Ambulatory Exam
1/92
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
93 Terms
Asthma
:-)
On an asthma action plan green is ____%, yellow is ___-___% and red is ___%.
What is the math?
>80 ; 79-50 ; <50
Current peak flow/personal best x100%
TRACK 1: >12 yrs with asthma
Step 1 & 2 → Symptoms ___ - ___ days/week with ____/____ ____ lung function. It’s treated with _____
3-5 days/week ; normal/mildly reduced ; AIR (as needed low dose ics-formoterol)
TRACK 1: >12 yrs with asthma
Step 3 → Symptoms ______ days/week or waking up _____ time/week or ____ lung function. It’s treated with _____
Most days/week ; >1 ; low ; MART (low-dose maintenance ICS-formoterol)
TRACK 1: >12 yrs with asthma
Step 4 → Symptoms ______ or waking up _____ time/week and ____ lung function. It’s treated with _____
Daily ; >1 and low ; MART (medium dose ics-formoterol)
TRACK 1: >12 yrs with asthma
Step 5 → Refer to an expert. Can
(1) ____ _____
(2) Consider ___-____ month of ____-dose ____ ____-____ therapy
(3) Add on biologic
(1) Add LAMA
(2) 3-6 months of high-dose maintenance ICS-formoterol therapy
TRACK 2: >12 yrs with asthma
Step 1 → Symptoms _____ . Treat with ___-dose ___ whenever ____ is taken.
Infrequently ; low-dose ICS whenever SABA is taken
TRACK 2: >12 yrs with asthma
Step 2 → Symptoms ___ - ___ days/week with ____/____ ____ lung function. It’s treated with ____-dose ____ _____
3-5 days/week ; normal/mildly lower ; low-dose maintainence ICS
TRACK 2: >12 yrs with asthma
Step 3 → Symptoms ______ days/week or waking up _____ time/week or ____ lung function. It’s treated with ____-dose ____ _____-____
Most ; >1 ; low ; low-dose maintainence ICS-LABA
TRACK 1: >12 yrs with asthma
Step 4 → Symptoms ______ or waking up _____ time/week and ____ lung function. It’s treated with _____-dose _____ ___-____
Daily ; >1 WITH low lung function ; medium-dose maintenance ICS-LABA
TRACK 1: >12 yrs with asthma
Step 5 → Refer to an expert. Can
(1) ____ _____
(2) Consider ___-____ month of ____-dose ____ ____-____ therapy
(3) Add on biologic
Add LAMA
3-6 ; high-dose ; maintenence ICS-LABA
Children 6-11
Step 1 → Symptoms ______ days/week. Treat with ___-dose ____ whenever ____ is taken.
<2 ; low-dose ICS ; SABA
Children 6-11
Step 2 → Symptoms ___-___ days/week. Treat with ___-dose ____.
2-5 ; low-dose ICS
Children 6-11
Step 3 → Symptoms _____ days/week or waking up _____ time/week. Treat with:
___- dose ____-___
__- dose ____
____-___-dose ___-___
most ; >1
low-dose ICS-LABA
medium-dose ICS
very low dose ICS-formoterol
Children 6-11
Step 4 → Symptoms _____ days/week and waking up _____ time/week and ____ lung function. Treat with:
___- dose ____-___
___-dose ___-___
daily & >1 & low lung
medium-dose ICS-LABA
low dose ICS-formoterol
Children 6-11
Step 5 → Consider:
(1) ___-dose ____-___
(2) Add on therapy (___ or ___)
higher doses ICS-LABA
LAMA or biologics
Children <5 (Not enough evidence for doing anything for step one)
Step 2 → Symptoms _____ days/week or waking up _____ time/week or SABA deliver needed ___ times/week or ____ ____ or ____ severe ____. Treat with: ____ ___-dose ____
>2 ; >1 ; >3 ; activity limited ; 1 severe exacerbation
Children <5
Step 3 → If still not controlled then ____ current ____-dose ____
double current low -dose ICS
Counseling steps for MDI without spacer:
____ _____
____ fully
_____ while ____ _____
Hold breath for ____ seconds
Shake inhaler
Exhale fully
Breath while pushing down
10
Counseling steps for MDI with spacer:
insert the inhaler into spacer
____ ____ ____
Can do up to ____ times
Breathe slowly
6
Counseling steps for DPI:
Open device
____ _____
____ ____ (away from device)
Inhale _____ through mouthpiece
Hold breath for ___ secs
Load dose
Fully exhale
Forcefully
10
Albuterol HFA Treatment for Exacerbation
Dose: ___ puffs every ____ ___ for up to___ doses in the ___ hour (s)
After that, ___ puffs every ____ ___ as needed
pred ___-___mg for ____ days if did not respond to SABA / recent corticosteroid use
2-4 puffs q 20 minutes 3 in one hour
2-4 puffs q4-6h PRN
40-60mg for 5-10 days
Mild exacerbation: Can often be managed __ ____ with increased ____ use and ___-__ ____.
