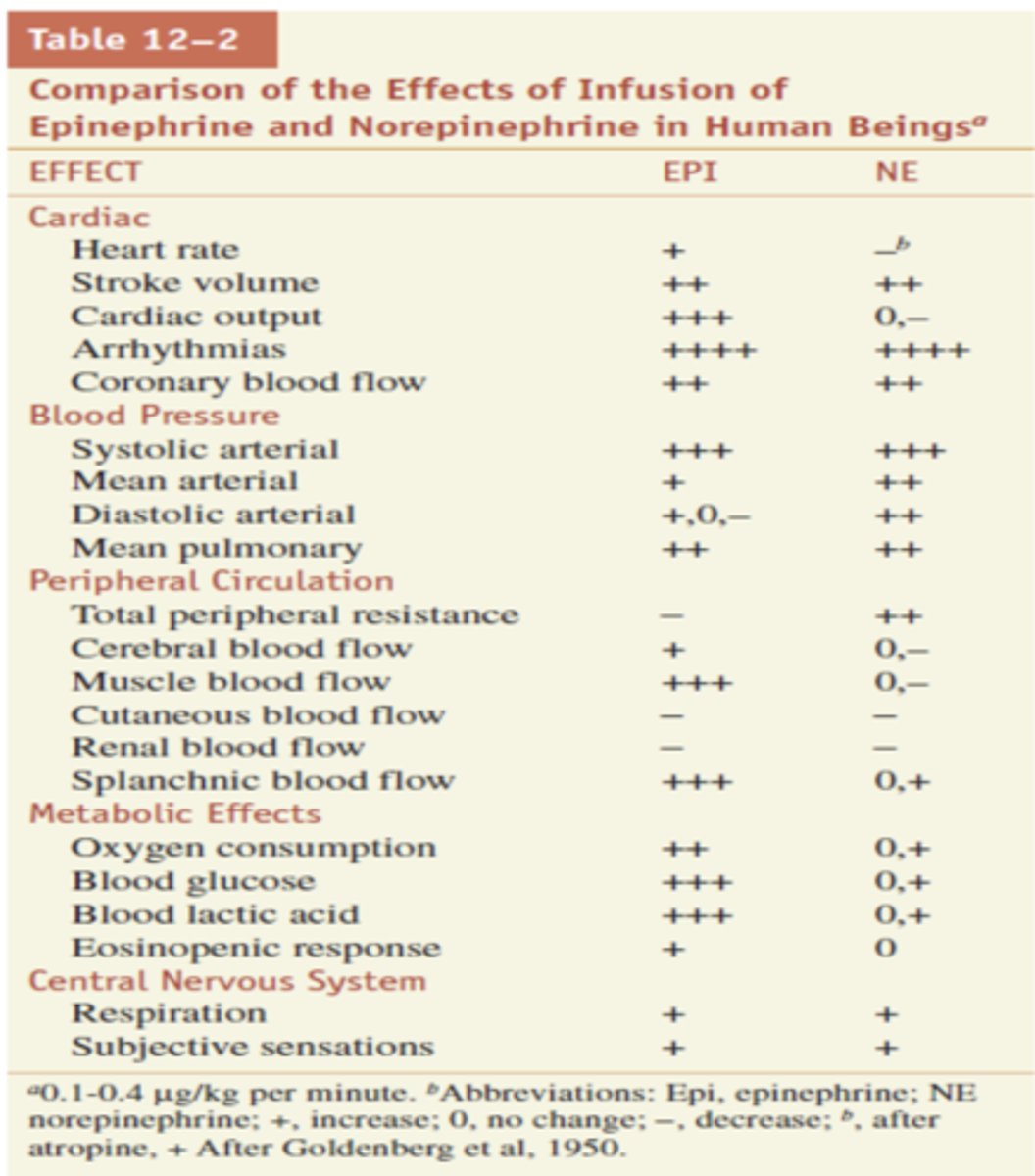
Between Epi and NE, which is more potent and usually has greater effect? ***
Epinephrine
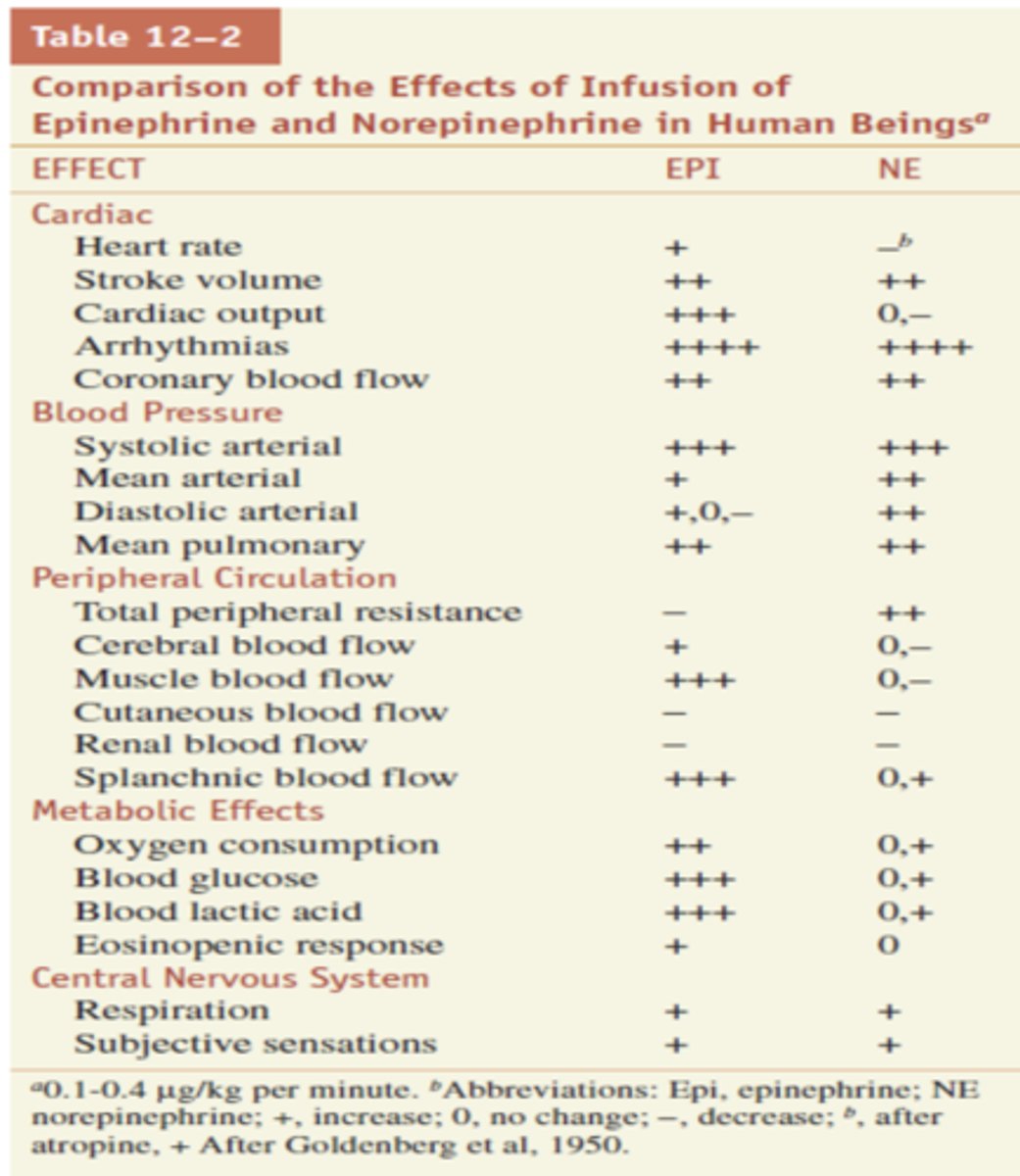
Between Epi and NE, which is more potent for blood pressure?
NE is a little more potent for BP
Directly acting non-selective adrenergic agonists: Isoproterenol (increase “fight or flight” response)
- non-selective for _____________
- what is it clinically used for? (3)
- non-selective for beta receptors
- long-term bronchitis, emphysema, asthma
Directly acting selective adrenergic agonists: Phenylephrine (increase “fight or flight” response)
- selective ________ agonist
- What is it clinically used for?
