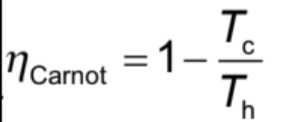B4: Thermodynamics
1/15
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Physics 11
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
16 Terms
Isobaric
Constant pressure change
Isothermal
Constant temperature change
Isovolumetric
Constant volume change
Adiabatic
Change with no exchange of heat with the surroundings
Entropy
A measure of how spread out or disordered energy is in a system.
First Law of Thermodynamics
The amount of heat energy Q added to a gas must equal the work done by the gas, W, plus the increase in internal energy
Second Law of Thermodynamics
In any cyclic process, entropy will stay the same or increase
Second Law of Thermodynamics
It is not possible for a heat engine working in a cycle to absorb thermal energy and transfer it to work (Kelvin-Planck)
Second Law of Thermodynamics
It is not possible for heat to be transferred from a cold body to a hot one without work being done (Clausius)
Amount of Thermal energy Formula

Work done by gas Formula
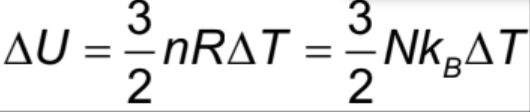
Change in Entropy Formula
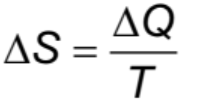
Entropy Formula
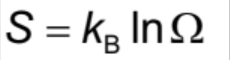
Pressure of Monoatomic Gas x Volume of monoatomic gas (adiabatic process)

Efficiency Formula

Efficiency of Carnot cycle Formula