At home ; reliever ; follow-up with provider
Moderate exacerbation: Requires ____ or ____ with possible ____ ____.
Pred ___-____mg for ___-___ days
ER or urgent care ; systemic corticosteroids
40-60mg for 5-10 days
Severe exacerbation: ____ may be needed, possibly requiring ____, continuous ____, or even mechanical ventilation. ADD ____.
WARD VS ICU
Hospitalization ; O2 ; nebulization ; SAMA
WARD → oral corticosteroids & SABA
ICU → IV corticosteroids & SABA continuous
Biostatistics
: D
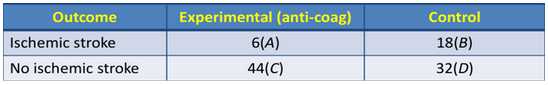
NNT/NNH calculation
Calculate ARR = [(A / A+C) – (B / B+D)]
(6/50) - (18/50) = -0.24
NNT/NNH = 1 / ARR
4.166 (NNT = 5 and NNH = 4)
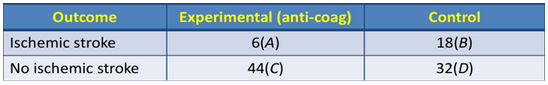
Calculate the Relative Risk Reduction (RRR)
RRR = 1 - [(A / A+C) ÷ (B / B+D)]
(6/50) ÷ (18/50) = 0.33
COPD
: O
Presentation: COPD typically presents with ___ , ___ ___ , and/or ___ ___ . Symptoms are ___ and often under-recognized until significant lung function is lost.
dyspnea that is ___ , ___ , and ___ with exercise
recurrent ___ , recurrent ___
dyspnea, chronic cough, and/or sputum production ; progressive.
recurrent, progressive, worsened
Wheezing ; LRIs
If your ____/____ is < ___ after a bronchodilator you have COPD
FEV1/FVC is <70
Based on FEV1 predicted
GOLD 1 → ___
GOLD 2 → ___
GOLD 3 → ___
GOLD 4 → ___
GOLD 1 → > 80
GOLD 2 → 79-50
GOLD 3 → 49-30
GOLD 4 → <30
GROUP A: Low symptoms, low exacerbation risk: (mMRC ___ and CAT ____.)
Start with a ___-___ ____
0-1 ; <10
long-acting bronchodilator (LAMA or LABA).
GROUP B: High symptoms or exacerbation risk: (mMRC ___ and CAT ____.)
Use: ____
>2 ; >10
LAMA+LABA combo
GROUP E: (____ moderate exacerbation or __ ____)
Eosinophils ≥300 cells/μL or history of asthma → ______
Do not use ____ if Hx of ____, ___/____ infections
>2 moderate exacerbations or >1 hospitalization
Consider LABA+LAMA+ICS.
ICS ; Pneumonia, TB/mycobacterial infections
New in 2025: ______ (PDE3/4 inhibitor) and ____ (anti-IL-4/13 biologic) are now options for select patients with frequent exacerbations despite optimized therapy.
Ensifentrine (PDE3/4 inhibitor) and dupilumab (anti-IL-4/13 biologic)
Exacerbation definition: ___ ____ of respiratory symptoms requiring additional therapy.
Acute worsening
Treatment for COPD exacerbation includes:
___-___ ____
____ ______
______ if >2 of 3 cardinal symptoms
Short-acting bronchodilator (SAMAs take a few minutes. SABAS instant.)
Systemic corticosteroids
Antibiotics
Treatment for COPD exacerbation includes: Dose of ____ is _____mg ___ for ___ days.