- selective α1 agonist
- nasal decongestant (reduces swelling of blood vessels in nasal cavity)
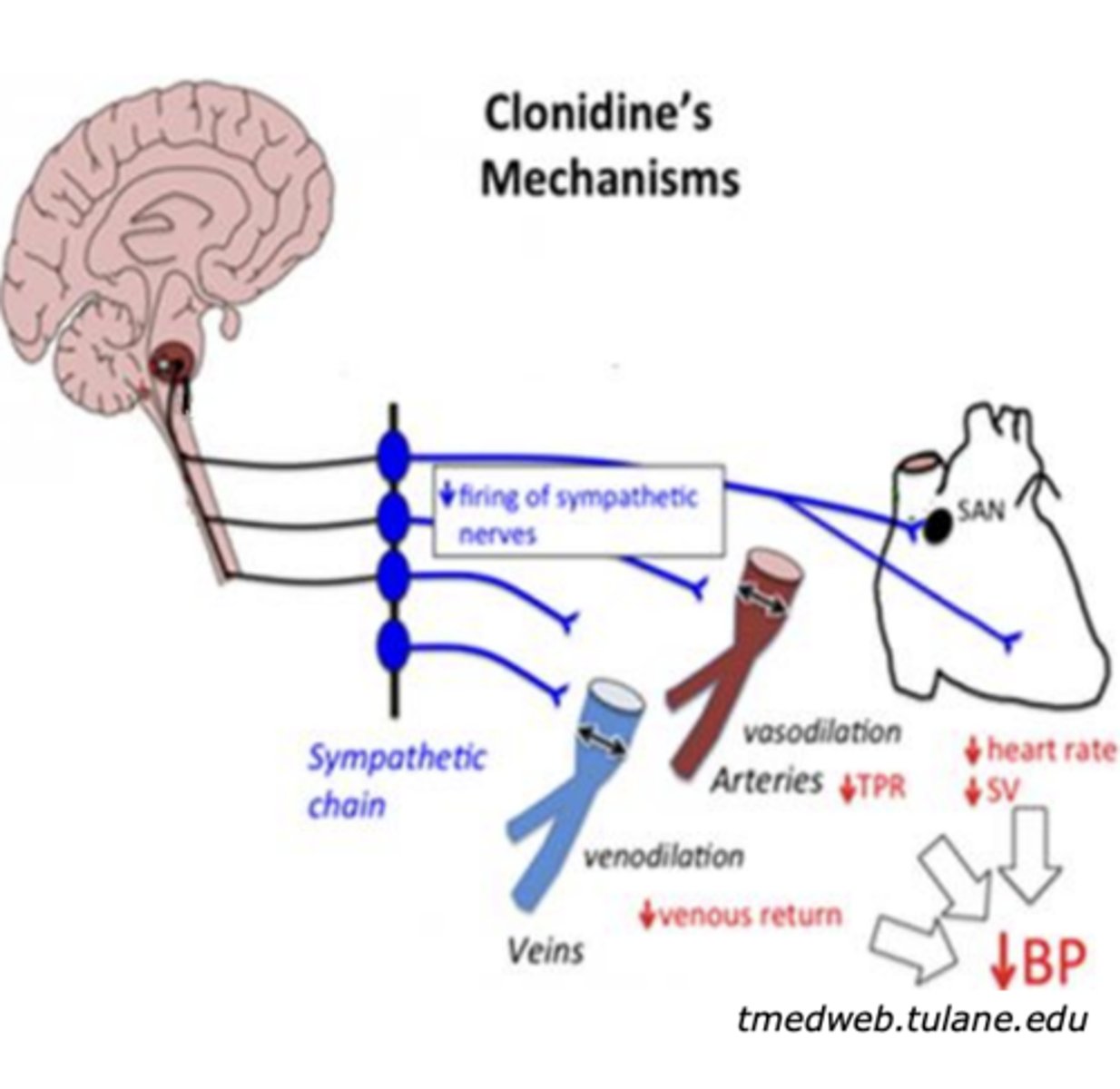
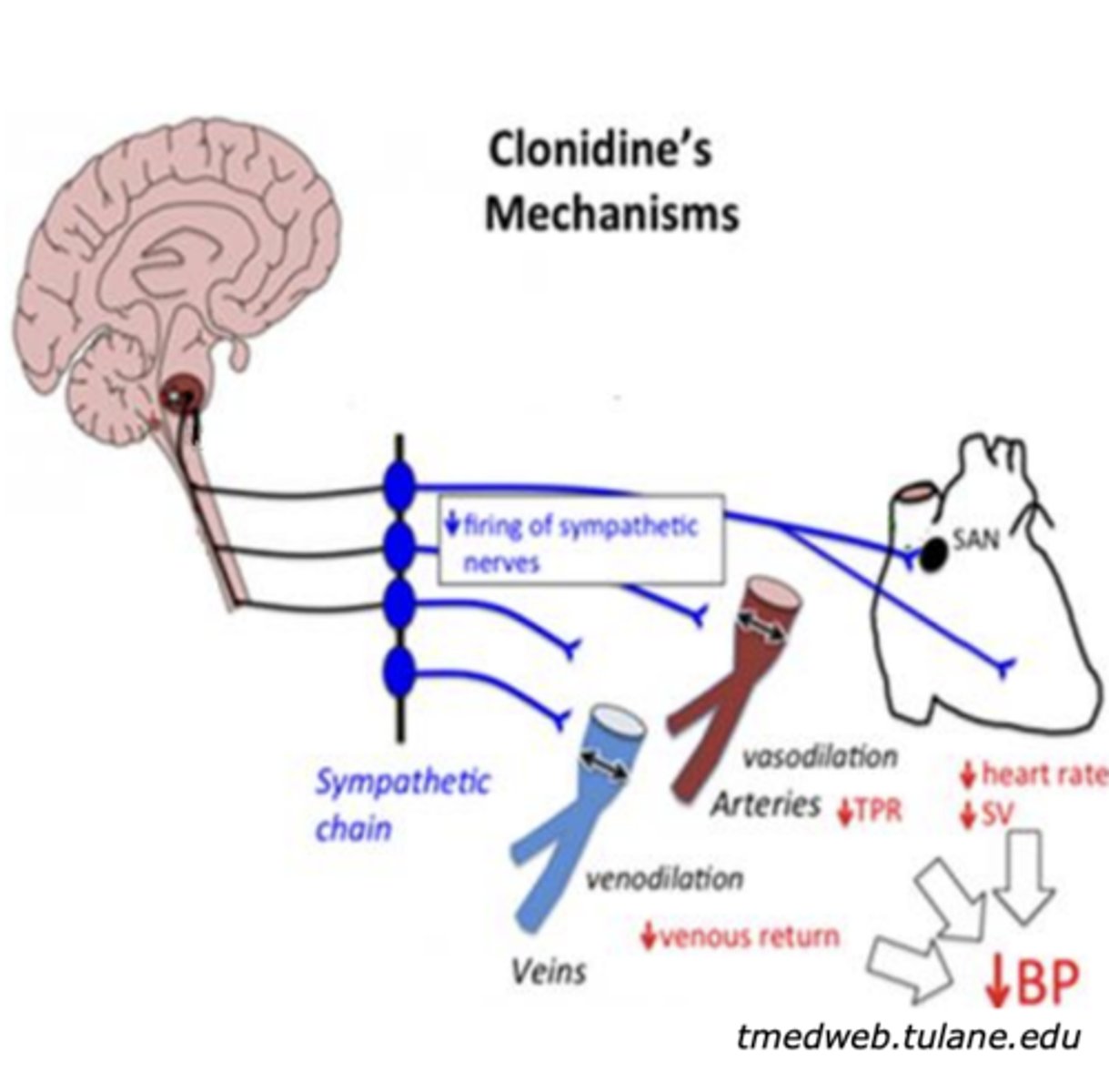
Directly acting selective adrenergic agonists: Clonidine (decrease “fight or flight”)
- Selective __________ agonist
- What is it clinically used for?
- selective α2 agonist
- hypertension
Directly acting selective adrenergic agonists: Guanabenz (decrease “fight or flight”)
- Selective __________ agonist
- What is it clinically used for?
- selective α2 agonist
- hypertension
Directly acting selective adrenergic agonists: Apraclonidine (decrease “fight or flight”)
- Selective __________ agonist
- What is it clinically used for?
- selective α2 agonist
- glaucoma
Common side effects of directly acting selective adrenergic agonists (4)
dizziness, headache, fatigue, dry mouth
α1 agonists increase fight or flight, so they are used for....
hypotension
α2 agonists decrease fight or flight, so they are used for...
hypertension
Directly acting selective beta agonists: Dobutamine was originally identified as a selective ___________ agonist; however, pharmacological actions are much more ____________
(increases “fight or flight” response)
- selective β1 receptor agonist
- complex
Dobutamine: the mixture used clinically contains _______________ and __________ forms of drug that work as ____ and _____ agonists
- enantiomeric and isomer forms
- β1 and α1 agonist
What are the clinical uses of dobutamine? (2)
- acute heart failure (following heart surgery)
- cardio stress testing
Directly acting selective beta agonists: Metaproterenol, Terbutaline, Albuterol, Pirbuterol, Bitolterol, and Salmeterol: (increase “fight or flight” response)
- Selective _____ agonists
- What are their clinical uses?
- Varied _________ and _________________
- selective β2 agonists
- treatment of bronchospasm and asthma
- varied onsets and durations of action
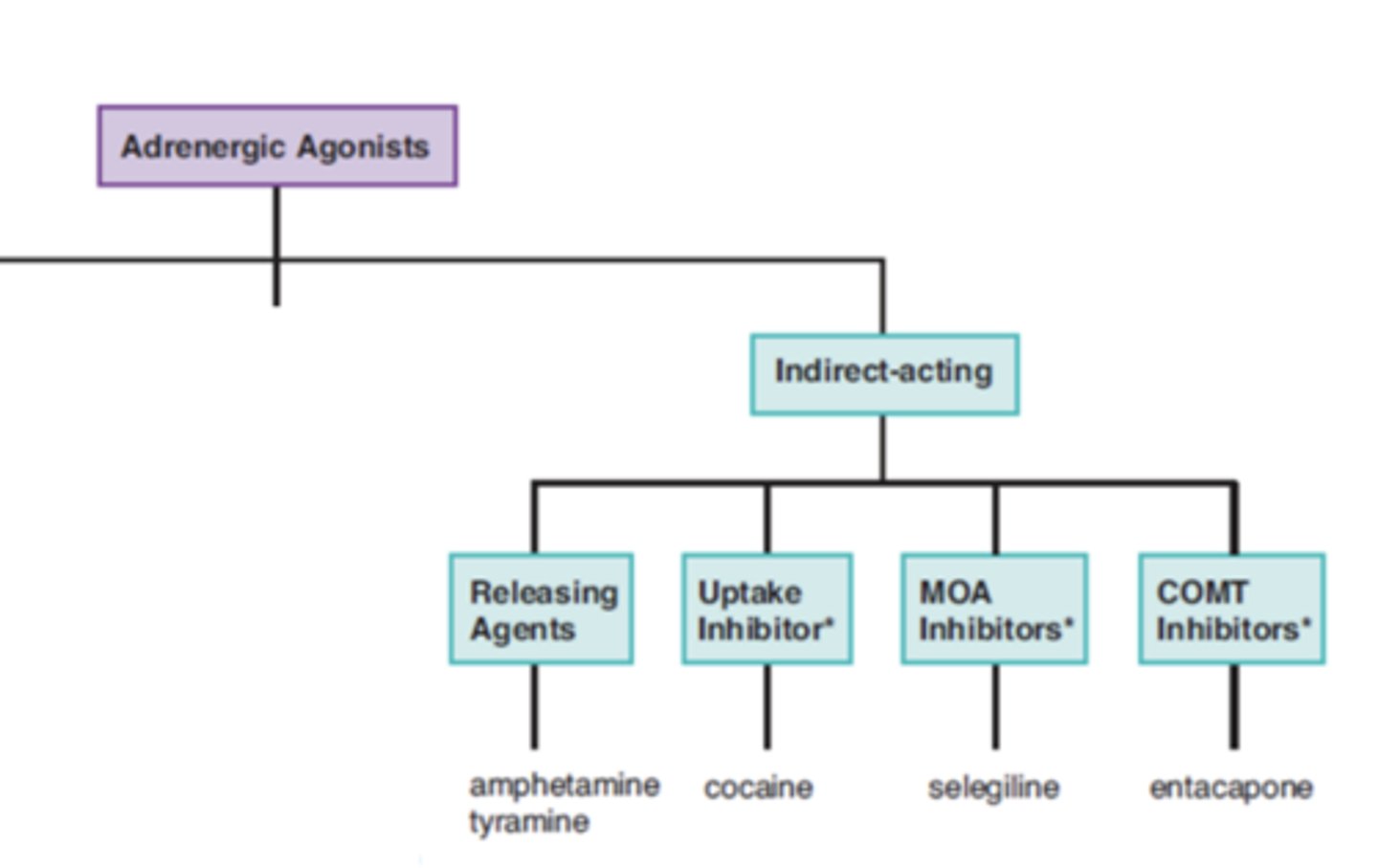
Indirect-acting adrenergic agonists can be.....(4)
- releasing agents
- uptake inhibitor
- MOA inhibitors
- COMT inhibitors
Indirect acting adrenergic receptor agonists: Cocaine (increase “fight or flight” response)
- What is it derived from?
- Blocks __________________ and prevents ________
- Clinical uses:
• Alkaloid derived from coca plant
• Blocks norepinephrine transporter and prevents reuptake
• Clinical uses: None clinically approved
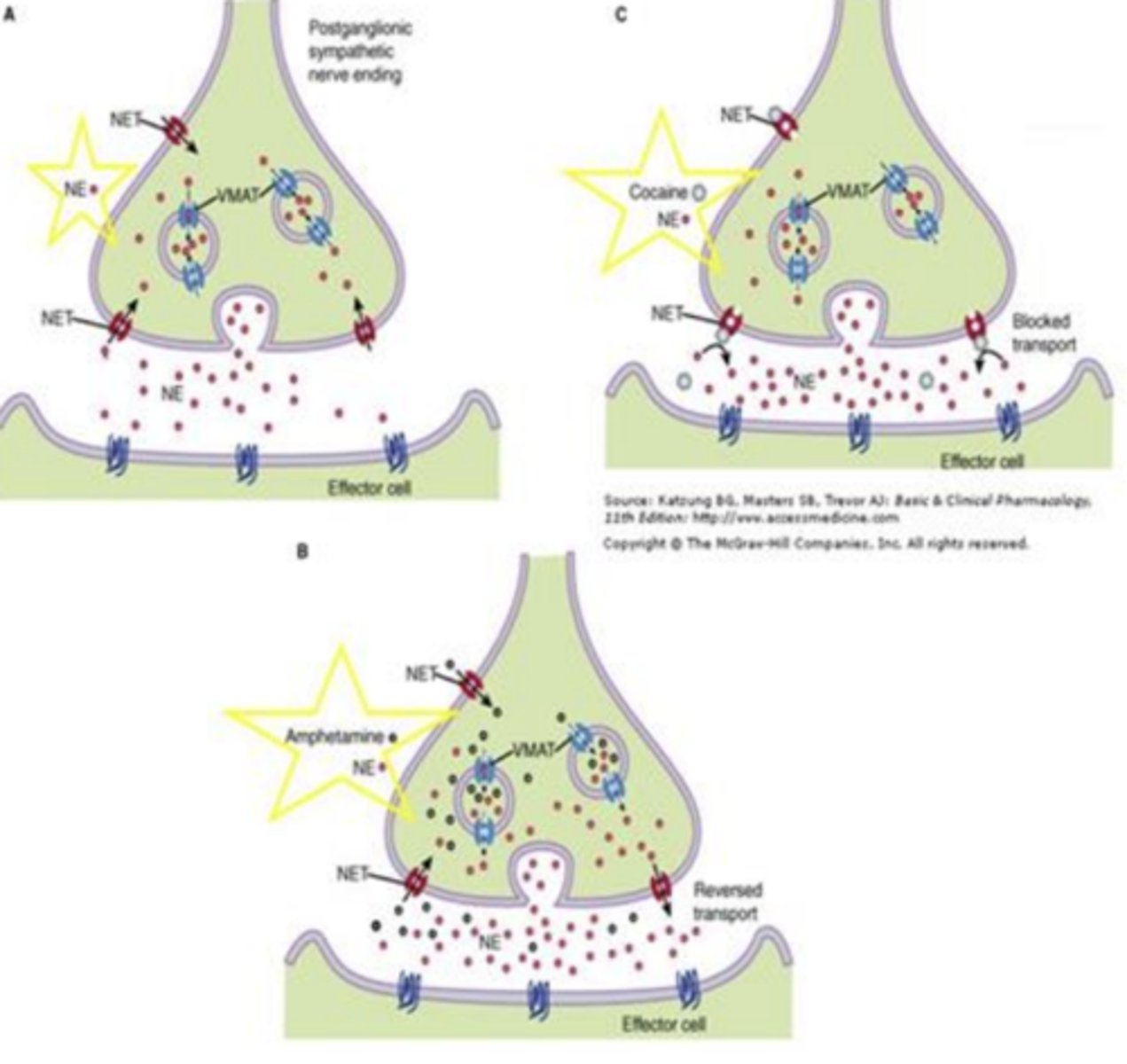
Indirect acting adrenergic receptor agonists: Amphetamine (increase “fight or flight” response)
- Synthetic or natural?