Prednisone 40mg daily x5 days
Treatment for COPD exacerbation includes: Antibiotics are needed if >2 of 3 cardinal symptoms are present. The cardinal symptoms are:
___ ___
___ ___
___ ___
Increased dyspnea
Increased sputum volume
Sputum purulence
DIABETES MELLITUS
U - U
A1C Target:
Fingerstick Blood Sugar Testing: Preprandial glucose target ____, peak postprandial glucose_____.
Continuous Glucose Monitoring (CGM): Time in range (TIR) ____ for at least ____ of the day is recommended.
Generally <7% but if a patient is very old and sic,k then <8% is fine.
Preprandial glucose target 80–130 mg/dL, peak postprandial glucose <180 mg/dL.
70-180 mg/dL for 70% of the day
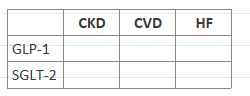
Fill this out
(maybe liraglutde also has CKD benefit? unclear)

Metformin Dosing:
eGFR >60 ml/min/1.73m³ →
eGFR 60-45 ml/min/1.73m³ →
eGFR 45-30 ml/min/1.73m³ →
eGFR <30 ml/min/1.73m³ →
1000mg BID
1000mg BID but monitor renal function every 3-6 months
Don’t initiate therapy… but if you must 500mg QD → 500mg BID (NMT 500BID if continued)
Use is contraindicated
Ozempic dose & titration
0.25mg → 0.5mg → 1mg → 2mg
Dulaglutide dose & titration
0.75mg → 1.5mg → 3mg → 4.5mg
Mounjaro dose & titration
2.5mg → 5mg → increase by 2.5mg q4weeks until NMT 15
Insulin dose of basal insulin: Start ___ units/day or ____-___ per day. Increase in increments of ___ units every ____ days. If they get hypoglycemia reduce units by ___-___.
Start 10 units ; 0.1-0.2/kg/units ; increase 2 units every 3 days ; 10-20%
Insulin dose of prandial insulin: Start ___ units/day or ____ of basal insulin dose. Increase in increments of ___ units or ___-___ twice weekly . If they get hypoglycemia reduce units by ___-___. Start with the ___ ___.
4 units ; 10% ; 1-2 units ; 10-15% ; biggest meal
Given a patient’s insulin dosage, calculate the number of pens needed for a 30- or 90-day prescription. The concentration and volume of the specific pen will be provided. Standard insulin pen: 300 units per pen.
If a patient takes 40 units/day and needs a 30-day supply then how many pens?
(Total daily dose × Days supply) ÷ 300 = Number of pens needed.
If a patient takes 40 units/day and needs a 30-day supply, they require (40 × 30) ÷ 300 = 4 pens.
Dyslipidemia
:-0
LDL goals: Primary prevention WITHOUT DM
LDL >190 →
Without DM 40-75 years + 7.5-20% ASVCD risk →
Without DM 40-75 years + 20+% ASVCD risk →
>50% reduction and LDL <100mg/dL
>30-49% reduction and LDL <100mg/dL
>50% reduction and LDL <70mg/dL
LDL goals: Primary prevention WITH DM
With DM 40-75 years + >7.5% ASVCD risk →
With DM 40-75 years + <7.5% ASVCD risk →
With DM 40-75 years + >20% ASVCD risk →
>30-49% reduction and LDL <100mg/dL
>50% reduction and LDL <70mg/dL
LDL goals: WITH ASVD/Secondary prevention
ASCVD not at very high risk →
Very high risk →
Baseline LDL >190 mg/dL WITH Familial hypercholesterolemia (FH) →
>50% reduction and LDL <70mg/dL
>50% reduction and LDL <55mg/dL
>50% reduction and LDL <70mg/dL
Low vs High intensity statins
LOW= Some People Love Flowers (Simvastatin 10mg, Pravastatin 10-20mg, Lovastatin 20mg, Fluvastatin 20-40mg)
HIGH= AR 40-20 (AR “420” a gun that shoots weed? lol idk)
Calculate the LDL via the Friedewald equation, given the patient’s total cholesterol, HDL, and triglyceride results
What are the limitations of this?
LDL-C = Total Cholesterol - HDL-C - (Triglycerides / 5)
This is not valid if the TGs of the patient are >400 mg/dL.