- ___________ norepinephrine and prevents ___________
- Clinical uses: (3)
• Synthetic drug
• Reverses norepinephrine transporter and prevents reuptake
• Clinical uses: Low doses used for ADHD, narcolepsy, obesity (though not approved for obesity anymore)
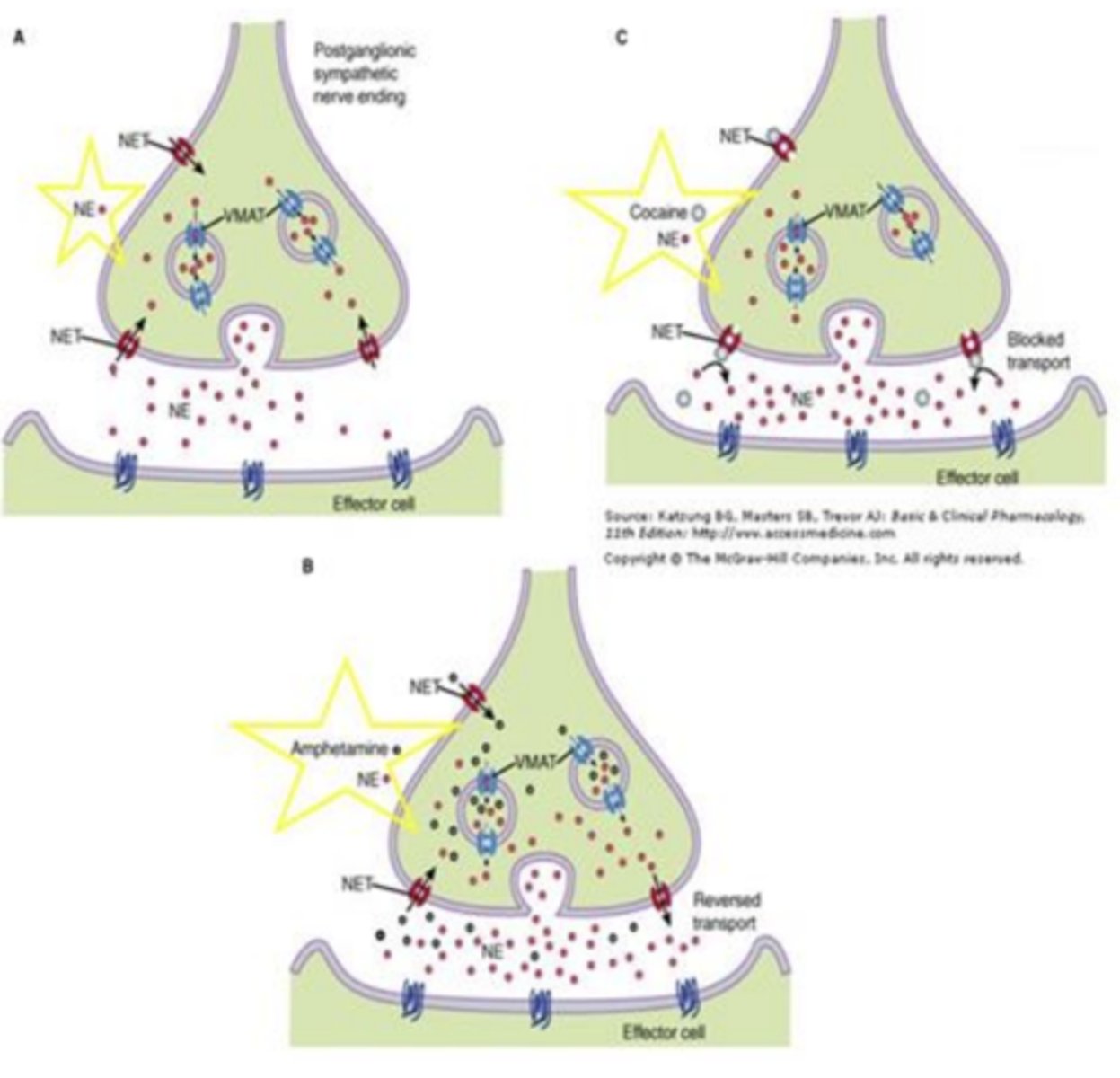
Side effects of indirect acting adrenergic receptor agonists
Both drugs (cocaine and amphetamine) cross BBB, have psychological effects
Indirect acting adrenergic receptor agonists: Selegiline (increase “fight or flight” response)
- What does it do in the metabolism of norepinephrine?
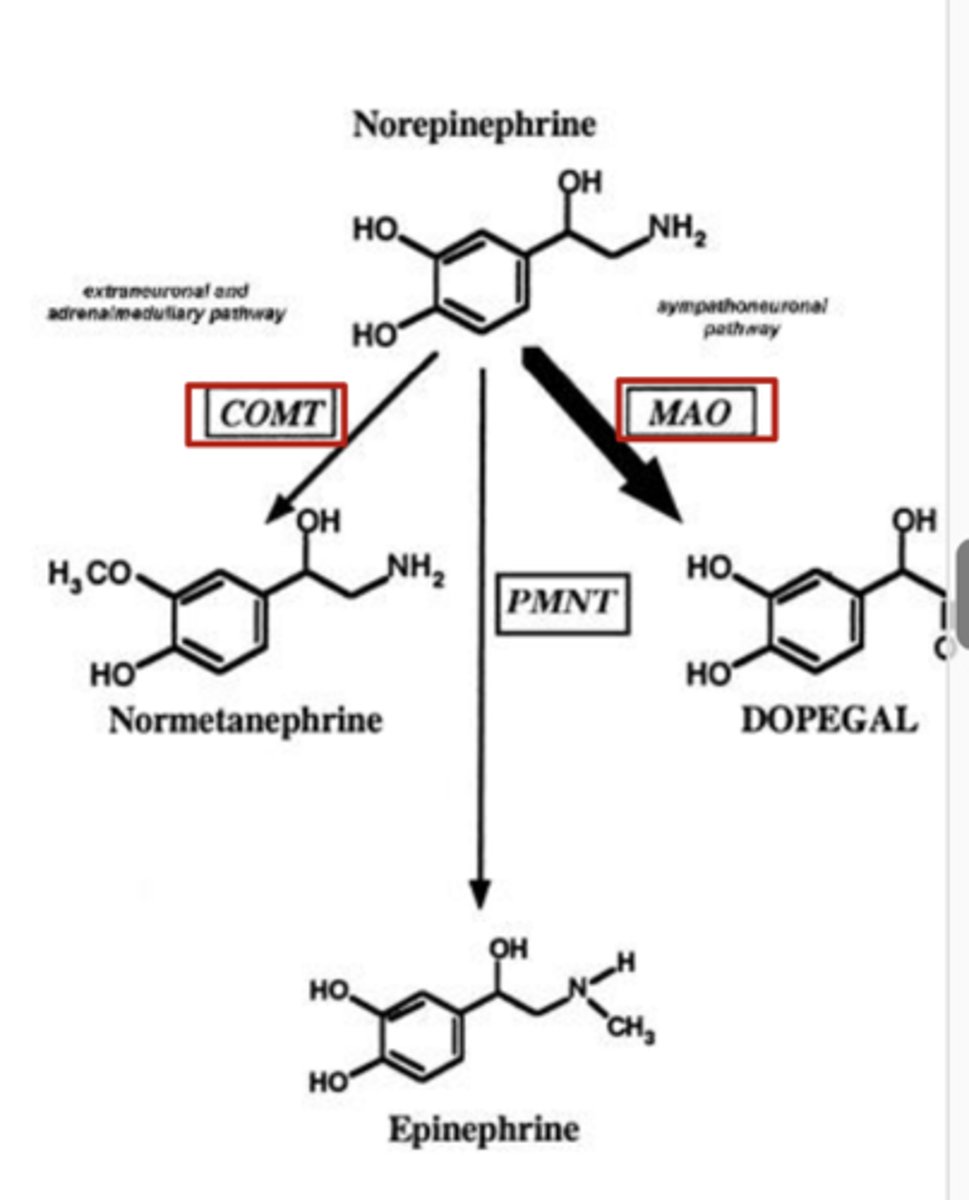
Irreversibly inhibits MAO of norepinephrine
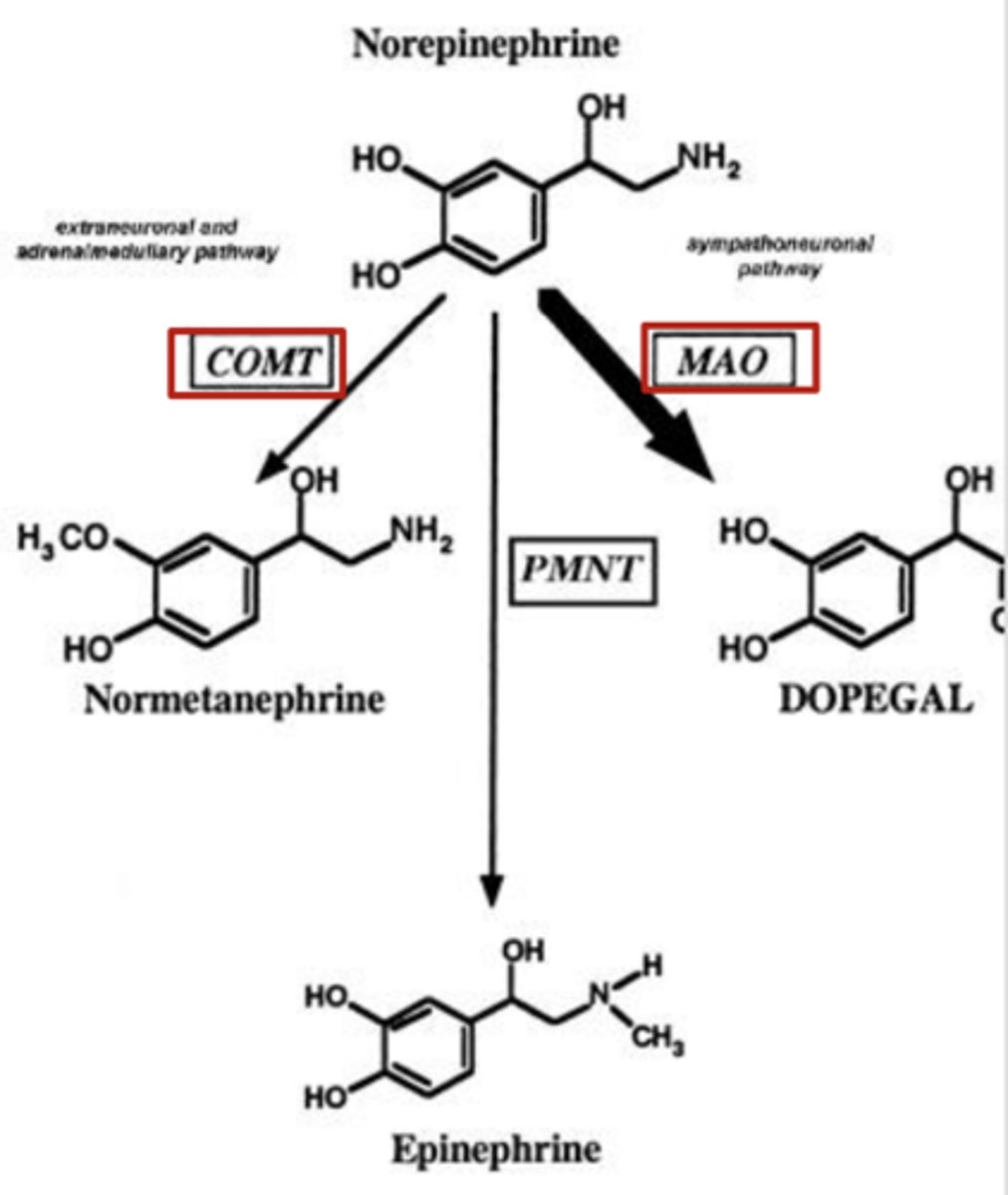
Indirect acting adrenergic receptor agonists: Entacapone (increase “fight or flight” response)
- What does it do in the metabolism of norepinephrine?