HEART FAILURE
: (
Categorize the difference
HFrEF →
HFpEF →
LVEF <40%
LVEF >50%
HF symptoms/staging (not same as NYHA class)
You ____ go back in stage
Stage A →
Stage B →
Stage C →
Stage D →
Cannot
Stage A → No structural heart disease or HF sx. Just other high risk conditions (like HTN, DM, obesity)
Stage B → Structural heart disease (previous MI, LV hypertrophy, low EF) but no current or prior symptoms
Stage C → Structural heart disease (previous MI, LV hypertrophy, low EF) with no current or prior symptoms
Stage D → Marked symptoms at rest despite optimal medical therapy; patients may require specialized interventions (e.g., inotropes, LVAD, transplant, palliative care).
NYHA class
You ____ go back in stage
Class I:
Class II:
Class III:
Class IV:
Can
Class I: No limitation
Class II: Slight limitation during ordinary activity
Class III: Marked limitation with less than ordinary activity
Class IV: Symptoms at rest
Identify medications that are considered potentially harmful when used in patients with HFrEF
___-___ ____
_____
______
_____-___ ____
____, _____
______
______
______
non-DHP CCBs
TZDs
NSAIDS
COX-2 inhibitors
Saxagliptan, alogliptan
Antiarrythmics (Flecainide, dronedarone, disopyramide, sotalol)
Dozasozin
PDD4is
HFrEF mortality benefit:
What are the four pillars
What deceases mortality in AA patients w/ NYHA-3 to 4 receiving optimal therapy
ACEs/ARNis/entresto, BBs (nebivolol, carvedilol, metoprolol succ, bisoprolol), MRAs, SGLT2is
Hydralazine/isosorbide dinitrate
What benefits HFpEF for mortality?
We learned nothing but the 2022 guidelines said this: … but I’m still not sure because the wording in the guideline was so ambiguous? To be discussed!

I’m not gonna re-do the dosing because we prob have other resources. Use prac 5.
I’m not gonna re-do the dosing because we prob have other resources. Use prac 5.
HIV/PrEP
—
Who should receive Pneumocystis jirovecii pneumonia prophylaxis?
Treatment?
CD4 count 100-200 cells/mm3 AND plasma HIV RNA levels are above detection limits
or
CD4 count <100 cells/mm3 (regardless of detection limits)
Treatment: Bacrim DS or SS once daily
Who should receive Mycobacterium avium complex prophylaxis?
CD4 count <50 cells/mm3 AND not receiving ART
Remains viremic on ART
Has no options for fully suppressive ART regimen
Treatment:
Azithromycin 1,200 mg PO once weekly (AI)
Clarithromycin 500 mg PO twice daily (AI)
Azithromycin 600 mg PO twice weekly (BIII)
NRTIs → Nucleotide reverse transcription inhibitors
____, _____/____, ____/____, _____
Class ADE:
_____ _____ (____ _____)
Lab monitoring:
___, ____, ___, ____/____
Abacavir, Emtricitabine/Lamivudine, TAF/TDF, zidovudine
Mitochondrial toxicity (lactic acidosis)
LDLs, Renals, CBC, CD4/Viral load
NNRTIs → Non-nucleotide reverse transcription inhibitors
(-___)
Class ADE:
_____
_____ ____
-Virine (Doravirine, Rilpivirine, Etravirine, Efavirenz)
Rash
Sleep disturbances (with Doravirine & Efavirenz and slightly Rilpivirine)
INSTIs→ Integrase strand transfer inhibitors (-___)
Class ADE:
_____ _____ ____
Lab monitoring:
___, ____/____
-Gravir
Class well tolerated (but bitegravir and dolutegravir cause false SCr elevations)
renal function, CD4/Viral load
Protease inhibitor→ (-___)
Class ADE:
__/__/__
Lab monitoring:
___, ____/____
-Navir
N/V/D
Liver, CD4/Viral load
PKN Booster
Cobicistat ADE →
Ritonovir ADE →
monitoring:
False SCr increase
GI, dyslimidemia
Monitor DDI (And remember this is not antiretroviral)
What are the 3 regimens recommended for PrEP?