Inhibits COMT metabolism of norepinephrine
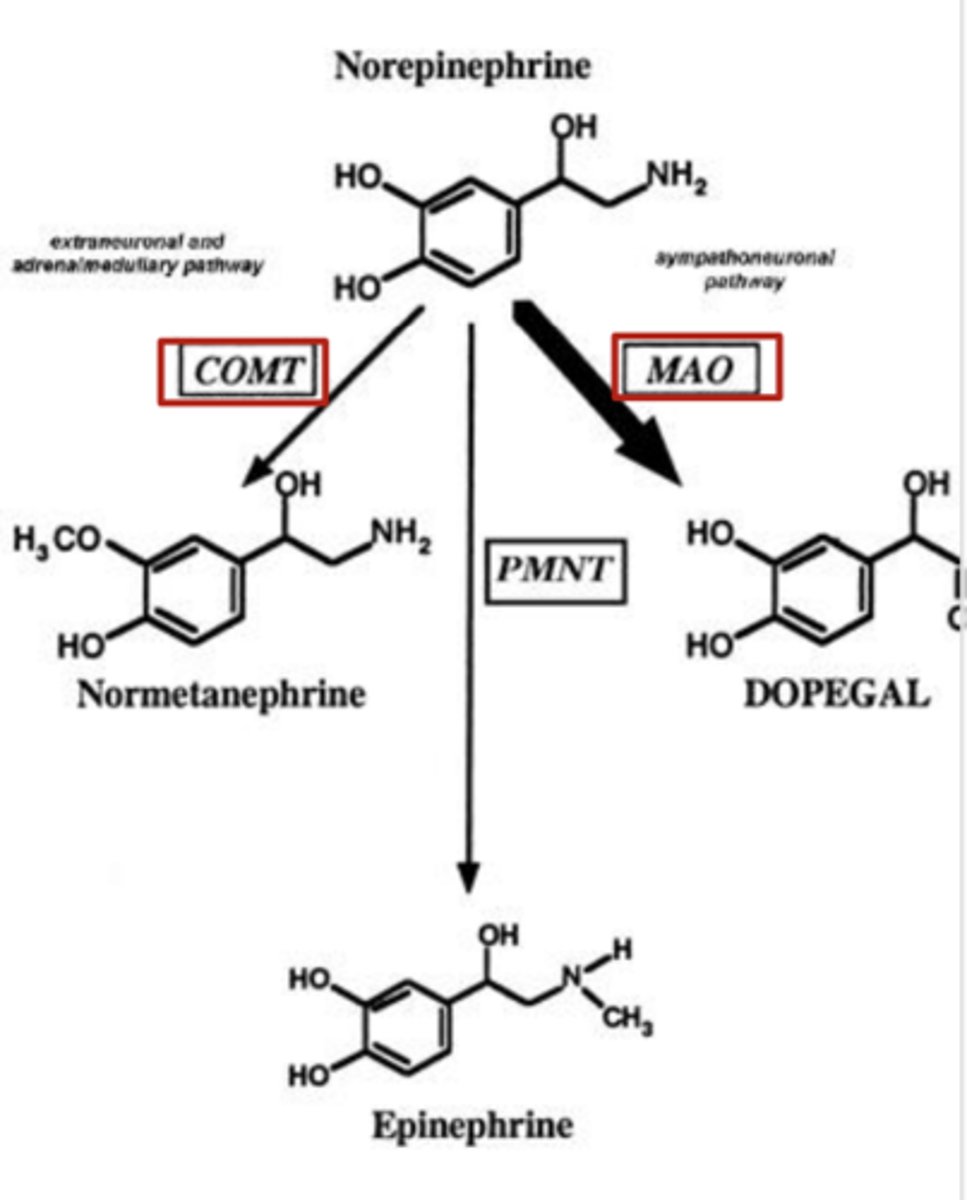
Clinical uses of selegiline and entacapone
MAO and COMT also metabolize other monoamines, so both drugs prescribed for treatment of dopamine deficiency seen with Parkinson's Disease
Side effects of selegiline and entacapone
both drugs can cause stomach pain
Mixed acting adrenergic receptor agonists: Ephedrine (increase “fight or flight” response)
- where is ti derived from?
- How does it work?
- Also has direct effects on....
• Alkaloid from ephedra plant
• Works mainly by reversing norepinephrine transporter
• Also has direct effects on α and β adrenergic receptors
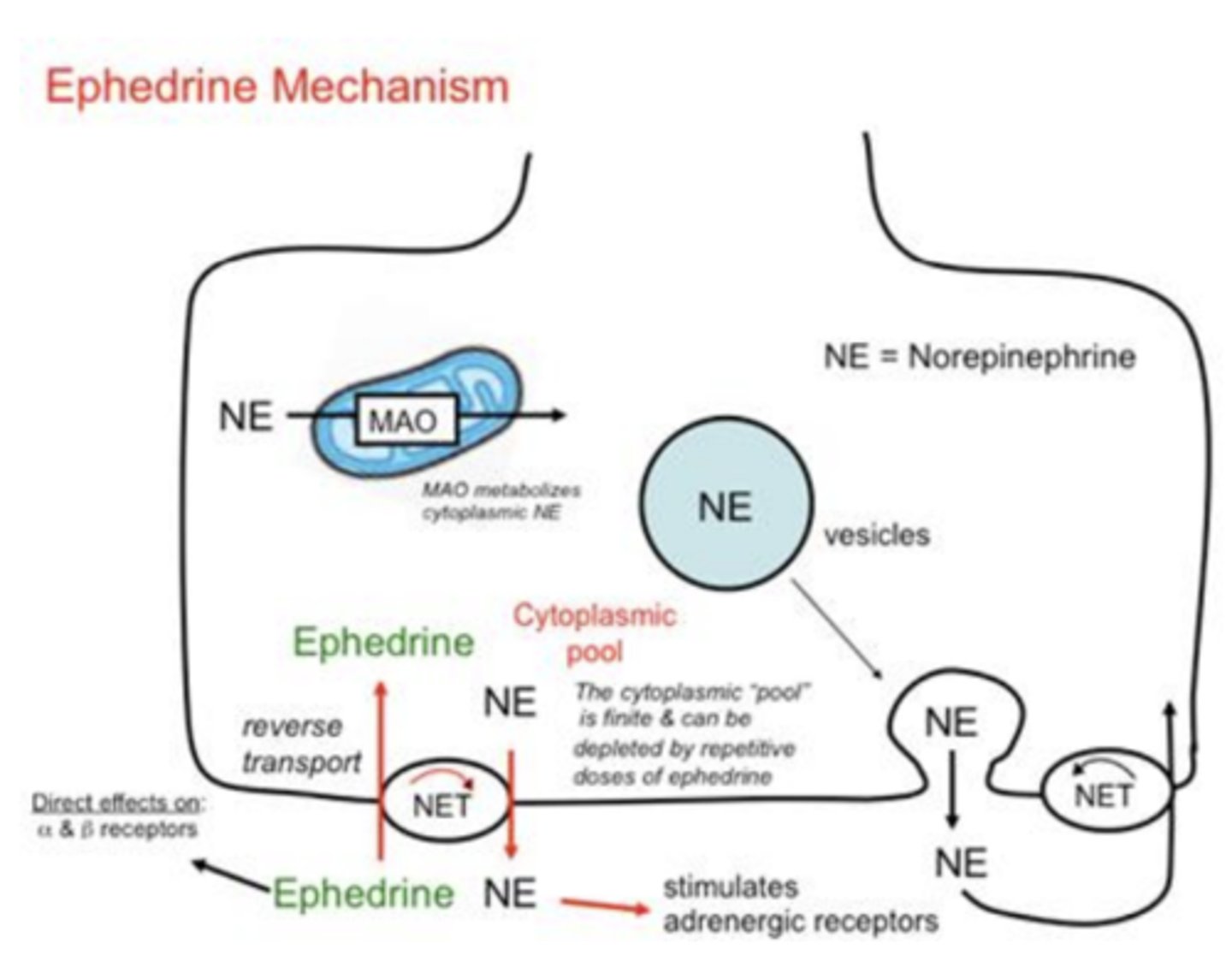
Side effects of ephedrine (7)
Skin reactions, dizziness, headache, insomnia, dehydration, hyperthermia, irregular heartbeat
What did the FDA ban the marketing of ephedrine for? Why?
Was it still allowed to be used in treatment of other things?
- FDA banned marketing ephedrine as a supplement for weight loss after several deaths linked to heart problems associated with use
- still allowed for the treatment of asthma, colds, and allergies
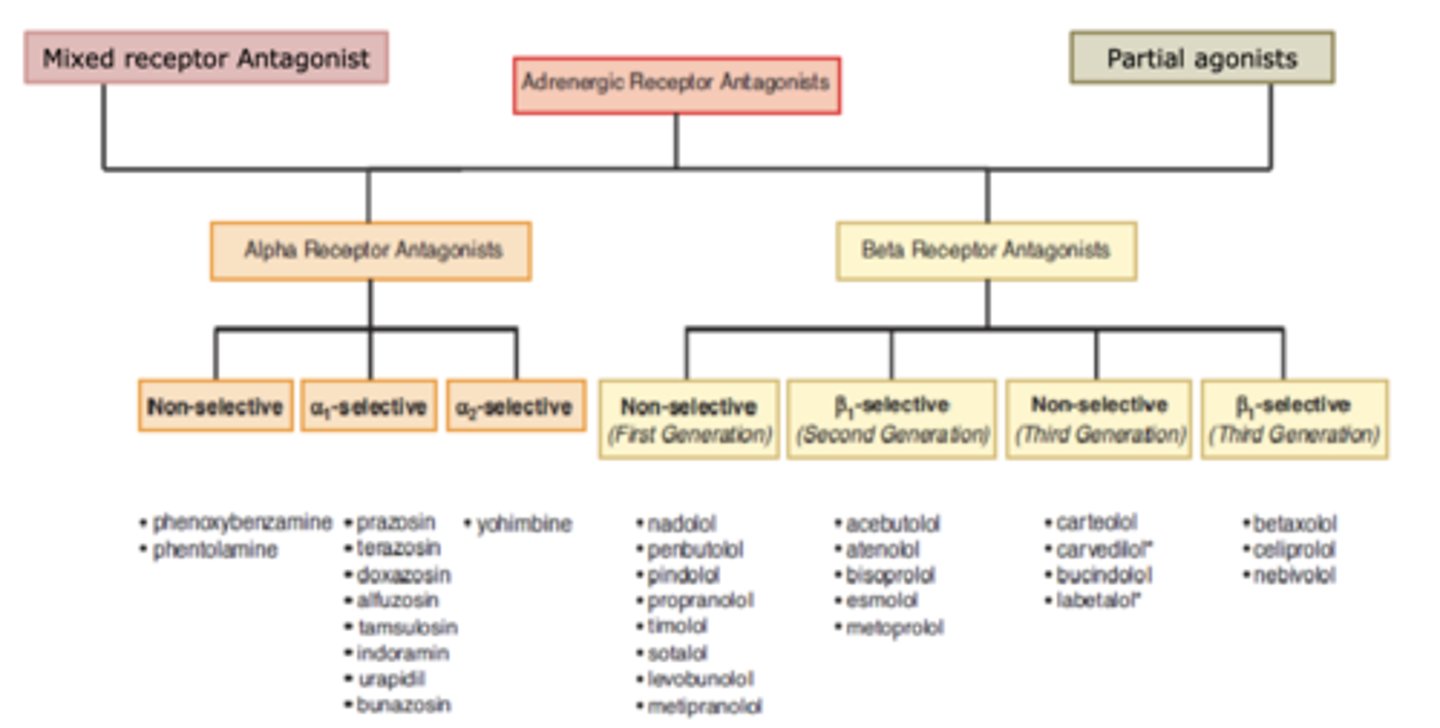
Adrenergic antagonists can be....(3)
• Direct acting
-For alpha OR beta receptors
-Selective or non-selective
• Mixed receptor acting
-For alpha AND beta
• Partial agonists
Adrenergic receptor antagonists will decrease "_____________" and increase "______________"
- decrease "fight or flight"
- increase "rest and digest"
Adrenergic Receptor Antagonists will decrease "Fight or Flight" and increase "Rest and Digest" ***EXCEPT FOR BLOCKADE OF.....
ALPHA2 WHICH HAS INHIBITORY EFFECTS (WORKS IN THE OTHER DIRECTION)
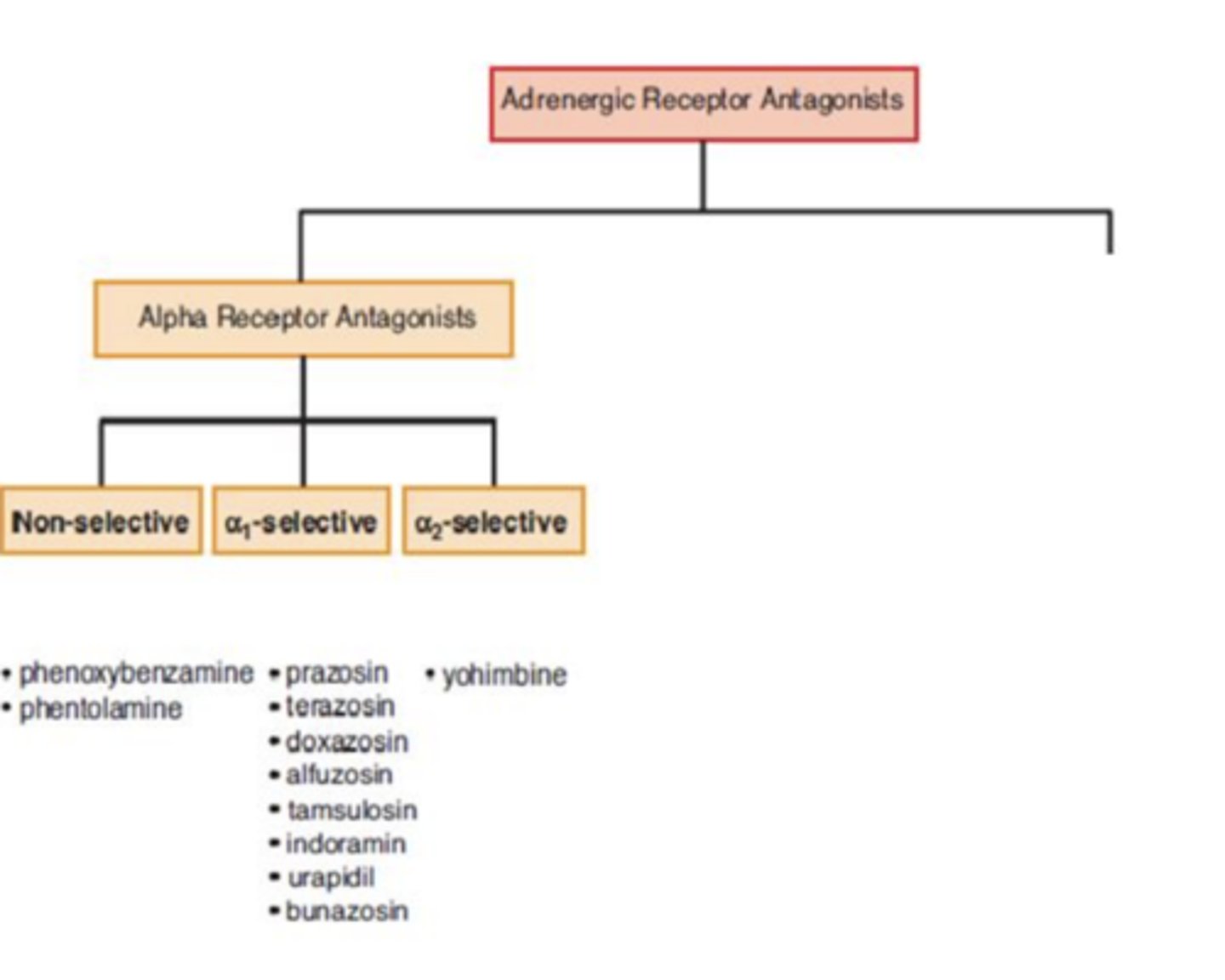
Alpha receptor antagonists can be categorized into...(3)
- non-selective
- α1-selective
- α2-selective
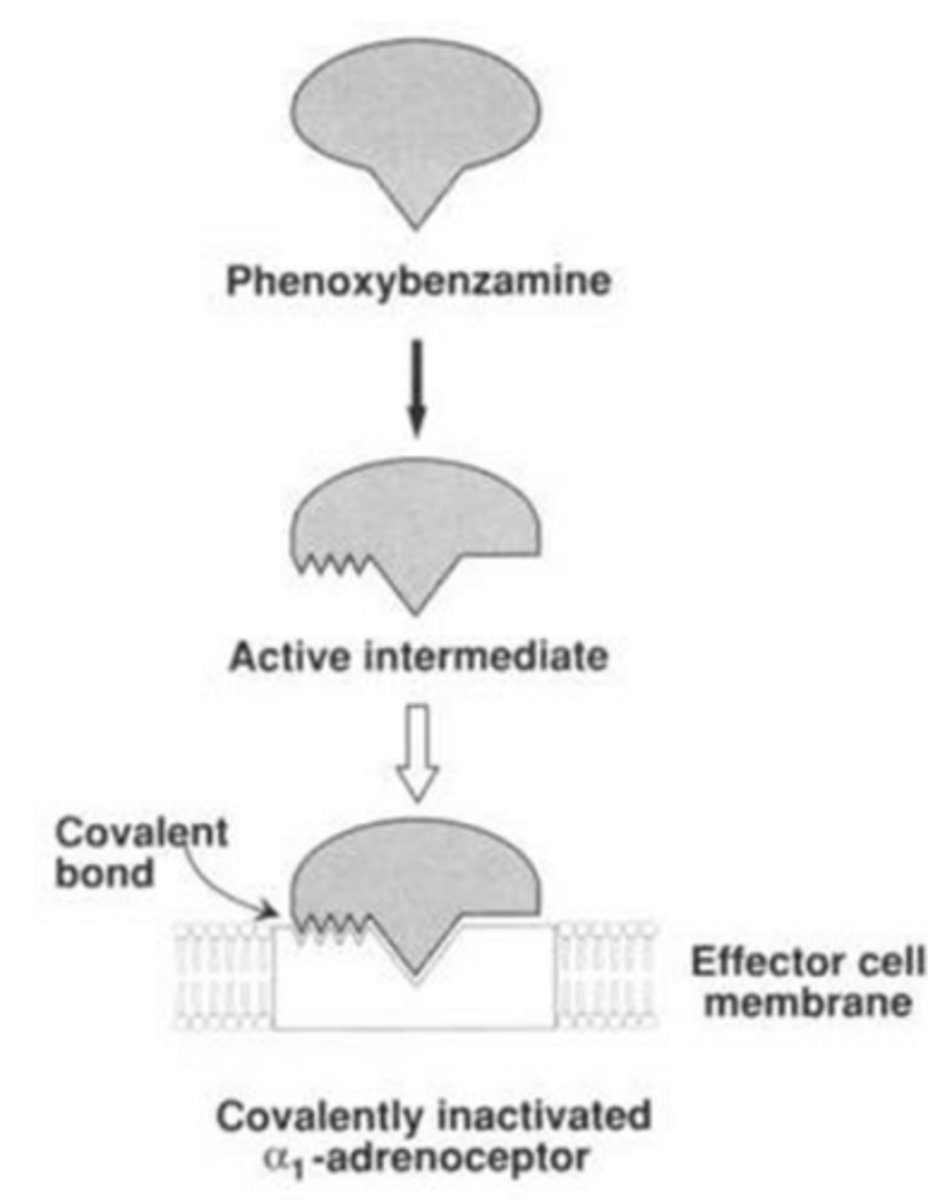
Non-selective alpha receptor antagonists: Phenoxybenzamine (decrease “fight or flight” response)
- _______________ antagonist
- Clinical uses:
- ___-drug, requires _________________
- Side effects:
- Irreversible α1 antagonist
- Clinical uses: Treating hypertension, pheochromocytoma
- Pro-drug, requires metabolic activation
- Side-effects: Hypotension, constriction of pupils
Non-selective alpha receptor antagonists: Phentolamine (decrease “fight or flight” response)
- Competitively blocks _______ and ________ receptors
- Clinical uses:
- Side effects:
- Competitively blocks α1 and α2 receptors