____ (___/___) ; classes ___ _____
____ (___/___) ; classes ___ _____
____ (___) ; class ___
Descovy (Emtricitabine/TAF) → 2 NRTIs
Truvada (Emtricitabine/TDF) → 2 NRTIs
Apretide (Cabotegravir) → INTSI
Descovy (Emtricitabine/TAF) is taken _____ ____.
Monitoring
At baseline monitor ____ and ___.
Documented negative HIV test (≤1 week before initiating or reinitiating PrEP, at least every 3 months while taking PrEP, and following discontinuation of PrEP)
once daily ; lipids and Hep B test
Apretide (Cabotegravir) _____ ____.
Monitoring
At baseline monitor ____
assess symptoms & test acute HIV infection (prior to initiation of PrEP at 1 month post-initiation, then every 2 months while taking while taking PrEP)… AKA test before every shot bc if they have HIV u could make them resistant to this
every 2 months; liver (no renal or Hep b testing needed)
Immunizations
: )
Tetanus, diphtheria, pertussis (Tdap)
Doses:
Population:
____
____
Inactivated
Doses: 1 every 10 years
Population:
Pregnant women (gestational age
Dirty wounds (if >5 yrs after lost shot)
Measles, mumps and rubella (MMR) 𖤒 𖤫
Dose: ___ dose (___ doses if _____, ____ or _____)
Population:
______
______
Live
Dose: 1 dose (2 doses if healthcare, international travelers, post-secondary school)
Population:
Born after 1957
Varicella (VAR) 𖤒 𖤫
Dose: ____ dose _____ ____ ____
Population:
______
______
It is CI in ______ _____ and ______ ______ _______ ______
Live
Dose: 2 doses 4-8 weeks apart
Population:
Born after 1980
Born before 1980, and in healthcare
Pregnant people ; after pregnancy before discharge
Zoster (RZV)
Dose: _____ dose ____ _____
Population:
______
______
Dose: 2 ; 2-6 months apart (at least 4 weeks apart)
Population:
50+ and older
Immunocompromised
Human papillomavirus (HPV)
Dose: ____ dose _____ ____ ____
Population:
______
Inactivated
Dose: 0, 1–2 and 6 months
Population:
Everyone until 26
Pneumococcal
Dose: ____ dose of _____ or _____ _____ of ____ ____ and then ______, ____ weeks after
Population:
______
______
Dose: 1 dose of PCV 20 or 1 doses of PCV15, then PPSV23 8 weeks after
Population:
50+
Immuno disease (CV, or lung)
Hepatitis A 𖤖 𖠘 𖠶
Dose: ____ dose _____ ____ ____
Population:
______
______
Inactivated
Dose: 2 doses 6 months apart
Population:
Anybody who requests it
Hep A risk (HIV, men having sex w/ men, inject drugs)
Hepatitis B
Dose: ____ dose _____ ____ ____
Population:
______
______
Dose: 2, 3 or 4 dose series
Population:
19-59
60+ w/ risk factors or if requested
Meningococcal B
Dose: ____ . dose _____ ____ ____ Then ________
Population:
______
______
Inactivated
Dose: 2 doses 6 months apart. Then dose 3 at least 4 months after
Population:
16-23 years not at increased risk
Anatomical or functional asplenia
Influenza
Dose: ____ dose _____ ____ ____
Inactivated
Dose: Once every year
COVID-19
Dose: ____ dose of the ____ or _____ of the ______
Population:
______
______
Dose: 1 dose of the 2024-2025 Moderna/Pfizer or 2 doses of the novavax 3-8 weeks apart
Population:
Everyone
If over 65 then 2 doses 6 mo apart
Respiratory syncytial virus (RSV)
Dose: ____ dose
Population:
______
______
Dose: 1 dose
Population:
Pregnant women of any age as 32-36 weeks
75+
Thromboembolic
o-(-(
(Assuming you already know how to calculate CHA2DS2VASc)
What is a CHA2DS2VASc score do you need in men or women to initiate oral anticoagulation?
What HAASBLED score tells you they are a high bleed risk?
2 in men 3 in women
3
When is Warfarin preffered over DOACS?:
____ _____
_____
____ _____
Valve disorders
Obesity
Adherence issues
Warfarin INR goals for non-valvular is _____ and for valvular/mitral valve it’s _____ because of the higher bleed risk.
2-3 ; 2-2.5