- Clinical uses: Treating hypertension, pheocromocytoma
- Side effects: Hypotension, constriction of pupils, similar to phenoxybenzamine
Selective alpha receptor antagonists: α1 ________________ "fight or flight", α2 __________ "fight tor flight"
α1 decreases "fight or flight", α2 increases "fight tor flight"
Selective alpha receptor antagonists: Prazosin, Terazosin, Doxazosin (decrease “fight or flight” response)
- Competitively blocks _______ receptors
- Clinical use: (1)
- Side effects: (2)
- Competitively blocks α1 receptors
- Clinical use: hypertension
- Side effects: arrhythmia, nausea
Selective alpha receptor antagonists: Yohimbine (increase “fight or flight” response)
- Derived from ______
- Competitively blocks ______ receptors
- Clinical use:
- Side effects:
- Derived from yohimbe tree
- Competitively blocks α2 receptors
- Clinical use: impotence (not sanctioned by FDA), reversal of antihypertensive effects of α2 receptor agonists (clonidine)
- Side effects: increased heart rate, excessive sweating
Beta receptor antagonists can be categorized into.... (4)
- non-selective 1st gen
- β1-selective 2nd gen
- non-selective 3rd gen
- β1 selective 3rd gen
β1 targeted for heart and β2 for pulmonary issues
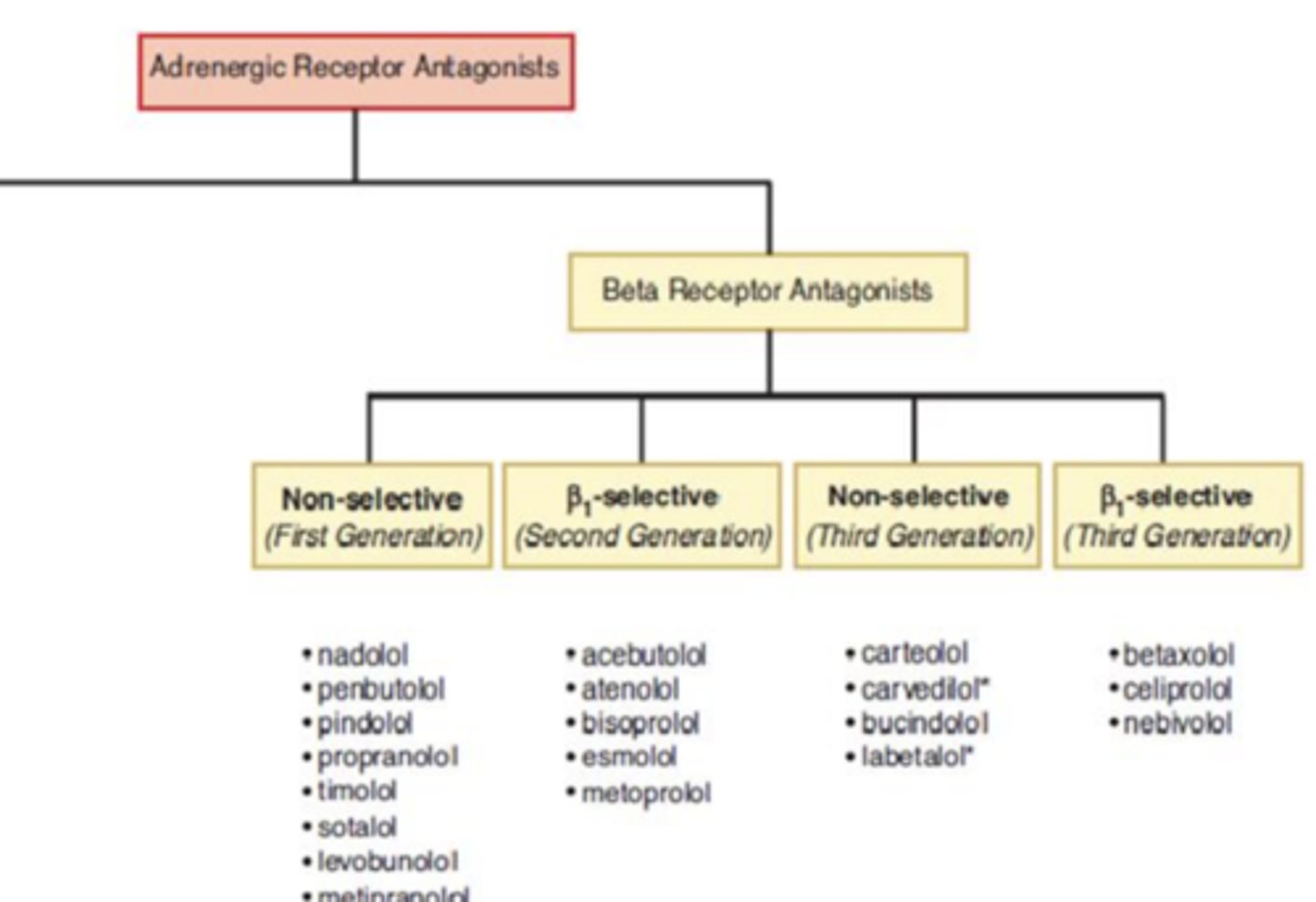
Non-selective beta receptor antagonists: Propanolol, Nadolol, and Timolol (decrease “fight or flight” response)
- Competitively block ________________ receptors
- known as __________ generation β-blockers
- Clinical use:
- Side effects:
- Blocking β2 can inhibit what?
- Competitively block all β receptors
- known as first generation β-blockers
- Clinical use: Propranolol and Nadolol--> hypertension, reduce risk of heart attack
Timolol---> glaucoma
- Side effects: Propranolol and timolol can cause arrhythmias and bronchospasms
Nadolol can cause dizziness and drowsiness
- Blocking β2 can inhibit glycogenolysis, inducing hypoglycemia
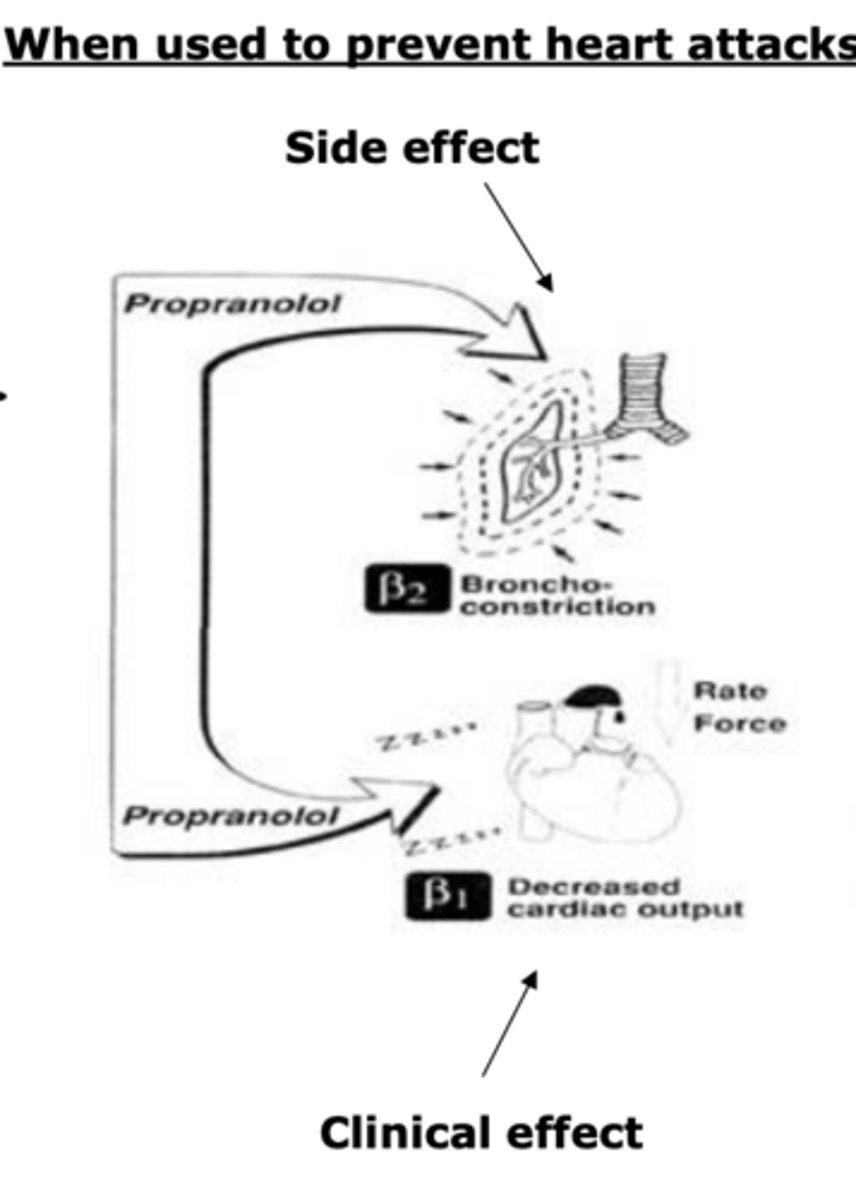
Propranolol, Nadolol, and Timolol: when used to prevent heart attacks
relaxes the heart, causes decreased cardiac output. Targets β1.
Causes bronchoconstriction, targets β2
Selective beta receptor antagonists: Atenolol, Carteolol, Betaxolol (decrease “fight or flight” response)
Second generation:
Third generation:
Clinical use: (2)
Side effects: (3)
Second generation are β1 antagonists and "cardioselective"
Third generation can be selective and non-selective antagonists, but have additional vasodilation mechanisms (production CV regulator, nitric oxide)
Clinical use: hypertension, reduce the risk of heart failure
Side effects: Dizziness, insomnia, stomach problems
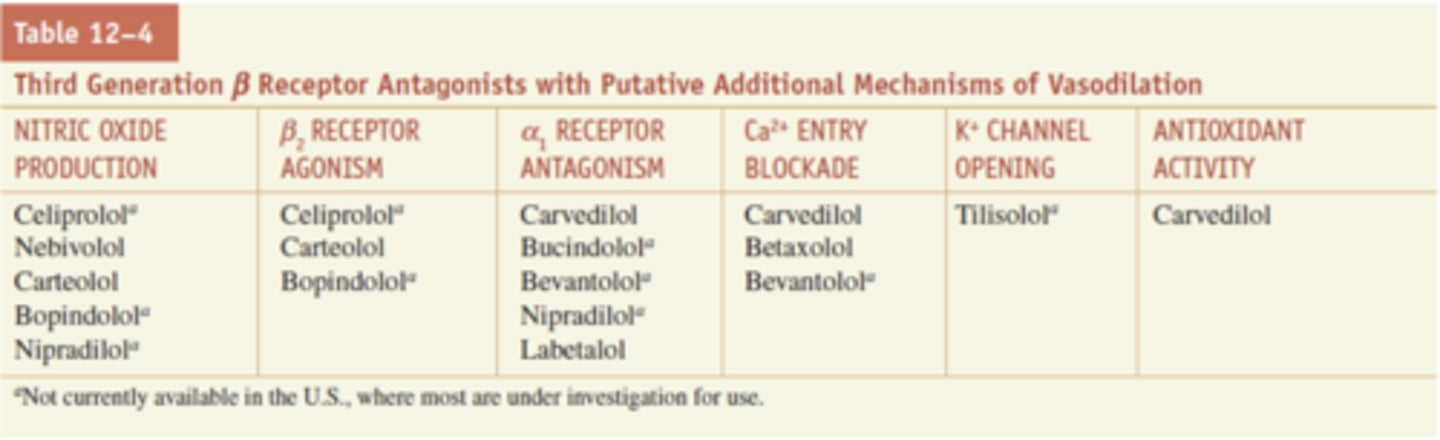
Mixed Receptor Antagonist: Labetalol
- _____ and _____ receptor blocker
- Clinical uses:
- Side effects: (2)
- α and β receptor blocker
- Clinical uses: treating hypertensive emergencies
- Side effects: dangerous hypotension and dizziness when in standing position
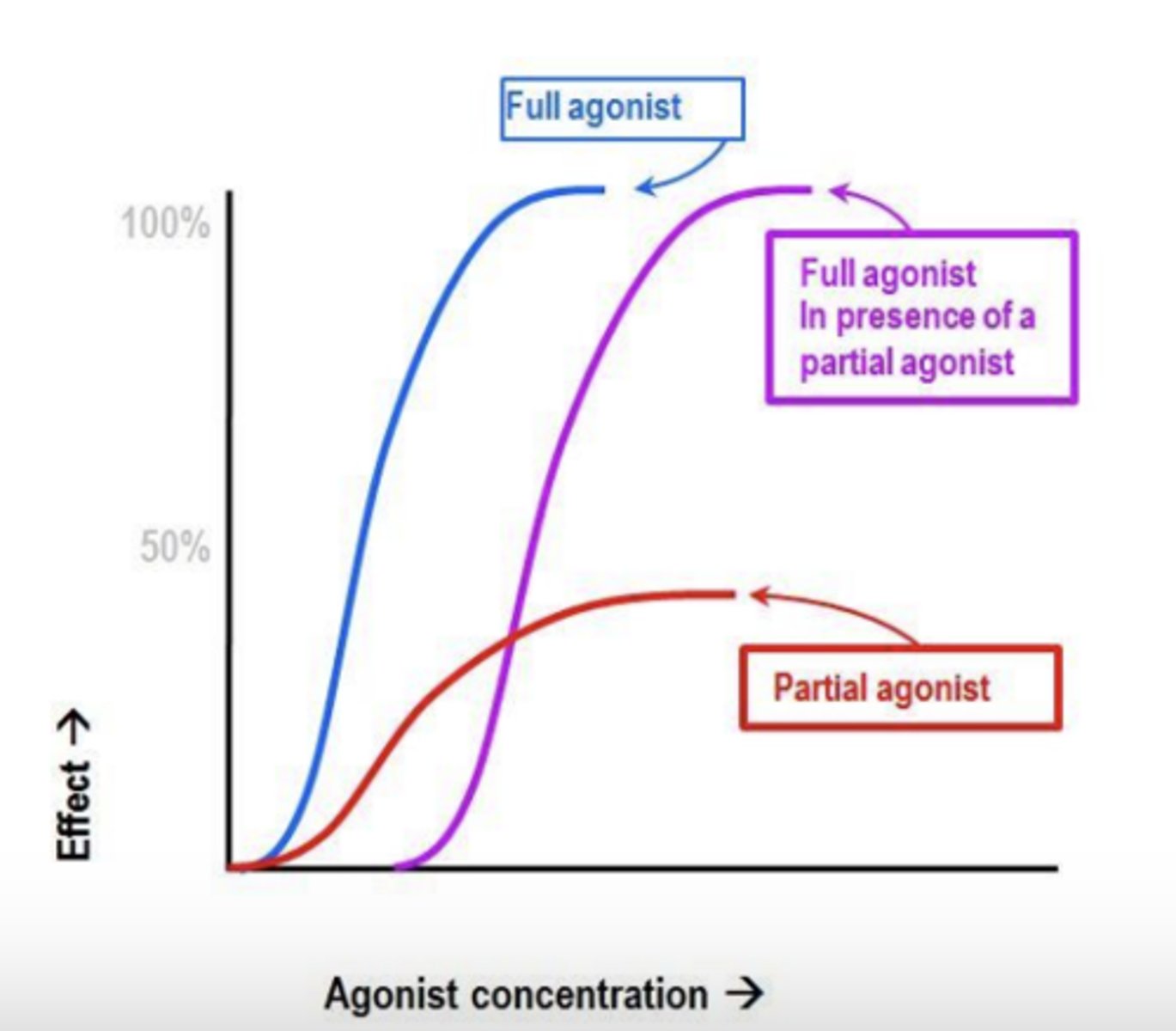
Partial agonists: Pindolol and Acebutolol
- Partial agonists at _____ and ____ receptors
- Modest effects on __________________, relative to _____________________
- Clinical uses:
- Side effects: (2)
- Partial agonists at β1 and β2 receptors
- Modest effects on CV system, relative to antagonists
- Clinical uses: Hypertension in pts with diabetes
- Side effects: decreased heart rate, upset stomach